Ch 4 | Electrons in Atoms
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
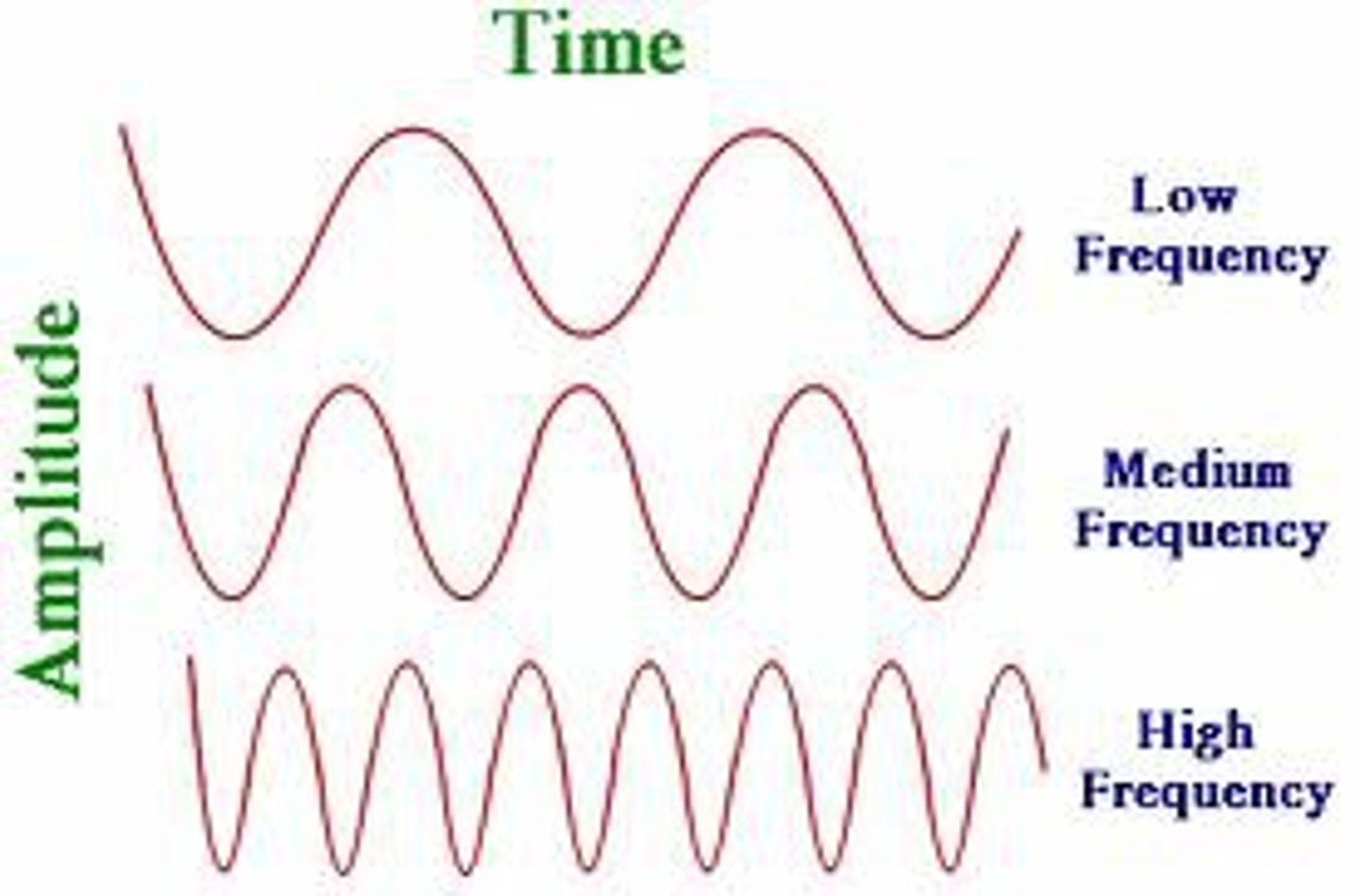
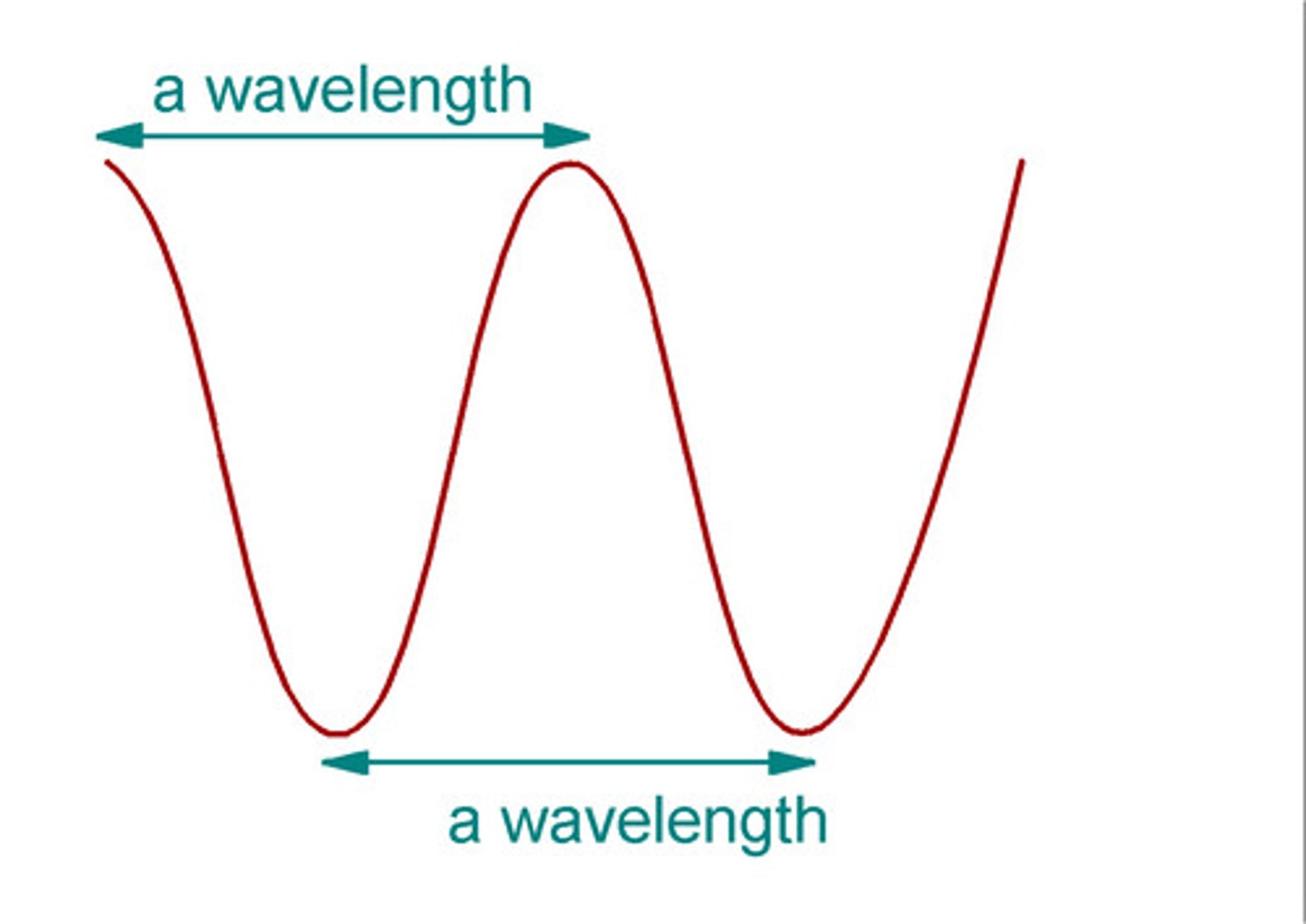
3 properties of waves
wavelength, frequency, and amplitude
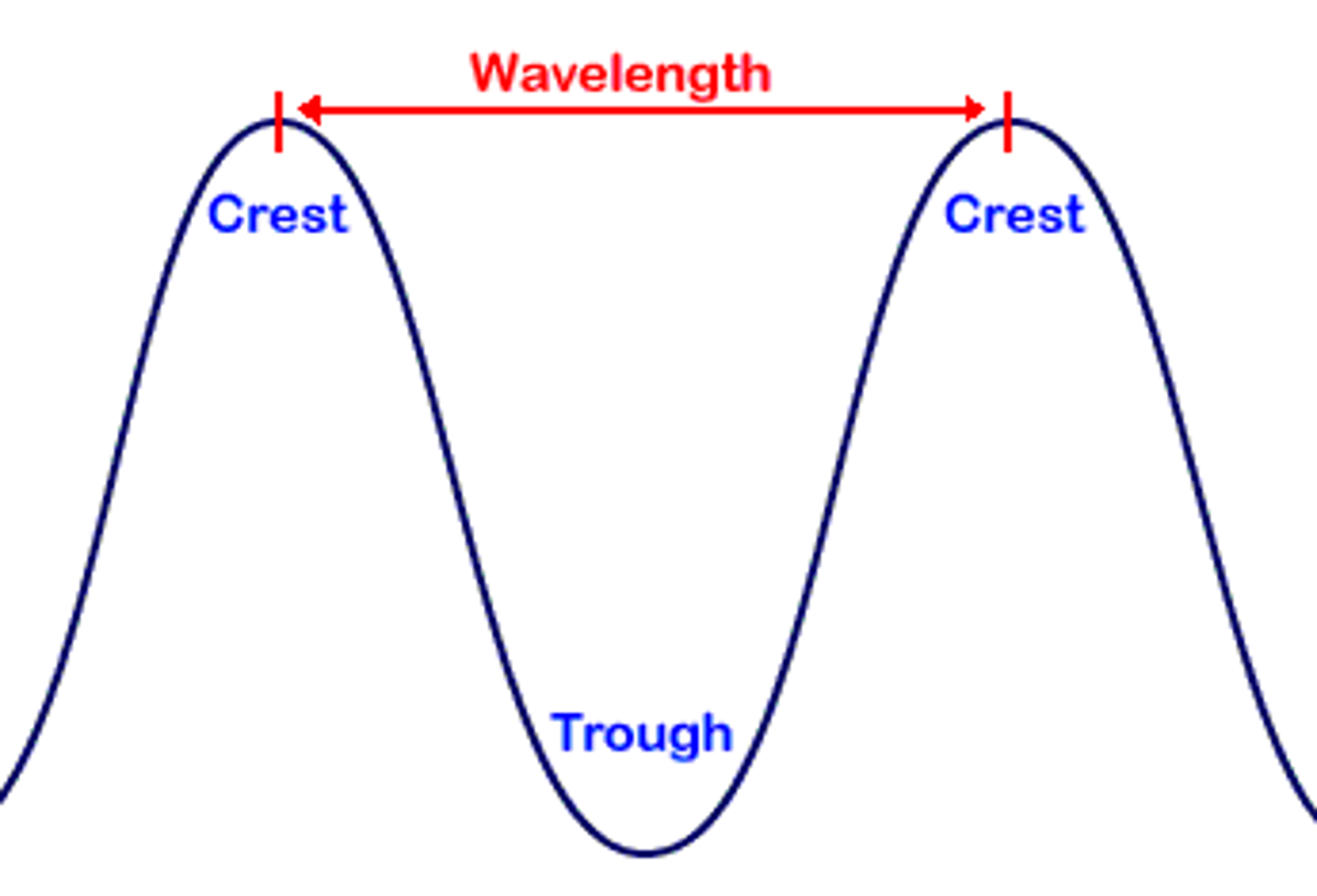
frequency
measure of how many waves pass a given point in a specific amount of time; measured in Hz or cycles per second; greek letter > 𝝂
wavelength
measure of the distance from 2 similar points on a wave; measured in length(m or nm); greek letter > λ
