Cognition and intelligence
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Set and information processing
we have a limited capacity to store and process info
keeping track of more than one or two quantities results in overload
we attend selectively to all input
Cognition
mental processes involved in thinking, knowing, perceiving, learning, and remembering, also the contents of these processes
Intelligence
the mental capacity to aquire knowledge, reason, and solve problems effectively
Good problem solvers are skilled at:
identifying the problem, selecting a strategy to solve it, working backwards (retracing steps), searching for analogies (comparing problem with something you already know), and breaking a big problem into smaller ones (chunking)
Standford-Binet Intelligence Scale: Lewis Terman of Stanford University
1st large scale of physiological testing during WW1; high score = more responsibilities, low score = errand runners/cooks
based on Binet’s formula
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS - V) & Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children - Fifth Edition (WISC - V)
verbal scale: vocab, writing, reading comprehension
performance scale: block designs, how long it take to get out a maze
For an IQ test to count, who does the test have to be given by?
Psychologist or doctoral students (physiologists in training)
How do you calculate IQ?
Mental age (test age) / chronological age (actual age when test was took) X 100
What is the average IQ score?
100
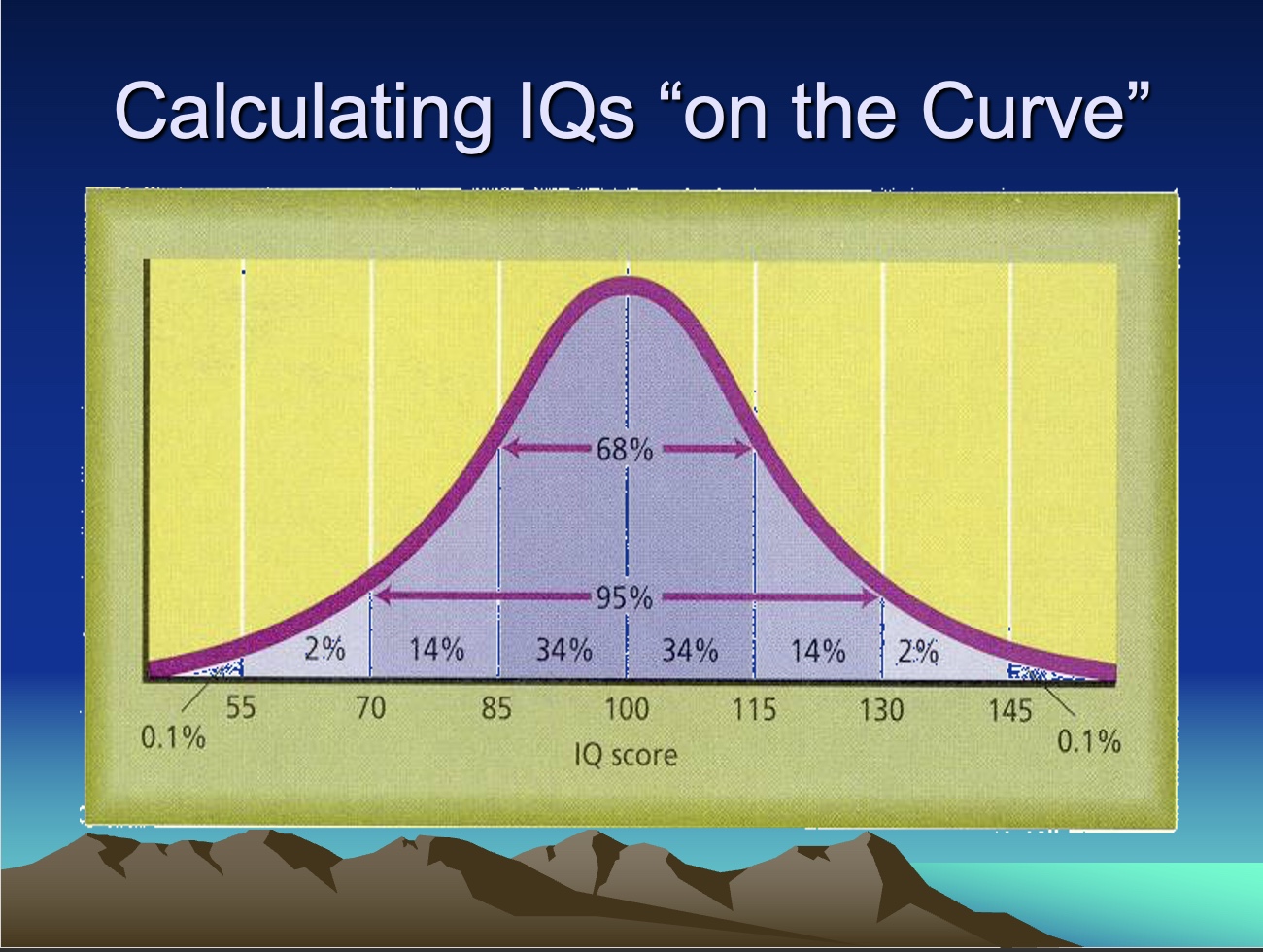
Normal Distribution & Normal Range
bell-shaped curve describing the spread of a characteristic throughout a population
scores falling in approximately the middle 2/3 of a normal distribution
What else is based on the bell-shaped curve?
