Enzymes (WIP)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Eduqas Core concepts alevel bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What are enzymes
globular proteins and biological catalysts. They are not used up.
Enzyme active sites
Enzymes are specific as they have an active site which is complementary to the shape of the substrate. Depends on the tertiary structure of enzyme.
Metabolism
all the enzyme/ chemical reaction in a cell
Anabolism
the reactions that build up new, more complex molecules from seperate substrates
Catabolism
the reactions that break down more complex molecules into seperate products
Metabolic Pathways
a series of reactions where the product of one enzyme is the substrate of another one. Can have branches with different routes
Extracellular enzymes
They work outside of the cell eg. digestive enzymes are made in pancreatic cells and then transported out of the cell to digest food in the gut
Intracellular enzymes
work inside the cell. eg. enzymes for aerobic respiration are found in mitochondria
How do enzymes work?
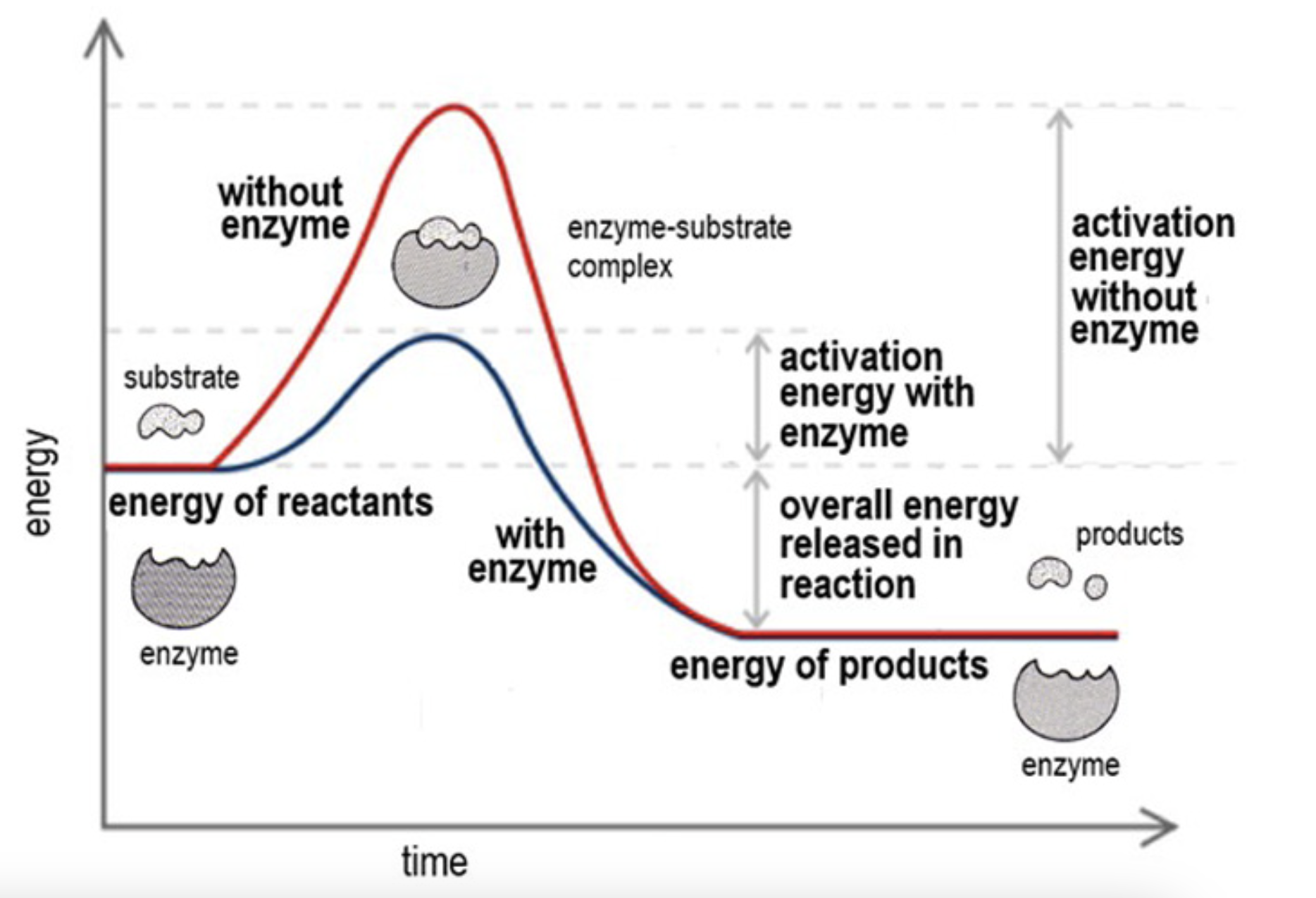
When a substrate and an active site collide the substare binds to the active site through interactions in the R group making an enzyme-substrate complex
Bonds in the substrate distort, straining the bonds that would break and increase the chance of them breaking
This brings new atoms in the substrate closer and new bonds can form
Activation energy required for the reaction decreases once they bond
Lock and key theory