amplititude
measure of the distance between a line through the middle of a wave and the highest/lowest point of it
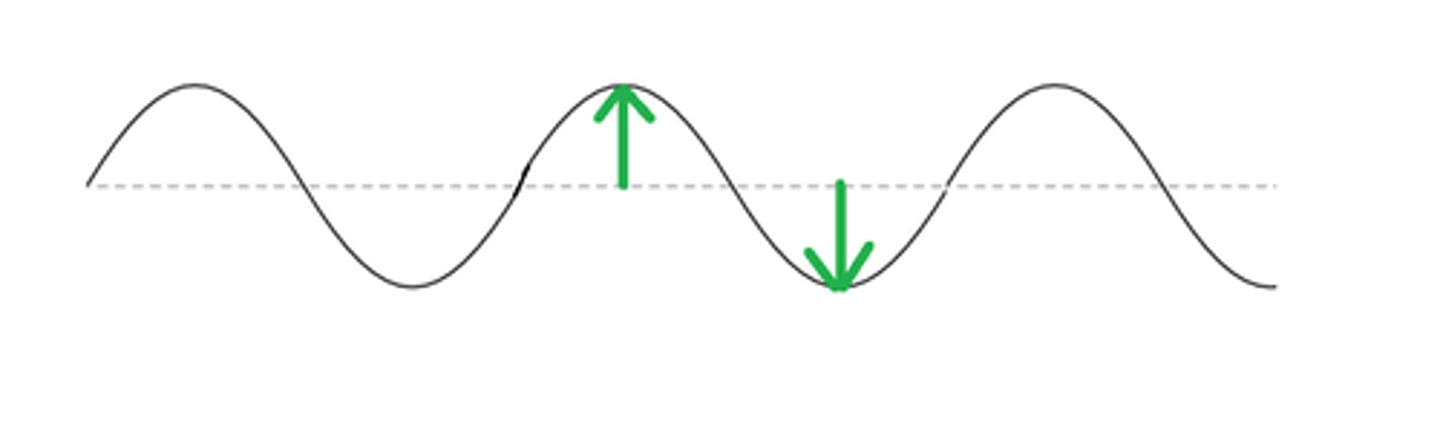
parts of a wave
crest - highest point & trough - lowest point
one cycle of a wave is
one up and down
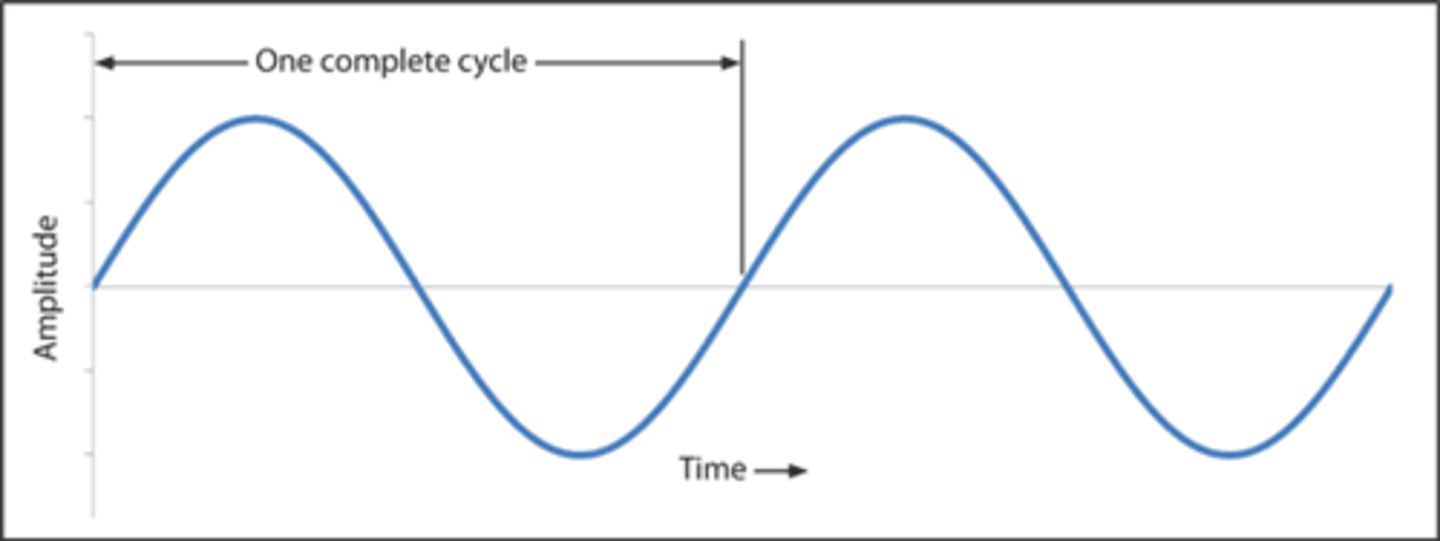
the higher the amplitude means
the higher the wave, the louder the sound, and the brighter the light
speed of all forms of electromagnetic radiation/waves
