Chapter 3 Bio: Nucleic Acids and Proteins
1/78
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Nucleic acids are _____ macromolecules
informational
What are nucleic acids?
polymers that store, transmit, and express heredity (genetic information)
The monomers of nucleic acids are…
nucleotides
What is a nucleotide?
a pentose + N-containing base + phosphate group
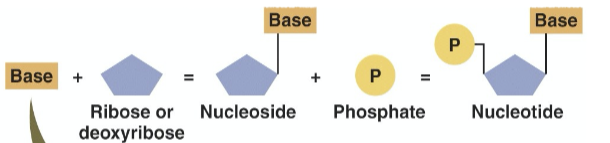
What is a nucleoside?
a pentose + N-containing base
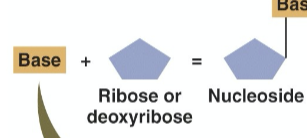
What is a pentose?
a simple sugar with 5 carbons
deoxyribose or ribose
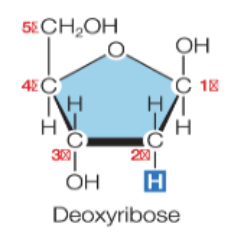
What is DNA?
deoxyribonucleic acid
a deoxyribose pentose + a base + a phosphate group
the deoxyribose pentose in missing an oxygen attached to the 2’ carbon; this is what makes it different from ribose
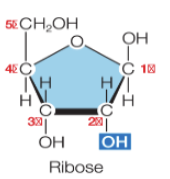
What is RNA?
ribonucleic acid
a ribose pentose + a base + a phosphate group
has —OH on carbon 2’
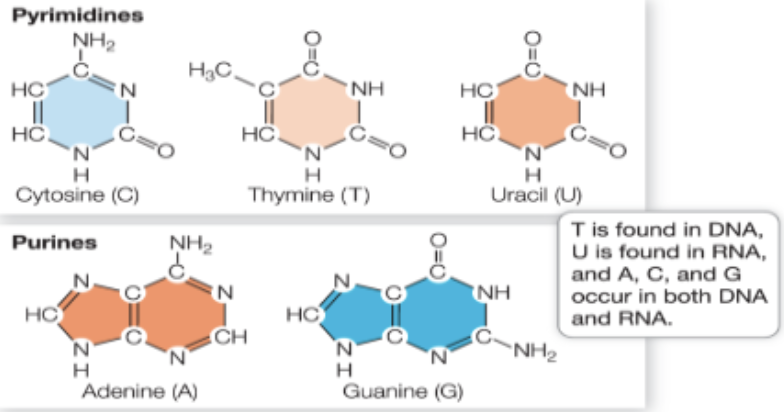
What are N-containing bases?
Pyrimidines- single rings (cytosine, thymine, and uracil)
C TUrtle eats single rings
“single rings” sounds like pyramids
Purines- double rings (astatine and guanine)
AlliGator jumps through two PURE rings
DNA and RNA have the same bases, except in RNA, thymine it replaces by uracil
DNA always will have an equal number of pyrimidines and purines
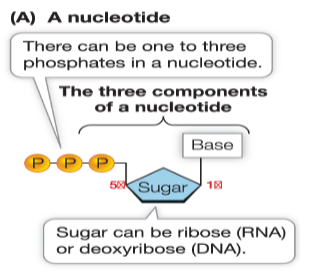
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
one to three phosphate groups, a sugar, and a base
What are the functions of nucleotides?
