Biochemistry: Gluconeogenesis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
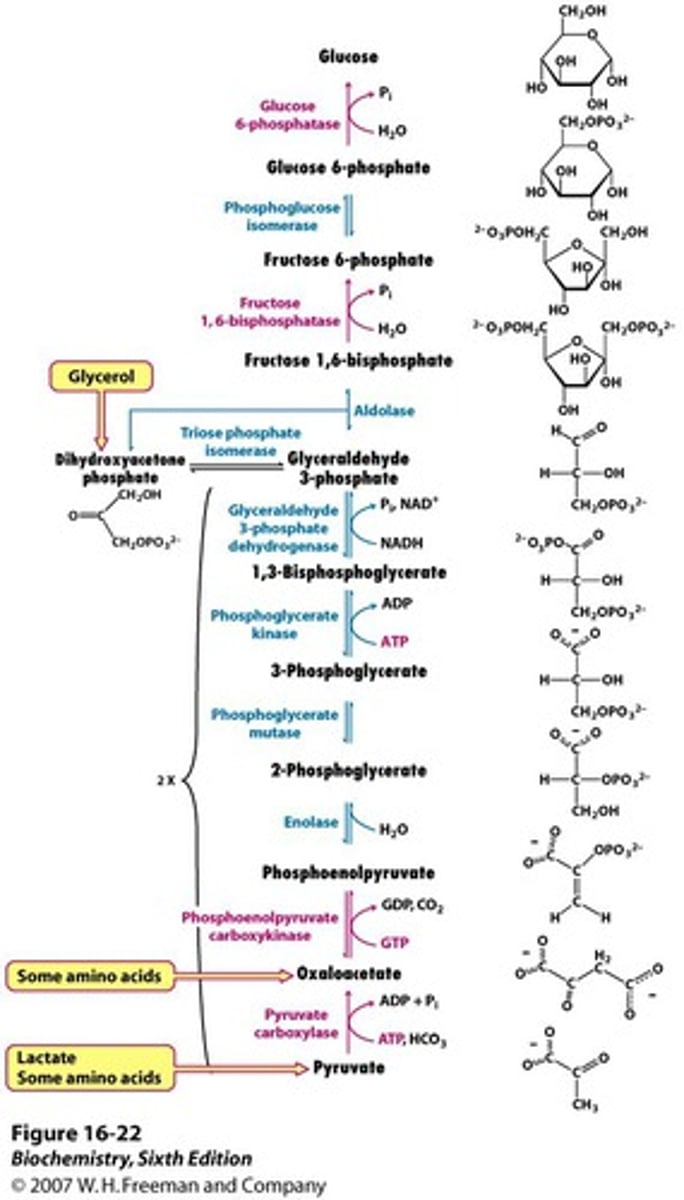
Gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in what organ? Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from compounds that are not ____________.
liver;carbohydrate
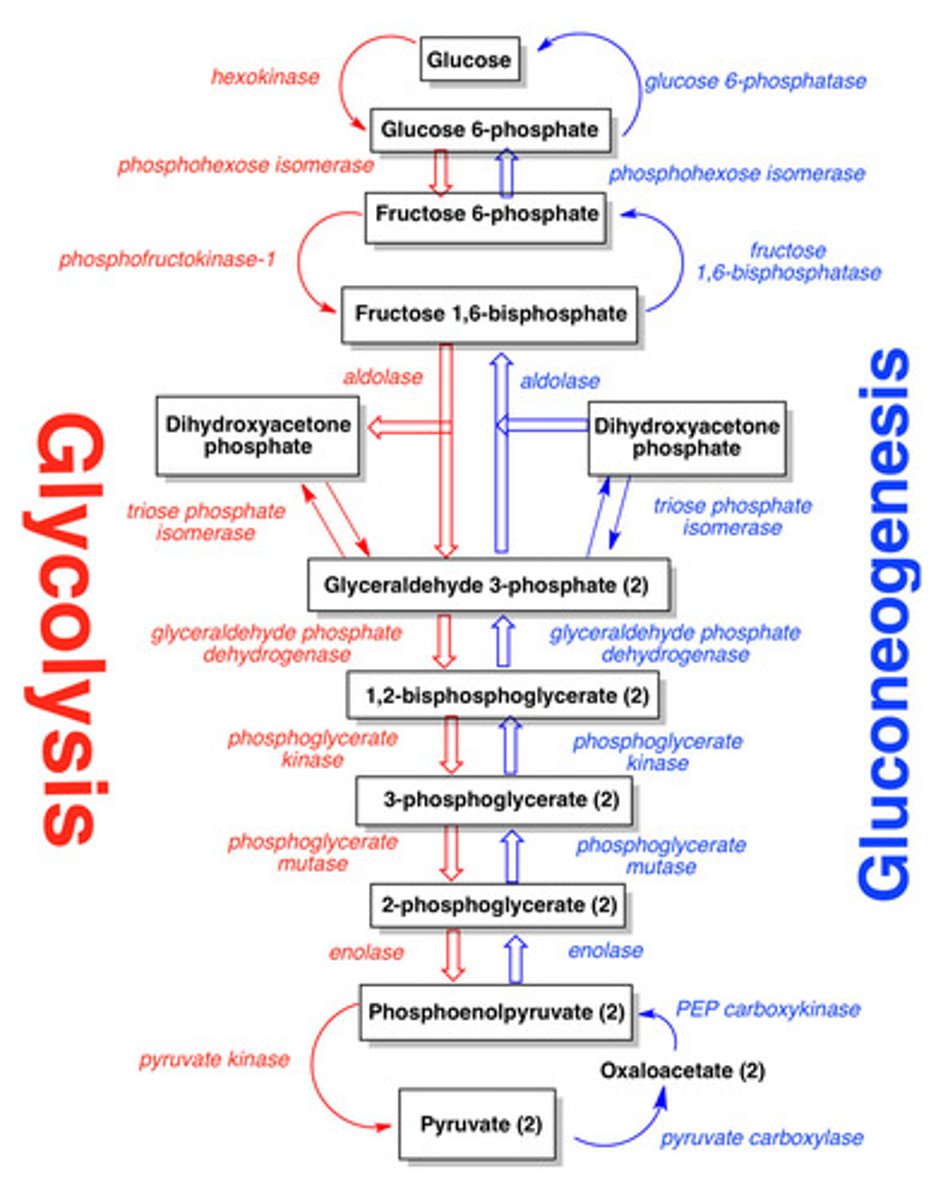
True or False: Gluconeogenesis is the reverse of glycolysis.