The active site is a fixed shape. The substrate collides with the active site in the correct oritientation.
Induced fit theory and an example.
As the substrate enters the active site forces of attraction are formed which causes the active site to change shape to fit the substrate.
Activation energy graph
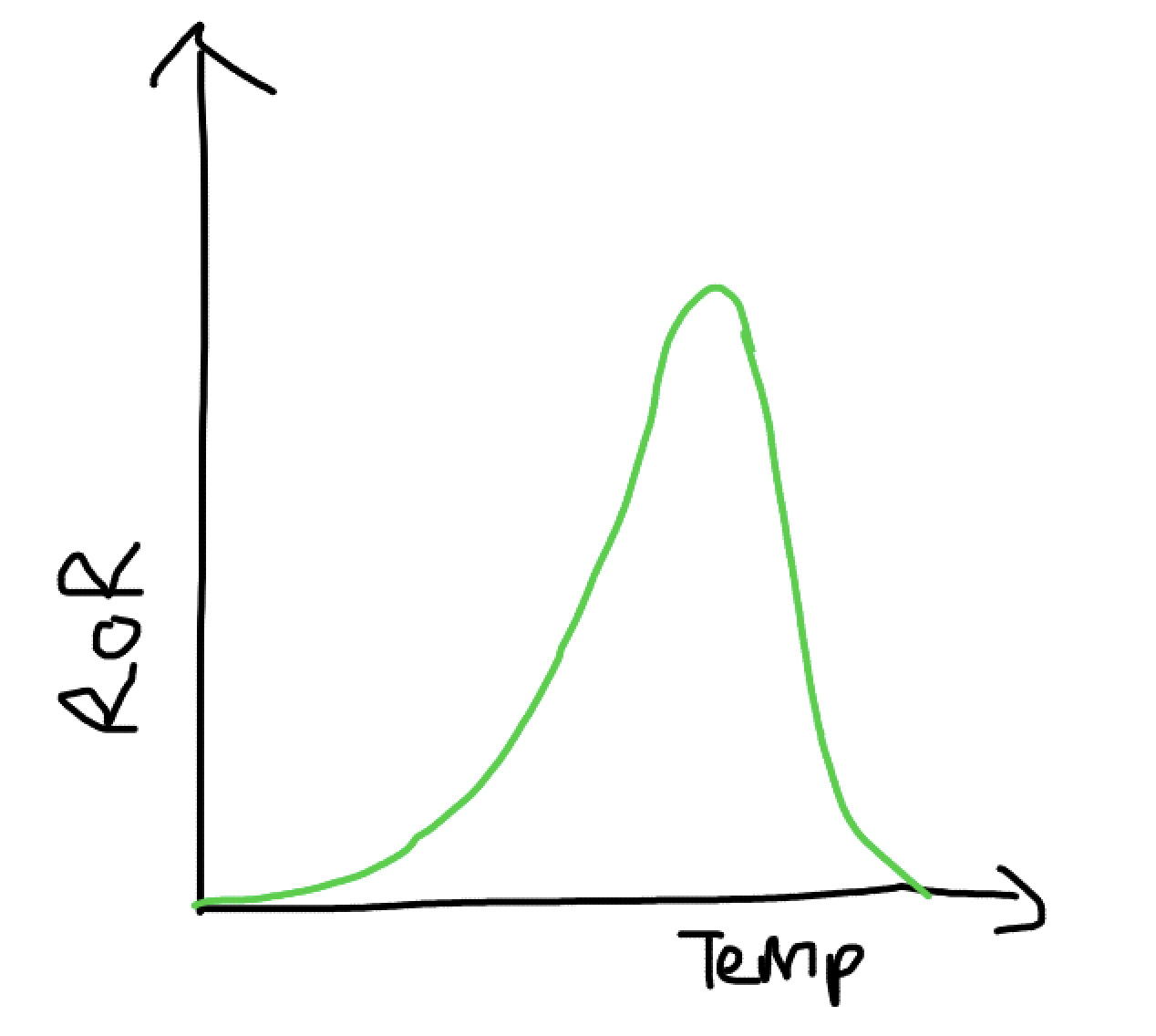
What does a graph showing the effects of temperature on enzymes?
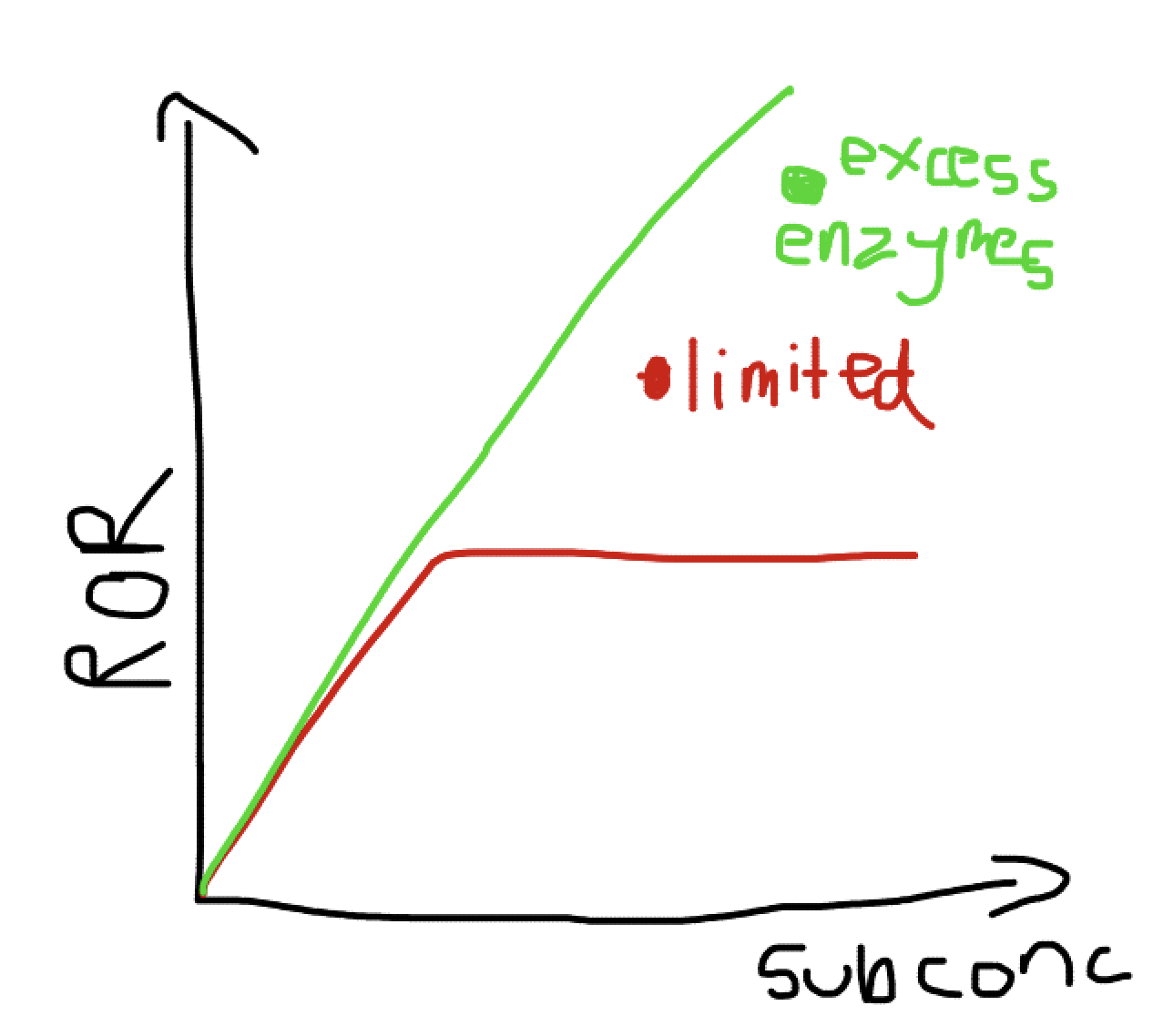
What does a graph showing the effects of substrate concentration on enzymes?
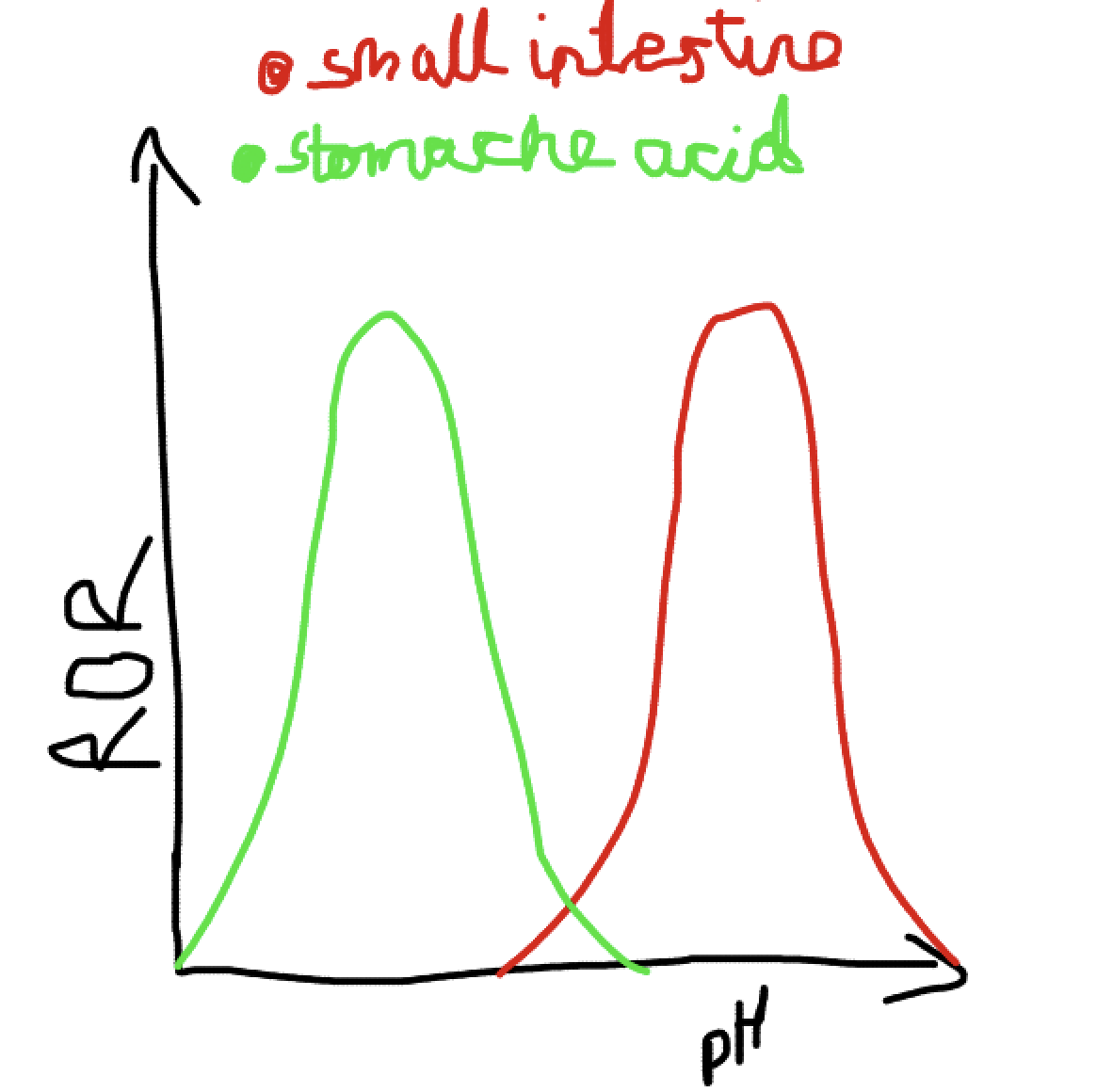
What does a graph showing the effects of pH on enzymes?
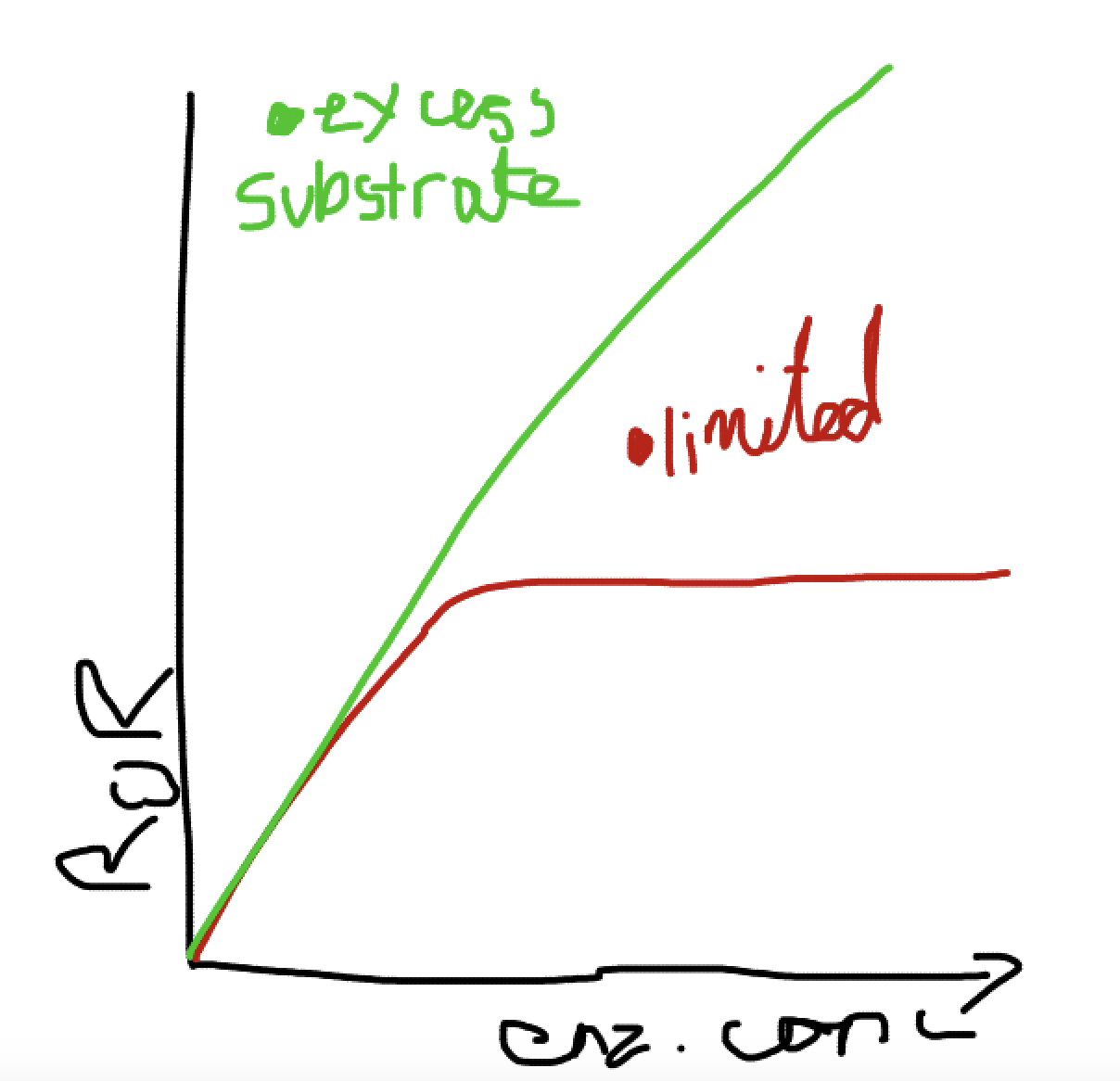
What does a graph showing the effects of enzyme concentration on enzymes?
How does temperature affect enzymes and denature them?