building blocks for DNA/RNA
energy transfer, signaling (ATP, GTP)
Synthesis of a nucleic acid:
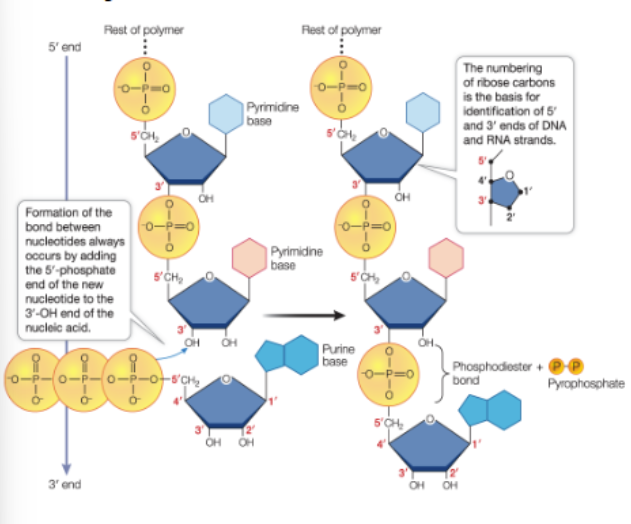
nucleotides bond in condensation rxns to form phosphodiester linkages (covalent bonds)
always occurs by adding the 5’-phosphate end of the new nucleotide to the 3’-OH end of the nucleic acid
condensation rxn —> to form phosphodiester linkages (covalent bond)
nucleic acids grow in the 5’ to 3’ direction
the linkage between the #5 carbon of one ribose and the #3 carbon on the next ribose forms a chain of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules— the sugar-phosphate backbone
What are oligonucleotides?
up to 20 monomers
mostly RNA molecules
small DNA or RNA oligonucleotides are important to initiate DNA replication
What are polynucleotides?
longest polymers in the living world
DNA and RNA are polynucleotides
What is a DNA/RNA strand?
a single polynucleotide chain of DNA/RNA
RNA is usually single strand
DNA is a double strand; two strands come together by complementary base pairing
Structure of DNA:
the two DNA strands are antiparallel
they run in opposite directions
their 5’ ends opposite of the molecule
the two strands form a “ladder” that twists into a double helix
sugar-phosphate groups form the sides of the ladder, and the hydrogen-bonded bases form the rungs!
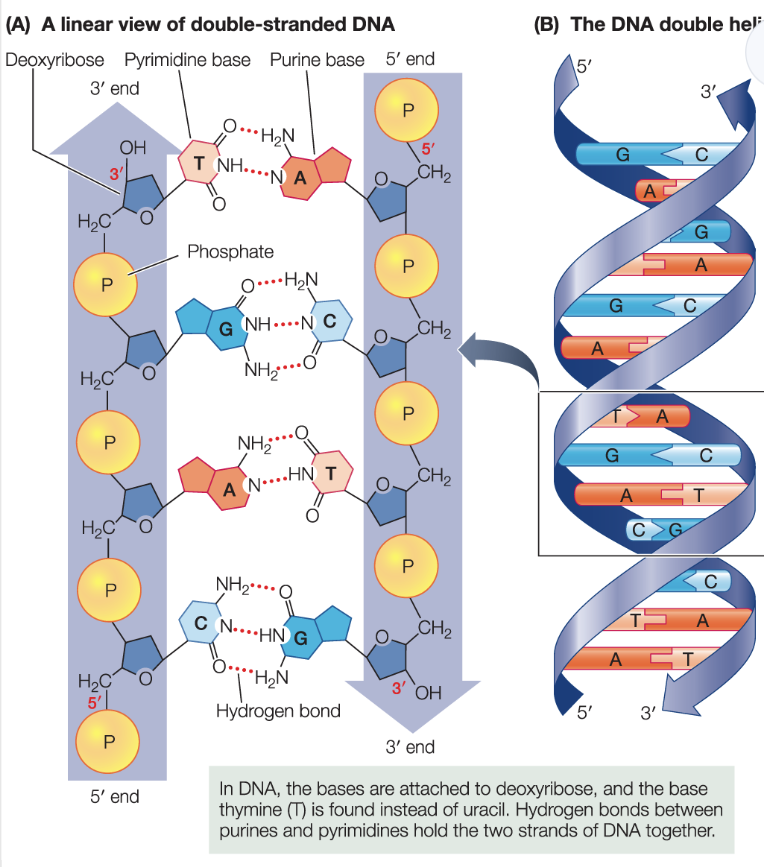
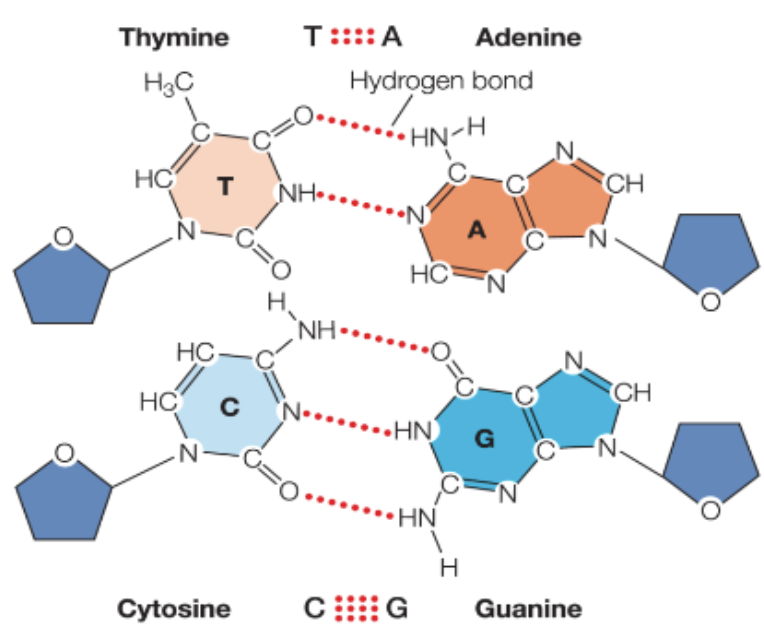
