Older Adults: Aging in Place
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Health Status of Older Adults
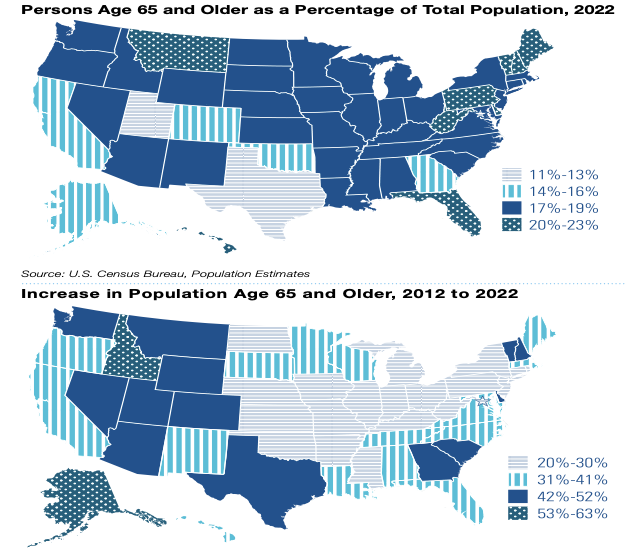
Growth in number and proportion of older adults living in the United States is projected to reach almost 30% of the population by 2060.
Increased demands on the public health system, medical and social services, and health care delivery.
Chronic diseases contributing to disability, diminished quality of life, and increased health care costs.
Globally:
Number of adults over the age of 65 are expected to reach 1.4 billion by 2050.
**Those over the age of 80 years old is growing faster than any other group.**
Ageism is…
Negative stereotyping of older adults and discrimination because of older age.
These stereotypes often arise from negative personal
experiences, myths shared over time, and a general lack of current
information.
A majority of older adults report having experienced ageism in
the form of being patronized, ignored, or treated as if they were incompetent
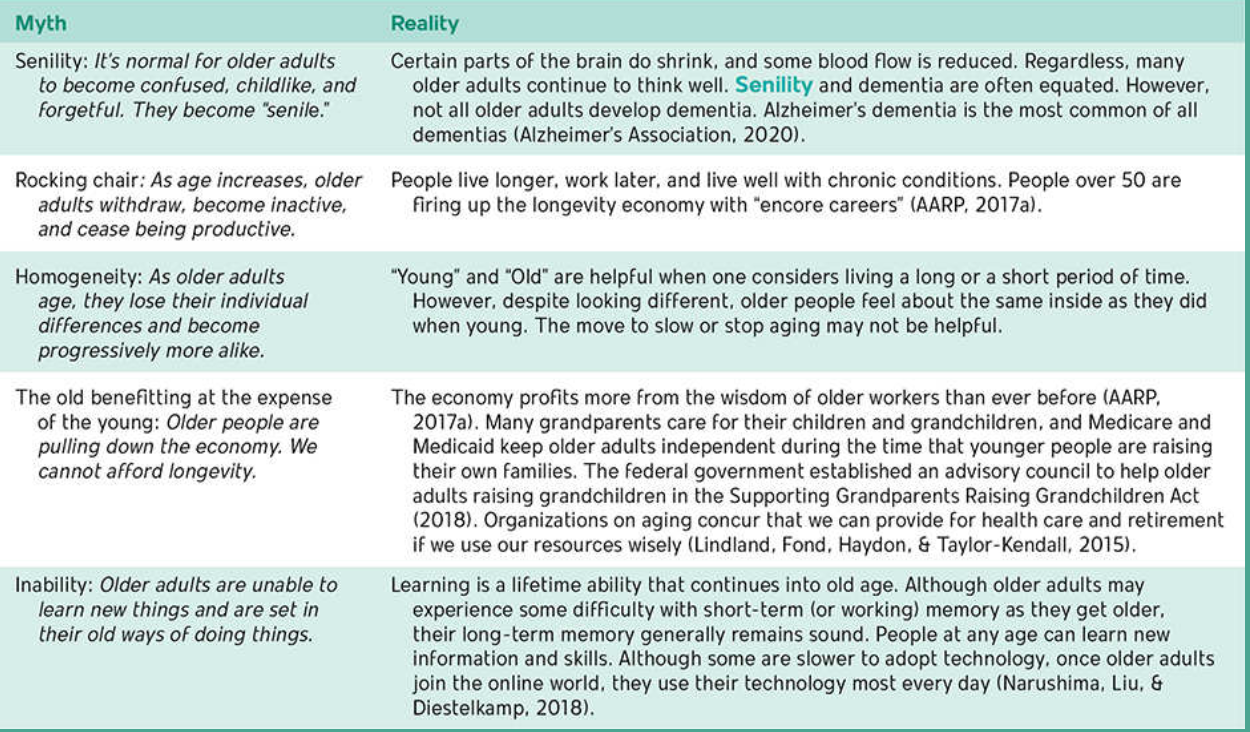
Ageism: Common Misconceptions About Older Adults
Inability to live independently
Most are with diminished intellectual capacity or senility
Homogeneity: all alike, with no individual differences
Inability to learn new things
Withdrawn, inactive, nonproductive
Liability: expensive, draining on the economy
Characteristics of Healthy Older Adults
Lifetime of healthy habits:
Exercising
Brushing teeth
Hobbies
Sun Protection
Strong social support system
Positive emotional outlook
Affected by:
Personality traits
