Determinants of Supply
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Supply - definition
Quantity of a good or service that a supplier is willing and able to produce at a given price during a given time period
What does a supply curve look like
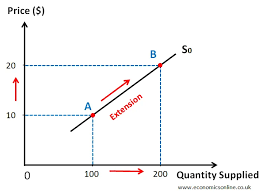
Why is a supply curve upwardly sloping?
Price and quantity supplied have a positive relationship.
Why do price and QS have a positive relationship?
If price increases, it’s more profitable for firms to produce the good, so supply increases
High prices also attract more new firms as it is profitable
With larger outputs, firms’ costs increase so prices must rise
What do movements along the curve show?
An increase/ decrease in price, which cause an increase / decrease in quantity demanded
Extension/contraction
What do shifts in a supply curve show?
A change in quantity supplied at the same price, caused by other factors
Leftward shift = Inward (less QS)
Rightward shift = outward (more QS)
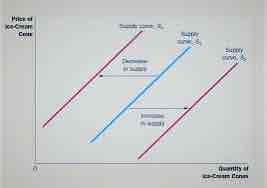
What are factors that shift the supply curve (7)
Changes to costs of production
Government policy
Technology
Change in no. of firms in the industry
Weather events
Future price expectations
Goods in joint or competitive supply
Changes to costs of production: How do they affect supply?
If prices to produce increase, firms will respond by decreasing supply
Inverse relationship
Government policies: Two types
Subsidies
Taxes
Subsidies: How do they affect supply?
Impacts cost of production, more subsidies = cheaper to produce = more supply
Positive relationship
Taxes: How do they affect supply?
Opposite to subsidies, higher taxes = higher cost of production = lower supply
Inverse relationship
Technology: How does it affect supply?
New technology increases productivity and efficiency, which decreases production costs, so supply increases
Aging technology has the opposite effect, more inefficient
Changes in the number of firms in the industry: How do they affect supply?
More firms in an industry = higher supply, as more producers
Direct relationship
Weather events: How do they affect supply?
Extreme weather can cause a supply shock usually in agricultural markets, which will decrease supply
Conversely, good conditions will increase supply of crops
Future price expectations: How do they affect supply?
If firms expects the price of a good/service to increase in the future, they will increase supply and vice versa.
Direct relationship
What are goods in joint supply and how does this affect supply?
Ones involving a process which yields multiple outputs, like beef and leather
If supply of beef increases, maybe due to price, supply of leather will also increase.
Positive relationship
What are goods in competitive supply and how does this affect supply?
When alternative products can be made with the same resources, e.g. a farmer can grow wheat or potatoes
When supply of one good (potatoes) increases, the supply of the other good (wheat) will decrease.
Inverse relationship