Complementary base pairing of DNA enables…
DNA to store genetic information AND transfer this information to future generations
Base pairing between _____ involves ____
nucleotides involves hydrogen bonding
Complentary base pairing:
adenine pairs with thymine
in RNA, adenine pairs with uracil
guanine pairs with cytosine
there is a fairly strong attraction of these bonds, but not as strong as covalent bonds
base pairs can be separated by a small amount of energy
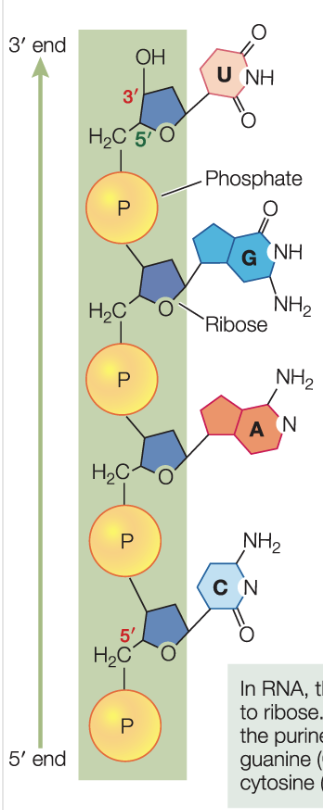
Structure of RNA:
usually single stranded —> folds back on itself to form short double-strand regions
folding occurs by complementary base pairing, so structure is determined by the order of bases
the double-strand region gives the molecule a 3d shape that affects how it interacts with other molecules
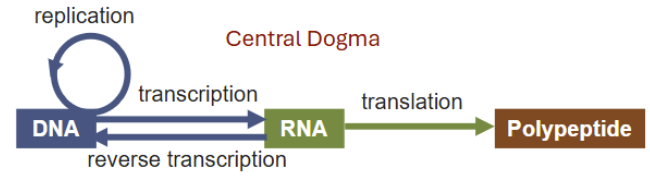
What is Central Dogma?
DNA is an information molecule: genetic information is encoded in the sequence of bases
Central Dogma describes the one-way flow of genetic information within a biological system: DNA —> RNA —> protein
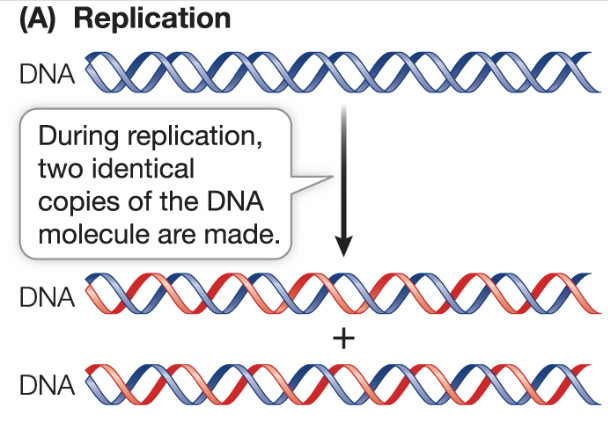
What are the functions of DNA?
Replication: DNA is copied into a new, identical DNA molecules that can be transmitted to daughter cells to offspring
Gene expression: sequences are copied to RNA (transcription) and specify amino acids sequences in proteins (translation)
What is DNA replication?