Life experiences
Current physical health
Current societal supports
Health Status of Older Adults Nationally
Increased life expectancy (female > males)
Older adults are healthier than ever before:
Young-Old (65 to 75 years)
Old-Old (75 to 85 years)
Oldest-Old (85 to 100 years)
Elite-old (centenarians)
Frail elderly (over the age of 85 years and need assistance with ADLs)
Primary Prevention in Older Adults
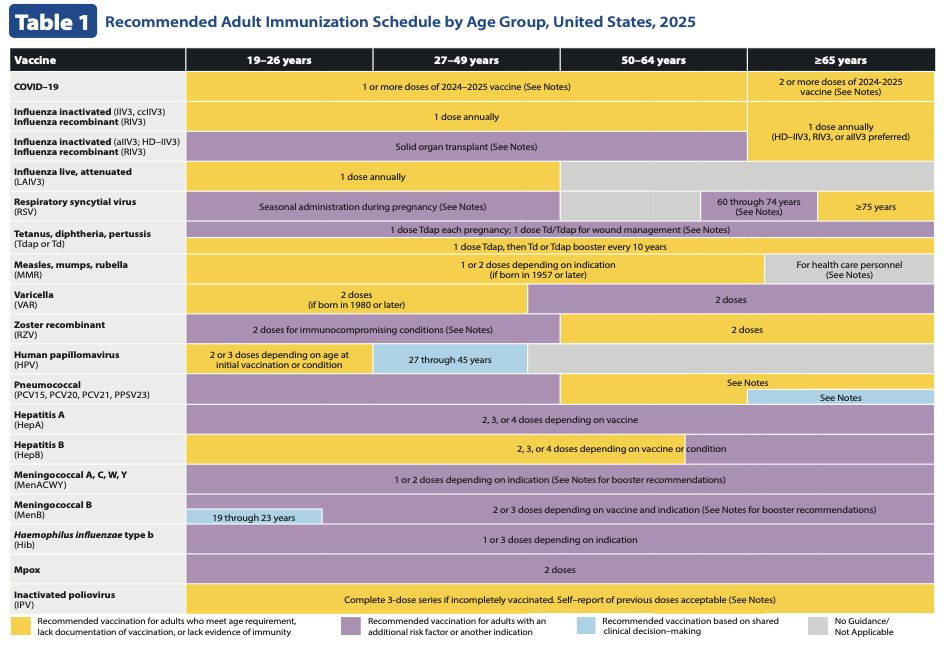
Health education; follow-through of sound personal health practices; recommended immunizations.
Nutrition, oral health, exercise, safety needs, sleep
Economic security needs
Psychosocial needs:
Maintaining interdependence
Social interaction
Companionship
Purpose
Spirituality, advance directives
Secondary Prevention in Older Adults
Focus on early education/detection of disease and prompt intervention.
Routine screening for hypertension, diabetes, and cancer.
Different screenings: mammograms, colonoscopies, bone density, dental, BP.
Tertiary Prevention in Older Adults
Involves follow-up and rehabilitation after a disease or condition has occurred or been diagnosed and initial treatment has begun.
Health issues:
Alzheimer's disease
Arthritis
Cancer
Depression
Diabetes
Cardiovascular disease
Osteoporosis
Older Adult Immunization Schedule
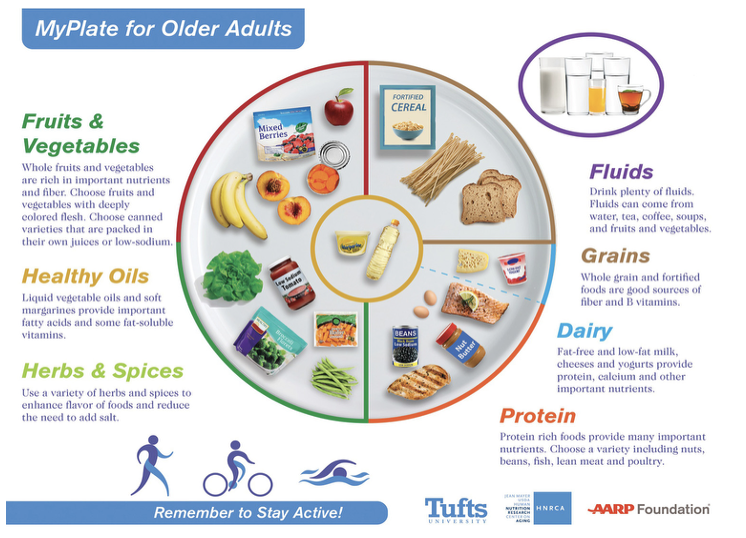
My Plate for Older Adults
It is generally believed that older people need to maintain their optimal weight by eating a diet that is low in fats, moderate in carbohydrates, and high in proteins with a daily calorie count of 1,200 to 1,600.
