Mirco-Biology Study
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:13 AM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1
New cards
Who is considered the “Father of Western Medicine”?
Hippocrates
2
New cards
What was Thucydides’ findings?
What is Laid the foundation for immunity
3
New cards
Who was the first to observe “animalcules“ under the microscope
**Antonie van Leeuwenhoek**
4
New cards
Carl Linnaeus is known as the father of_____.
Binomial Nomenclature
5
New cards
Name at least 4 things about Louis Pasteur
**Pioneer for Microbio, Fermentation, Vaccines, Pasteurization, Disproved spontaneous gen. with swan neck flasks**
6
New cards
Define Microscope
Produce magnified images of microorganisms, human cells, and tissues, and many other types of specimens too small to be observed with the naked eye
7
New cards
**What is an inoculation loop?**
**A handheld tool that is a small wire that is used to capture and streak growth media**
8
New cards
**What is growth media?**
**Used to grow microorganisms in a lab setting**
9
New cards
**We use a bunsen burner to create a flame to ___ pieces of equipment**
**Sterilize**
10
New cards
**What do we use stains and dyes for?**
**They are used to add color to microbes so they can be better observed under a microscope**
11
New cards
**What are the two common features for all living cells?**
**Plasma Membrane &**
**Genetic Material**
**Genetic Material**
12
New cards
**What are the three domains?**
**Bacteria,**
**Archaea, &**
**Eukarya**
**Archaea, &**
**Eukarya**
13
New cards
**What is the difference between Prokaryotes and Eukarotes?**
**Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus**
**Eukaryotes do have a nucleus**
**Eukaryotes do have a nucleus**
14
New cards
What is the difference between the domain bacteria & archaea, which are both prokaryotes?
**Bacteria has cell walls called peptidoglycan**
**Archaea does not have peptidoglycan but pseudo-aquamarine membrane**
**Archaea does not have peptidoglycan but pseudo-aquamarine membrane**
15
New cards
**What is the hierarchy of classification? (High to Low)**
**Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species**
16
New cards
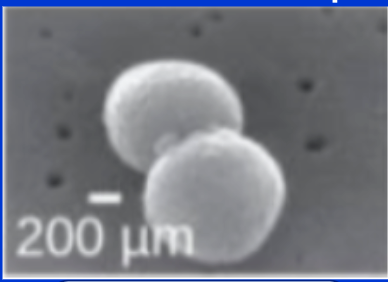
Name the shape:
**Coccus, Cocci**
17
New cards

Name the Shape:
**Bacillus, Bacilli**
18
New cards
**What do you call a straight chain of bacilli?**
**Streptobacilli**
19
New cards
**What do you call a curved rod?**
**Vibrio**
20
New cards

**Name & Describe the**
**Name: Spirochete**
**Shape: Corkscrew**
**Shape: Corkscrew**
21
New cards
**Are viruses cellular or acellular?**
**Acellular meaning that they are not composed of cells**
22
New cards
**The process by which microbes turn grape juice into wine is called ___.**
**Fermentation**
23
New cards
What is the name?
**The study of bacteria**
24
New cards
**What is Bacteriology?**
**The study of bacteria**
25
New cards
**Name at least 3 things you know about viruses**
**Acellular**
**DANN or RNA core**
**Core surrounded by protein coat**
**Maybe enclosed by lipid envelope**
**Pathogenic**
**They can live outside the host for a long time**
**DANN or RNA core**
**Core surrounded by protein coat**
**Maybe enclosed by lipid envelope**
**Pathogenic**
**They can live outside the host for a long time**
26
New cards
Who made the phylogenetic tree? ( Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya)
Woese & Fox
27
New cards
What are the 4 sub domains of the Eukaryotes?
* Plant
* Animals
* Fungi
* Protist
* Animals
* Fungi
* Protist
28
New cards
What is the difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus, while Eukaryotes do.
29
New cards
What is the Hierarchy Classification?