DNA is copied into a new, identical DNA molecules that can be transmitted to daughter cells and offspring
What is transcription?
information encoded in DNA base sequences is used to synthesize RNA
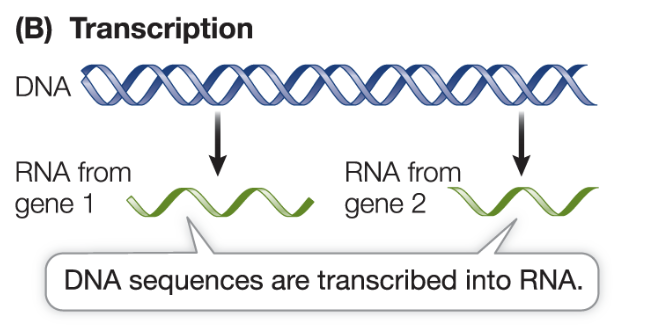
What is translation?
information in RNA base sequences is used to synthesize proteins
What does DNA replication and transcription depend on?
base pairing
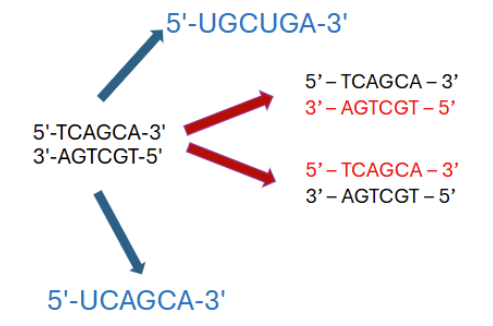
How to read transcription/replication
read from 5’ to 3’
example: 5’- ATTGCTAG- 3’ = 5’- CTAGCAAT- 3’
if a strand runs 3’ to 5’, the complementary strand runs 5’ to 3’ so flip it around
What are genes?
DNA sequences that encode specific proteins and are transcribed into RNA; not all genes are expressed in every cell
What is a genome?
a complete set of DNA in living organisms; not all DNA in the genome encodes genes
Proteins are polymers with…
variable structure
Major functions of proteins
enzymes- catalytic proteins
defensive proteins (antibodies)
hormonal and regulatory proteins— control physiological processes
receptor proteins— receive and respond to molecular signals
storage proteins store amino acids
structural proteins— physical stability and movement
transport proteins carry substances
genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and what extent a gene is expressed
Every Dragon Holds Rare Stones, Shields, Treasures, Genes
Proteins are polymers made up of…
amino acids
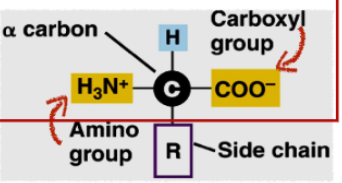
How are amino acids identified?
by their side chains
side chains = unique chemical groups attached to the alpha carbon of each amino acid
How is the structure and function of a protein determined?
the SEQUENCE of amino acids making up the polypeptide chain
What are the two common functional groups of amino acids?
carboxyl and amino
the R group (side chain) differs in each amino acid
What are oligopeptides/peptides?
short polymers o 20 or fewer amino acids (some hormones and signaling molecules)
What are polypeptides?
larger polymers; proteins made up of one or more polypeptides
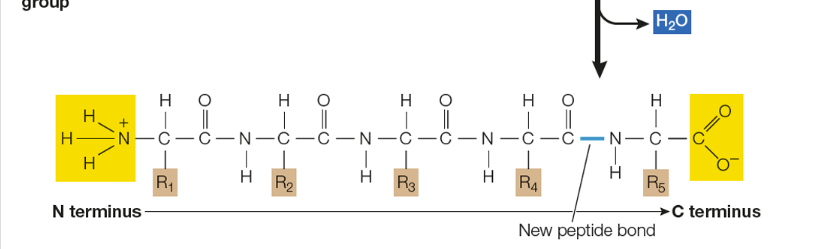
Amino acids are linked in ____ rxns to form _____
condensation exns; peptide bonds
In what direction does polymerization take place?