False: It is not. Gluconeogenesis involves several enzymatic steps that do not occur in glycolysis.
What enzymes are unique to gluconeogenesis?
1. pyruvate carboxylase
2. phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK)
3. fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
4. glucose 6-phosphatase
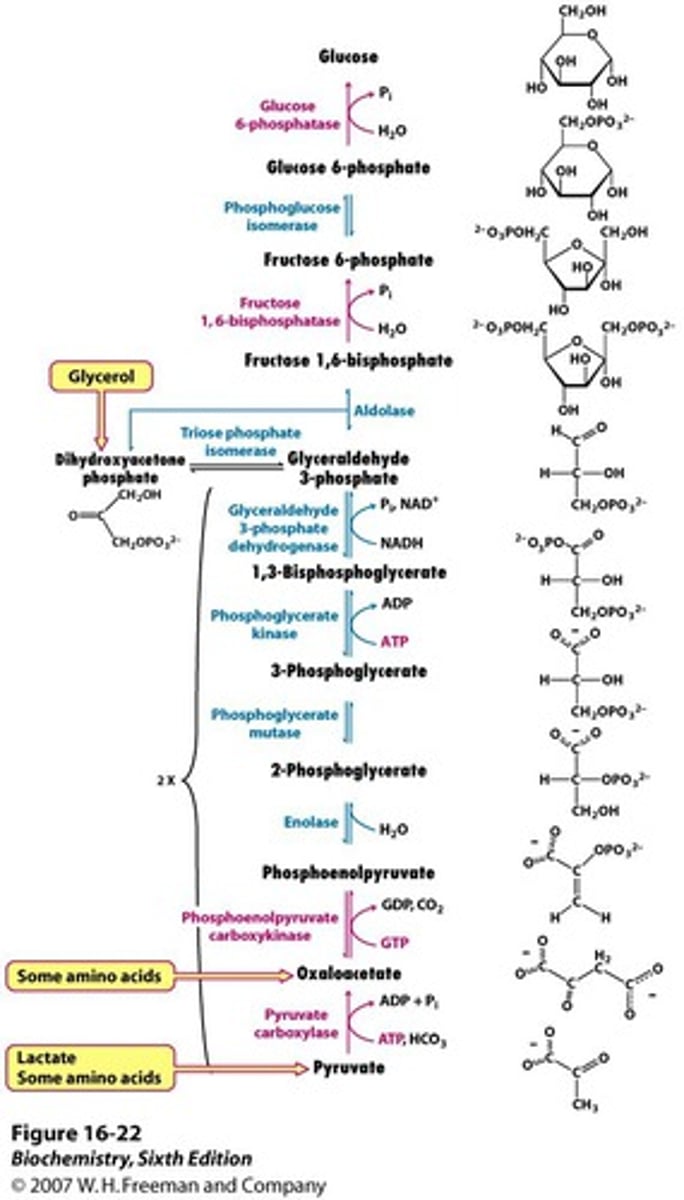
The function of gluconeogenesis is to...
help maintain blood glucose levels between meals.