* Kingdom
* Phylum
* Class
* Order
* Family
* Genus
* Species
(keep pots clean or family gets sick)
* Phylum
* Class
* Order
* Family
* Genus
* Species
(keep pots clean or family gets sick)
30
New cards
What is the study of virology?
The study of viruses
31
New cards
Label the parts of microscope parts: 1, 3, 4, and 5.
**Ocular lens/eyepiece 3. Objective lens 4. Course focus (for 10x) 5. Fine focus (40x and 100x)**
32
New cards
Which type of microscope can you use to visualize molecules?
**AF (atomic force) M and ST (scanning tunneling) M**
33
New cards
What are the advantages of bacterial fixing?
**Adheres specimen to the slides and kills bacteria**
(**Heat and chemical fixing)**
(**Heat and chemical fixing)**
34
New cards
Basic stains are — charged and acidic stains are — charged?
**Positively charged, negatively charged**
35
New cards
What is the charge on cells? What does acidic stains stain: the cell or background?
**Negative charge, acidic stains color background**
36
New cards
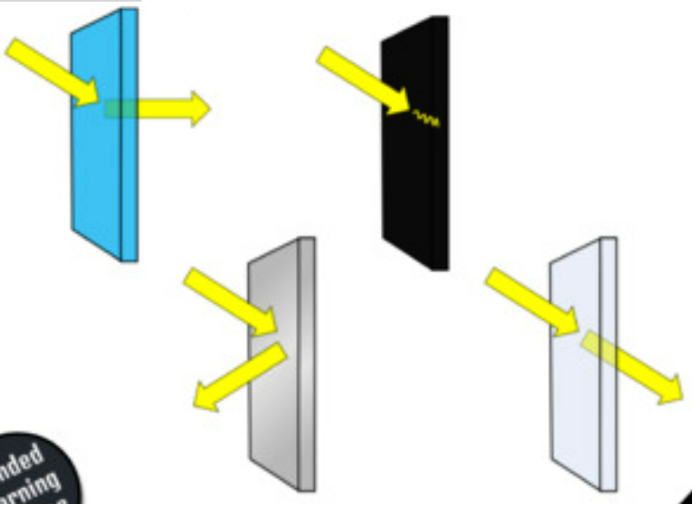
Which image represent: reflection, transmission, absorption, and refraction
**Blue: refraction, black: absorption, silver: reflection, white: transmission**
37
New cards
What are the difference between light and electron microscope?
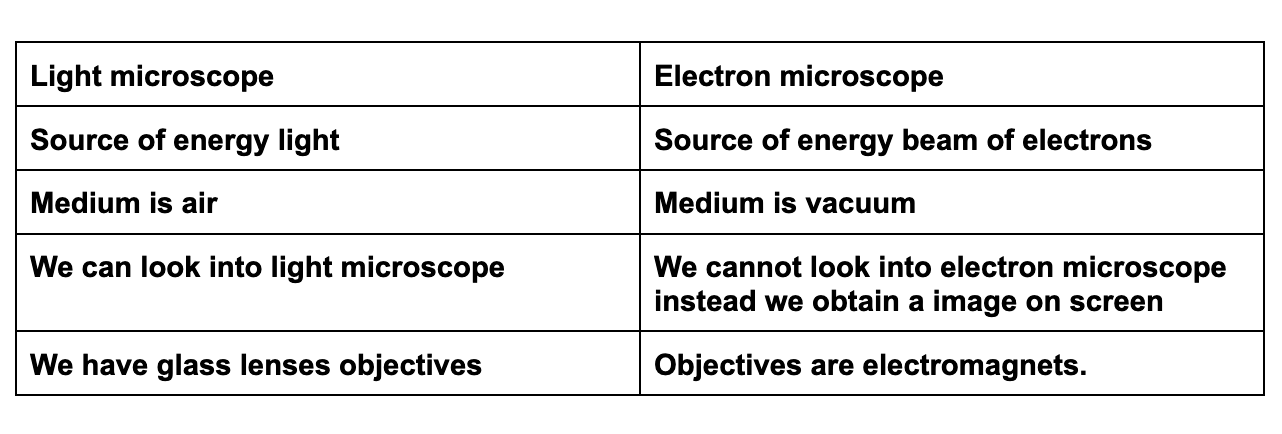
38
New cards
What is the use of oil immersion?
