215 Fluid and Electrolyte Terms
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
isotonic solutions (0.9 nacl and LR)
are given to expand intravascular fluid volume and have the same osmolality as plasma. They do not move from the vascular system; these solutions replace fluid volume caused by vomiting and diarrhea, burns, and traumatic injury
hypotonic solutions (d5W, 0.45 Sodium Chloride)
when infused, water moves by osmosis from the vascular system into the cells
hypertonic solutions (D5 0.9 Sodium Chloride; D5 0.45 Sodium Chloride, D10W, 3% Sodium Chloride)
when infused, water moves by osmosis from the cell into the vascular system
Situations that promote thirst
excessive fluid loss, excessive sodium intake, decreased fluid intake
Situations that inhibit thirst
a high intake of fluids
fluid retention
excessive IV infusion of hypotonic solutions
and low sodium intake
Sensible and Insensible fluid loss
Sensible fluid loss is measurable (e.g. urine output)
Insensible fluid loss is not measurable (e.g. exhalation water loss, evaporation from skin); insensible water loss approx. 900mL per day
Sodium
135-145 meq/L; regulates fluid volume; conducts electrical impulses
Potassium
3.5-5 meq/L; regulates cardiac rhythm, conducts electrical impulses
Calcium
transmission of nerve impulses, cardiac automaticity
Magnesium
maintains potassium, involved in electrical activity in nerve and muscles including the heart
Phosphate
assists with acid base balance, promotes muscle and nerve action
dehydration
loss of water in the intracellular, extracellular or intravascular spaces. Can be caused by insufficient fluid intake, excessive fluid loss or fluid shifts.
hypervolemia
shift of fluid from cells into the extracellular fluid
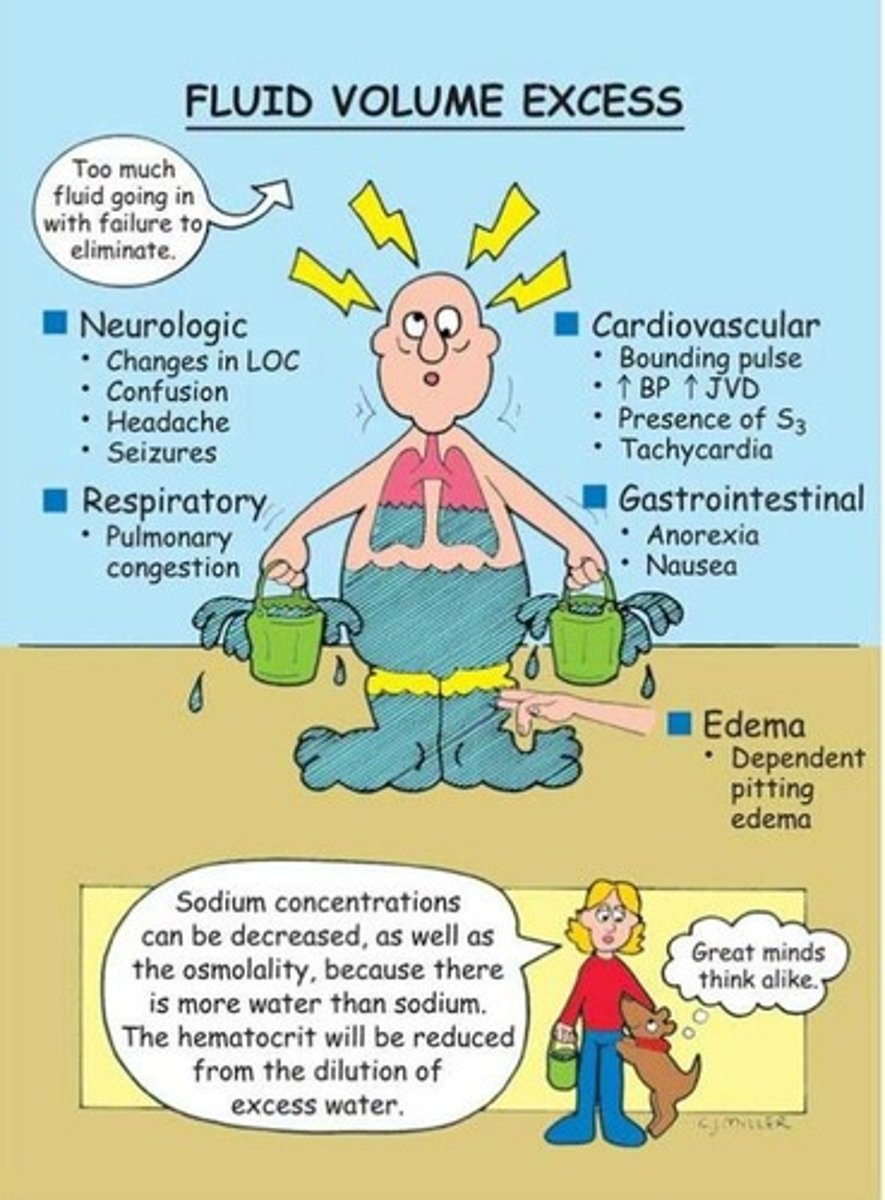
Signs of fluid overload
-elevated BP, bounding pulse, distended neck veins, and increased shallow respirations
SEVERE= crackles in lungs, dyspnea, and ascites.
ascites
accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity
Hyponatreima s/s
anorexia, nausea and vomiting , weakness, lethargy, confusion, muscle cramps or twitching, seizures
Hypernatremia S/S
thirst, elevated temperature, dry mouth Severe=hallucinations, irritability, lethargy, seizures
Hypokalemia S/S
Fatigue, Anorexia, N/V, Muscle weakness, Decreased GI motility, Dysrhythmias, Paresthesia
Hyperkalemia S/S
Muscle weakness
Dysrhythmias
Flaccid paralysis
Intestinal colic
Tall T waves on ECG