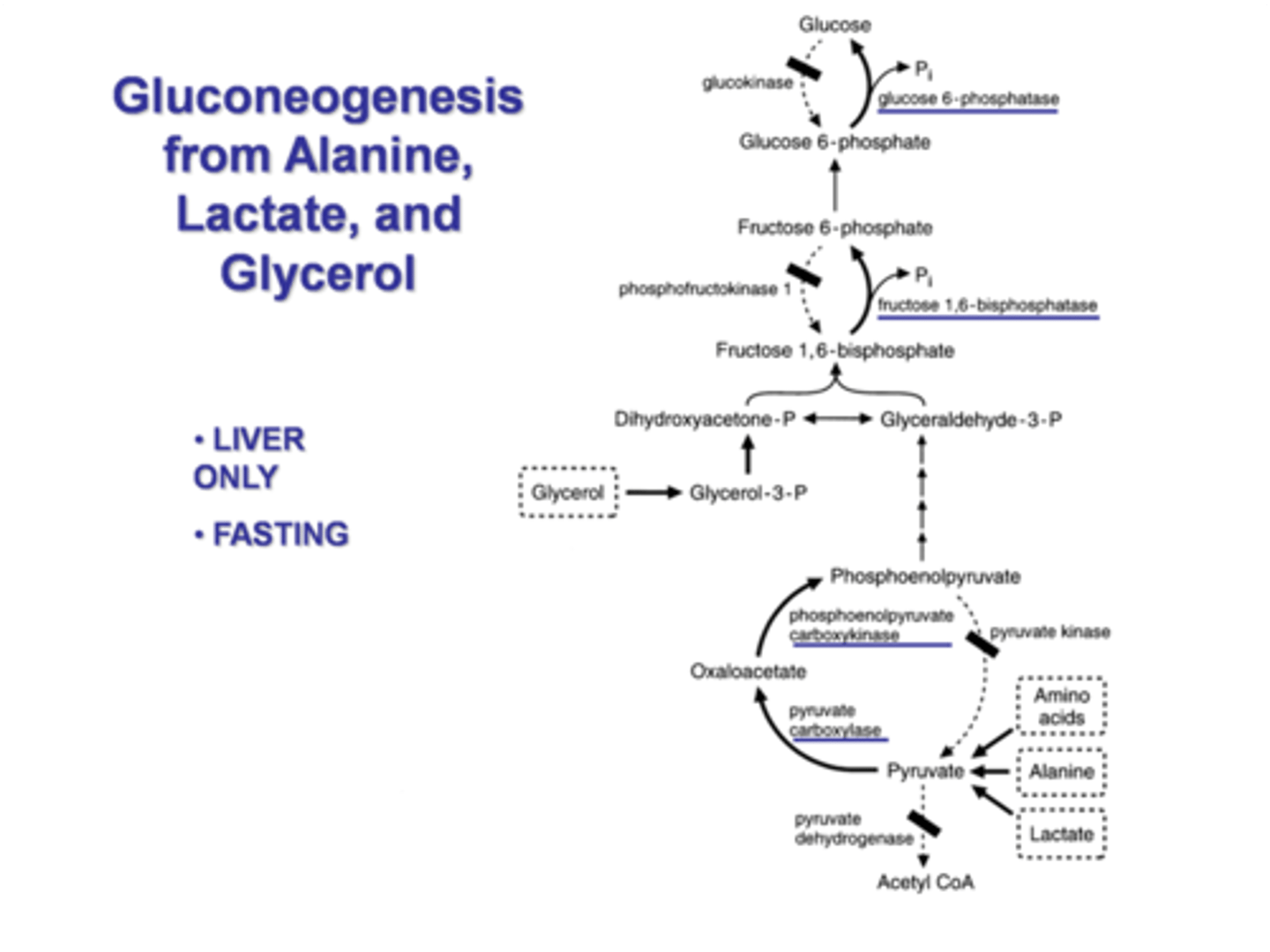
What are the precursors to gluconeogenesis?
Glycerol
Lactate
Glucogenic amino acids (comes from muscle)
TCA Cycle intermediates
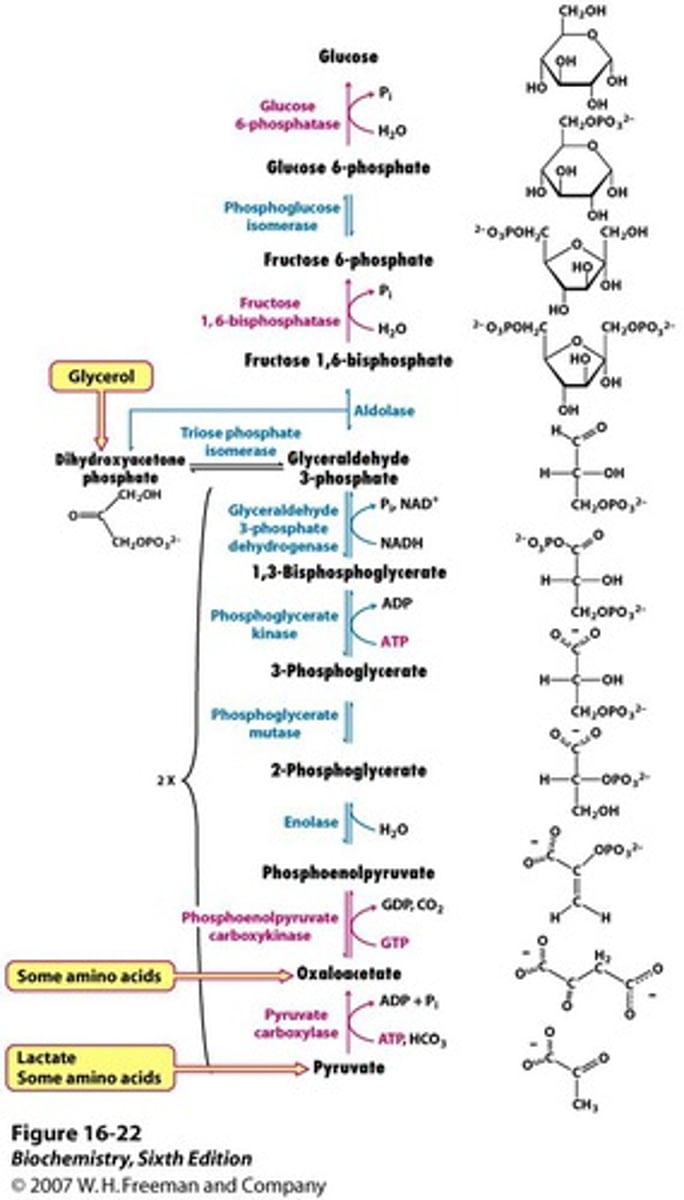
What are the three irreversible enzymes of glycolysis?
