Lec 19 Plant Physiology
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Tissue Systems in Plants
Dermal tissue (epidermis)
Vascular tissue
Ground tissue
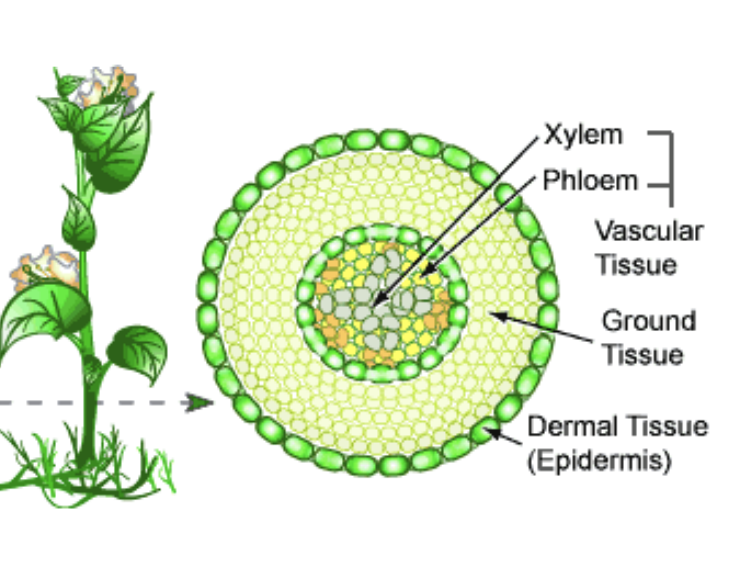
Dermal Tissue (epidermis)
Single layer of tightly packed epidermis forming the outer layer of the plant roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, seeds
Protects the plant from injury/water loss
No chloroplasts
Vascular Tissue
Transport system for water and nutrients in the leaves, stems, roots, fruits
Ground Tissue
Photosynthetic tissue (not dermal or vascular), found in all plant organs
Important for plant growth, healing after injury, produce and store food
Provides structural support
Shoots
above-ground parts of a plant
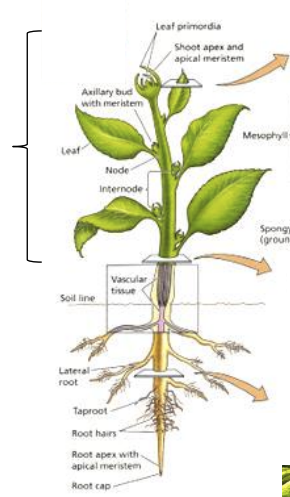
Cuticle/Stomata/mesophyll/Bundle Sheath Parenchyma
Components of the shoots: _____, _____, _____, and _____
Cuticle
waxy layer secreted by the epidermal cells of leaf, decreases water permeability
Stomata
pores in leaf surrounded by two guard cells, regulates gas and water exchange with air
two guard cells
Stomata are surrounding by _________
Mesophyll
tissue between epidermal layers of leaf containing two types of cells
Pallisade parenchyma/Spongy mesophyll
The cell types in the mesophyll: _____ and ______
Pallisade parenchyma
Type of cell in the mesophyll that contains lots of chloroplasts, columnar and tightly packed→ primarily photosynthetic
Spongy mesophyll
Type of cell in the mesophyll that is irregularly shaped, lots of space between cells with high humidity→ primarily involved in gas exchange
Bundle Sheath Parenchyma
Conduit between mesophyll and vasculature
Stem
bridge between the roots and leaves
Structural and transport role
Tissue layers: epidermis → cortex → pith
Epidermis/cortex/pith
Tissue layers of the stem in outermost to innermost order?
