Exam 2 Content: Telescopes and Solar Physics
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Refracting telescope
Uses lenses to pass and focus light.
Reflecting telescope
Uses mirrors to bounce and focus light.
Aperture
Diameter of primary lens or mirror.
Focal length
Distance from lens/mirror to image.
Light-gathering power
Ability to collect more light for faint objects.
Photon collection
Total photons collected proportional to area.
Area formula
A = pi*r², where r is radius.
Largest visible light telescope
Diameter ~10m (>32 feet).
Angular resolution
Smallest angle details can be separated.
Resolution and diameter
Resolution inversely proportional to telescope diameter.
Atmospheric blurring
Caused by air movement affecting telescope images.
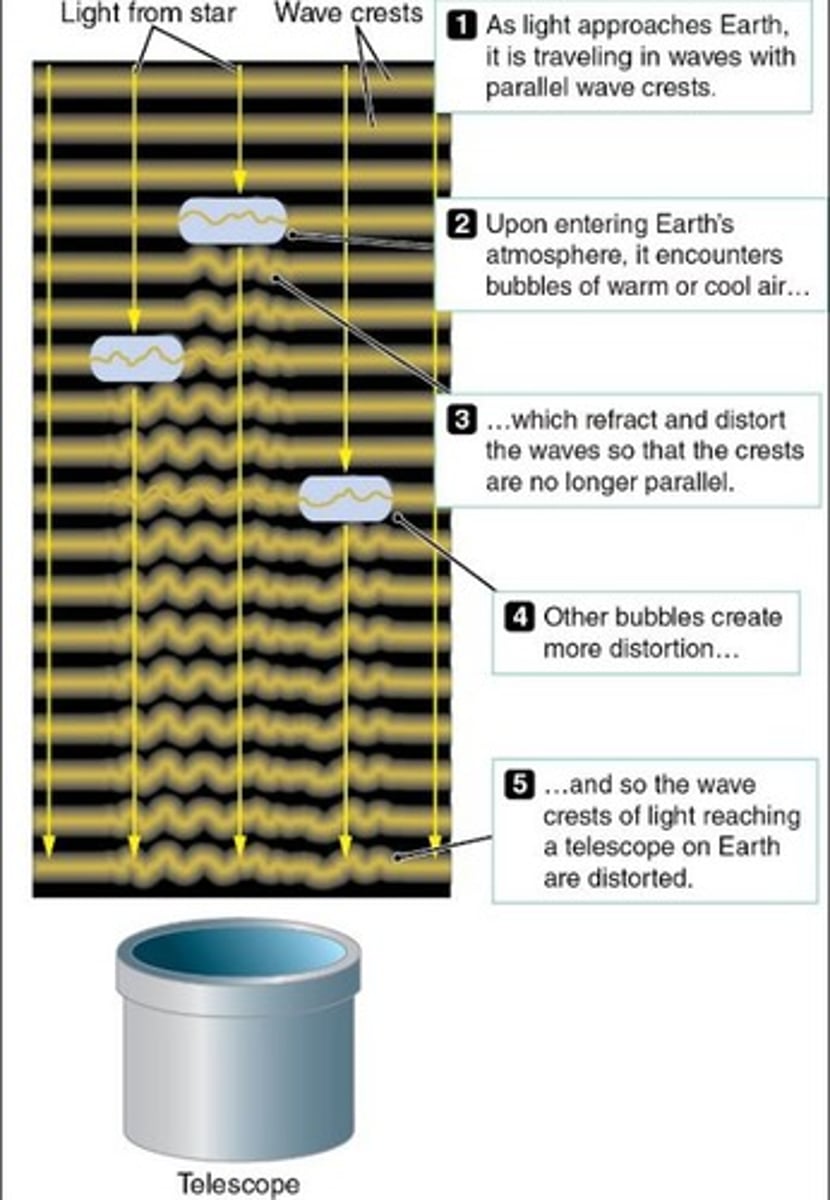
Seeing
Term for atmospheric blurring in astronomy.