**Improve resolution by reducing refraction is the use of oil immersion**
39
New cards
1. Complete the table chart below
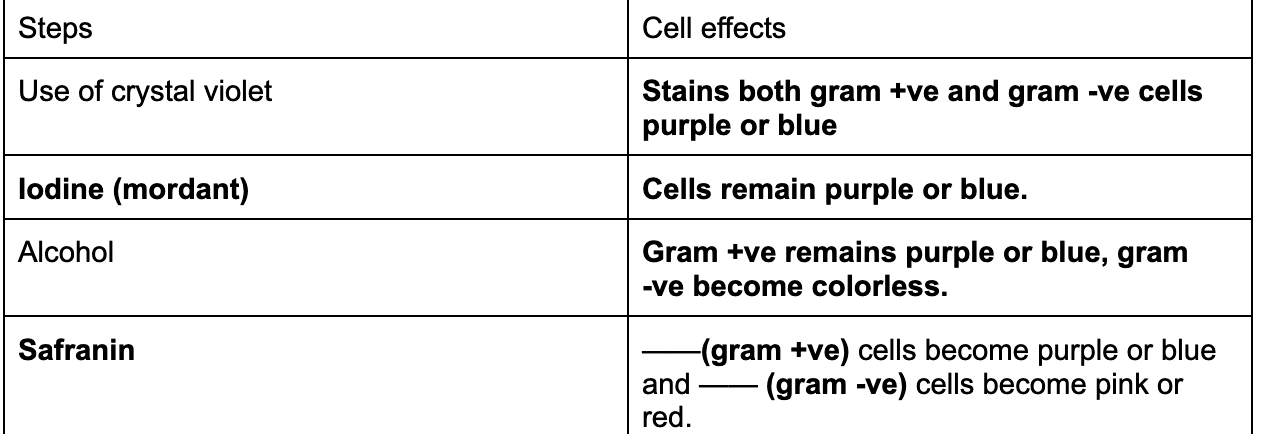
40
New cards
What type of staining is used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis?
**Acid-fast staining or Ziehl-Neelson staining**
41
New cards
What will be the total magnification if the objective magnification is 40x in a light microscope?
**400x (40x X 10x)**
42
New cards
Who observed the dead cork cells under the microscope?
**Robert hooke**
\
**( Discovery of Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek: first person to see live microbes and called them animalcules )**
\
**( Discovery of Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek: first person to see live microbes and called them animalcules )**
43
New cards
Which theory states that life arises from non-living matter?
**Spontaneous generation**
44
New cards
What was the discovery of Joseph Lister?
**Using chemical disinfectant to prevent surgical wound infections**
45
New cards
Who proposed the importance of handwashing in preventing transfer of disease between patients by physicians?
**Ignaz Semmelweis**
46
New cards
Who conducted the first epidemiological study?
**John Snow**
**(Which disease was the study about? Cholera breakdown)**
**(Which disease was the study about? Cholera breakdown)**
47
New cards
Who performed an experiment to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation?
**Francesco Redi Maggot experiment and Louis Pasteur Swan neck experiment**
48
New cards
Define the theory of biogenesis?
**Life comes only from life.**
49
New cards
Chloroplast is one of the organelles that were derived from bacteria as a result of spontaneous generation theory? ( T or F)
False
**(Correct: Endosymbiotic theory)**
**(Correct: Endosymbiotic theory)**
50
New cards
**What are the organelles? From Endosymbiotic theory**
**Mitochondria &** Chloroplast
51
New cards
How are mitochondria and chloroplasts similar to bacteria?
**Resemble bacteria in shape and size**
**Contain circular DNA**
**Contain 70s ribosomes**
**Contain circular DNA**
**Contain 70s ribosomes**
52
New cards

Name the bacterial shape?
**Streptobacilli**
53
New cards
The cell with a cell wall is placed in hypertonic solution. What will happen to the cell and name the term to describe the change occurring?
