Models, Errors and the Normal Distribution
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Formula
Error =
Error = Data - Model
𝑒𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟𝑖 = 𝑦𝑖 − ŷ𝑖
Mode as measuring error
ŷ𝑖
The most common value
A very simplified measure
Mean as measuring error
Summing all data points then dividing by number of data points - Ȳ represents the mean.
Looks at the average value.
Poor measure of error - allows values to cancel each other out.
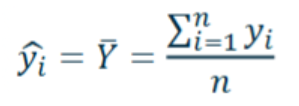
Squared error as measuring error
𝑒𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟𝑖 = (𝑦𝑖 − ŷ𝑖)2
Can only be positive because you're squaring it.
Sum Squared Error (SSE) as measuring error
Sums all of the data points
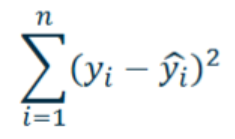
Mean Squared Error (MSE) as measuring error
Often seen being used in model fitting literature.
Sum of all the squares divided by number of data points.
Problem with units being squared.
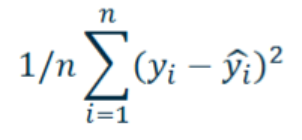
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) as measuring error
Unit generated makes the most sense in measuring the model error.
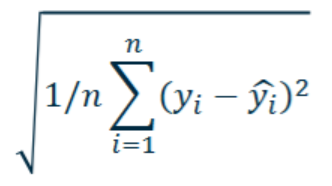
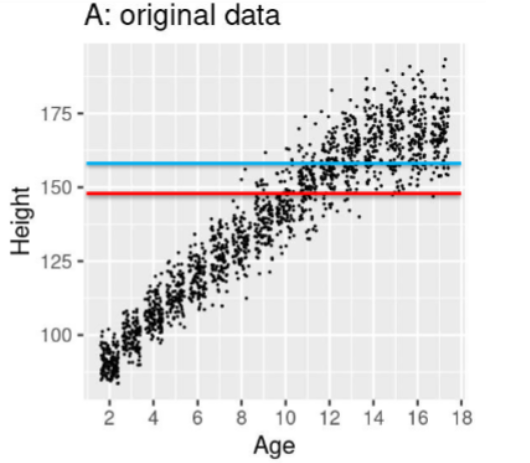
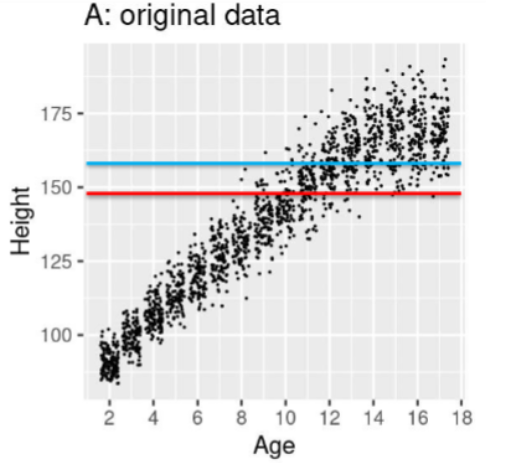
Model A: Judge this model
Equation: ŷ𝑖 = B̂𝑖 ∗ 𝑎𝑔𝑒𝑖
Takes into account that there actually are differences across age.
Model for each data point now depends on age of the specific child, multiplied by a parameter (the slope of the blue line).
Problem that this model goes through 0 - no child born at 0cm.
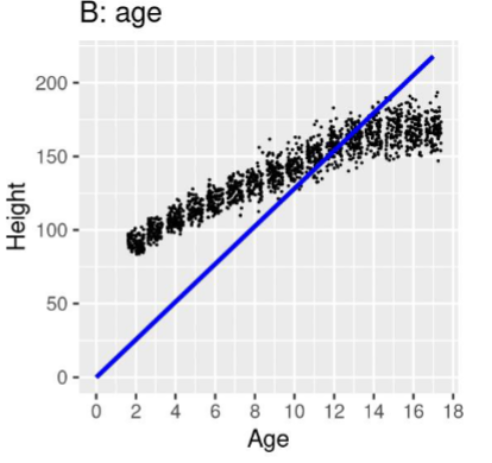
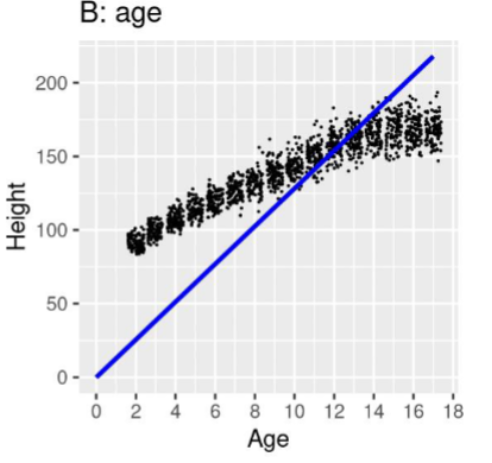
Model B: Judge this model
Equation: ŷ𝑖 = B̂0 + B̂1 ∗ 𝑎𝑔𝑒𝑖
Adds a constant - good job at explaining data, but could be split into other factors.