Adaptive optics
Technique to correct atmospheric turbulence in real time.
Artificial star
Laser-created reference for measuring atmospheric turbulence.
Wavelength impact
Smaller wavelengths improve resolution of telescopes.
Eye as telescope
Eye collects light, focuses image on retina.
Poor angular resolution
Limited by small pupil size in the eye.
Telescope size limit
Atmosphere blurs images more than telescope resolution.
Image size relation
Longer focal length results in larger image size.
Fine details
Bigger telescopes can resolve more intricate details.
Real-time adjustments
Mirrors adjusted based on atmospheric changes.
Deformable Mirrors
Mirrors can be adjusted to reduce blurring.
Keck Telescopes
10m diameter mirrors located on Maunakea, Hawaii.
Mountaintop Telescopes
Built to minimize atmospheric interference.
Atmospheric Water Vapor
Interferes with infrared observations from ground.
Large Telescopes
Designed with diameters of 20-40 meters.
Segmented Mirrors
Used to save weight and cost in telescopes.
Space Telescopes
Not affected by Earth's atmospheric blurring.
Hubble Space Telescope
2.4m mirror; observes visible and infrared light.
James Webb Space Telescope
6.5m mirror; designed for infrared observations.
Radiation Blocked by Atmosphere
X-rays and gamma rays require space telescopes.
Radio Telescopes
Less sensitive to imperfections; made from metal.
Parabolic Dish
Reflector design used in radio telescopes.
Resolution Limitation
For telescopes >10" diameter, limited by atmosphere.
Sun's Radius
700,000 km, compared to Earth's 6,500 km.
Sun's Mass
2 × 10^30 kg, significantly larger than Earth.
Sun's Average Density
1400 kg/m³, less than Earth's 5500 kg/m³.
Sun's Surface Temperature
5800 K, much hotter than Earth's 300 K.
Sun's Composition
91% hydrogen and 8.7% helium by nuclei.
Sun's Energy Output
Luminosity measures energy radiated per second.
Thermal Emitter Spectrum
Sun's spectrum resembles ideal thermal emitter.
Sun's Rotation Period
25-31 days, longer at the poles.
Infrared Observations
Studying star and galaxy formation in space.
Luminosity
Total energy output of the Sun per second.
1 Joule
Energy to lift an apple 1 meter.
Solar energy received
Energy from the Sun reaching Earth per square meter.
1 AU
Average distance from Earth to the Sun.
Surface Area (SA)
SA = 4𝝅R² for a sphere.
Photosphere
Visible surface layer of the Sun.
Core
Site of nuclear fusion in the Sun.
Radiative zone
Energy moves via light, takes 170,000 years.
Convective zone
Energy moves via convection, takes about a week.
Opacity
Measure of how easily photons pass through matter.
Granulation
Pattern of bright and dark regions on the Sun.
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
Flux increases rapidly with temperature for blackbodies.
Thermal emitter
Photosphere emits light as a thermal emitter.
Chromosphere
Layer above photosphere, emits reddish hydrogen spectrum.
Convection
Hot material rises, cools, then sinks.
Energy transport
Movement of energy from core to surface.
Nuclear fusion
Process generating energy in the Sun's core.
Solar atmosphere
Layers above the photosphere, observable.
Energy transport efficiency
Convection is more efficient than radiation.
Hydrogen spectrum
Emission lines from hydrogen in the chromosphere.