in the amino to carboxyl direction
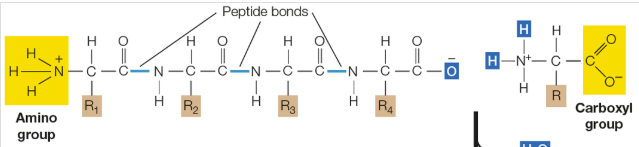
How to read peptide bonds
read from N terminus to C terminus —> forms water —> condensation rxn
How can common amino acids be grouped?
according to the properties conferred by their side chains
the side chains differ in their charge, polarity, size, and functional groups
proteins have HUGE structural diversity and specificity of interactions with other molecules and ions
The charged amino acids
positively charged: Arginine, Histidine, Lysine
positive- All Hail Lizards!
negatively charged: Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid
negative- Asp and Glu
The polar, uncharged amino acids
Serine
Threonine
Asparagine
Glutamine
Tyrosine
Some Tigers Always Growl Tonight
The nonpolar amino acids
Alanine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Tryptophan
Valine
All Iguanas Love Making Pretty Tiny Vests
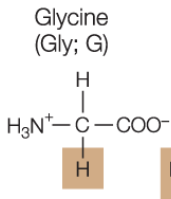
Glycine amino acid
small, and can fit into tight corners
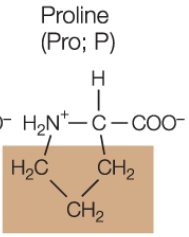
Proline amino acid
forms a covalent bonds with hydrocarbon side chains, resulting in a ring structure
proline more like pro ring
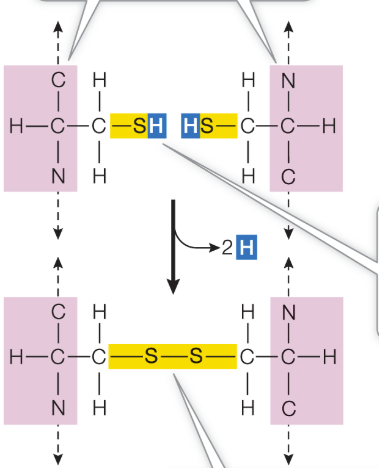
Cysteine amino acid
terminal sulfhydryl group, can react with another cysteine side chain to form a covalent bond called a disulfide bridge (—S—S—)
example: insulin has 3 S—S bonds
Among the four major macromolecules, proteins are…
the most active and the most diverse in structure and function
____ determines function
structure
How many levels of protein structure are there?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
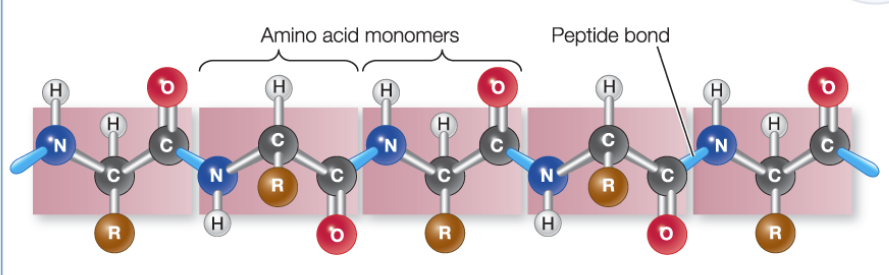
Primary Structure
the sequence of amino acids; amino acids monomers are joined, forming polypeptide chains
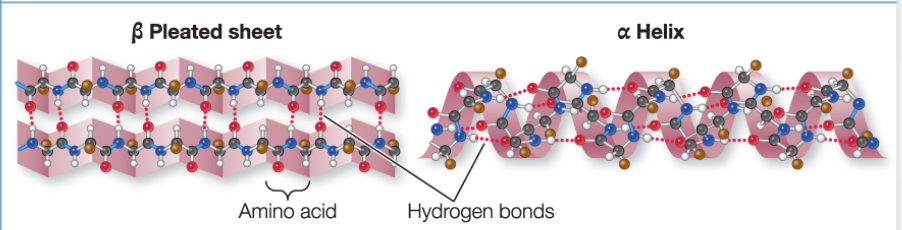
Secondary Structure
repeated patterns in different regions, due to hydrogen bonding
alpha helix: right- handed coil
beta pleated sheet: 2+ sequences of amino acids that are extended and aligned in the polypeptide
both are determined by hydrogen bonding between the —NH and —CO groups of the amino acids that make up the primary structure