Hexokinase/Glucokinase
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
Pyruvate Kinase
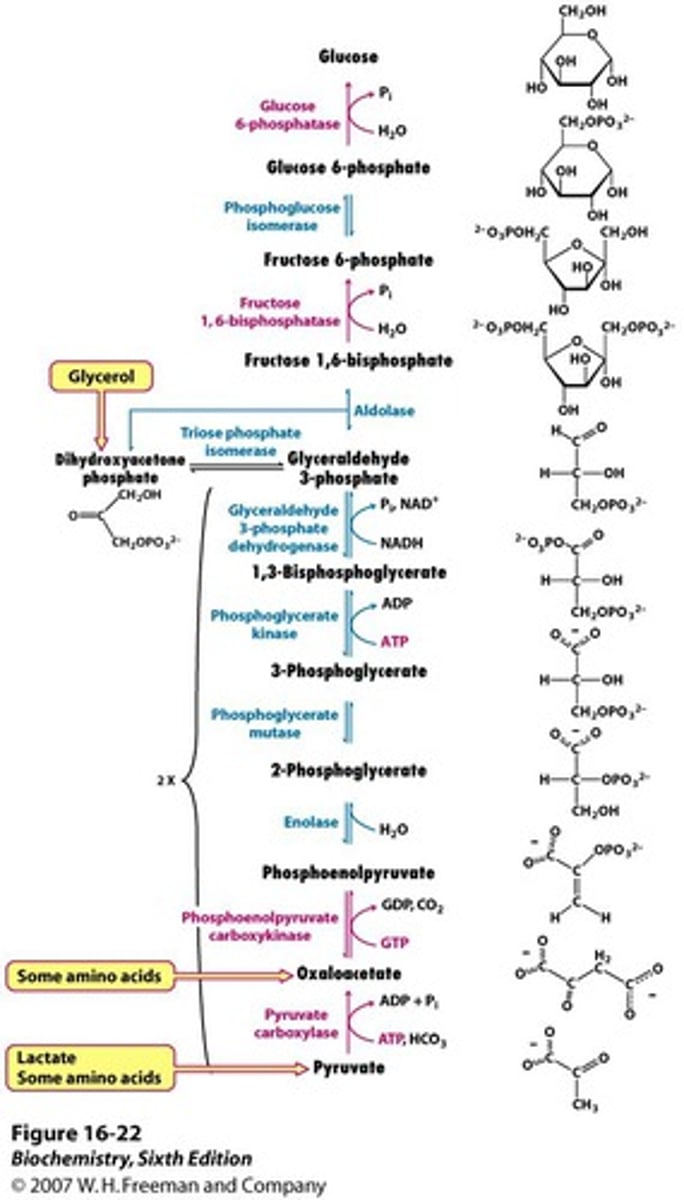
True or False: Glycolysis is a completely reversible pathway.
False: It is an irreversible pathway. (∆G°`=⁻22 kcal/mol)
The enzyme ___________ ___________ will change pyruvate to oxaloacetate. What is the co-factor that is needed to do this?
pyruvate carboxylase;biotin
What does the enzyme PEPCK (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase) do?
Catalyzes the change of oxaloacetate to PEP.