As temperature increases, kinetic energy increases which measn it is more likely for the substrate and enzyme to collide and with enough energy so there are more enzyme substrate complexes. After the optinum the hydrogen bonds vibrate and break so the active sites tertiary (and secondary) shape change and denature.
How does pH effect enzymes?
Small changes can cause reversible changes to the active site.
When the pH is low there is more H+ ions so the amine groups takes some and becomes positively charged. When the pH is high there are less H+ ions so the OH group deposits some and becomes negative. This changes how the active site is able to bond so the enzyme cannot lower activation energy and the enzyme is denatured/ inactive
Regulatory enzymes
The rate that a substrate is used or a product is made in metabolic pathways can be controlled by regulatory enzymes at each step
Allosteric enzymes
Two types of reversible inhibators?
Non competitive and competitive
Competitive reversible inhibitor
Structurally similar to normals substrates and compete with them for the active site, slowing down rate of reaction
What happens with competitive inhibators if substrate concentration increases?
Eventually the competitive inhibitors will be outcompeted and reach the maximum rate of raction
Non-competitive reversible inhibitors?
They react with the enzyme (not at active site) and change the shape of the whole enzyme including the active site, meaning the substrate can no longer bond
Irreversible inhibitors?
bind covalently and permanantly to the enzyme preventing normal enzyme function.
Rate of Reaction equation
Mass change/ time change
Investigation into the effect of temperature or pH on enzyme activity
Phenolphthalein is pink when alkali but colourless when in an acidic solution.
Place a beaker of lipase solution in 25 degree water bath
Add 5cm of milk in a test tube with 5 drops of phenolphthalein and 7cm of sodium carbonate. Repeat this four more times.
Place one of each in 15, 25, 35, 45, 55 degrees and let them acclimate for 10 minutes.
Add 1cm of the lipase solution and, keeping it in the waterbath, stir and begin to time how long it takes for th4e solution to become colourless. The same person must determine if it is colourless each time.
Repeat each one 3 times
What are the industrial uses of enzymes?