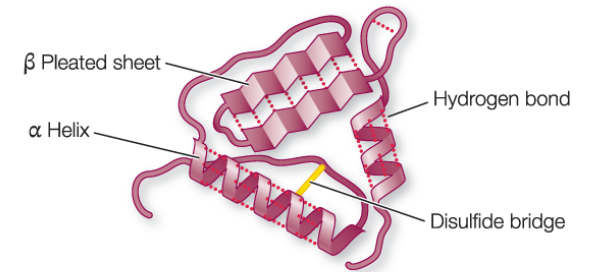
Tertiary Structure
polypeptide chain is bent and folded; results in the definitive 3d shape
structure is determined by the interactions between R groups
covalent disulfide bridges between cysteines
ionic bonds between charged side chains
hydrogen bonds between side chains
van der waals interactions between hydrophobic side chains
functional groups on a protein’s exposed outer surface can interact with other molecules
Quaternary Structure
results from the ways in which 2+ polypeptide chains (subunits) bind together and interact
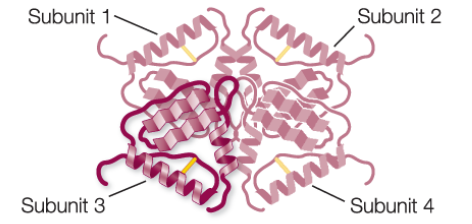
What are subunits?
many functional groups containing 2+ polypeptide chains
Example of quaternary structure
hemoglobin: binds oxygen in red blood cells; it has 2 alpha subunits and 2 beta subunits that assemble
What is denaturing?
heat or chemicals disrupt weak interactions in a protein, destroying secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
Factors that can cause denaturing:
temperature
concentration of H+ (pH)
high concentration, charged substances
nonpolar substances containing molecules
Can a protein return to normal after denaturing?
in some cases it can when it is cooled or the chemicals are removed— all of the information is contained in the primary structure
What is the function of a protein determined by?
by the protein’s structure and its binding characteristics
Amino acid side chains on the protein surface form…
weak bonds with functional groups on other molecules or ions
Typically, ____ molecules/ions can bind to a particular protein
just one or a few
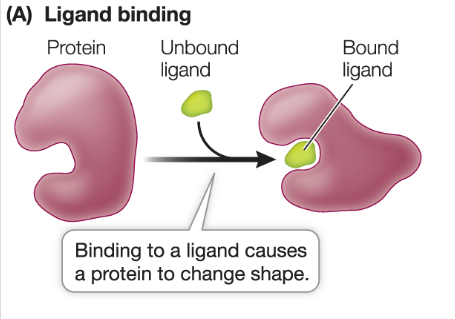
What is a ligand?
molecule or ion that binds to another molecule
ligand bonding is specific and can involve several weak bonds, making a strong interaction
binding can cause conformational change (change in shape), which affects the proteins function
binding to a ligand changes receptor structure
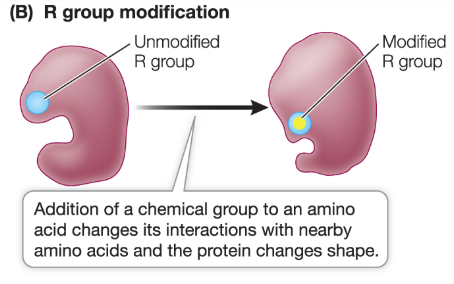
What is R-group modification?
Phosphorylation: a phosphate group is added on an amino acid residue
includes serine, threonine, and tyrosine
protein changes shape
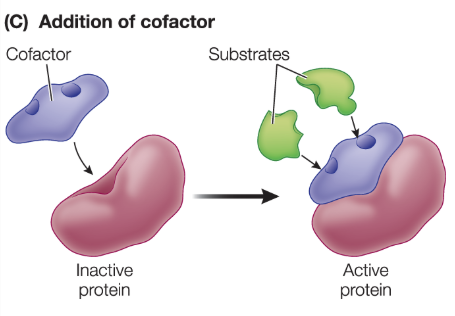
What are cofactors?
