6.1.4 External eye pathology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Dry Eyes causes
Aqueous layer deficiency
Impaired lid function
Epitheliopathy - irregular corneal epithelium = thin and unstable TF
Medication e.g CNS acting drugs or BB
RA - glands in eye don’t work properly
Acne Rosacea
Dermatitis
Sjogren’s syndrome
Environment - air conditioned and heated + windy, dry/dusty
Aqueous Layer deficiency
Adequate production and drainage of aqueous layer is necessary due to;
Tear nutriants e.g Oxygen supply to cornea
Anti-bacterial agents e.g lysozyme produced by lacrimal glands
the mechanical flushing action of tear movement
Sx;
soreness and burning
in dry eyes the osmolarity of aqueous increases = ocular damage
Impaired Lid function
Lid function is important for mucus distribution during blinking
leads to tear deficiency and exposure keratitis - can lead to ulceration
Tear Substitues
Carbomers (GelTears, Viscotears)
Hypermellose
Liquid Paraffin (hycosan night)
Macrogels (systane)
Sodium Hyaluronate (Hycosan)
Diet (omega 3/6, fatty acids)
Carbomers
Semi-solid formulations of high molecular weight
Protective during sleep
good retention time
Can cause blurry due to viscosity
Liquid Paraffin
Hycosan night
lubricates eye surface in case of recurrent corneal erosion
Sodium Hyaluronate
Hycosan
viscoelastic high molecular weight polymer
increases goblet cell density and reduces inflammation of ocular surface
improves tear stability and wettability
Causes of Anterior Blepharitis
due to bacteria (staphylococcal) - lives on the skin
Seborrheic Dermatitis (disorder of ciliary sebaceous glands)
Bacterial Bleph
Lid margin hyperaemia
margin swelling
crusting of margin (scales on base of lashes)
misdirection of lashes
Recurrent styes
conjunctival hyperaemia
Seborrheic
Lid margin hyperaemia
Oily or greasy deposits on lid margins
conjunctival hyperaemia
When would you refer Blepharitis?
Routine: if pharmacological therapy doesn’t help
Urgent; if unilateral as suspect MG carcinoma
Dacryocystitis
Inflammation or infection of lacrimal sac
most often secondary to nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Sx;
sudden onset
pain
tender swelling
epiphora
fever
Signs;
Red, tender swelling centred over lacrimal sac and around the orbit
Purulent discharge from the puncta
frequent conjunctivitis and pre-septal cellulitis
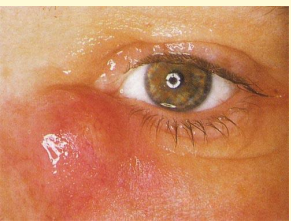
Management of Dacryocystitis
Emergency if;
Children
Severe case if Px is unwell
Cases which don’t respond to anti-biotics for 7 days
Urgent otherwise
should respond to systemic antibiotics, manage to resolution
Entropion and its sx
Inward rotation of the tarsus and lid margin, causing lashes to come into contact with the ocular surface
sx;
Irritation (FB sensation)
Epiphora
Lid spasm
Red eye
Causes of Entropion
Age related laxity
trachoma
surgery
congenital
Management of entropion
Initial management;
Tape the lid to the skin of the cheek for temporary relief
Therapeutic CL to protect the cornea
Ocular lubricants
Refer routinely for surgery
Ectropion and its Sx
Outward rotation of eyelid margin - usually bilateral
Sx;
Sore, red, watery eye
Causes of Ectropion
Age related lid laxity
scarring and contraction of skin
trauma
congenital
lid swelling due to inflammation
skin tumours
Management of Ectropion
Mild cases = tape lid at night to avoid corneal exposure, ocular lubricants
Refer in severe cases for surgery
Trichiasis, sx & causes
Inward misdirection of lashes towards the cornea
Ocular discomfort
irritation
FB sensation
Epiphora
red eye
Causes can be congenital and acquired - e.g repeated trachoma infections & scarring
Signs of Trichiasis
Lashes in contact with ocular surface
Conjunctival injection
Corneal epithelial abrasion
Staining of cornea and conjunctiva
If longstanding;
Pannus
Ulcer
Infective keratitis
Management of Trichiasis;
Epilation of lashes
Therapeutic CL for temp relief
Ocular lubricants
lid hygiene for associated bleph
Routine referral if secondary to entropion for lid surgery
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Malignant tumour of the skin, rarely metastasizes, slow growing and locally invasive
Slow developing
non resolving lesion of eyelid skin
not painful
Signs of BCC?
