17 Carbonates
Calcium Oxide and Calcium Carbonate

Limestone consists mainly of calcium carbonate, CaCO3
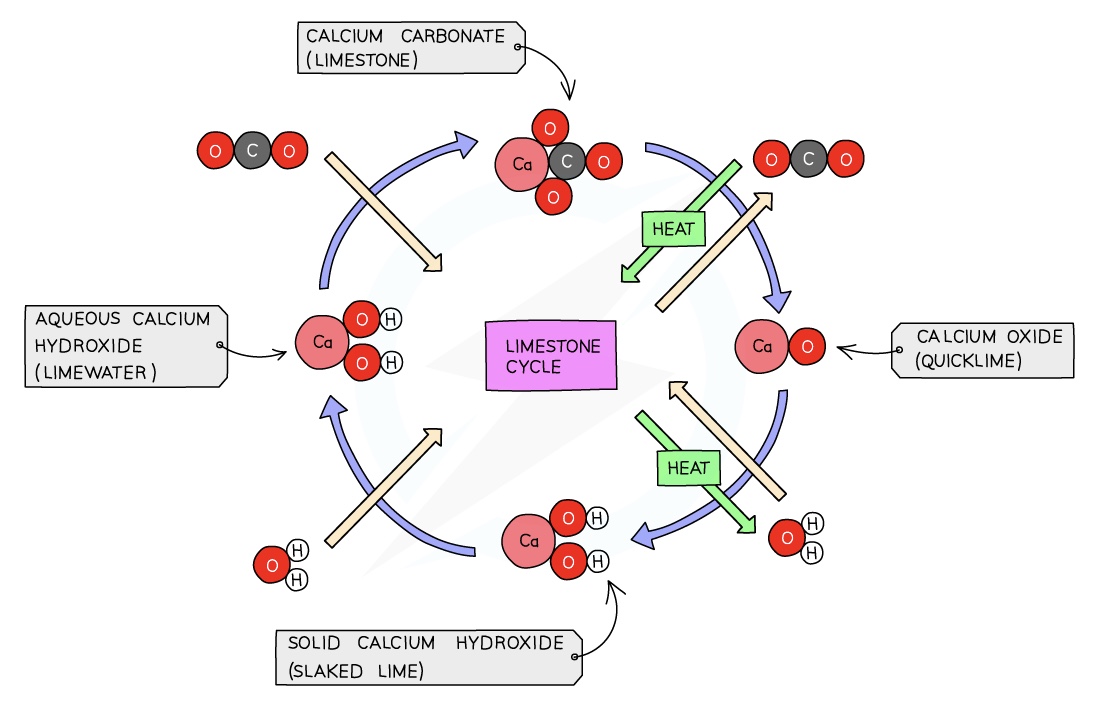
Lime which is calcium oxide, CaO, is manufactured from calcium carbonate by thermal decomposition:
- CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Slaked lime, calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, is made by adding a small amount of water slowly to calcium oxide:
- CaO+ H2O → Ca(OH)2
The water is added slowly because the reaction is quite exothermic
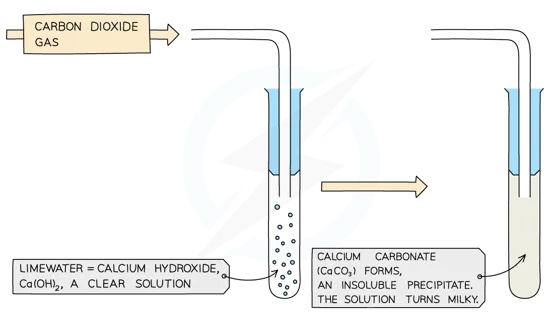
Limewater is a solution of calcium hydroxide in water, hence it is weakly alkaline
Bubbling carbon dioxide through limewater produces a cloudy white precipitate of calcium carbonate, so the sequence of reactions has gone in a complete cycle, returning to the starting material:
- CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H20
This reaction is the basis of the standard chemical test for CO2
The combination of these three reactions constitute the limestone cycle
Use of limestone and limestone products
Limestone (calcium carbonate) is used in the manufacture of iron and cement
In the production of iron, limestone is added to the blast furnace where it decomposes to form lime (CaO) and carbon dioxide
The CO2 produced is reduced to carbon monoxide, CO, by coke (almost pure carbon) where it acts as a reducing agent transforming iron ore into iron:
CO2 + C → 2CO
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
The lime reacts with silica impurities in the iron ore to form calcium silicate, which floats to the top of the molten iron as slag and is removed:
- CaO + SiO2 CaSiO3
Cement is manufactured by heating a mixture of powdered limestone and clay in a rotary kiln
Once heated, calcium sulfate and water are added which produce cement
Cement is a hardened, interlocked structure of calcium aluminate (Ca(AlO2)2 and calcium silicate (CaSiO3)
@@CaCO3 is also used in treating excess acidity in@@ soils and lakes where it is often preferred to lime because it does not make the water excessively alkaline
@@Lime (calcium oxide) is used in lime mortar, the material used to bind bricks together, and in flue-gas desulphurisation@@
Flue-gas desulphurisation involves spraying jets of slaked lime slurry into acidic sulfur dioxide emissions to reduce pollution by neutralising these gases before they leave the factory chimneys
Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) is used in treating acidic soils and neutralising acidic industrial wasted products

\n \n