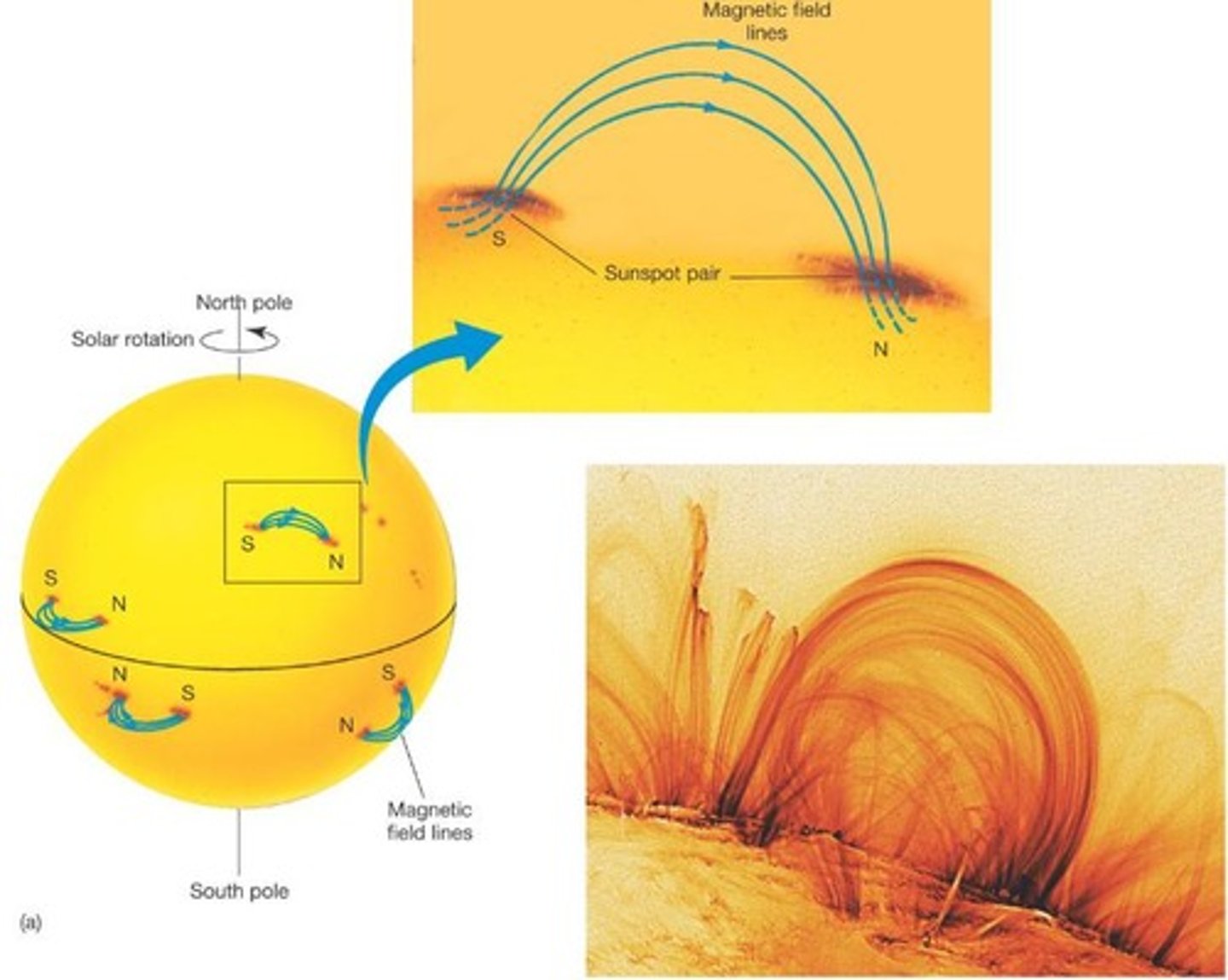
Sunspots
Dark regions on the Sun's surface due to cooler temperatures.
Pressure balance
Pressure from temperature prevents collapse under gravity.
Chromosphere
Layer where solar color originates, appears red.
Solar Atmosphere
Temperature varies in outer layers of the Sun.
Density Gradient
Density decreases with distance from Sun's center.
Corona
Outer layer above the chromosphere, very hot.
Temperature Inversion
Higher temperature in corona than lower layers.
