Micro loose ends
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
What are the types of market failure?
Every Monday dogs play catch in muddy fields
Externalities
Merit goods
Demerit goods
Public goods
Common access resources
Income inequality
Monopoly power
Factor immobility
What is a merit good?
Good deemed more beneficial than consumers realise MSB>MPB
What are examples of merit goods?
Hospitals, education, exercise
What type of failure is with merit goods?
Information failure, asymmetric information
This can cause irrational decisions
What is adverse selection?
When one party has greater knowledge than another party e.g car seller
What is moral hazard?
People take greater risks when they are insured, behaviour change after transaction
What’s a demerit good?
Goods that are more harmful than consumer realise. MPB>MSB
What are examples of demerit goods and why do they fail?
Cigarettes, alcohol, gambling
Fail due to information failure and asymmetric information
What are features of public good?
Non-excludable (no efficient way to price) and non-rivalry (quantity doesn’t diminish upon consumption)
What are examples of public goods?
Flood defences, road signs, street lights, roads and beaches
What is the free rider problem?
People wait for others to contribute to public goods then benefit without paying, leads to complete market failure of missing market
What is a quasi public good?
A public good which can be excludable and/or rivalrous such as roads and beaches
What are common access resources?
Resource with no private ownership that has been established
What do common access resources lead to?
The tragedy of the commons such as for seafood, people will deplete the good especially firms to make money which will lead to the good no longer existing. Negative externality of production from their self interest
What is government failure?
When the costs of intervention outweigh the benefits of intervention , worsens resource allocation and harms social welfare
What are the 4 types of government failure?
Information failure - Valuing externalities
Regulatory capture - when regulating monopoly power, CEOs influence regulators
Admin and enforcement cots are very high - Regulation, subsidies, state provision and price controls
Unintended consequences - Black markets, impact on poor, impact on firms, employment
How does an indirect tax work on NE of production?
Increase costs of production, internalises externalities as polluter pays, solves overconsumption, promotes allocative efficiency
MPC + Tax = MSC
How does indirect tax fix NE in consumption?
same as production but curve shifts MSC=MPC upwards which lowers quantity and increases price, at society optimal level
Where does indirect tax not work?
Price inelastic demand
Setting tax at the wrong level
Regressive
Black markets
What does the government subsidise?
Merit goods or goods with positive externalities
What does subsidising merit goods do to its externality curve?
Shifts MPC outwards, for production it shifts MPC equal to MSC
What are the drawbacks of subsidy?
Costs
Setting it at the right level
Will firms use it correctly
Price inelastic demand
What is regulation?
Non-market approach to solve market failure, law that must be followed by economic agent to encourage change in behaivour
What are drawbacks of regulation which lead to market failure?
Cost
Setting the right regulation
Black markets and unintended consequences
Equity
What are the stages of tradable pollution permits?
Set a cap, permits issued to match cap, firms make decisions based on least cost, enforcement. Lower pollution to social optimum, allocative efficiency
What decisions will firms make to reach pollution cap?
Invest in green technology
Buy spare permits
What are long run incentives of tradable pollution permits?
Investing in green tech:
Increases profit and they are not burdened when permits price rise
What are drawbacks of tradable pollution permits?
Enforcement
Imperfect information for government
Unintended consequences
Need for international cooperation
How does state provision solve market failure?
Government provide these merit goods as firms will not due to profit motive, they solve equity issues
What is the issue with government providing merit (public goods)?
There is excess demand and it is very difficult to solve
Cost
Imperfect information
Inefficiency of state organisations
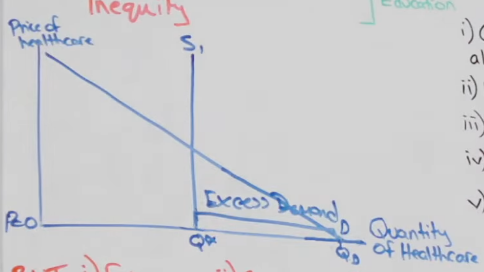
How do property rights work?
There is incentive to not exploit common access resources, negative externalities are internalised so if enforced Q is reduced to socially optimum level
What are the drawbacks of property rights?
Can they be distributed efficiently
Enforcement is needed which has a cost
Equity - Who gets the rights?
What is productive efficiency?
Minimum of AC at any quantity
What is X efficiency?
When a firm is operating on the average cost curve at any given quantity
What is dynamic efficiency?