Older adults need less vitamin A but more calcium and vitamin D (for healthy bones), more folic acid, and more vitamins B6 and B12 (for cognitive health) than younger adults.
Many communities offer meals to seniors, either at senior centers or by way of Meals on Wheels, through grants provided by the Older Adult Nutrition Program.
Common Health Problems of Older Adults
Alzheimer's disease
Arthritis
Cardiovascular disease
Cancer
Depression
Diabetes
Hearing loss
Obesity
Osteoporosis
Elder Abuse is the…
Intentional or neglectful acts by a caregiver or any other person that causes harm or a serious risk of harm to a vulnerable adult.
Physical abuse
Neglect
Emotional or psychological abuse
Verbal abuse and threats
Financial abuse and exploitation
Sexual abuse
Abandonment
Criteria for Effective Health Services
Comprehensiveness:
Affordable housing options
Adult day and memory care programs
Access to high-quality health care services
Health education (including preparation for retirement)
In-home services
Recreation and activity programs
Specialized transportation services
Safe and outdoor spaces
Services for Healthy Older Adults
Goal: Maintenance of functional independence
Living Arrangements and Care Options:
Day care and home care services
Arrangements based on level of care:
Skilled nursing facilities
Intermediate care; assisted living
Personal care homes
Continuing care communities
Presbyterian Village in Austell, GA
St. George Village in Roswell, GA
Respite care services
Hospice and palliative care
Community Health Nursing in an Aging America Involves:
Case management for resources and referrals.
Encouragement of health lifestyle changes to avoid diseases and disability.
Development of creative living arrangements and services.
Education about immunizations and safety measures including fall prevention.
D. The over-80-year age group is the fastest-growing segment of the group.
Which would be most accurate when describing the changes occurring in the older adult population globally?
A. Males have a longer projected life expectancy than females.
B. Most countries have adequate social programs for older adults.
C. Adults over age 65 are expected to account for about 25% of the population by 2050.
D. The over-80-year age group is the fastest-growing segment of the group.
Common Interview Techniques
Open-ended questions
Affirmations
Reflection
Summarize
Motivational Interviewing
Compassions
Acceptance
Partnerships
Evocation
Chapter 22 (book) Summary
Community/Public Health Nurses (C/PHNs) work with older adults and families in a variety of settings—wherever they are found and whatever health needs are present. While the primary focus of community/public health nursing is health promotion and disease prevention, C/PHNs also work with older adults who have chronic health conditions and are aging in place, helping them achieve their maximum health potential.
Because the trend for older adults is to remain in the community, C/PHNs must assess their living situations and gather as much information as possible about the community’s support systems, available resources, and service gaps.
As the number of older adults in America continues to grow, the demand for health care services and professionals who serve this population in community settings will increase.
The goal for the aging population is healthy longevity, which is a key focus of Healthy People initiatives. This goal emphasizes the ability to:
Function as independently as possible
Maintain physical, mental, and social wellness
Adapt to chronic conditions and functional impairments
Through advocacy, education, counseling, case management, and collaboration with clients, families, and healthcare providers, the community health nurse can help improve both quality of care and social conditions for older adults.
Most older adults prefer to age in place and live independently. Public health nurses are essential in delivering care to this large and rapidly growing population.
Alzheimer’s disease is currently the sixth leading cause of death in the U.S. and the only disease among the top 10 causes that cannot be prevented or cured. Between 2017 and 2025, every U.S. state is expected to experience at least a 14% increase in the prevalence of Alzheimer’s (AA, 2020b). C/PHNs play a critical role in supporting families and caregivers of those affected.
A variety of living arrangements and care options are available to meet the preferences and needs of older adults. These include:
Continuing care communities
Villages
Day and memory care centers
PACE programs
Assisted living facilities
Skilled nursing facilities (SNFs)
Long-term care centers
Hospice care
The community health perspective incorporates a case management approach, which provides a centralized systemfor assessing the needs of older adults and matching those needs with appropriate services.
C/PHNs should aim to serve the entire older adult population by:
Assessing population needs
Examining available services
Analyzing service effectiveness
Program effectiveness can be measured by evaluating four key criteria:
Comprehensiveness
Effective coordination
Accessibility
Quality