A&P Exam #2
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
Skin and its appendages
hair, nails, sebaceous glands, sweat glands
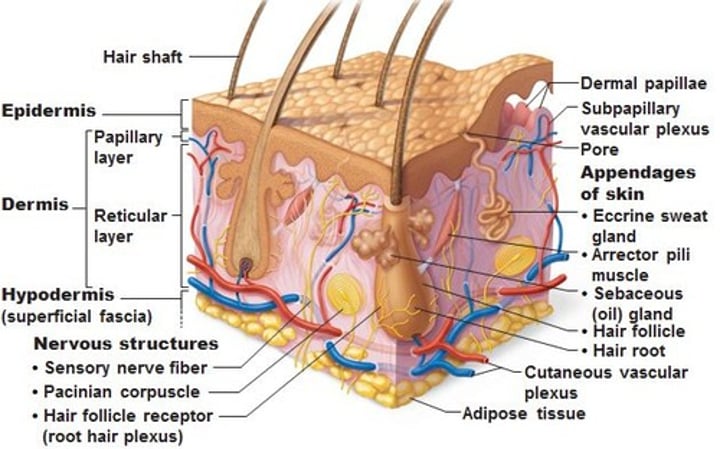
Intregumentary system (skin and its appendages)
Functions in protection, sensing the environment, excretion of salt and water (sweat gland), synthesis of Vitamin D (hormone), and thermoregulation
Cells playing role in skin protection
-Keratin cells (keratinocytes)
-Melanocytes
-Langerhans cells
Keratinocytes
-Keratin protein makes & supports the skin + skin repair, restoration of epidermis + Protection against UV light + help make skin water-proof barrier
Melanocytes
melanin absorbs harmful UVA, UVB, UVC & blue light. Protection against reactive oxygen species (ROS) byproducts of cell's processes.
Langerhans cells
-send immune T and B cells after sensing any kind of danger in the skin. (help activate immune system)
Skin receptors
-Merkel discs (touch/pressure),
-Meissner's corpuscles (tactile) ,
-Pacinian corpuscles (deep pressure),
-Ruffini endings (skin stretch),
-Krause bulb (cold), free nerve endings (tactile),
-thermoreceptors,
-nociceptors.
Skin Functions: Thermoregulation
Control of body temperature is affected by a number of playing factors:
-sweat glands,
-Vasculatures of the dermis
-Vasculatures of the hypodermis
Skin Functions: Excretion
- By secreting sweat through the sweat glands, the skin can regulate the total body volume of fluid and the amounts of certain waste products (uric acid, ammonia, urea).

Skin Functions: Hormone Production
-Production of vitamin D.
-When the skin is exposed to sun a chemical (7-dehydrocholesterol) which is normally found in the skin is converted into a substance called cholecalciferol.
-This chemical is then transported through blood to the liver and kidneys where it is converted into the active form of vitamin D.
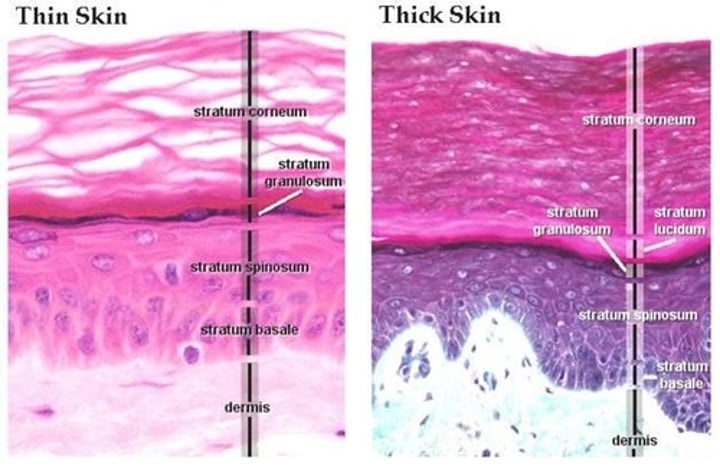
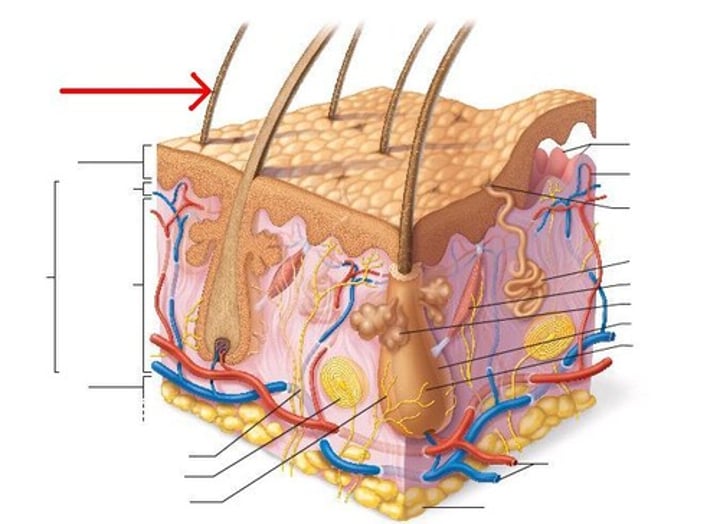
Skin Structures
-Epidermis: the superficial thin layer. Composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, consisting of four distinct cell types and four or five layers
-Dermis: the deep, thicker layer.