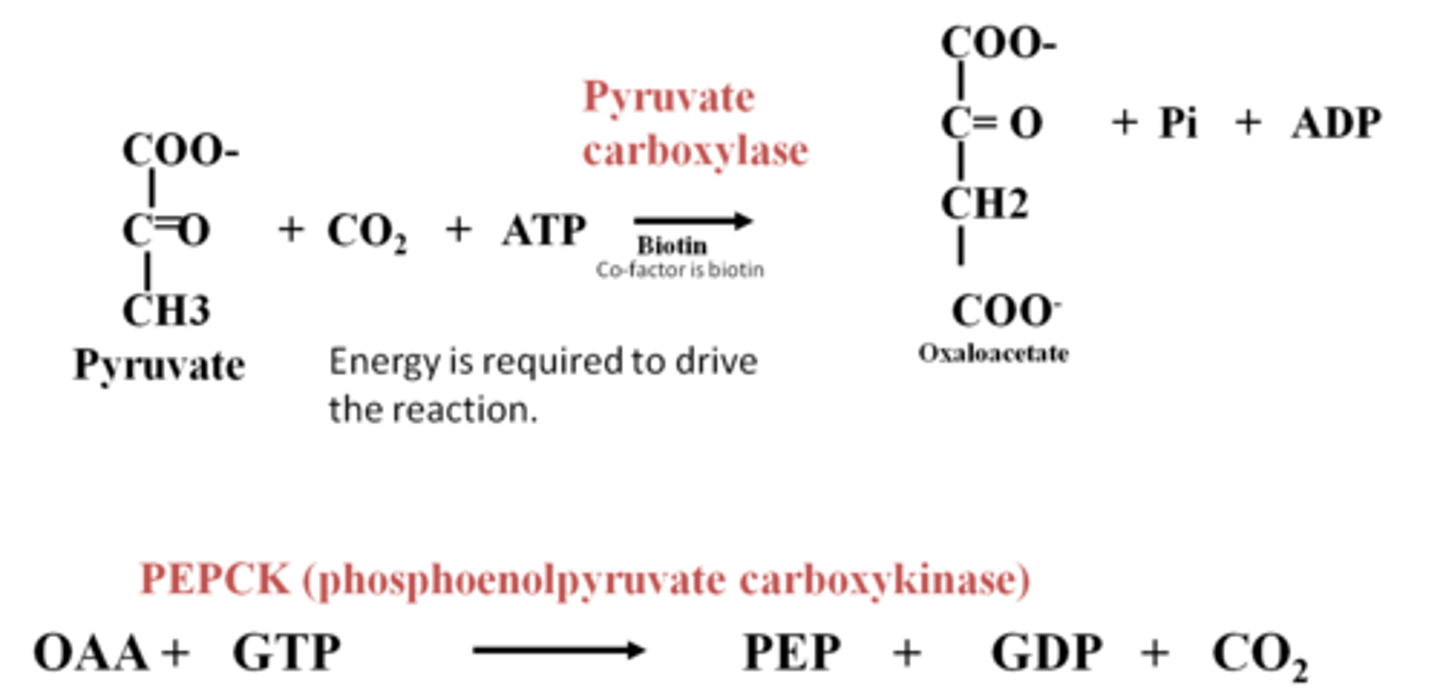
___________ _,_-_________ catalyzes fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-bisphosphate.
fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase
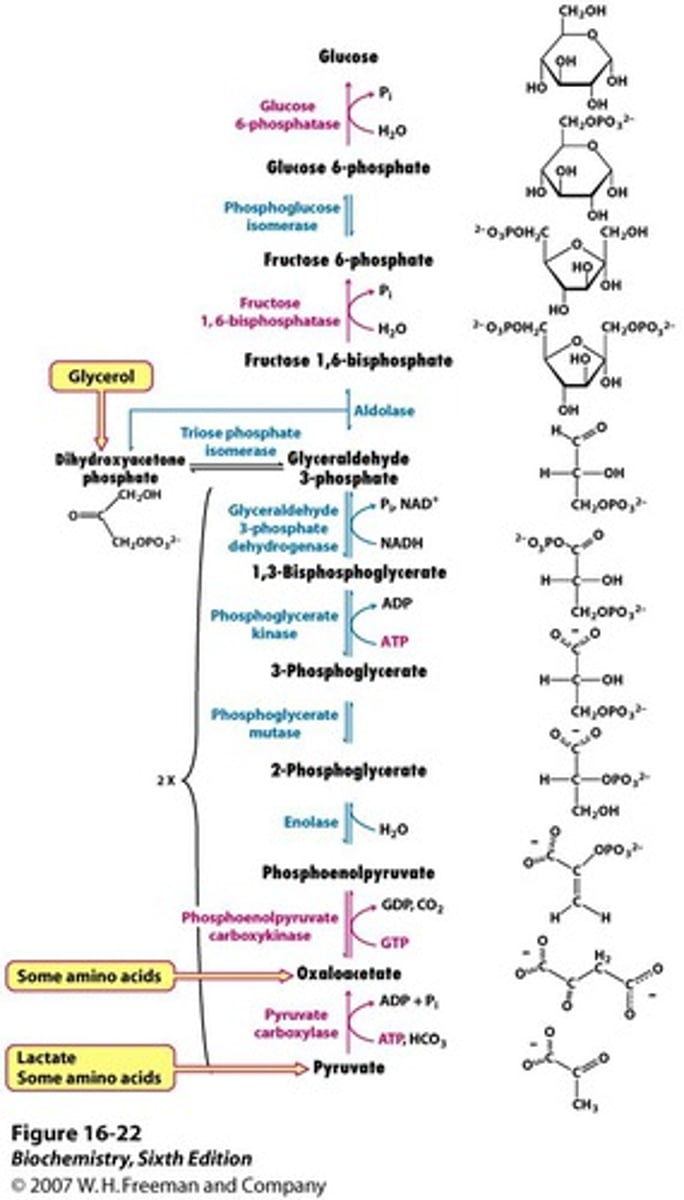
What will enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase do?
catalyze the change of glucose-6-phosphate to glucose.