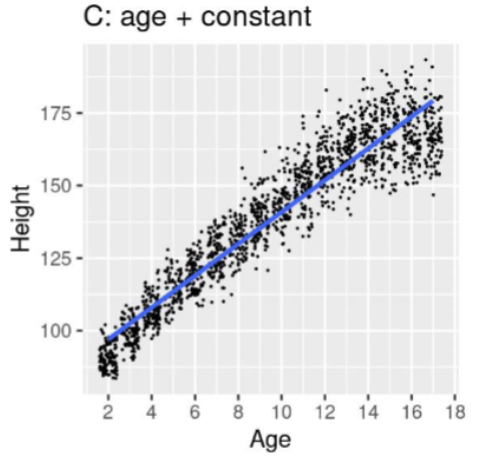
Model C: Judge this model
Equation: ŷ𝑖 = B̂0 + B̂1 ∗ 𝑎𝑔𝑒𝑖
Equation: ŷj = B̂2 + B̂3 ∗ 𝑎𝑔𝑒j
Two separate models.
Estimating slope and adding a constant for both male and female.
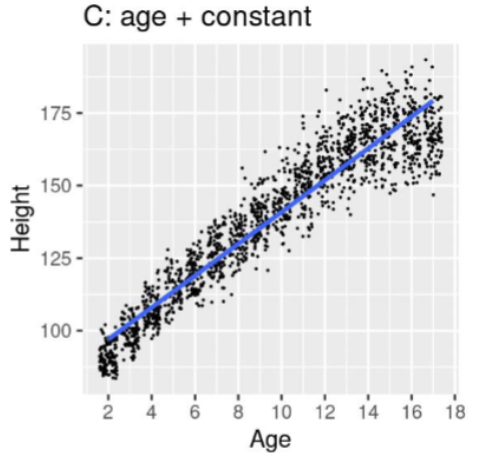
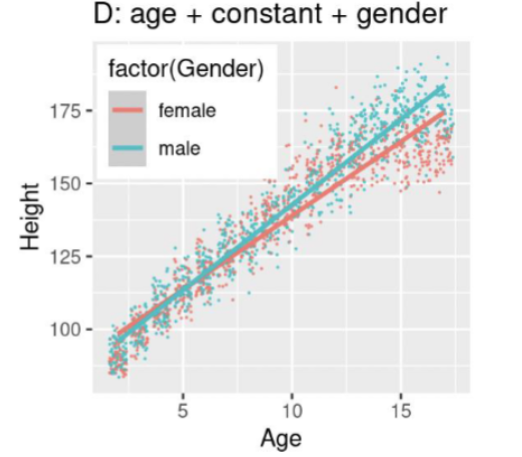
Model D: Judge this model
ŷ𝑖 = B̂0 + B̂1 ∗ 𝑎𝑔𝑒𝑖
ŷj = B̂2 + B̂3 ∗ 𝑎𝑔𝑒j
ŷ𝑖 = Ȳ

Equation for a normal distribution
𝑁(𝜇, 𝜎2)
𝜇 - specifies where centre of the distribution is placed.
𝜎2 - how wide the distribution is.
Likelihood equation
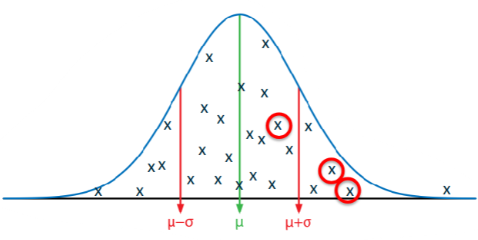
𝑃(𝑥|𝜇, 𝜎2)
Probability of obtaining a certain value - $x$ - given the two parameters in the model.
Circled point closer to the middle - highly likely, compared to lower circled point.
Can take all data points and multiply probabilities together to get likelihood of the data set - 𝑃(𝑥1|𝜇, 𝜎2) * 𝑃(𝑥2|𝜇, 𝜎2) * 𝑃(𝑥3|𝜇, 𝜎2)
Log likelihood equation
Uses logarithm to describe the likelihood equation
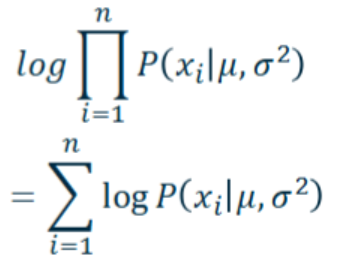
Maximising likelihood = …
Minimising MSE
Minimising MSE = …
Maximising likelihood