-catalysing specific processes
-can be obtained from microorganisms- easy to get
-highly efficient
-less energy required
-can be immobilised
Compared to chemical catalysts why are enzymes better for industrial use?
more efficient, less needed for a higher result
work at normal temperatures and pressures so less energy needed
can be obtained from microorganisms- high growth rates, can be genetically manipulated
What is an immobilised enzyme?
when an enzyme is bound to a surface so they cannot move
How can enzymes become immobilized (5)
Absorption (carrier-bound)- onto the surface of a material- must be insoluble
Micro/encapsulation- within a partially permeable structure (polymer)
covalent bonded (cross-linked)- bound to a binding compound
entrapment (enzyme inclusion)- within the internal structure of a silica gel lattice
Cellulose-bound- entrapment within insoluble particle and cross linked
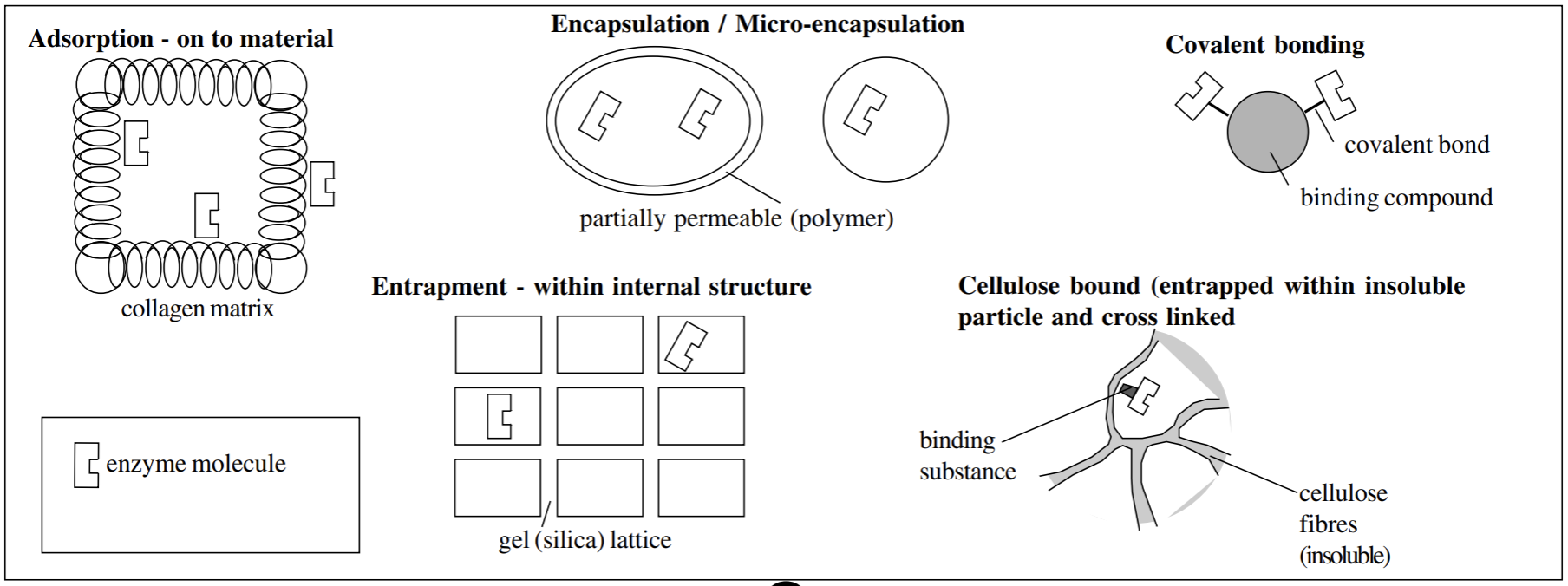
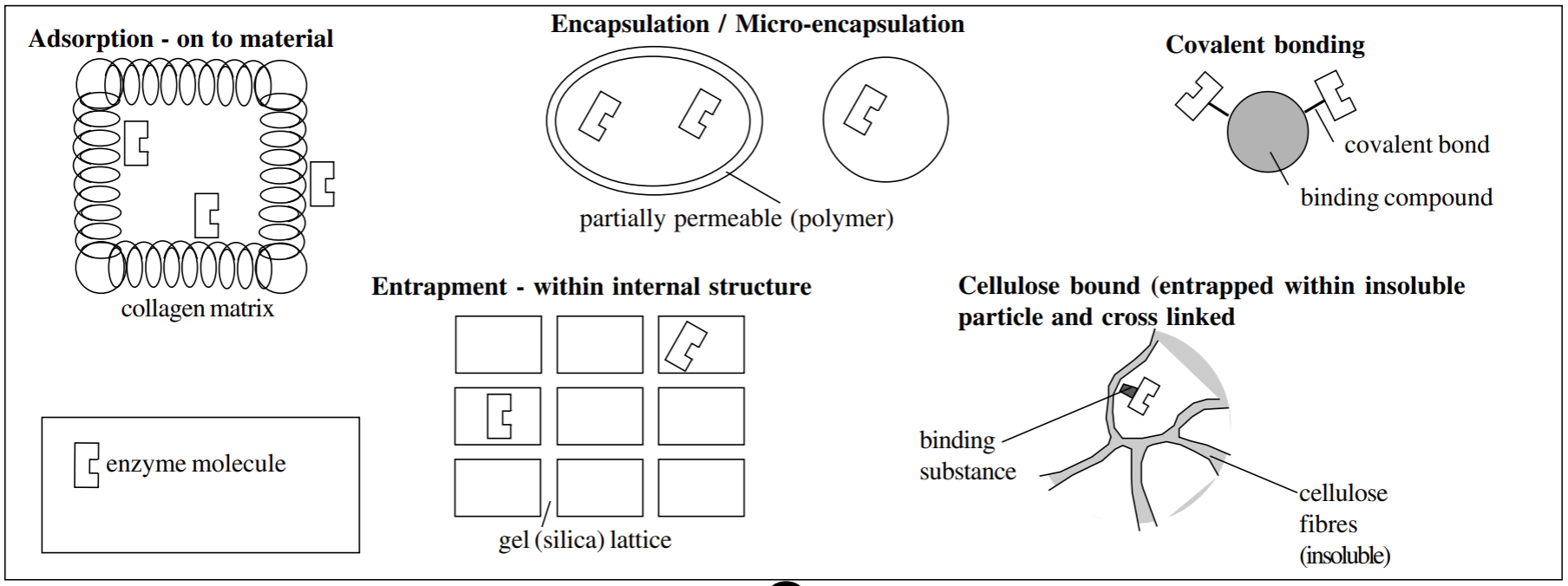
Advantages of immobilisation
more stable- tolerate a wider range of pHs and stable at higher temps
enzyme and product are more easily separated so can be reused easier and removal is less expensive
product isn’t contaminated with the enzyme
continuous process
increased product
immobalising enzymes in an inert substance reduces the ability of the polypeptide chain to move and changes in temp and pH have less effect on the 3D shape (wider range of optinum) + they are more likely to collide
Disadvantages of immobalistion?
may bind to substrate with lower attraction
What is a typical use of immobilized enzymes in industry?
Making lactose free milk- milk is poured in a tube with pellets of immobilized lactase, this breaks down the lactose
Biological detergents
starch hydrolysis
What is a biosensor?
a use of immobilized enzymes in medicine. An analytical instrument which converts a biological response into an analytical signal.
They detect specific substances or conditions
eg.glucose oxidase electrode which can detect glucose levels in blood
Why does decreasing flow rate increase volume of product collected?
Increases contact time between the enzyme and substrate, so more time of enzyme to form more successful collisions and more enzyme substarte complexes are formed
How do Biosensors work?
the substrate in the sample is added and passes through a semipermeable membrane (controls which substances enter to results are not affected). The immobilized enzyme binds with the substrate and breaks it down. The product is then detected by an electrode which produces a current which is amplified and displayed
effect of