Stoma
Term for mouth in plant context
xylem/phloem
Vascular tissue consists of _____ and _____, which occur together and transverse all plant tissues
Xylem
Types of vascular tissue involved in transport of mainly water and dissolved ions from the root to the shoot
Phloem
Type of vascular tissue involved in transport metabolites (primarily sugars, amino acids, ions) from the “source” of production (i.e. photosynthetic cells in leaves) to “sinks” (developing roots, leaves, fruits, seeds)
anchors
The root _____ the plant to the ground
water/nutrients/soil
The root absorbs _____ and ______ (mineral and metal elements) from the _____.
food/sugars
The root stores ____ and ____
Roots
Underground portion of the plant
epidermis/cortex/pericycle/endodermis
Tissue layers of root from outermost to innermost
Lateral Roots
Secondary root system that arise from the pericycle
Root Hairs
long tubular outgrowths of the root epidermal cells that increase surface area for absorption
Root cap
mass of cells covering the sensitive root tip
Protection of root meristem, gravitropism, regularly replaced
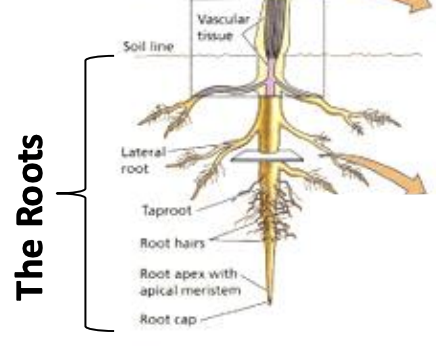
Apical meristem
specialized region at the tip of a plant's root, responsible for continuous growth and development of the root system
Undifferentiated cells
gravitropism
plant's growth response to gravity, causing roots to grow downward and shoots to grow upward
cuticle
The roots have no ______ unlike the stem and shoots
Vascular cambium
undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into vascular tissue
Stem cells in plants
Apical meristem
Vascular cambium
cell wall/middle lamella/chloroplast/vacuole/tonoplast
Structures only found in plant cells: ______, _____, _____, _____, and ______
Middle lamella
layer in plant cell walls that acts as a "cement" to hold adjacent cells together
Cellulose microfibril/rigidity
Plant cells can form ________ in the cell wall similar to human myofibrils, which creates _____ in the cell wall
Pectin
Soluble dietary fiber found in the cell walls of plants, particularly in fruits and vegetables
Aquaporins
family of channel proteins, also known as water channels, that facilitate the movement of water across cell membranes (facilitated diffusion)
Plasmodesmata
Channels passing through the cells walls that connect the cytoplasm of one plant cell to the cytoplasm of the neighboring plant cells that allows for communication and controlled exchange of substances between cells
Desmotubule
continuous tube connecting the smooth ER of one cell to that of the other
gap junctions/simple/larger/substrate/PD
Plasmodesmata are:
Similar to _______ in animal cells
Small molecules (sugars, amino acids) and ions can move by _____ diffusion
____ molecules overcome the size exclusion limit by modifying the ________ so it can move through the PD or induce transient changes of the ___ to allow the molecule through.
diameter/callose
For plasmodesmata, the ______ of opening can be reduced / increased via the deposit of the plant polysaccharide, _____, to change movement
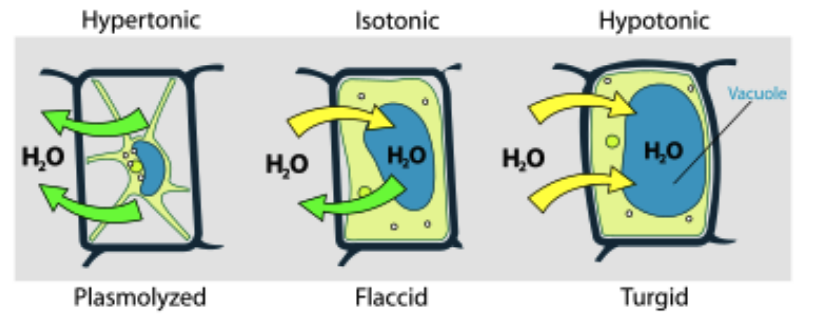
Functions of the Vacuole
Storage
Helps keep the chloroplasts exposed to light
Maintain structural integrity of the cell and plant by turgor pressure against the cell wall.
cytoplasm
Water, nutrients and other molecules are transported in and out of vacuole for storage when not needed in the ________.
chloroplasts/membrane
The vacuole elps keep the ________ exposed to light by pushing all of the contents of the cell cytoplasm up against the cell ______.
tonoplast
membrane of the vacuole
K+ pumps/aquaporin/turgor pressure
Transporters (ie. _______) in the tonoplast (membrane of the vacuole) move ions in and out of the vacuole. If ions are pumped in, this draws water into the vacuole (through _______ water channels), causing the vacuole to swell and exert more pressure against the cell wall (______) – this is essential in supporting plants in an upright position.
photons/ATP
Light-dependent reactions (_____ -> ____)
sugar
Light-independent reactions (____ synthesis)
photopigment
molecule that undergoes a chemical change when it absorbs light
Chlorophyll
main photopigment in green plants. It absorbs light at wavelengths around blue (430 nm) and red (660 nm), so green (550 nm) wavelengths are reflected.
