nucleophilic substitution
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
why does nucleophilic substitution occur?
in a haloalkane, the C-halogen bond is polar
this means the δ+ C is attacked by nucleophiles which replace the halogen
what is a nucleophile?
a species attracted to areas w/ low e- levels, meaning they are lone pair donors
give 3 examples of nucleophiles:
OH- (reagent = NaOH/KOH)
CN- (reagent = KCN)
NH3
draw the mechanism for nuc sub w/ chloroethane and NaOH/KOH:
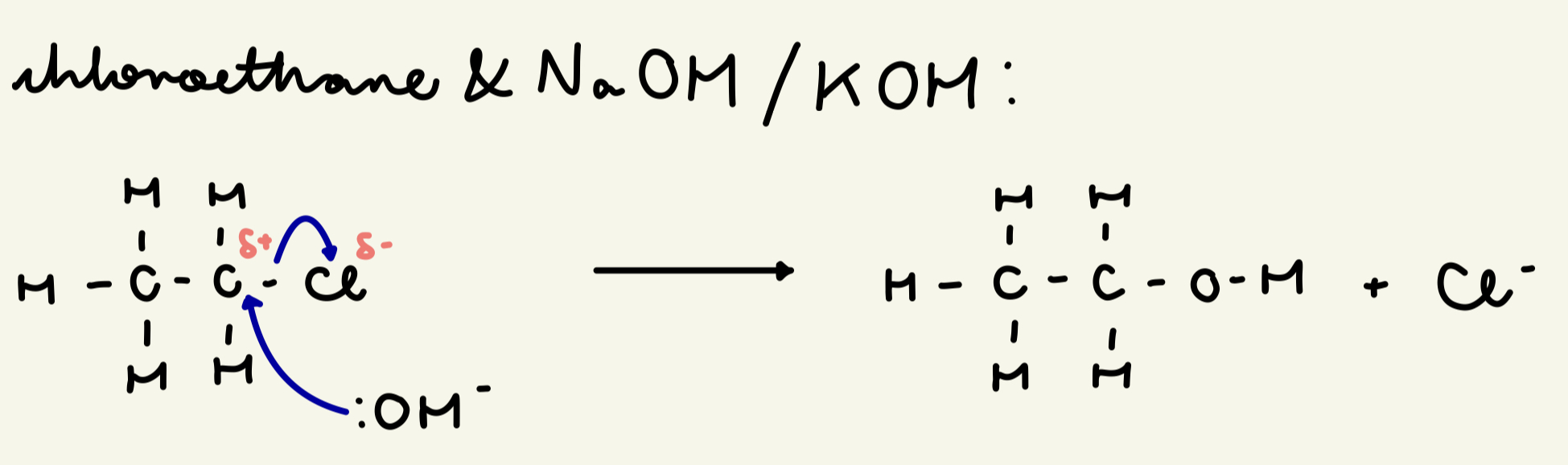
draw the mechanism for nuc sub w/ bromoethane and ethanolic KCN:
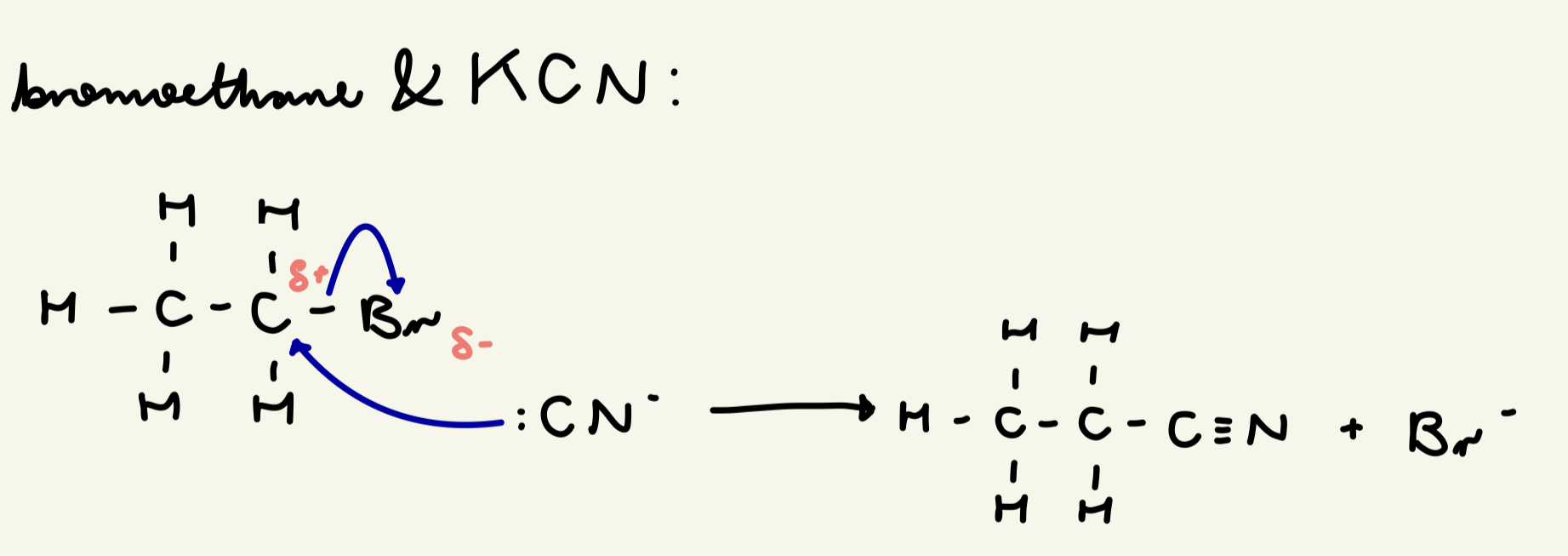
what can nuc sub form and how?
