chem final
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
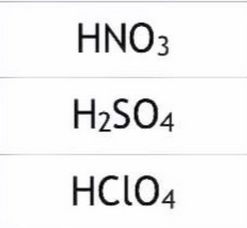
strong acids with one element

strong acids with compounds
strong bases with one OH
group 1

strong bases with two OH
group 2

molarity (big M)
moles/liters
what makes a molecule more soluble in water
polar molecules, hydrogen bonding, salts, high charges on salts, smaller molecules, higher temps
phosphate

mass percent
mass of component/mass of mixture *100
molality
mol/kg
what does adding a solute do
increases the extremes: raises boiling point, lowers freezing point, lowers vapor pressure
how to identify electrolytes
ionic compounds are electrolytes.
if it completely ionizes, it is a strong electrolyte
if it partially ionizes, it is a weak electrolyte
equation for freezing/boiling point
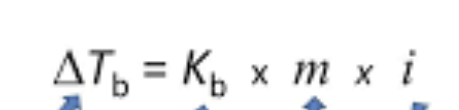
ralout’s equation

mole fraction (big X)
moles of solute/moles of solution
relationship between K for pressure and concentration
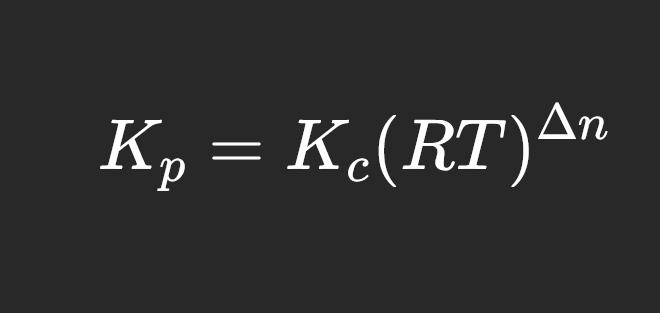
endothermic
heat on products
exothermic
heat on reactants
kinds of molecular bonding
ion dipole
hydrogen
dipole dipole
ion induced dipole
dipole induced dipole
dispersion
how to find Ka/Kb if given one
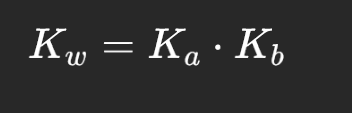
what is Ka
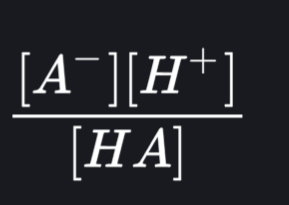
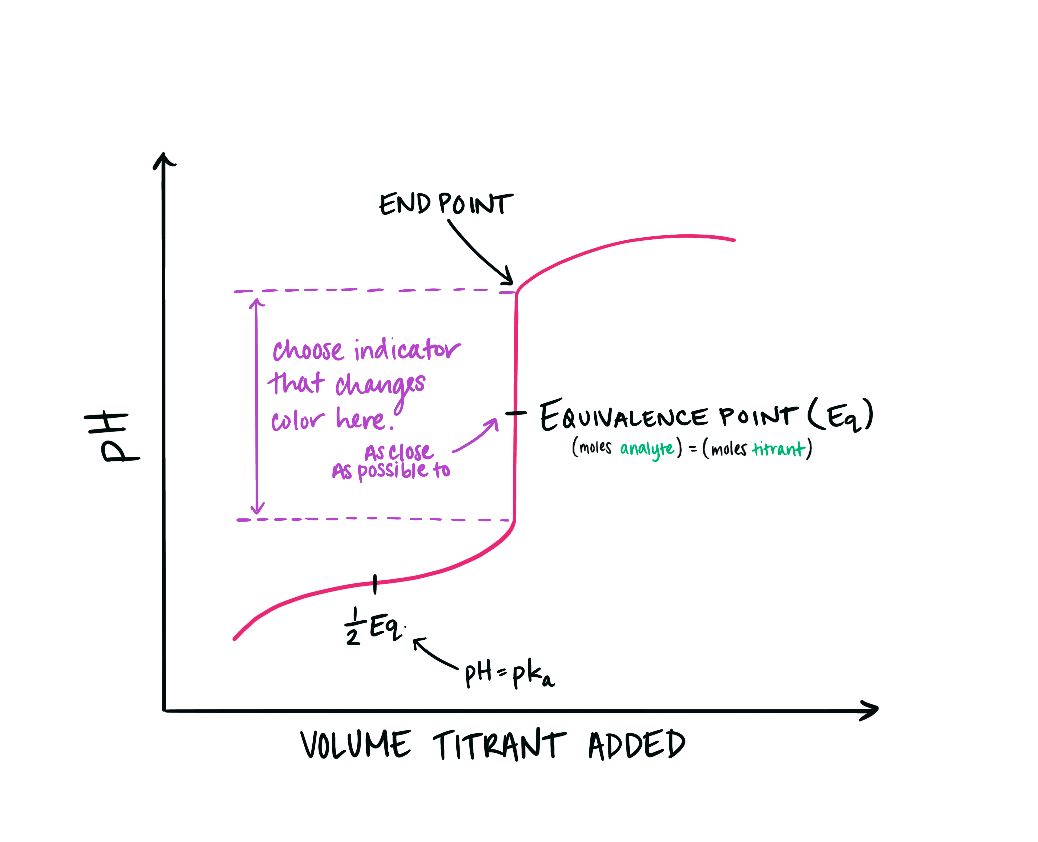
equivalence point on titration curve
how to determine pH after strong acid-strong base titration
determine limit reactant, calculate excess, divide by the total volume of solution, and convert to H+ / OH- to find pH
how to find volume required to reach equivalence in polyprotic acid-base titration
multiply moles of acid by # of neutralizable protons, then use M1v1 = M2V2
requirement for buffer
weak acid/base and conjugate pair
pH at equivalence
if strong acid/base → neutral
if weak conjugates → acidic/basic
how to determine which salt is most soluble
higher ksp means higher solubtility
how is Ksp related to molar solubility
use algebra to relate xs^y to Ksp and solve
how to know if precipitate forms
if Q is greater than Ksp
how does adding a strong acid affect solubility
increases solubility of salts with basic anions
what is a conjugate base of weak acid
whats left over after the weak acid donates proton
when will a dissolved salt give a neutral solution?
when the ions result in two non acids/bases