Carotenoids
Pigment in plants that absorb light at wavelengths at 400-500 nm (blue/bluegreen), giving them an orange color (carrots). Are in thylakoid membranes. Transfer energy to chlorophyll.
yellow/orange/always/decrease
Carotenoids look ______ and _____. They are ______ present in leaves; Visible when chlorophyll levels ______
Anthocyanins
Pigment that’s Red and Purple
Produced in leaf during Fall
Protect against photo-inhibitory effects of excess photons that would have been absorbed by chlorophyll
photo-inhibitory
Anthocyanins protect against _______ effects of excess photons that would’ve been absorbed by chlorophyll
Photosystem II
In the Electron and Proton Transfer in the Thylakoid Membranes of Plants, step 1 involves ______
Photosystem II
transmembrane protein complex made up of many different proteins and pigment compounds
Chlorophyll/electrons/plastoquinone
________ molecules in PSII absorb energy from light. The transfer of energy among molecules in the complex excites _______, which are donated to _________.
two/two H+/stroma
Plastoquinone picks up ____ electrons from PSII and ______ ions from the _____ and then moves through the membrane to bring electrons to the next complex.
H2O/atmosphere/lumen
The electrons that are transferred by plastquinone are replaced by splitting two _____ into O2 , H+ ions. O2 is released to the _____, H+ ions are released into the ______, generates H+ gradient across the thylakoid membrane
Cytochrome b6f
In the Electron and Proton Transfer in the Thylakoid Membranes of Plants, step 2 involves ______
Cytochrome b6f
large, multi-subunit protein complex embedded in thylakoid membrane.
cytochrome b6f
Plastoquinone transfers the two electrons it picked up from PSII to _______ and the two H+ ions are released into the lumen.
protons/electrons
Cytochrome b6f complex actively translocates _______ from the stroma into the lumen as ______ flow through it.
plastocyanin/PSI
Cytochrome b6f transfers the electrons to ________ (small peripheral membrane protein), which carries them to ___
Photosystem I
In the Electron and Proton Transfer in the Thylakoid Membranes of Plants, step 3 involves ______
Plastocyanin
________ delivers the electrons to Photosystem I
NADP/NADPH
Chlorophyll molecules from PSI absorb energy from light allowing for the donation of two electrons and the addition of H+ to _____ to produce _______
stroma/gradient
To form NADPH, H+ ions are taken from the ______, which contributes to the H+ _______ across membrane
ATP synthase
In the Electron and Proton Transfer in the Thylakoid Membranes of Plants, step 4 involves ______
stroma
The energy generated by movement of H+ ions from inside the thylakoid lumen to the stroma is harvested to combine ADP and P to make ATP. The NADPH and ATP both end up in the ________
H+ gradient/ATP synthase
In both ETCs (chloroplasts vs mitochondria), electron flow is coupled to the generation of a _______, which is used by _______ to generate ATP
thylakoid membranes/ATP/NADPH
Light-dependent reactions occur in the _______ producing ___ and _______
stroma/CO2/H2O
Light-independent reactions occur in the _______. Uses ATP and NADPH from light-driven reaction as well as ___ and ___ to produce carbohydrates (glucose)
synthesis/breakdown
In plants, sucrose is made both during the day (______) and night (_______ of stored starches)
Sucrose
disaccharide formed of glucose and fructose
Maltose
disaccharide formed of two glucose
Triose phosphates
3 carbon molecules that can be combined to form 6 carbon sugars
Hexose
General term for a 6 carbon sugar (e.g. fructose & glucose)
triose phosphates/hexose phosphates
When producing sucrose during the day, ________ are converted to ________, which then make sucrose
starch/maltose/glucose/hexose phosphates
When producing sucrose during the night, ______ is broken down to _____ and _____. Then ______ are made, which can then be turned into sucrose.