Corona Temperature
Ranges from 1 to 2 million K.
X-rays Emission
Corona emits X-rays, visible during solar eclipses.
Magnetic Field Tracing
Gas in corona follows Sun's magnetic field lines.
Core
Sun's center where nuclear fusion occurs.
Radiation Zone
Energy transported via photons in the Sun.
Convection Zone
Energy transported by boiling motions in the Sun.
Sunspots
Dark spots on Sun, cooler than surrounding areas.
Galileo's Observation
First observed sunspots, challenging classical views.
Magnetic Field Dynamics
Sun's magnetic field connects to ionized gas.
Sunspot Temperature
Sunspots around 4500 K, cooler than photosphere.
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
Relates temperature to emitted radiation intensity.
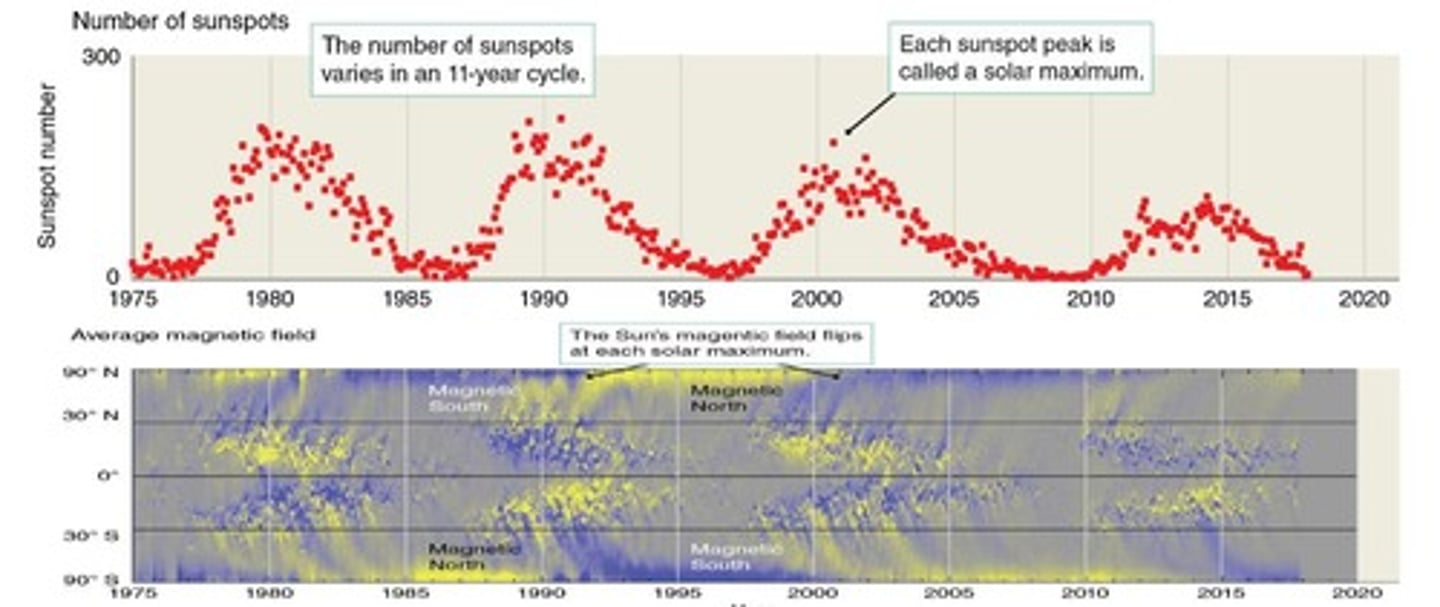
Sunspot Cycle
11-year cycle of rising and falling sunspot numbers.
Prominences
Large loops of solar material, up to 100,000 km.
Solar Flares
Explosive bursts on Sun's surface, last seconds to minutes.