Life (ex: middle class, upper class, etc")
When are IQ increases typically seen?
ages 4-9, maybe 9-14; cannot work to improve IQ
Mental deficiency
often conceived as representing the lower 2% of IQ range
Giftedness
often conceived as representing the upper 2% of IQ range
Robert Sternberg’s components of intelligence
Practical, Analytical, Creative
Practical intelligence
ability to cope with the environment (street smarts: daddy in Jamaica and New York)
Analytical intelligence
ability to analyze problems and find correct answers; measured by most IQ tests (book smart: what Jade calls me)
Creative intelligence
helps people see new relationships among concepts, involves insight and creativity; anticipation needs of others before its there (ex: uber, youtube)
Howard Gardner’s 8 Intelligences
Linguistic, Logical-Mathematical, Spatial, Musical, Bodiliy-Kinesthetic, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal, Naturalist
Linguistic
often measured on IQ tests with reading comprehension and vocab tests (may be skilled at vocab use or picking up languages)
Logical-Mathematical
often measured on IQ tests with analogies, math problems, and logical problems
Spatial
ability to form mental images of objects and think about their relationships in space (spatial: depth and perception and how objects fit in relation to space; visual: some learn best by visualizing things)
Musical
ability to perceive and create patterns of rhythms and pitches (musical instrument players, preference to learn rhytmatically)
Bodily-Kinesthetic
ability for controlled movement and coordination (athletes, some prefer learning hands on)
Interpersonal
ability to understand other peoples emotions, motives, and actions (social skills)
Intrapersonal
ability to know oneself and develop a sense of identity (understanding strengths and weaknesses, looking at high meaning of life as it relates to you; not letting outside opinions influence you)
Naturalist
ability to know and interact among diverse species (can survive in wilderness; others more inclined to the outdoors or get energy from it)
Cultural Definitions of Intelligence
someone born in pacific islands would place more significance in ability to navigate boat or SAT?
ability to navigate a boat
West Africa’s definition
intelligence viewed as having good social skills and memory
Native American culture’s definition
intelligence involves wisdom and respect for others
Gardner’s argument
intelligence has different meanings in different cultures thats suitable to that persons environment and what they’ve chosen to do for a living (skill set)
Hereditarian (nature) argument
intelligence is substantially influenced by biology and genetics (you inherit that genetic predisposition)
Environmental argument
intelligence can be dramatically shaped by influences such as health (good quality health and access), economics (money, resources that allow you to have health access and education), and education
What is the ratio of intelligence based on genetics and environment?
60% based on genetics and 40% based on environmental factors
Heritability and Group Differences example
historically white ppl score 10-15 points higher than black and hispanic people on standardized tests; taken with a grain of salt because of environmental factors: not everyone had the same access to resources, healthcare, education, etc
Racial and class differences based on:
health, economics, and education
What circumstance can cause someone to not be gifted anymore?
head injury/trauma
Geographical bias in IQ test example:
What piece of equipment used to shovel show? someone born in southern states wouldn’t know
Age bias in IQ test example:
If you were lost while driving, what would you use? Younger kids would say GPS, but answer is map