When long run SN profit is reinvested
What is the shutdown condition
AR=AVC
What is a market economy?
Markets are allowed to be free
What is a command economy?
Things like socialism
What are the benefits of the free market?
EPIC
Allocative efficiency
Competition
Dynamic efficiency so investment
Job creation and economic growth
Freedom, liberty and choice
No risk of government failure
What are the drawbacks of the free market?
Markets can fail
Inequity
Excessive profiteering
Creative destruction
Price volatility
What are advantages of specialisation?
Higher output
Wider range of goods/services
Greater allocative efficiency
Higher productivity through better use of workers
Quality improvements
What are disadvantages of specialisation?
Finite resources
Changes in fashion/tastes
De-industrialisation
National interdependence
What are advantages of division of labour?
Workers highly productive
Specialist capital for workers
Lower prices, higher quantity/choice and quality
What are disadvantages of division of labour?
Worker demotivation
High worker turnover
Risk of long term unemployment
Highly standardised goods/services
Which part of the demand curve is elastic?
The first half and the second is inelastic
What are returns to scale?
Positive %output>%input
Negative %output<%input
Constant %output=%input
What is the minimum efficient scale?
The lowest level of output required to fully exploit all EoS
What are the types of internal EoS?
Risk bearing
Managerial
Financial
Purchasing
Technical
Marketing
What are types of external EoS?
Better transport infrastructure
Component suppliers move closer
R&D firms move closer
What are types of DEoS?
Communication
Coordination
Control
Motivation
PC conditions?
Many buyers/sellers, Homogeneous goods, Perfect information, Price takers, No barriers to entry/exit
When is total revenue maximised?
MR=0 as it cannot rise anymore
What are explicit and implicit costs?
Explicit are physical costs like TFC and TVC
Implicit is opportunity cost
Why are firms profit maximising?
Reinvestment
Dividends for shareholders
Lower costs and prices for consumers
Reward for entrepreneurship
What are drawbacks of profit maximising?
Knowledge of MC and MR needed
Greater scrutiny from regulators
Key stakeholders harmed
Other objectives are more appropriate
What is profit satisficing?
Sacrificing profit to satisfy as many key stakeholders as possible
Why do firms revenue max?
EoS
Predatory pricing (undercut and drive competitors out)
Principle agent problems (Persuade shareholders with benefits)
When do firms sales max?
AC=AR
Why do firms sales max?
EoS
Limit pricing, takes incentive of profit from new firms
Principle agent problem
Flood the market
What is the principal agent problem?
When there is a divorce between ownership and control
What are some other examples of firm objectives?
Survival
Public sector organisations (P=MC which is allocatively efficient)
Corporate social responsibility
Where on a graph does profit satisficing occur?
Anywhere between profit and sales max along AR curve
What are the 4 main barriers to entry?
Legal - Patents, licenses, red tape, standards, insurance
Technical - Start up costs, sunk costs, EoS, natural monopoly
Strategic - Predatory pricing, limit pricing, heavy advertising
Brand loyalty
What are 4 barriers to exit?
Undervalued assets
Redundancy costs
Penalties for leaving contracts early
Sunk costs
What is society surplus and when is it maximised?
Producer + Consumer surplus
Maximised at allocative efficiency MC=AR
What is productive efficiency?
Lowest point of LRAC curve, fully exploiting EoS
What is X-efficiency?
Minimising waste and producing on AC curve
What is dynamic efficiency?
When LR supernormal profit is re-invested
What is static vs dynamic efficiency?
Static - allocative, productive and x. Occur at one production point
Dynamic - happens over time
What does allocative efficiency do to consumers?
Resources follow demand of consumers
Low prices
Maximisation of consumer surplus
High choice and quality
What does allocative efficiency do to producers?
Retain or increase market share
Stay ahead of rivals
Increase profit
What does productive efficiency do to consumers?
Lower prices
High consumer surplus
Full exploitation of EoS
What does productive efficiency do to producers?
More production at lower AC
Higher profit
Lower prices = Greater market share
What does dynamic efficiency do to consumers?
New innovation
Lower prices over time
High consumer surplus
What does dynamic efficiency do to producers?
LR profit max
Lower costs over time
Retain/increase market share
Stay ahead of rivals
What does x-efficiency do to consumers?
Low prices, high consumer surplus
What does x-efficiency do to producers?
Lower costs, higher profits
Increase market share
What is the shutdown condition?
When PC firms should consider a shut down AR=AVC
What is the breakeven condition?