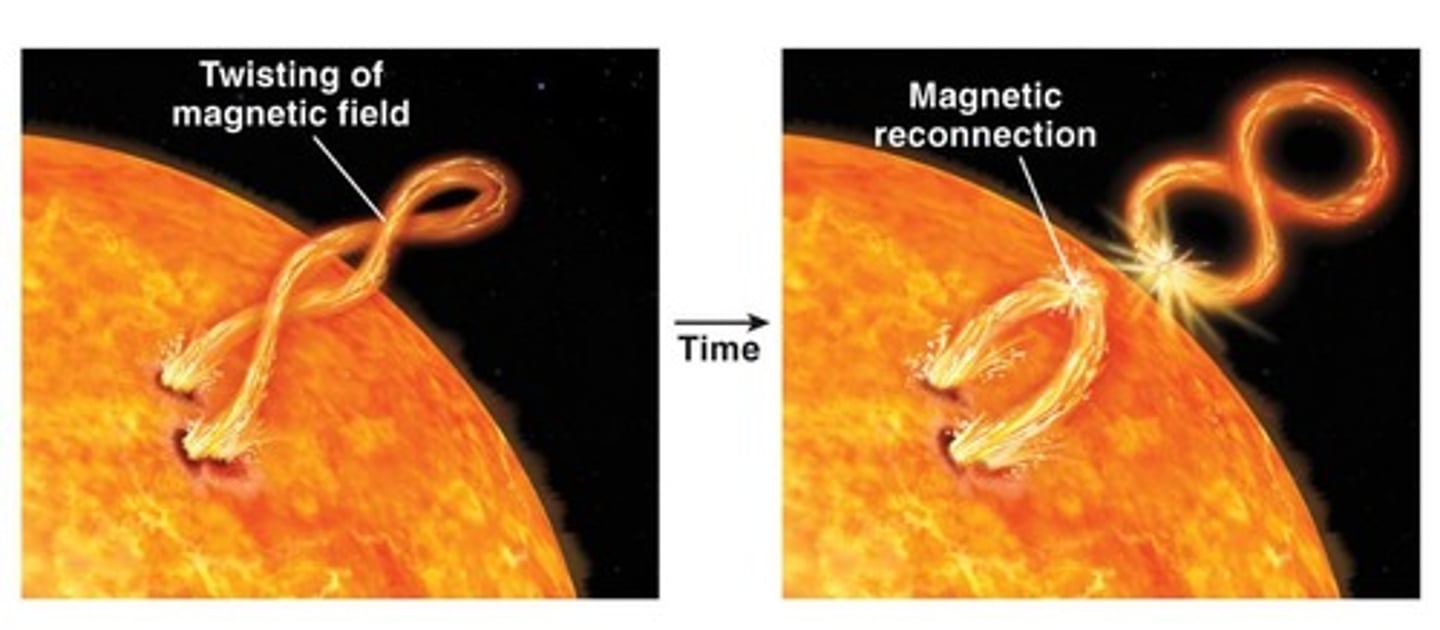
Coronal Mass Ejections
Large outflows of solar material associated with flares.
Solar Wind
Particles escape Sun at 400-800 km/sec.
Space Weather
Solar activity affects Earth's atmosphere and technology.
Solar Wind
Stream of charged particles from the Sun.
Auroras
Glowing skies caused by solar particles.
Magnetosphere
Earth's magnetic field protecting from solar particles.
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Gravitational force balanced by outward pressure.
Energy Density
Energy per unit mass; nuclear is higher than chemical.
Proton-Proton Fusion
Fusion process combining protons into helium.
Einstein's Equation
E=mc²; mass-energy equivalence principle.
Coronal Mass Ejections
Large expulsions of plasma from the Sun.
Photosphere
Sun's visible surface layer.
Chemical Energy
Energy from chemical reactions, nuclei intact.
Nuclear Fission
Energy release from splitting heavy nuclei.
Neutrinos
Neutral particles with very little mass.
Positron
Antimatter counterpart of the electron.