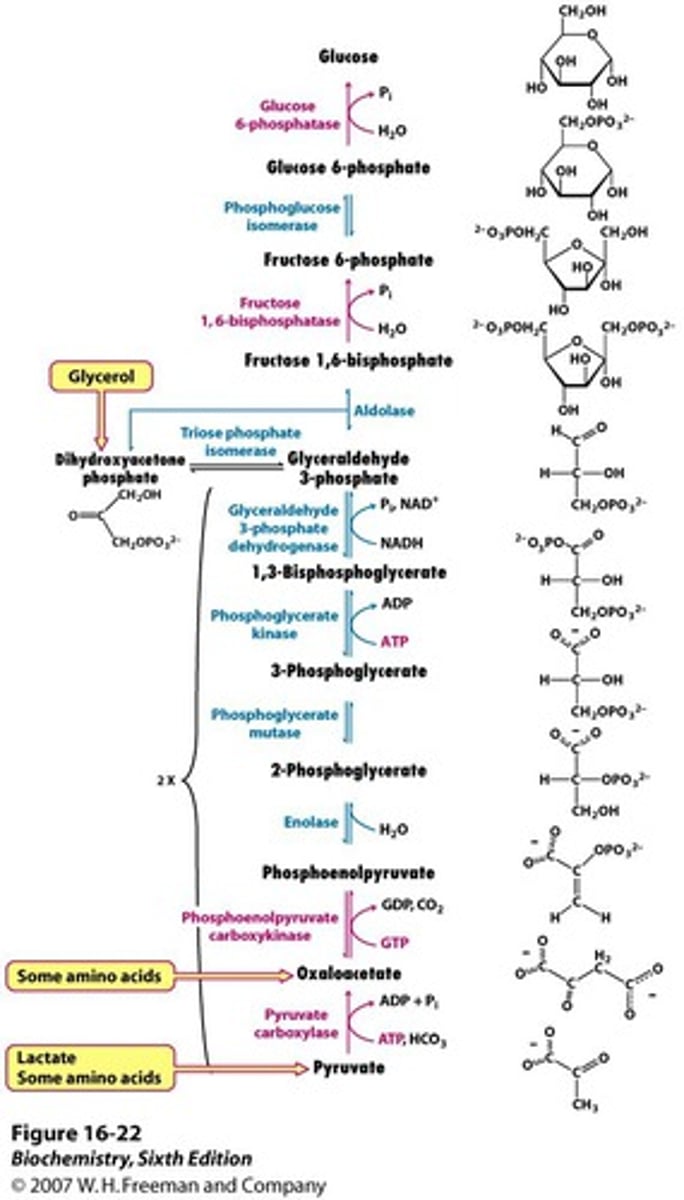
How can alanine, lactate, and glycerol be used for gluconeogenesis?
They can all be converted to pyruvate in the liver, during fasting and then go through gluconeogenesis.
What molecule mirrors blood glucose levels in liver?
fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
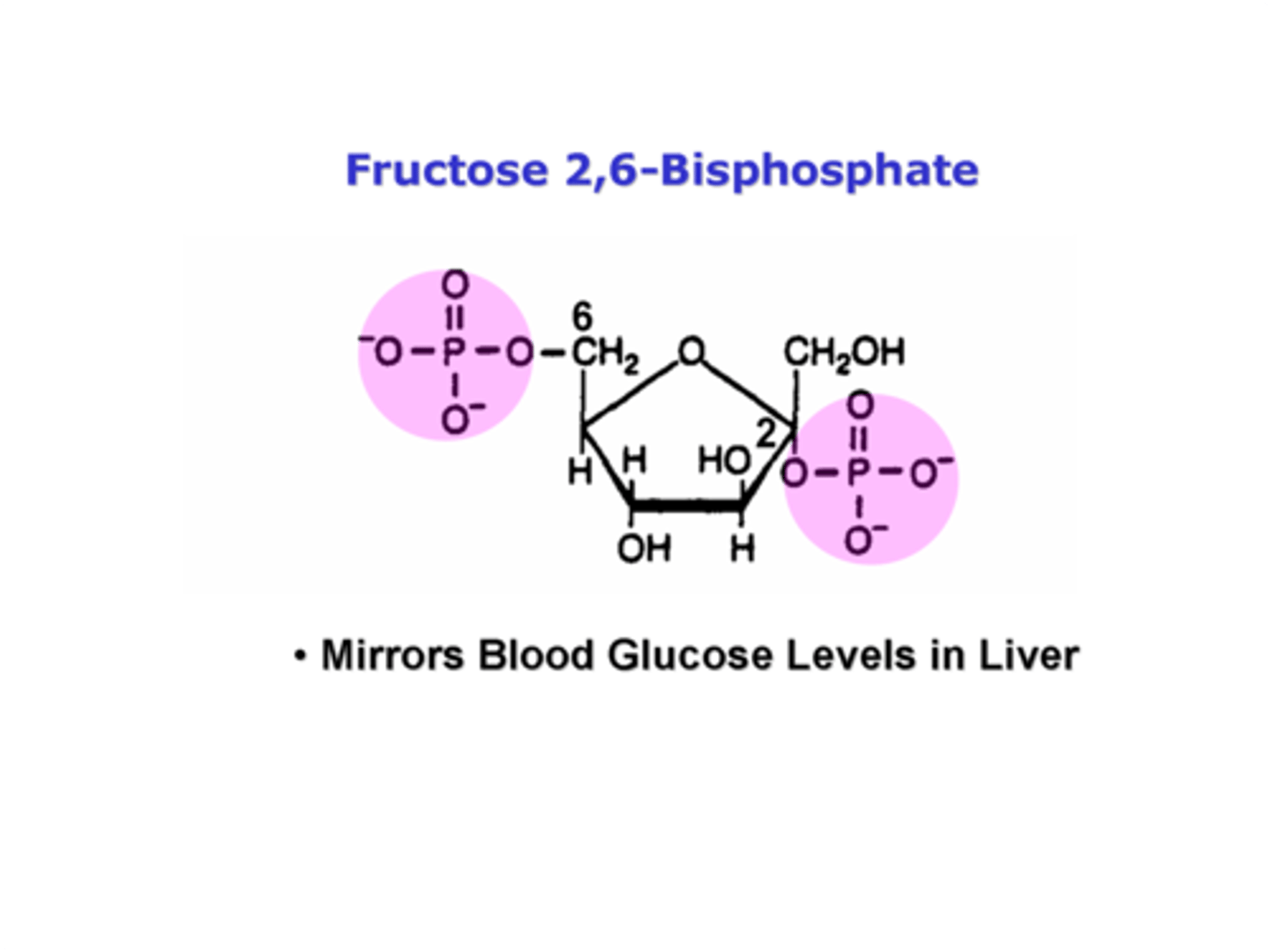
True or False: PFK-2 has both kinase and phosphatase activity.
