BIO 202: Chapter 1.6 and 2.1 Blood Typing and Cardiac Muscle Histology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
blood transfusion
infusion of a recipient with a donor’s blood cells
blood types
determined by the presence or absence of specific molecules called antigens and antibodies
agglutination
clumping of foreign erythrocytes
hemolysis
process in which clumped cells are destroyed by the immune system
transfusion reaction
agglutinated red blood cells block small blood vessels which may lead to kidney failure and death
packed red blood cells
erythrocytes with most plasma removed which help reduce the risk of transfusion reactions
anti-B antibodies
type A blood have A antigens and produce …
anti-A antibodies
type B blood have B antigens and produce …
anti-A or anti-B antibodies
type O blood have neither A nor B antigens and produce …
do not
people with Rh-positive blood have Rh antigens and ____ produce anti-Rh antibodies
do
people with Rh-negative blood do not have Rh antigens and ___ produce anti-Rh antibodies
(+), (+) and (-)
if the blood type has a positive sign (+), it can give to ___ only, but receive from both _____
(+) and (-), (-)
if the blood type has a negative sign (-), it can give to ___, but receive from ___ only
receive
people with AB+ blood can ___ from any donor blood type
donate
people with O- blood can ___ to any recipient blood type
AB+
universal recipient
O-
universal donor
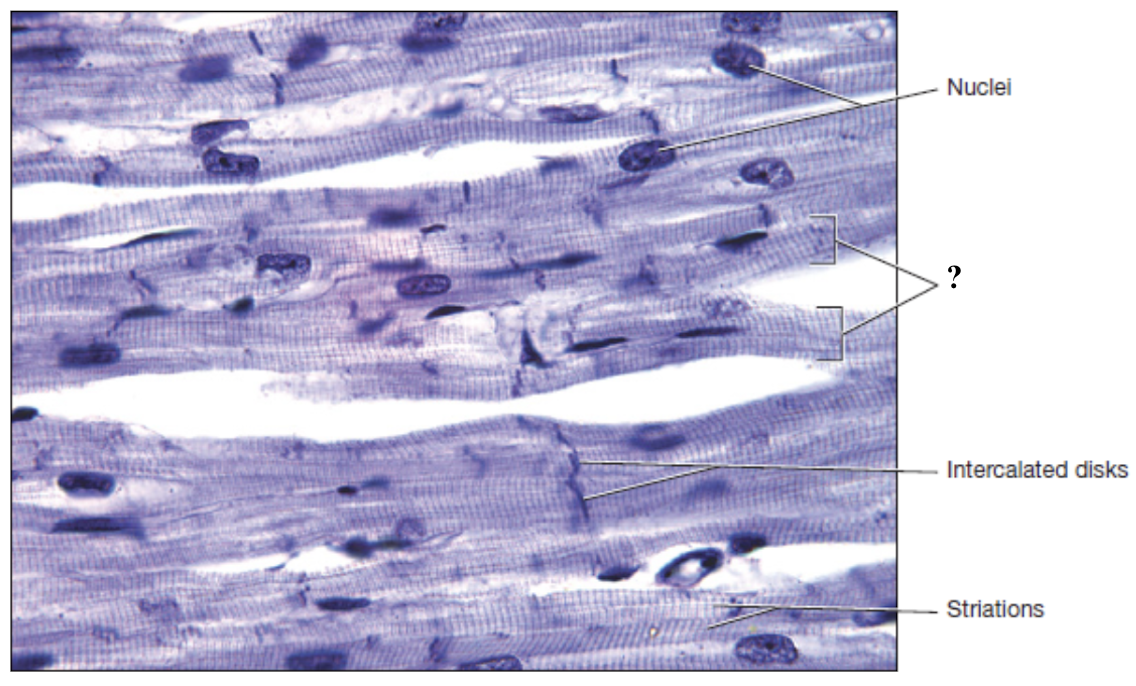
cardiac myocytes
cells of cardiac muscle
uninucleate
one single nucleus that is typically in the center of the cell
intercalated discs
specialized structures that contain desmosomes and gap junctions which enable the heart to contract as one coordinated unit
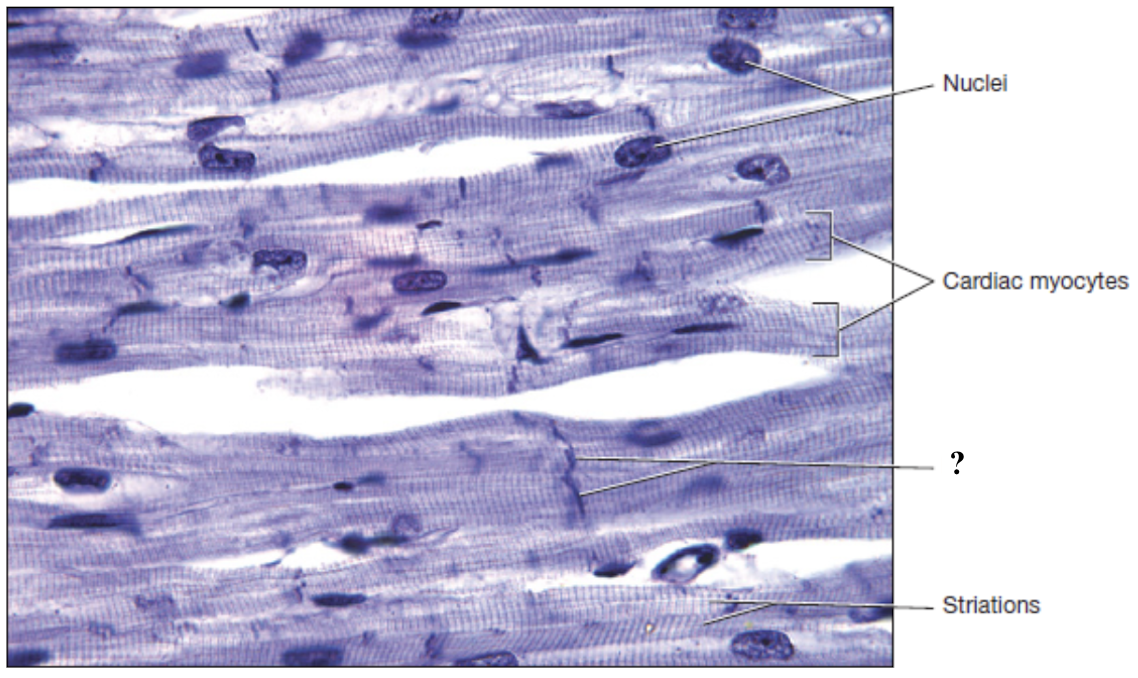
desmosomes
hold adjacent cardiac cells tightly together
gap junctions
allow adjacent cardiac cells to communicate chemically and electrically
arrhythmias
irregular heart rhythms