3.0 x 10^8 m/s
electromagnetic spectrum
all the forms of electromagnetic radiation
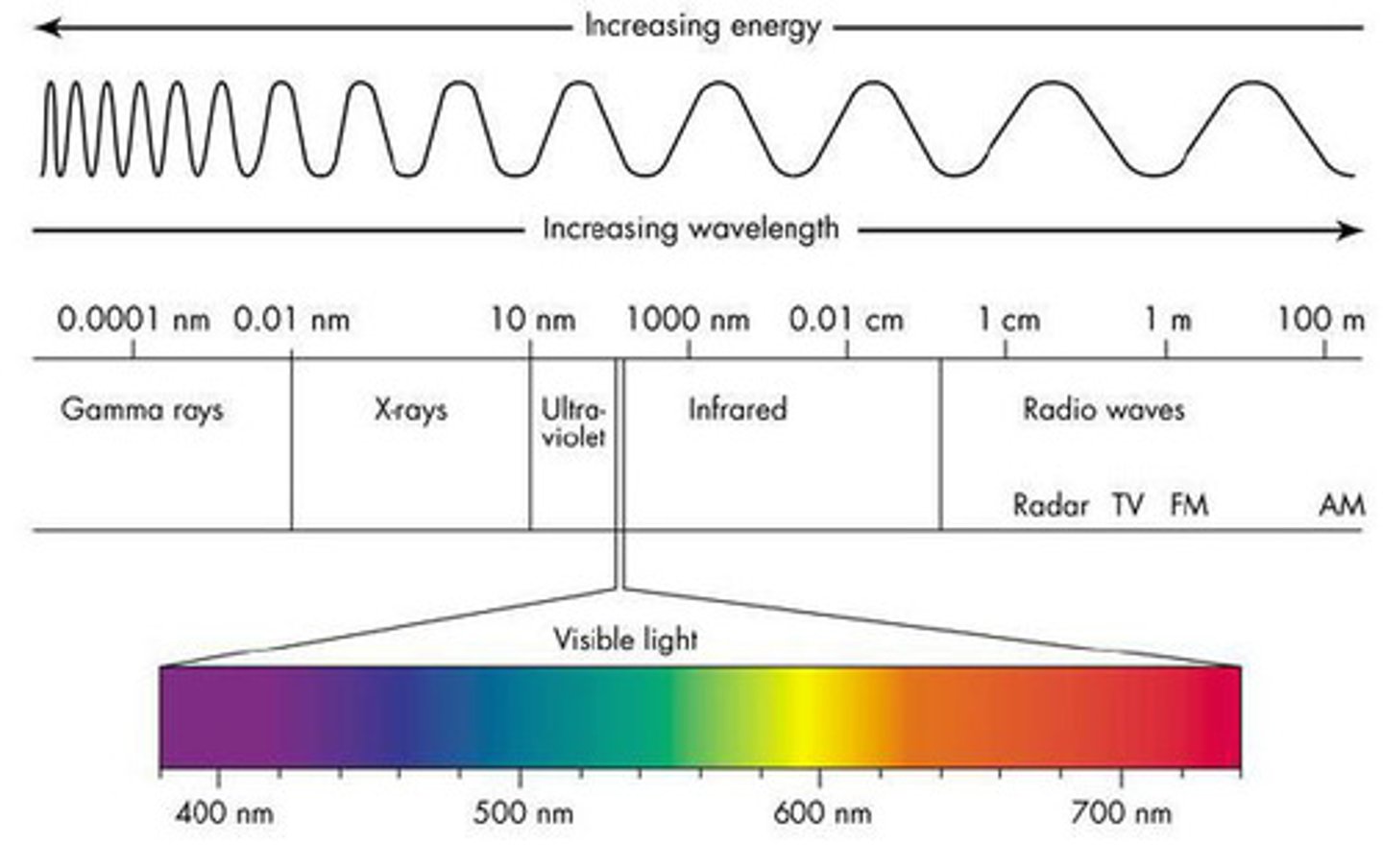
gamma rays vs radio waves
frequency: gamma rays largest & radio waves smallest
energy: gamma rays largest & radio waves smallest
wavelength: radio waves largest & gamma rays smallest
ROYGBIV
what white light separates into; red light has the larger wavelength and smaller frequency
how are wavelength and frequency related?