Nodular - pearly appearance with abnormal vessels
May bleed
Ill defined borders
Change in lid contour
sclerosing - flat hardened plaque of thickened skin
Management of BCC
Routine referral with details of location, size - likely surgery
advise sun protection
Chalazion (Meibomian cyst) & its Sx
Blockage of the Meibomian gland duct with a chronic granulomatous inflammatory lesion - usually caused by non infection MG occlusion
Painless lid lump, usually single, may be recurrent, may rupture
occasionally blurred vision from induced astigmatism
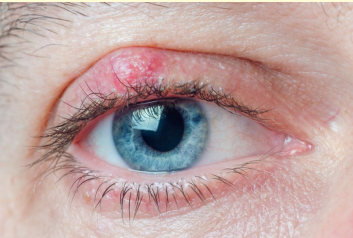
Signs of Chalazion
Well defined - 2-8mm nodule in tarsal plate
Lid eversion may show external conjunctival granuloma
Associated blepharitis
Induced astigmatism
If recurrent consider carcinoma
Management of Chalazion
Self resolving (2 weeks - months)
regular lid hygiene
Refer if persistent, large and recurrent or causing corneal distortion
Hordeolum & Sx
External (stye) - Acute bacterial infection of the lash follicle and its associated gland of Zeiss or moll
Internal (oil) - Acute bacterial infection of MG - usually staphylococcal, can develop into chalazion
Sx;
Tender lump in eyelid
Epiphora
Local redness of eye and lid
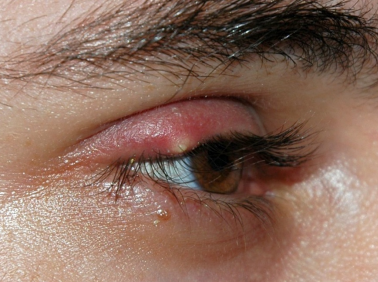
Signs of Hordeolum
External - tender inflamed swelling on the lid margin, may point anterior through skin
Internal - tender inflamed swelling within the tarsal plate that’s more painful than stye. May point anteriorly through skin or posteriorly through conjunctiva
Management of Hordeolum
Most resolve spontaneously, or discharge by resolution
Remove lash from infected follicle
Manage bleph
return if it persists or worsens
topical antibiotics
Refer - in cases which do not discharge (internal hordeolum)
Pre-septal Cellulitis & SX
Bacterial infection of tissues lying anterior to the orbital septum
Common in infants under age of 10
Caused by Staphylococcal, Streptococcal
Sx;
Acute onset of swelling, redness and tenderness of lids
Fever
Malaise - discomfort/illness
Irritability
Signs of Pre-septal Cellulitis
Erythema of skin - reddening, dilation of BV
Lid oedema, warmth and tenderness
Ptosis
Pyrexia (fever > 38 degrees)
Orbital Cellulitis & Sx
Bacterial infection of tissues lying posterior to the orbital septum (within the orbit) - severe and life threatening
Sudden onset of unilateral swelling of conjunctiva and lids
Pain on ocular movement
blurred vision
dipl.
fever
severe malaise
Signs of Orbital cellulitis
Proptosis
Restriction of EOM
Pain with eye movement
Reduced VA + Cv
RAPD
Pyrexia
Management of Pre-septal & Orbital Cellulitis
Emergency referral