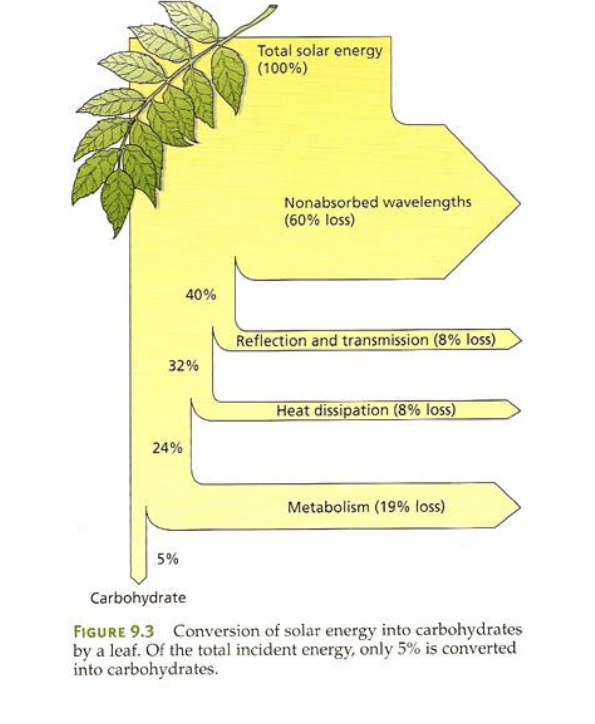
small/solar
Only _____ amount of _____ energy is converted to carbohydrates
upwards/vascular/xylem
Water and minerals move ______ in plant through ______ tissue called _______
hydrostatic pressure/surface tension/evaporation
The movement of water up a plant is due to ________, _______, and ________, and may be up a “column” several hundred feet tall
Water is pulled from the xylem into the cells walls of the mesophyll, where is evaporates into the air spaces within the leaf. Water evaporates then diffuses through the leaf air space, through the stomata.
xylem/mesophyll/air spaces/diffuses/stomata
Water is pulled up from the plant's roots through the _____ vessels.
Once in the leaf, water moves into the _______ cells where it evaporates into the _______ within the leaf and ______ through the leaf's internal air spaces, eventually leaving through the _______
stomata/cuticle
95% Water Loss: The majority (95%) of water loss occurs through the _____, which are tiny pores found on the lower epidermis of the leaf.
The _______, which covers the leaf's surface, serves as a barrier against water loss. However, only about 5% of total water loss happens through the ______
Guard Cells: The stomata are controlled by guard cells, which regulate their opening and closing, thereby controlling water loss and gas exchange (CO₂ in, water vapor out).
negative hydrostatic pressure/evaporation/surface tension
due to ________ (negative tension) from _______ occurring in the leaves, water is drawn upwards by ________.
Guard cells features
Thicker Cell Walls: The cell walls of guard cells are thicker near the stomatal pore. This thickness makes the area inflexible, affecting how the guard cells swell and change shape.
Inelastic Fibers: Bands of inelastic fibers run around the guard cells, which also influence how the cells deform.
Thicker cell walls/inelastic fibers
____ and _____ determine how guard cells will change shape when they swell
water/away/pore/guard cells/buckle
When _______ is taken up by the guard cells, they expand. However, the expansion is limited to the sides of the cells _____ from the _____ (due to the thick walls and fibers).
This limited expansion causes the _______ to _______ and open the pore between them, allowing gas exchange (such as CO₂ in and water vapor out) and water loss through transpiration.
morning/afternoon/K+/sucrose
Stomata are open in _______ and _______: pump ___ and ______ into guard cells, this causes water to enter, cells swell and buckle, pore opens. Cells shrink and stomata are closed at night.
Endodermal
In the root, the _______ layer contains the Casparian strip
Casparian strip
A band of radial cell wall that is impregnated with a wax-like hydrophobic substance called SUBERIN
apoplast/transmembrane
The casparian strip prevents water movement through the _______ pathway and forces water across the cell membranes (___________ pathway)
SYMPLAST Pathway
a network of cell cytoplasm connected by plasmodesmata
APOPLAST pathway
a system of cell walls and intercellular spaces: it is the predominant pathway
TRANSMEMBRANE pathway
move across cell membranes
open
Under normal conditions, aquaporin channels are ____
close/serines
During drought, aquaporin channels ____ when ______ dephosphorylated