INDIRECTLY; as λ increases, 𝝂 decreases
how are frequency and energy related?
directly, as 𝝂 increases, E increases
calculations for λ, 𝝂, and E
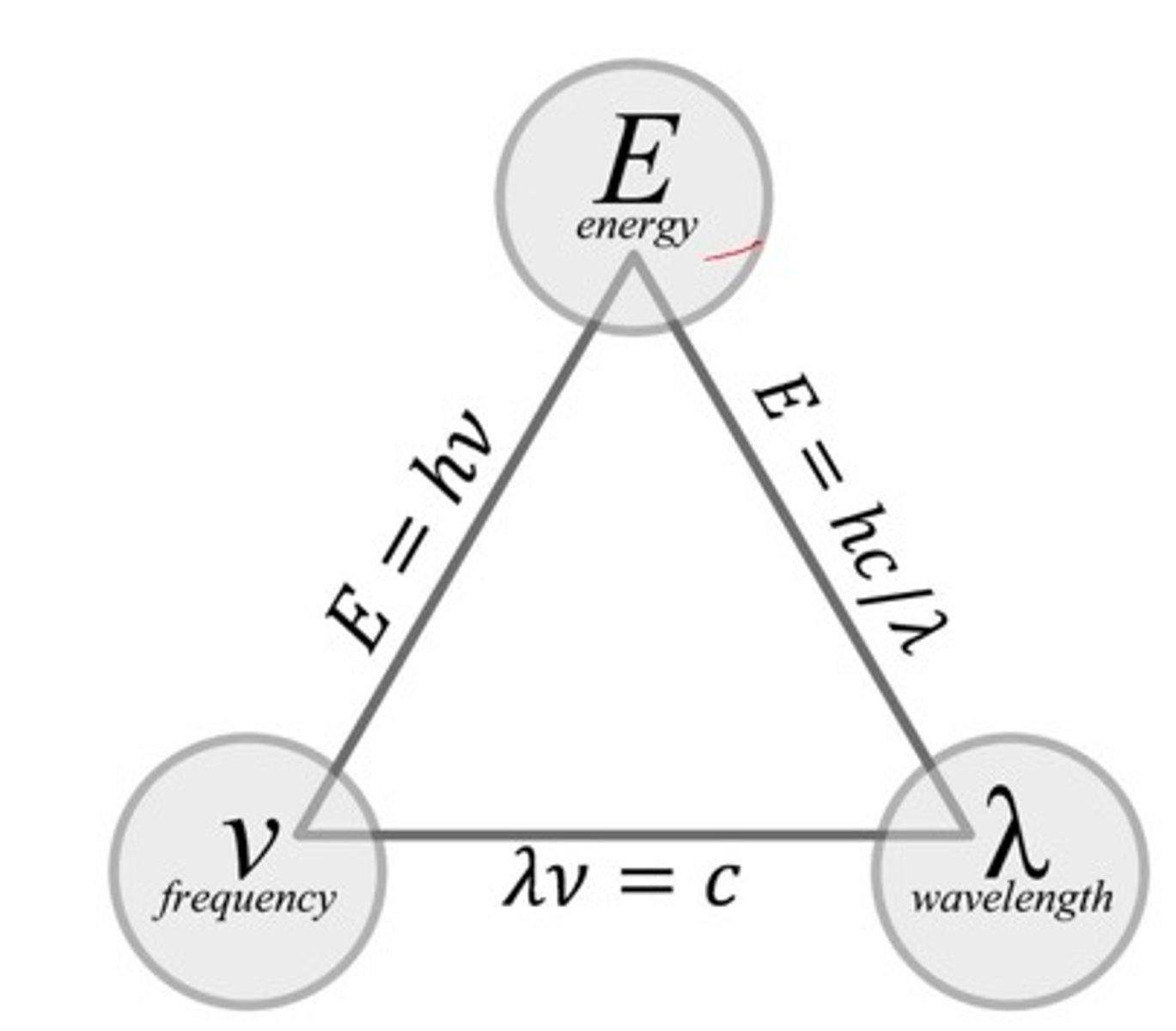
Planck's constant
6.626 x 10^-34
as energy increases
frequency increases and wavelength decreases
atomic spectrum/bright line spectrum
when energy is added to an element in gas phase; it glows one color when see through a prism; result of emission/ energy changes of electrons
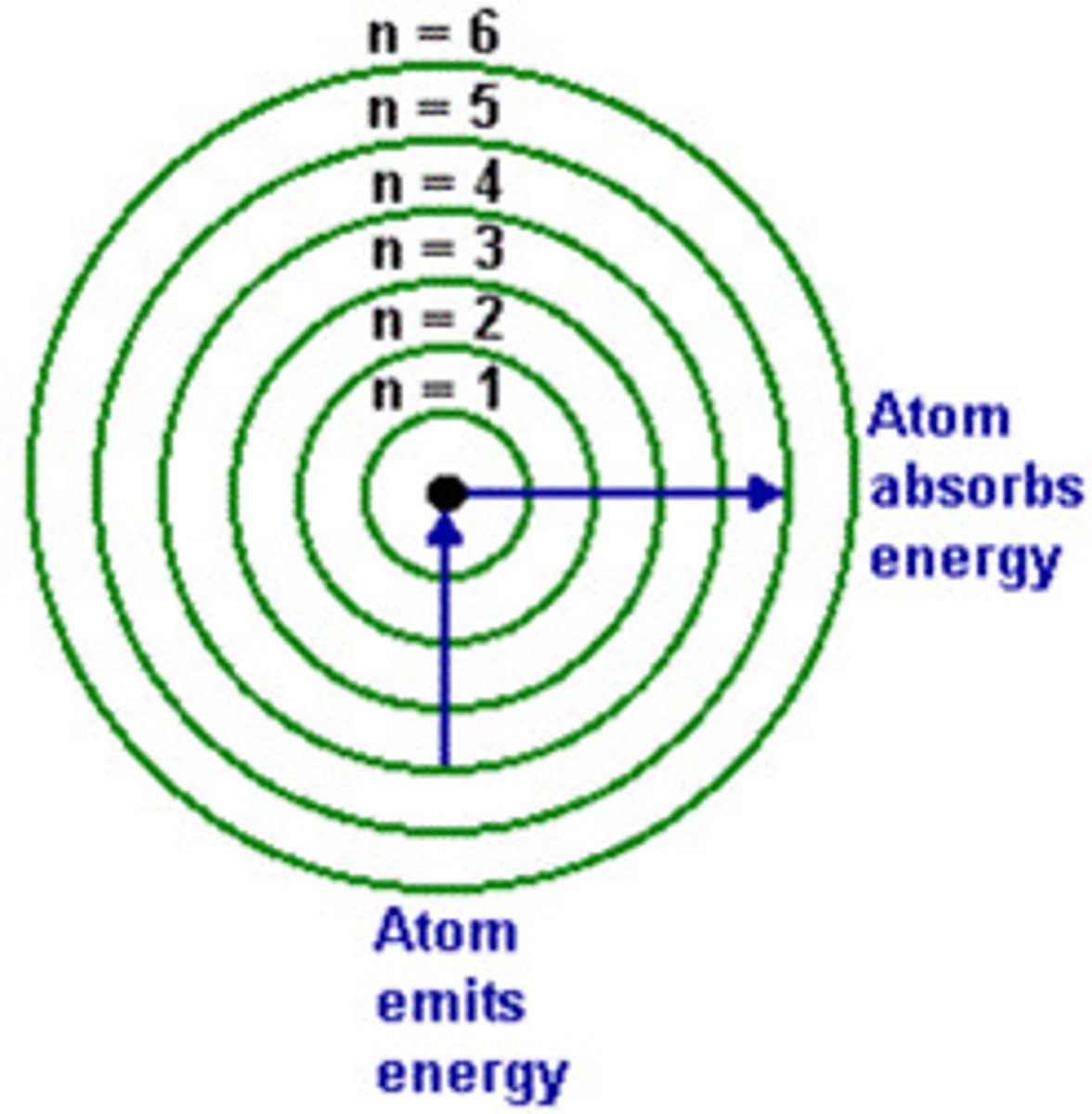
absorption
when electrons gain energy; electron goes away from nucleus
emission
when electrons lose/give off energy; electron goes toward nucleus