**The cell membrane will shrink as the cell loses water and this is called plasmolysis.**
54
New cards
The cell with no cell wall is placed in hypertonic solution. What will happen to the cell and name the term to describe the change occurring?
**Cell will shrink as it loses water and it is called Crenation.**
55
New cards
The cell without a cell wall is placed in hypotonic solution. What will happen to the cell and name term to describe the change?
**The cell will gain water and swell and burst which is called lysis.**
56
New cards
What is the structure of a plasma membrane?
**Phospholipid bilayer**
**Peripheral proteins**
**Integral proteins**
**Peripheral proteins**
**Integral proteins**
57
New cards
Which transport mechanism requires the use of energy: active or passive transport?
Active
(why: **Because the substance moves from low to high concentration against the concentration gradient which requires energy.)**
(why: **Because the substance moves from low to high concentration against the concentration gradient which requires energy.)**
58
New cards
Teichoic acids are present in which cell wall:
Gram Positive
59
New cards
**Does Gram Positive have thick or thin peptidoglycan layer?**
Thick
60
New cards
**Does Gram Negative have thick or thin peptidoglycan layer?**
Thin
61
New cards
What is the color of gram negative bacteria at the end of gram staining?
**Red or pink**
(**Why: Because it have thin peptidoglycan layer.)**
(**Why: Because it have thin peptidoglycan layer.)**
62
New cards
**What is the glycocalyx and its function?**
“Sugar Coat” and contributes to virulence. Capsules prevent phagocytosis and glycocalyces allow cells to adhere to surfaces, aiding in the formation of biofilms
63
New cards
**What are the two types of glycocalyces?**
Capsule and Slime layer
64
New cards
**What is the difference between fimbriae and pili?**
Fimbriae:
* a few to several hundred per cell
* Allow attachment rather than motility
\
Pili:
* longer and fewer than fimbriae,
* Attachment and motility
* For DNA transfer or sexual reproduction
* a few to several hundred per cell
* Allow attachment rather than motility
\
Pili:
* longer and fewer than fimbriae,
* Attachment and motility
* For DNA transfer or sexual reproduction
65
New cards
**What are the three parts of a flagella?**
Filament, Hook, and Basal Body
(Basal body: anchors flagellum to the cell wall and membrane.)
(Basal body: anchors flagellum to the cell wall and membrane.)
66
New cards
**What is the flagella made of?**
Made of chains of the protein flagellin
67
New cards
**What is motility?**
Enable cells to move toward a desired environment or flee from a harmful environment.
68
New cards
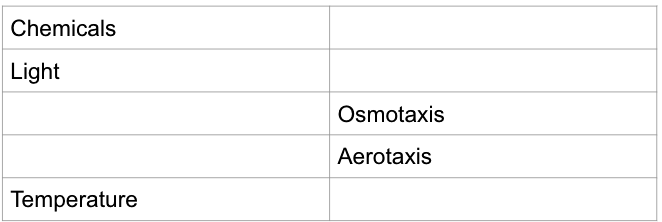
**Fill in the blank of the missing external stimuli:**
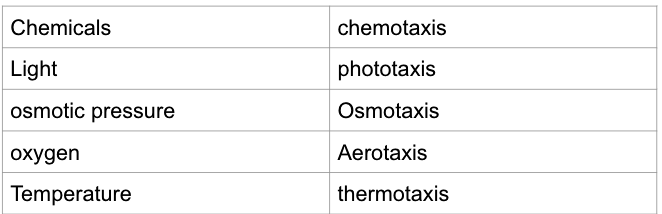
69
New cards
**If a cell with a peritrichous flagella rotates in a counterclockwise direction, it results in a ___.**
**When the flagella rotates in a clockwise direction, it results in a ___.**
**When the flagella rotates in a clockwise direction, it results in a ___.**
Run
Tumble
Tumble
70
New cards
**Name the following types of flagella:**
mono = 1
amphi = 2, but opposite sides “ambidextrous”
loph = “lopp” sidded
peri = around
amphi = 2, but opposite sides “ambidextrous”
loph = “lopp” sidded
peri = around
71
New cards
**What happens to the length of the runs when there is a chemical gradient of an attractant? What happens to the length of the tumbles?**
Runs is extended and tumbles decreased.