Normal profit AR=AC
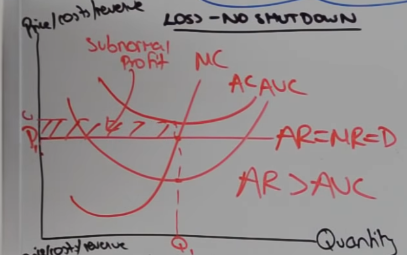
Why do PC firms stay with a subnormal profit like the diagram?
AR is covering AVC so they can hope firms leave the industry due to higher costs and then can convert their subnormal into normal profit
Features of monopoly?
One seller dominating market >25% or pure 100%
Differentiated products
High barrier to entry and exit
Imperfect information
Firm is profit maximising
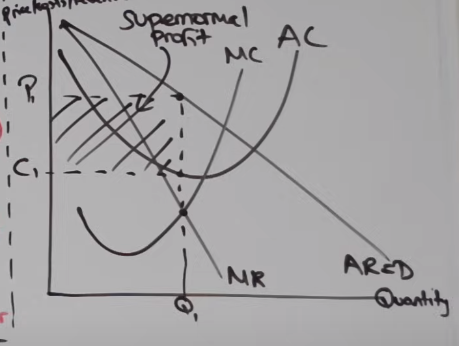
What is the efficiency of this monopoly?
Dynamic efficiency as they will reinvest LR profit
What is welfare loss?
A loss in society surplus due to inefficient allocation of resources
Why are monopolies bad for society surplus?
They lower society surplus in the economy leaving a DWL
What is price discrimination?
Setting different prices to different consumers for an identical good/service
What conditions are needed for price discrimination?
Price making ability
Information to separate the market (such as elasticity)
Prevent re-sale (Market seepage)
What is 1st degree price discrimination?
Charging consumers what they are willing and able to pay to achieve monopoly profit so no consumer surplus
What is 2nd degree price discrimination?
Lowering last minute pricing to get away all excess supply e.g airlines . There is a gain in CS
What is 3rd degree price discrimination?
Separating consumers into different PEDs e.g train tickets more expensive for daily travellers than leisurely travellers
What are pros and cons of price discrimination?
Dynamic efficiency, EoS, Some consumers benefit, Cross subsidation
Allocative inefficiency, inequalities, anti-competitive pricing
What characteristics does a natural monopoly have?
Huge fixed costs
Enormous potential for EoS
Rational for 1 firm to supply entire market as competition is undesirable
Competition would result in wasteful duplication of resources and non exploitation of full EoS
What is good about natural monopoly?
Regulators make them produce at lower price to allocative efficiency level but government subsidise them so they are not in a loss
What are cons of monopoly?
Allocative, productive and x inefficiency
Inequalities in necessity markets
What are pros of monopoly?
Dynamic efficiency
Greater EoS
Natural monopoly
Cross subsidisation
What are pros of competitive markets?
Allocative, productive and X efficiency
Jobs
What are cons of competitive markets?
Lack of dynamic efficiency
Lack of EoS
Cost cutting in dangerous areas
Creative destruction
Features of MC?
Many buyers/sellers
Differentiated goods - Price makers and PED
Low barriers
Good information
Non-price competition
Firms are profit maximisers
Features of oligopoly?
Few firms
Differentiated goods - price makers
High barriers
Interdependence - Price rigidity
Non-price competition
Profit max not sole objective
How does the kinked demand curve work?
Shows interdependence, PED is initially elastic as firms will not raise price to obtain market share but becomes inelastic after a point as firms will also lower prices to increase their market share.
In vertical gap there is no need to change prices, rigidity
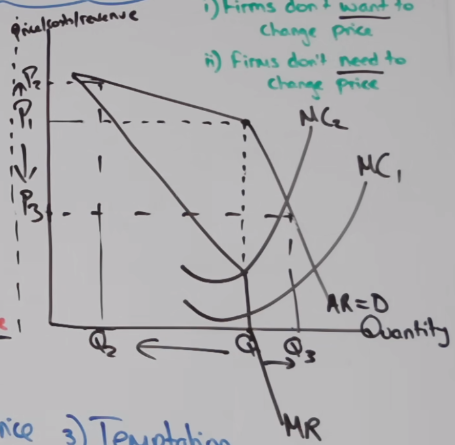
Facture that promote competitive oligopoly?
Large no of firms
New market entry possible
One firm with significant cost advantage
Homogeneous goods
Saturated market