# of orbitals on energy level
n^2
# of electrons that can fill an energy level
2n^2
# of sublevels of an energy level
n
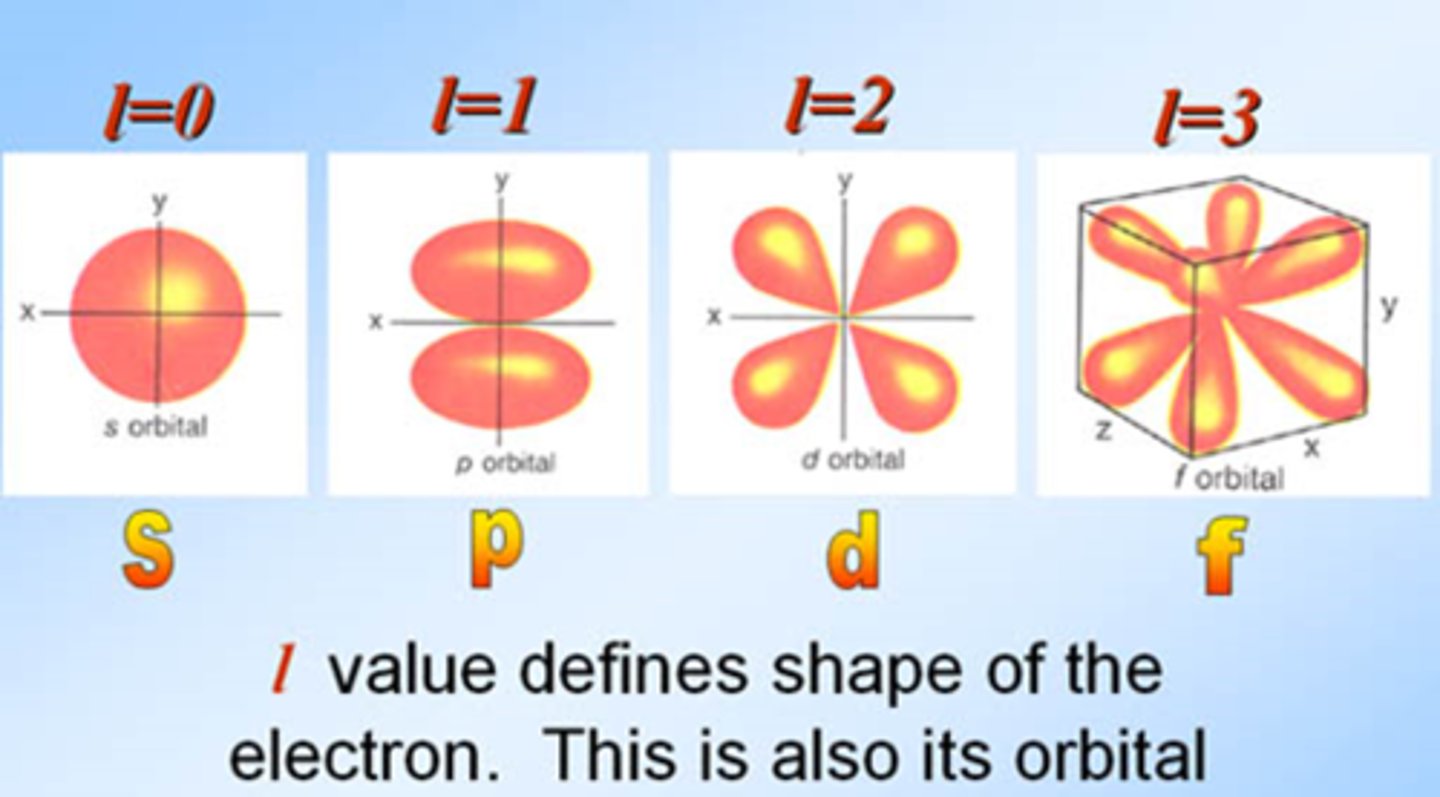
sublevels
subdivisions of energy levels > s (1 orbital), p(3), d(5), f(7)
spacing in energy levels
no evenly spaced; most space between 1S and 2S; get closer as you go up; higher energy levels are away from nucleus
ground vs excited state
ground - lowest energy state; excited - higher potential energy
quantum of energy
the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom
quantum numbers
specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals
