physics - electromagnetic induction (13.1 - 13.11)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
13.1 how to produce electric current - small scale in lab
changing magnetic field can induce voltage/p.d. in wire - causes current to flow
p.d. also induced if wire moved in magnetic field
13.1 how to produce electric current - large-scale generation of electrical energy
generator: coil of wire rotated inside magnetic field
as coil turns, voltage induced in wire
causes current to flow
generators in power stations have rotating electromagnet surrounded by coils of wire
13.2 factors that affect size & direction of induced p.d.
number of turns in coil of wire
strength of magnetic field
how fast magnetic field changes/moves past coil
13.2 how does number of turns in coil of wire affect size & direction of induced p.d.
more turns in coil of wire = larger induced p.d.
13.2 how does strength of magnetic field affect size & direction of induced p.d.
stronger magnetic field = larger induced p.d.
13.2 how does how fast magnetic field changes/moves past coil affect size & direction of induced p.d.
magnetic field changes/moves past coil faster = larger induced p.d.
13.2 what does magnetic field produced do to original change?
p.d. causes current to flow - magnetic field of current opposes original change
13.3 how is electromagnetic induction used in alternators to generate a.c.?
coil of wire rotated inside magnetic field
induces p.d. in coil of wire
induces current in coil of wire
ends of coil connected to slip rings
electrical contact with external circuit made with carbon brushes (press on slip rings)
slip rings & brushes - connections don’t switch every half turn
produces a.c.
13.3 how is electromagnetic induction used in dynamos to generate d.c.?
coil of wire rotated inside magnetic field
induces p.d. in coil of wire
induces current in coil of wire
coil connected to split-ring commutator - connections switch every half turn
produces d.c.
13.4 how do microphones work?
convert pressure variations in sound waves → variations in current in electrical circuits
sound waves cause variations in air pressure
pressure variations make diaphragm vibrate
diaphragm moves coil of wire back & forth
13.4 how do loudspeakers & headphones work?
convert variations in electrical current → pressure variations in sound waves
varying current flows through coil in magnetic field
causes force on coil - moves back & forth as current varies
coil connected to diaphragm - movements of diaphragm produce sound waves
transformer
transformer: 2 coils insulated wire wound onto iron core - no electrical connection between 2 coils of wire
electricity supplied to primary coil
electricity in second coil at diff. voltage
13.5 how can a.c. in one circuit induce current in another circuit in transformer?
a.c. in primary coil creates continuously changing magnetic field
iron core carries magnetic field to secondary coil
changing magnetic field induces changing p.d. in secondary coil
13.6 what can transformer change size of?
transformer can change size of alternating voltage
(secondary coil has more turns than primary coil - p.d. greater in secondary coil)
13.7 turns ratio equation for transformers - calculate missing voltage or missing number of turns
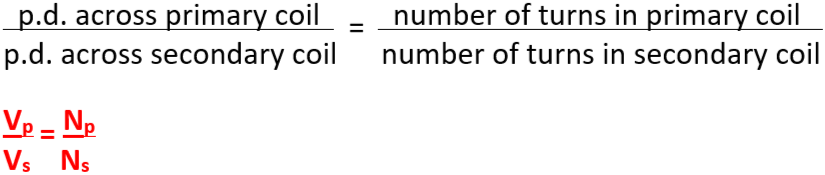
13.8 in national grid why is electrical energy transferred at high voltages from power stations then at lower voltages in each locality for domestic uses?
electricity flows through wire - wire heats up
amount of energy wasted by heating in wires significant for transmission lines in national grid
p.d. of electricity passing through wire increased = current decreased
current smaller = less energy transferred by heating = efficiency improved
13.9 where are step-up transformers used in transmission of electricity in national grid?
after electricity leaves power station
before electricity travels through transmission lines
13.9 where are step-down transformers used in transmission of electricity in national grid?
after electricity travels through transmission lines
before electricity reaches factories, homes, shops, offices
13.9 why are step-up transformers used in transmission of electricity in national grid?
increases voltage
decreases current
13.9 why are step-down transformers used in transmission of electricity in national grid?
decreases voltage
increases current
13.10 power equation (for transformers with 100% efficiency)
p.d. across primary coil (V) x current in primary coil (A) = p.d. across secondary coil (V) x current in secondary coil (A)
Vp x Ip = Vs x Is
13.11 advantages of power transmissions in high-voltage cables (using equations)
P = E/t
P = IV
P = I2R