True.
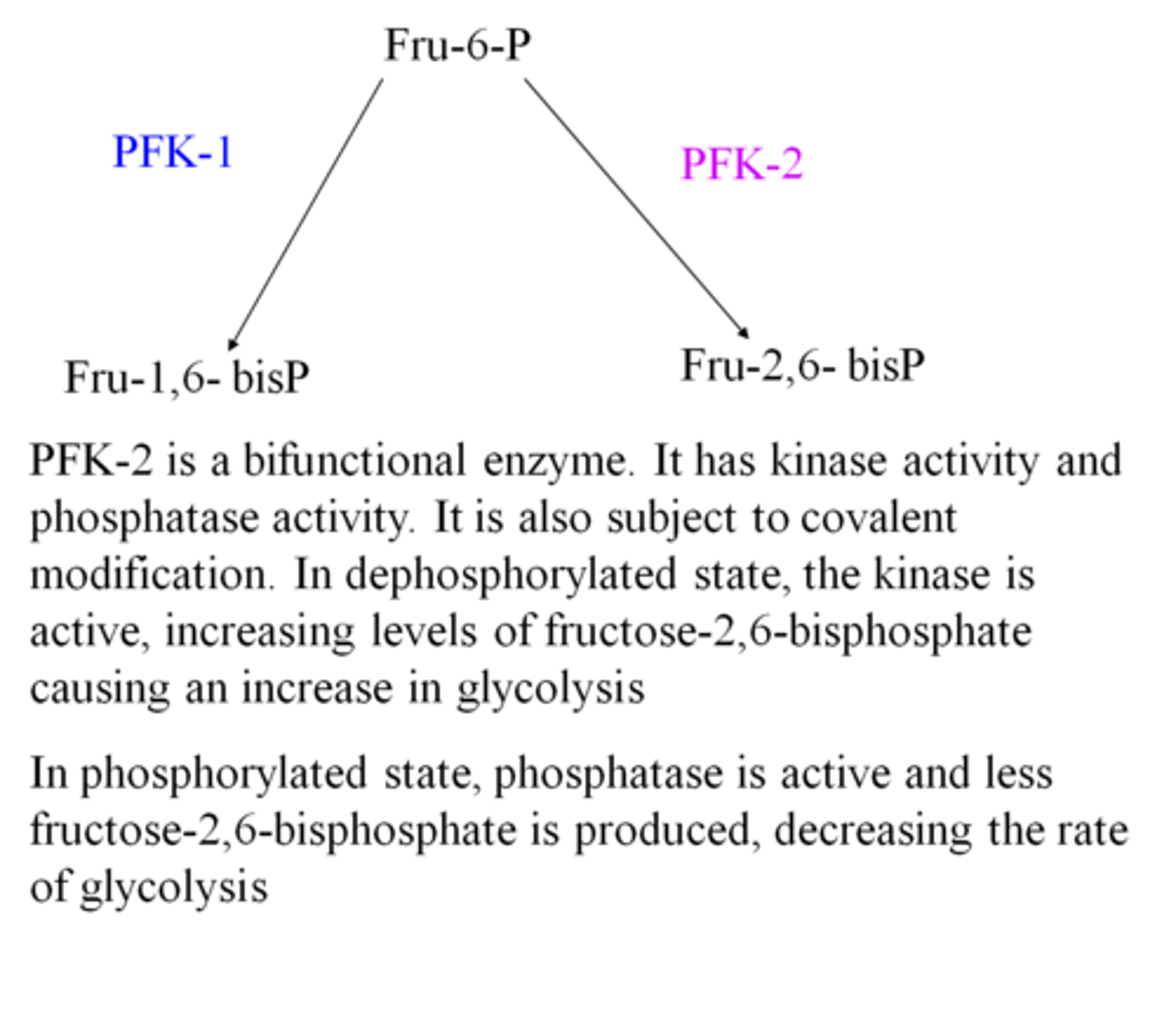
PFK-2 will convert Fru-6-P to....