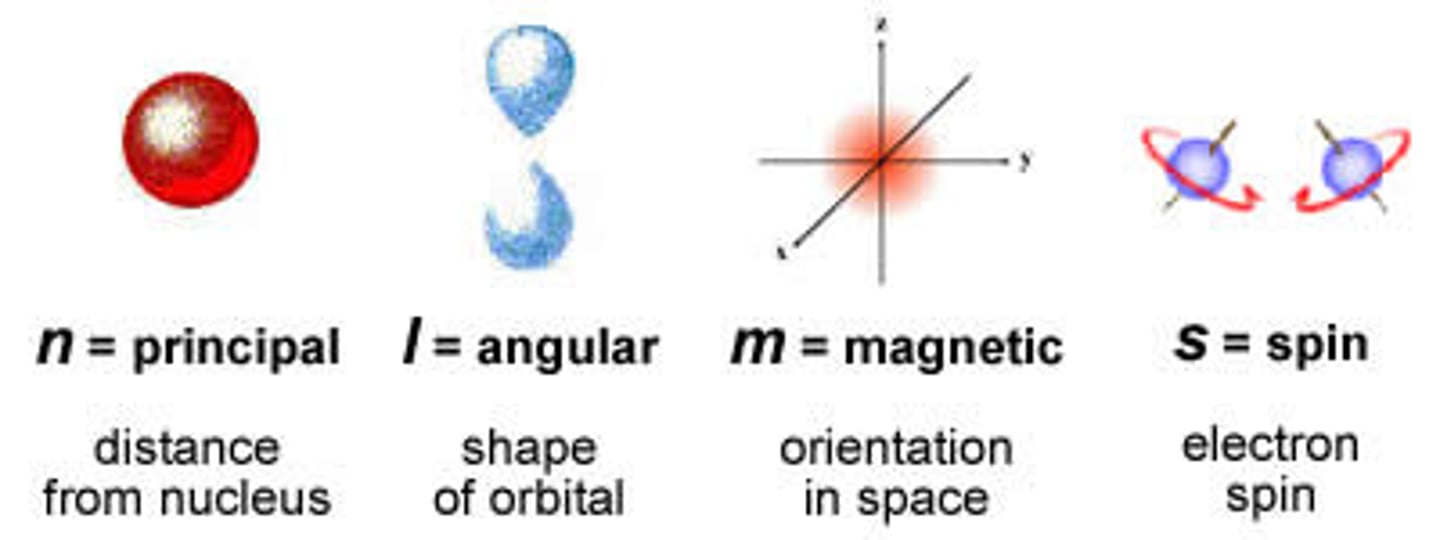
principal quantum number
symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron; roughly determines the size
angular momentum quantum number
symbolized by l, indicates the shape of the orbital
magnetic quantum number
symbolized by m, indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus
spin quantum number
has only two possible values (+1/2, -1/2) which indicate the two fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital; symbolized by m_l
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it
pauli exclusion principle