nonprotein molecules or inorganic ions, often a metal ion, that some proteins require in order to function; includes coenzymes and ATP
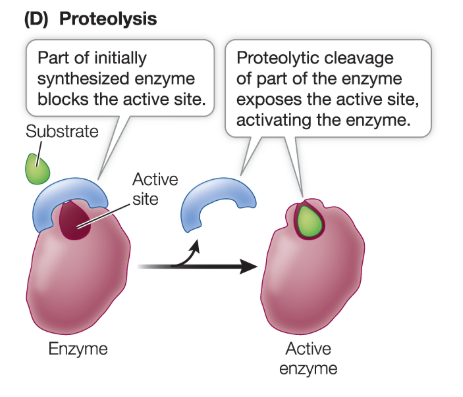
What is proteolysis?
some proteins are nonfunctional when synthesized and must be cleaved to become functional
What are catalysts?
substances that speed up (catalyze) chemical rxns without being permanently altered
most catalysts are proteins (enzymes)
enzymes lower the EA in almost all chemical rxns
think: speedy Cat
An enzyme…
does not cause a reaction to occur, it just increases the RATE of the reaction
Some enzymes change shape when…
substrate binds to them
Enzymes are specific, meaning…
each one catalyzes only one chemical rxn
Reactants are…
substrates: they bind to specific sites on the enzyme— the active sites
What is the enzyme-substrate complex?
held together by hydrogen bonding, ionic bonds, van der waals interactions, or temporary covalent bonding
How do enzymes impact EA?
they lower it by inducing strain, substrate orientation, or by adding chemical groups
Cells can regulate…
synthesis of enzymes only when they are needed, and regulate the activity of enzymes
How can activity of enzymes be regulated?
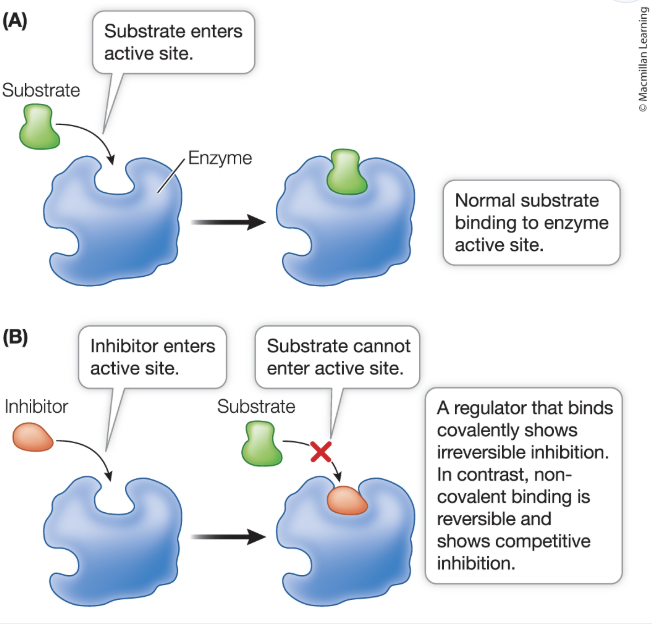
active site regulation: inhibitors are molecules that bind to the active site, preventing the substrate from entering
competitive inhibition: inhibitor is similar to the substance, but no reaction occurs; reversible
irreversible inhibition: rare, mostly occurs in drugs
allosteric regulation: non-substrate molecule binds a site other than the active site (allosteric site)
enzyme changes shape —> alters activity
can activate or inactivate enzymes
Allosteric regulation
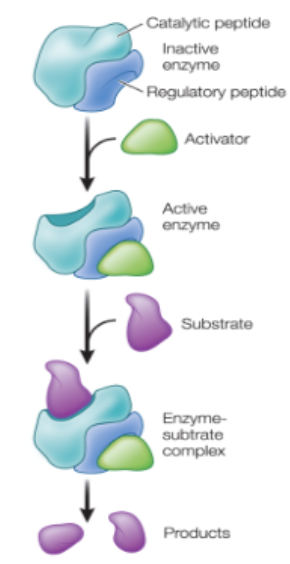
Allosteric sites can be modified…
by reversible covalent binding of a molecule
What is phosphorylation?
a phosphate group is added by a protein kinase on an amino acid residue (serine, threonine, or tyrosine)
alters a protein’s charge and conformation
extremely important mechanism by which cells regulate enzymes and other proteins
Protein phosphates…
remove phosphate groups from proteins —> “off switch” to reverse the actions protein kinase