Fructose 2,6-bisP
How does PFK-2 have kinase and phosphorylase activity?
In the dephosphorylated state the kinase is active and this increases the levels of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate causing an increase in glycolysis. In the phosphorylated state, phosphatase is active and less fructose 2,6-bisphosphate is produced and this decreases the rate of glycolysis.
What will a high insulin/glucagon ratio do fructose 2,6-bisP levels?
It will decrease protein kinase A activity which favors the dephosphorylated form of PFK-2 and this will favor the formation of PFK-2. This activates PFK-1 and leads to increased rate of glycolysis.
What will a high glucagon/insulin ratio do fructose 2,6-bisP levels?
It will increase protein kinase A activity which favors the phosphorylated form of PFK-2 and this will inactivate PFK-2. This decreases the inhibition of FBP-1 and leads to increased rate of gluconeogenesis.
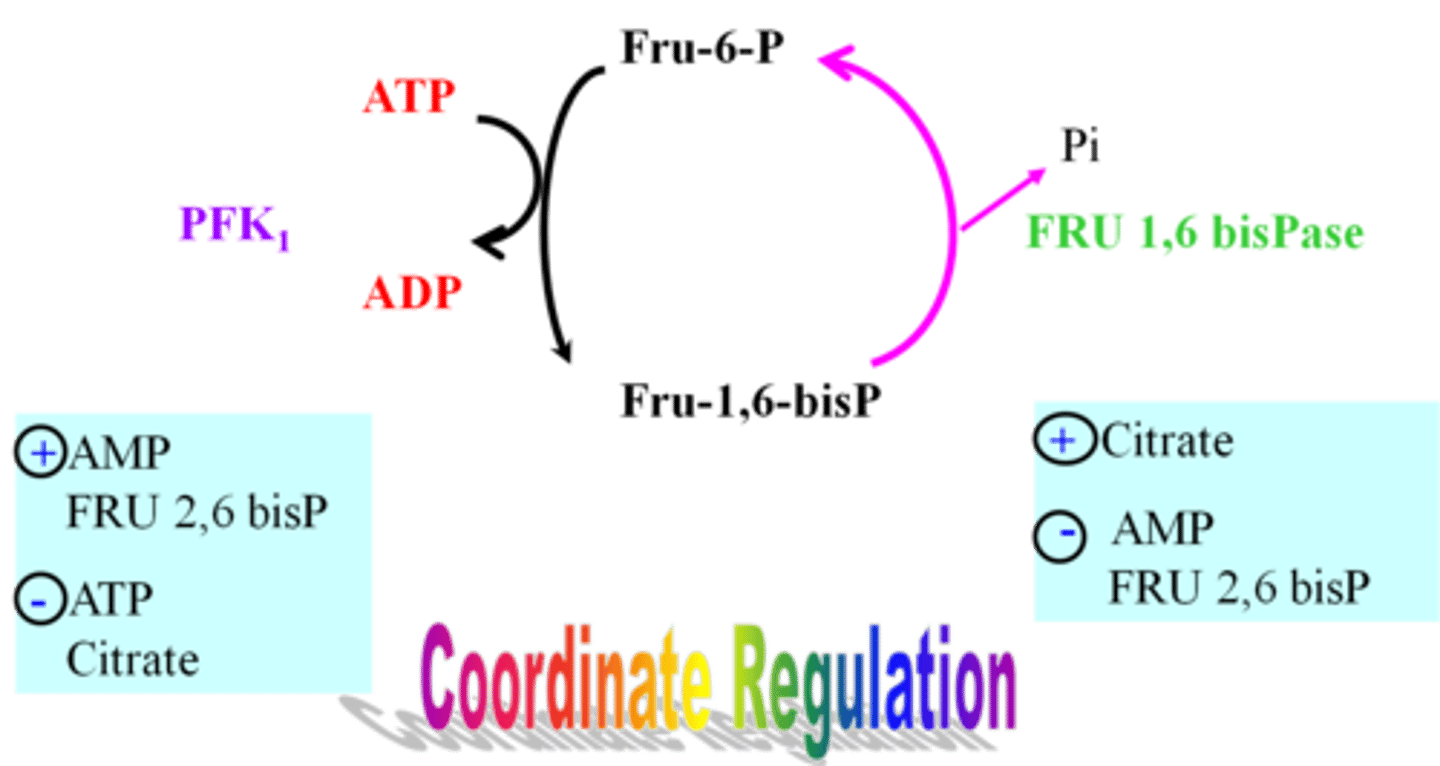
How will citrate, AMP, and frucose 2,6-bisP affect gluconeogenesis?
Citrate will increase gluconeogenesis, AMP and fructose 2,6-bisP will decrease it.
True or False: the PEPCK gene is turned on by glucagon and turned off by insulin.
True.
Where is glucose 6-phosphatase located in the cell?
in the endoplasmic recticulum (ER)
How does Acetyl CoA effect gluconeogenesis?
it will promote gluconeogenesis
A patient presented with a bacterial infection that produced an endotoxin that inhibits phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK). In this patient, under these conditions, glucose production from which of the following precursors would be inhibited?
Alanine, Lactate, Oxaloacetate