electrons in the same orbital will have opposite spins
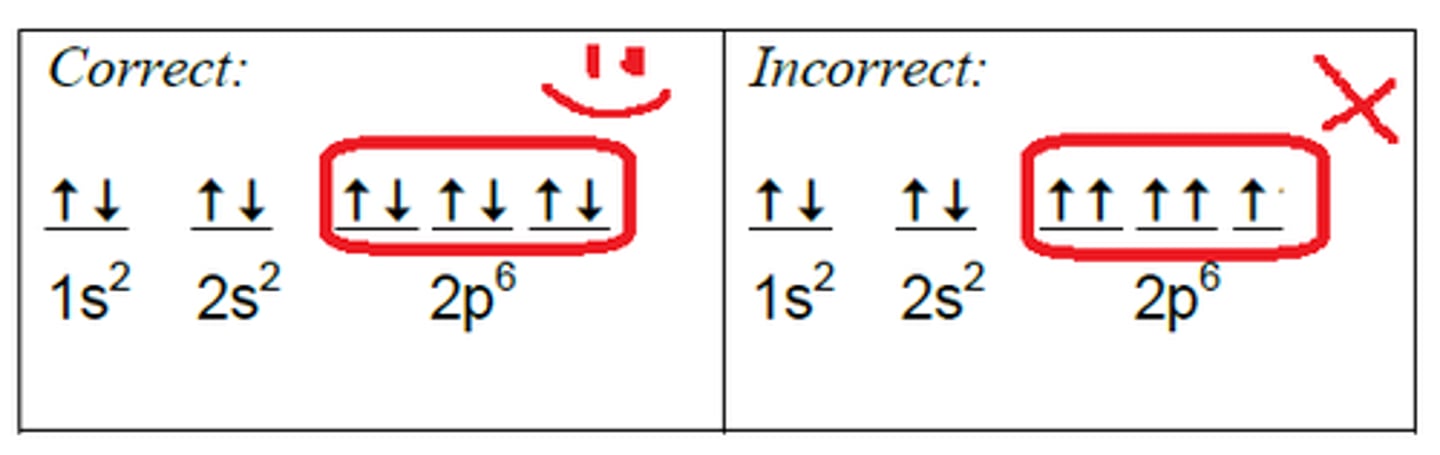
hund's rule
orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin; to avoid electron repulsion
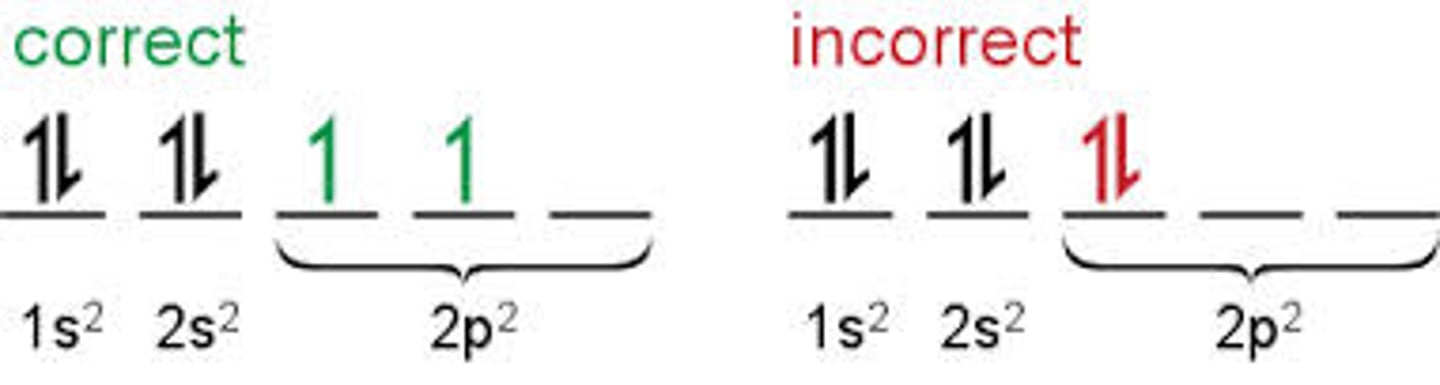
HOEL (highest occupied energy level)
the energy level with the highest value of n; contains orbitals furthest away from the nucleus
Outer shell
orbitals in the HOEL
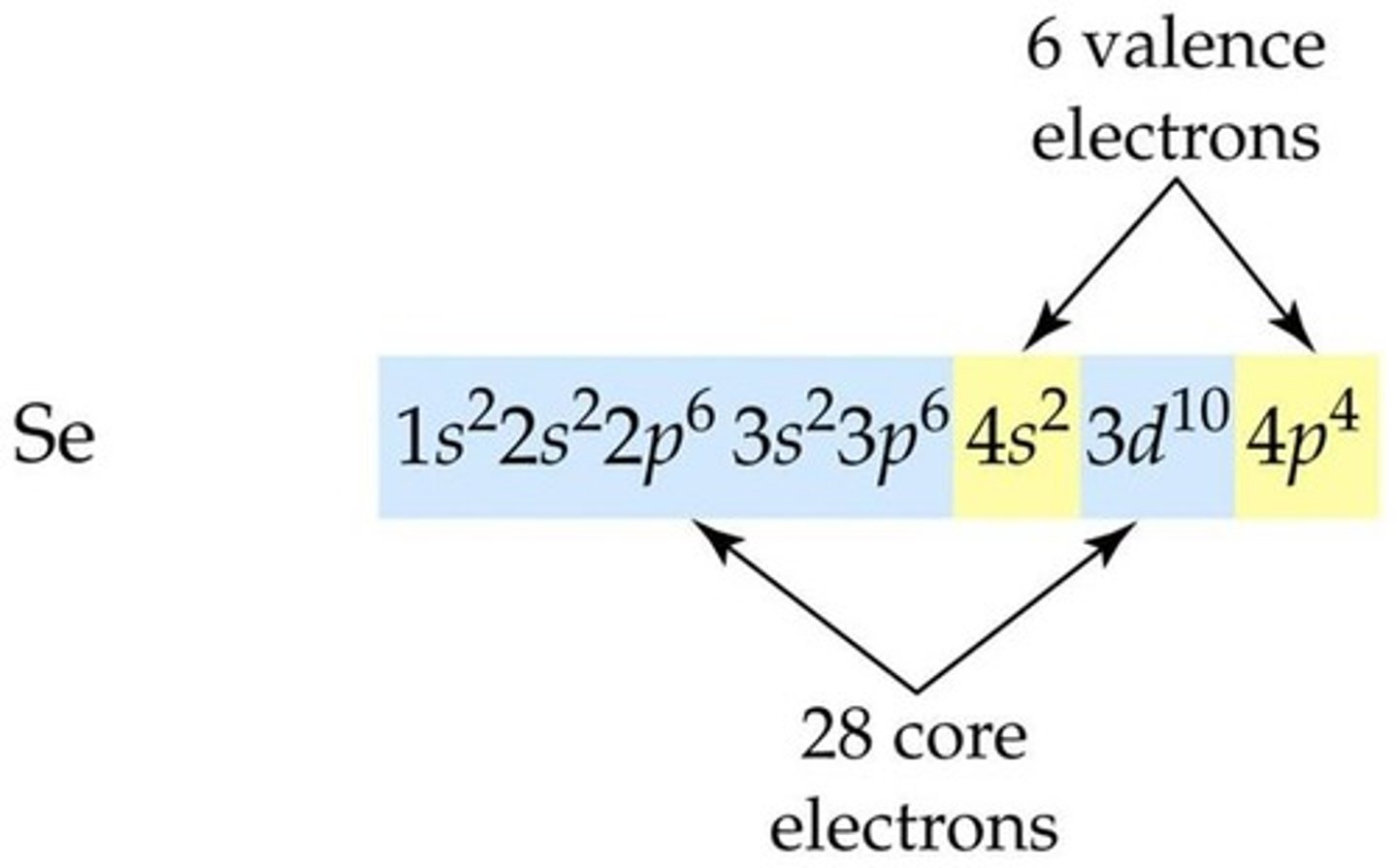
Valence electrons
electrons found in the HOEL; furthest away from nucleus
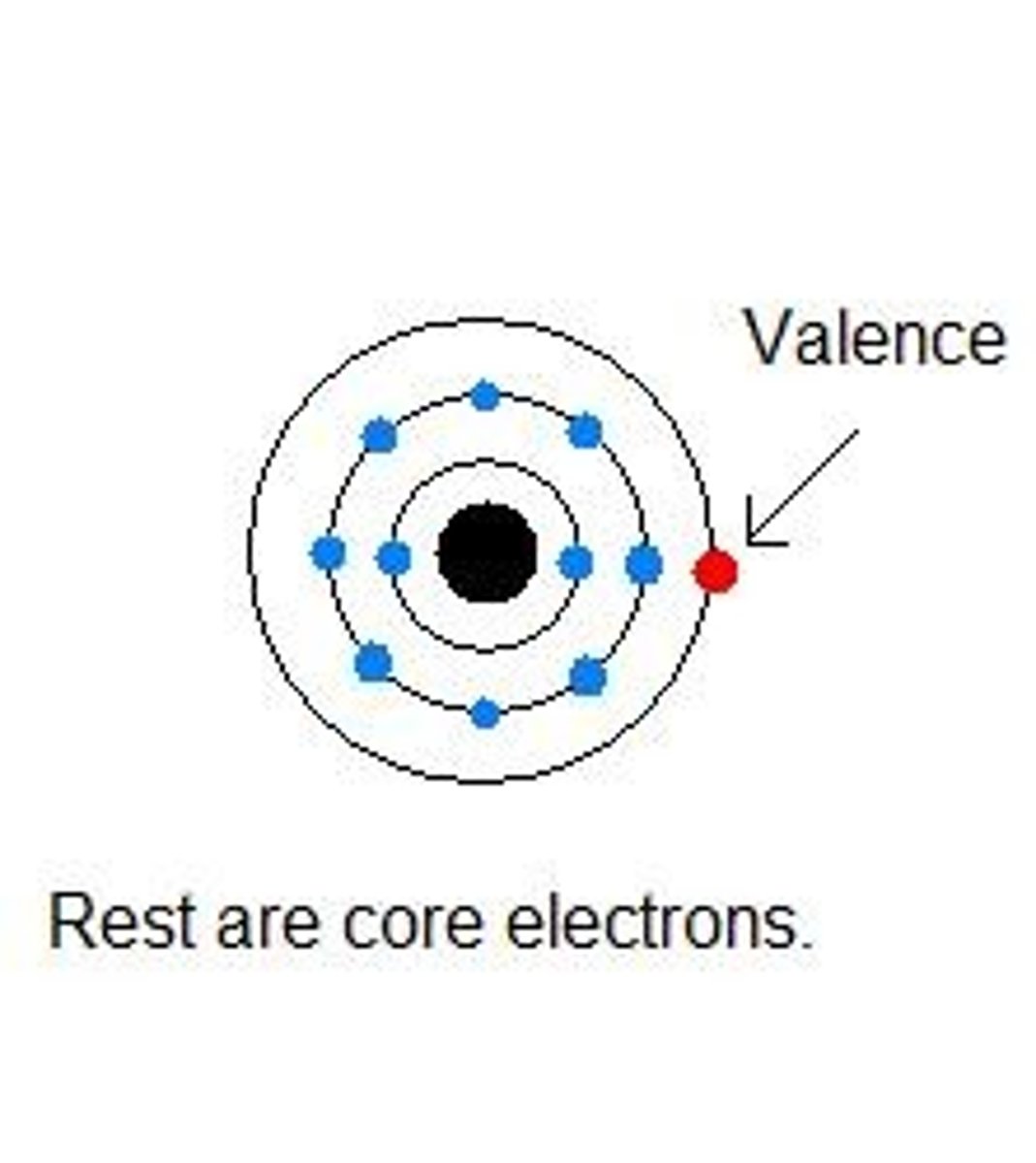
Core electrons
electrons closest to the nucleus
Inner shell