alcohols by reacting w/ NaOH/KOH - OH-
nitriles by reacting w/ ethanolic KCN - CN-
amines by reacting w/ ethanolic NH3 - NH3
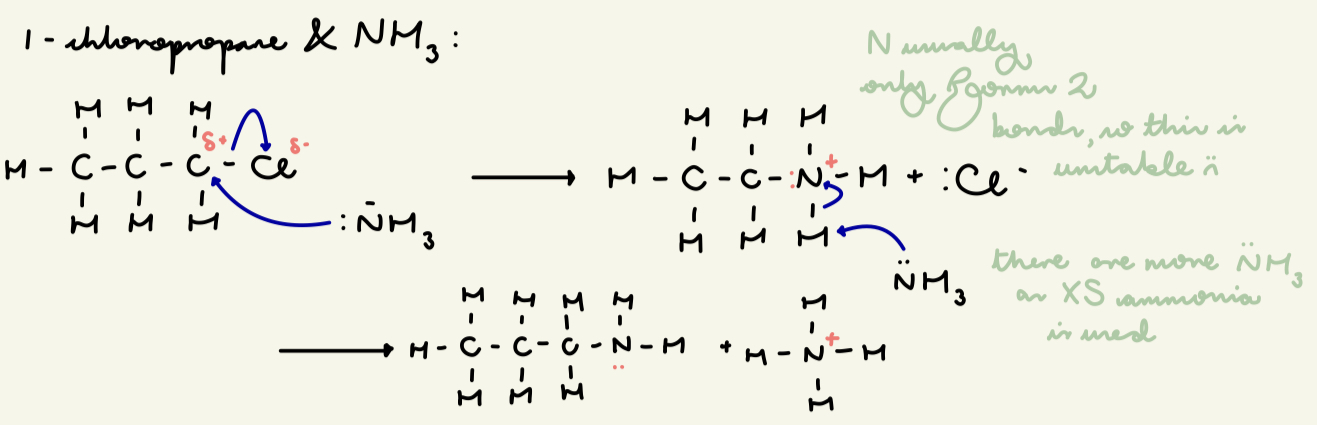
draw the mechanism for nuc sub of 1-chloropropane and XS ethanolic NH3:
which solvent is the reagent dissolved in nuc sub?
aqueous
what temperature is a nuc sub reaction carried out at?
cold
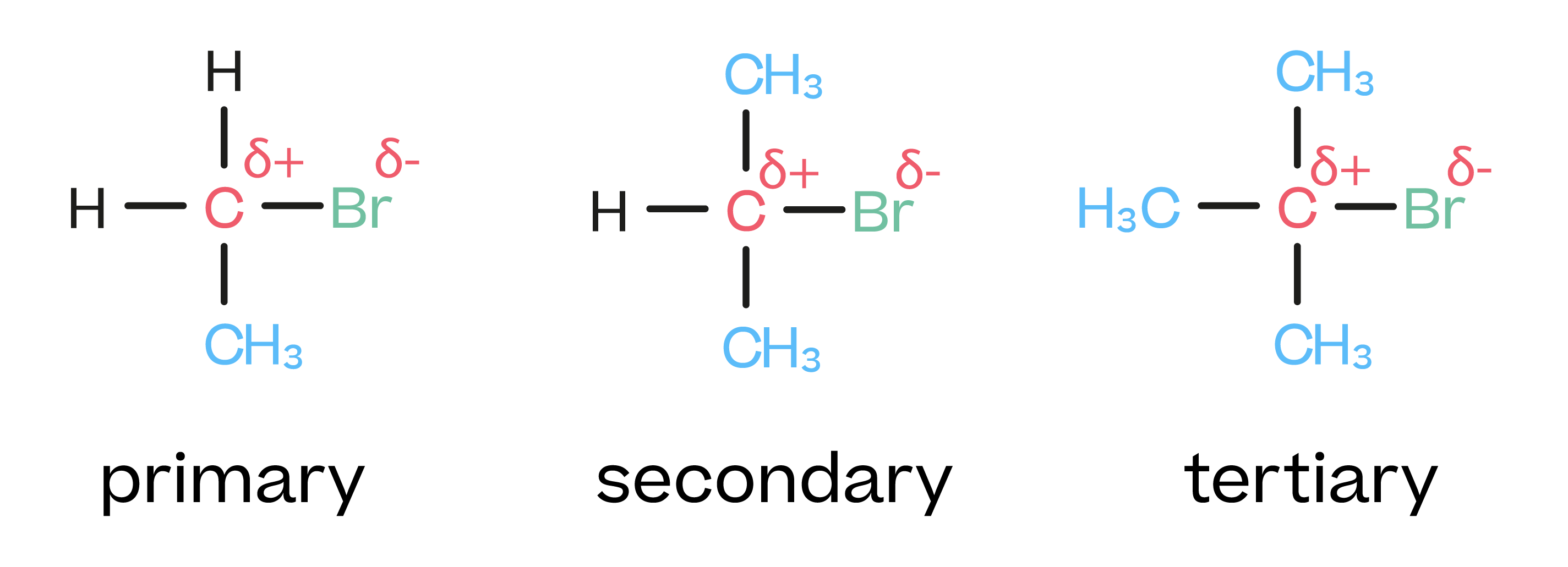
which type of haloalkane is most likely to carry out nuc sub?
primary
what is a primary haloalkane?
a haloalkane w/ 1 C atom bonded directly to the C atom which is bonded to the halogen