72
New cards
**What are the 3 main characteristics of eukaryotic organisms?**
Nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane
Membrane-bound organelles
Cytoskeleton
Membrane-bound organelles
Cytoskeleton
73
New cards
**What is the nucleolus?**
Small, round granular body composed of protein and RNA, where ribosomal RNA is synthesized.
74
New cards
**What surrounds the nucleus?**
The nuclear envelope
75
New cards
**What are the four organelles that consist of the endomembrane system?**
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vesicles
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vesicles
76
New cards
**What is the difference between Rough ER and Smooth ER?**
Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes; sites of protein synthesis
Smooth ER: no ribosomesl synthesizes cell membranes, fats, hormones
Smooth ER: no ribosomesl synthesizes cell membranes, fats, hormones
77
New cards
**What is the cytoskeleton made up of? What is its function?**
1. Made of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
2. Structural support
3. Network allowing for the Transport of material within the cell
78
New cards
**What is the mitochondria’s function?**
**What kind of membrane does it have?**
**What kind of genetic materials does it have?**
**What kind of membrane does it have?**
**What kind of genetic materials does it have?**
a. “Powerhouse of the Cell” – ATP production
b. Double membrane-
* Outer membrane that is smooth
* Inner membrane: series of folds – cristae, where chemical reactions occur
c. Matrix contain 70ss ribosomes and mitochondrial DNA>
b. Double membrane-
* Outer membrane that is smooth
* Inner membrane: series of folds – cristae, where chemical reactions occur
c. Matrix contain 70ss ribosomes and mitochondrial DNA>
79
New cards
**What do you call a membrane--enclosed structure containing chlorophyll and enzymes necessary for photosynthesis? (Not chloroplast)**
thylakoids
80
New cards
**What are sterols of the plasma membrane?**
Types of lipids on the plasma membrane of eukaryotes
81
New cards
**What is the cell wall of fungi made up of?**
Chitin
82
New cards
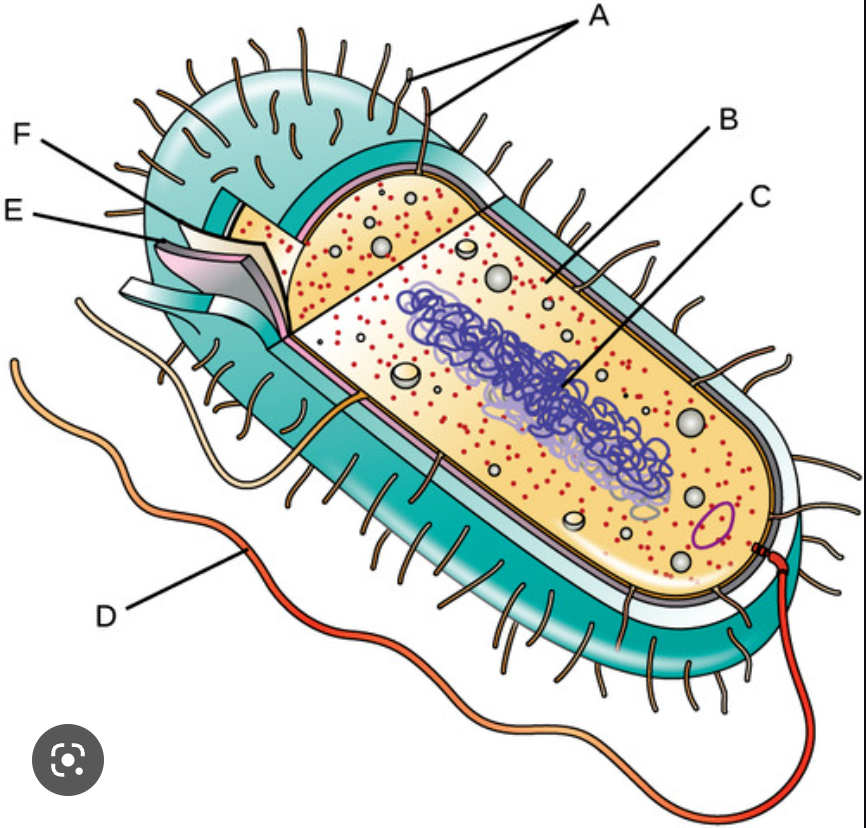
Name the Parts
a. - flimbria
b. cytoplasm
c. nucleoid
d. flagella
e. Cell wall
f. Plasma membrane
b. cytoplasm
c. nucleoid
d. flagella
e. Cell wall
f. Plasma membrane
83
New cards
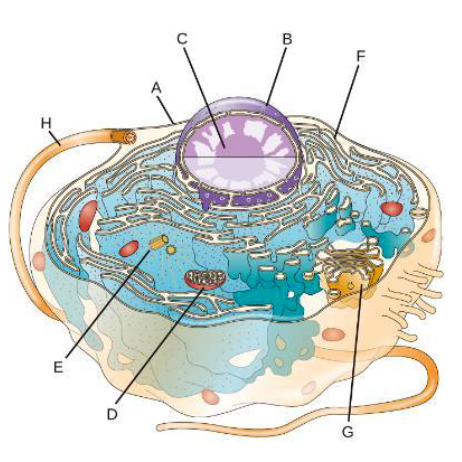
Name the Parts
a. Plasma membrane