orbitals that contain the core electrons
electron configuration
organization of electrons in atoms from orbitals of lowest energy to orbitals of highest energy

exceptions for electron configuration
half filled or half/full to avoid electron repulsion or make it more stable
energy level
distinct region where electrons in an atom occupy/are found
orbitals
indicates probable location of an electron; holds 2
electron configurations for ions
anions-add electrons
cations-remove valence electrons
s orbital shape
sphere
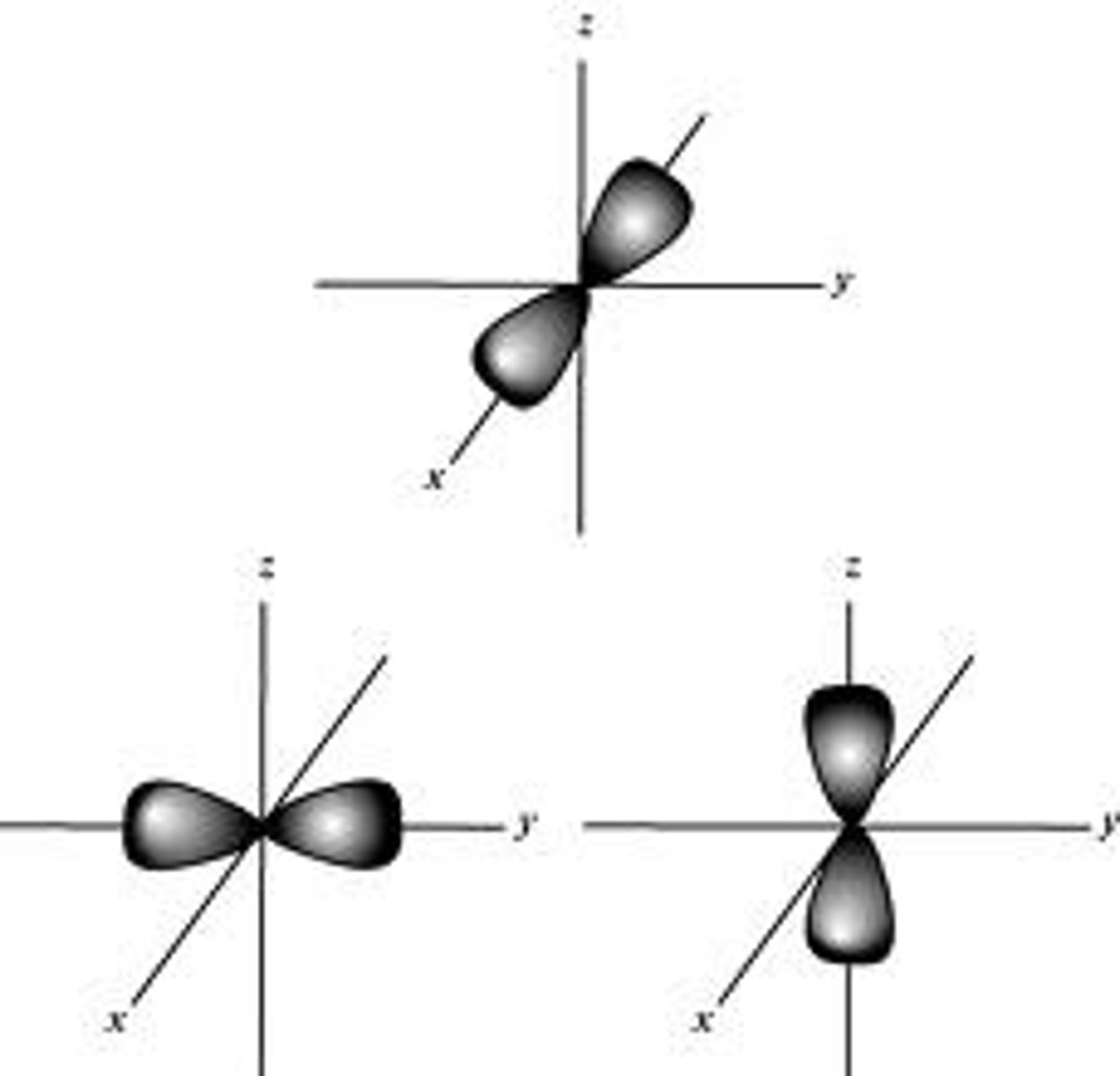
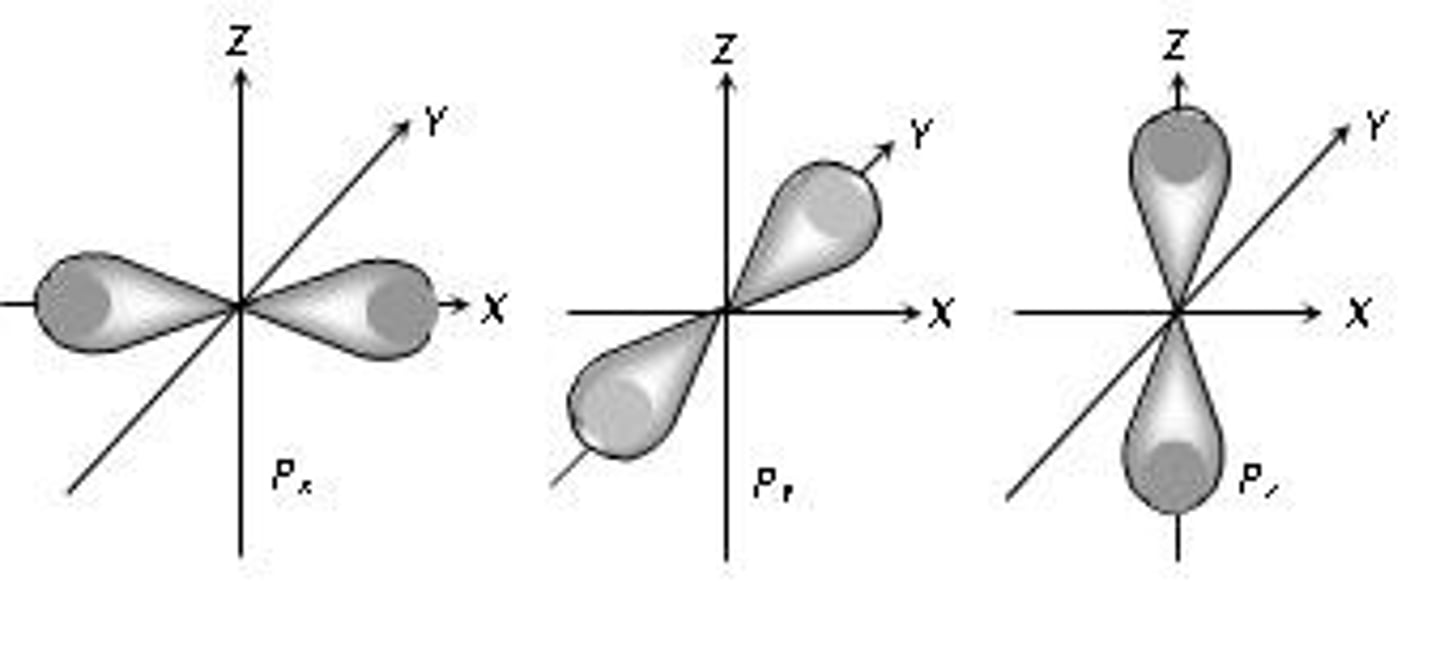
p orbital shape
double lobed