b. nucleus
c. nucleolus
d. mitochondria
e. centrioles
f. Rough endoplasmic rectum
g. Golgi apparatus
h. flagella
b. nucleus
c. nucleolus
d. mitochondria
e. centrioles
f. Rough endoplasmic rectum
g. Golgi apparatus
h. flagella
84
New cards
A. *Staphylococcus epidermidis* uses the dead cells of the human skin as nutrients. This is an example of what type of relationship?
**Commensalism**
85
New cards
In what type of relationship one population is harmed and one is unaffected.
**Amensalism**
86
New cards
What is the other name of class alphaproteobacteria?
**Oligotrophs**
(**Why: Because they are capable of growing at a very low level of nutrients)**
(**Why: Because they are capable of growing at a very low level of nutrients)**
87
New cards
**What is other name of betaproteobacteria?**
**Eutrophs.**
(**Why: Because they are capable of growing at a very high level of nutrients.)**
(**Why: Because they are capable of growing at a very high level of nutrients.)**
88
New cards
Which organism causes sexually transmitted disease that is common on college campuses?
***Chlamydia trachomatis***
(**What else does it cause? Trachoma leading to blindness)**
(**What else does it cause? Trachoma leading to blindness)**
89
New cards
Most diverse and largest subgroup of gram negative bacteria?
**Gammaproteobacteria**
90
New cards
Smallest subgroup and largest subgroup of gram negative bacteria?
**epsilonproteobacteria**
91
New cards
Bacteria that are able to ferment lactose completely are called?
**Coliforms**
92
New cards
**What are non coliforms?**
**Either cannot lactose or lactose incompletely.**
93
New cards
Name an organism that causes typhoid fever?
***Salmonella typhi***
94
New cards
Name the toxin released by the strains of *E. coli* that can cause bloody diarrhea and peritonitis?
**Shiga toxin**
95
New cards
Match the following?
96
New cards
Which subgroup of proteobacteria include bacteria that are predators on other bacteria?
**Deltaproteobacteria**
97
New cards
Campylobacter and helicobacter and found in which subgroup of proteobacteria?
**Epsilonproteobacteria**
98
New cards
What are three subgroups of gram negative nonproteobacteria?
**Spirochetes, CFB group, and Cytophaga**
99
New cards
Bacteroides comprise upto what percent of normal microbiota in the human gut.
**30%**
100
New cards
What are the subgroups of gram positive bacteria?
**Actinobacteria**
**Bacilli**
**Bacilli**