-Hypodermis: Composed mainly of adipose tissue (fat).
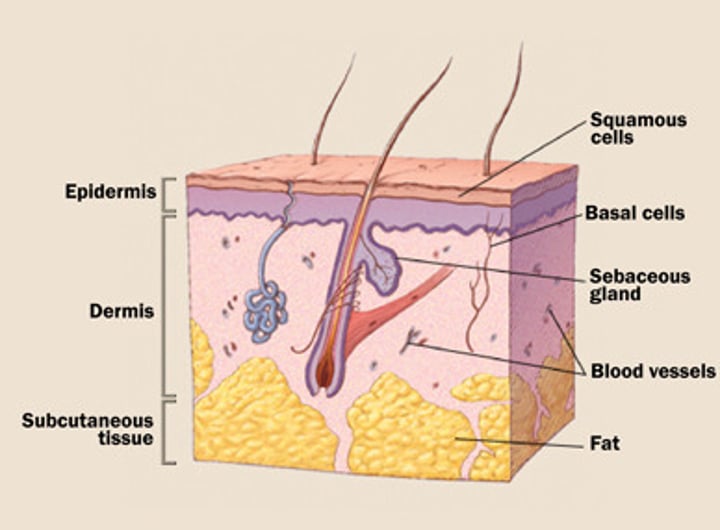
Epidermis: Cell types
1- Langerhans cells: deep cell layers of the epidermis, send B and T cell to kill invaders (e.g bacteria).
2- keratin cells: 90% of the epidermis. Together with the oil secreted by the sebaceous glands they form a water-proof barrier.
3- Melanocytes: 5% of the epidermis. Contribute color to skin. Protect the body from ultraviolet light.
4- Merkel cells - function as touch receptors in association with sensory nerve endings
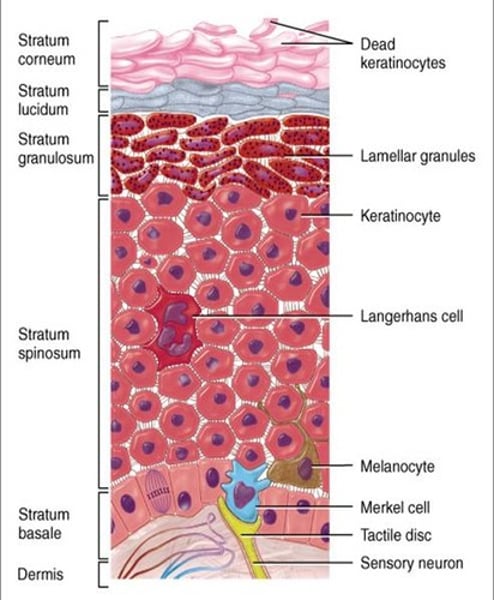
Epidermis: Cell layers
These layers are from the deepest to the most superficial:
1- stratum basale/germinativum (base layer): single layer.
2- stratum spinosum (spinous layer): multilayered. Keratin synthesis is initiated in this layer.
3- stratum granulosum (granular layer): multi-layered. Keratin formation continues in this layer.
4- stratum corneum (cornified layer): most superficial layer. Composed of dead cells.
-Fifth layer (stratum lucidum in thick skin) right below corneum.
thin vs thick skin
THICK SKIN:
-hairless, consists of a thick epidermis (w/ 5 strata)
-soles of feet, palms of hands, surface lining of fingers & toes
THIN SKIN:
-contains hair, its thickness varies based on the thickness of the dermis (epidermis has 4 strata).
-covers rest of body
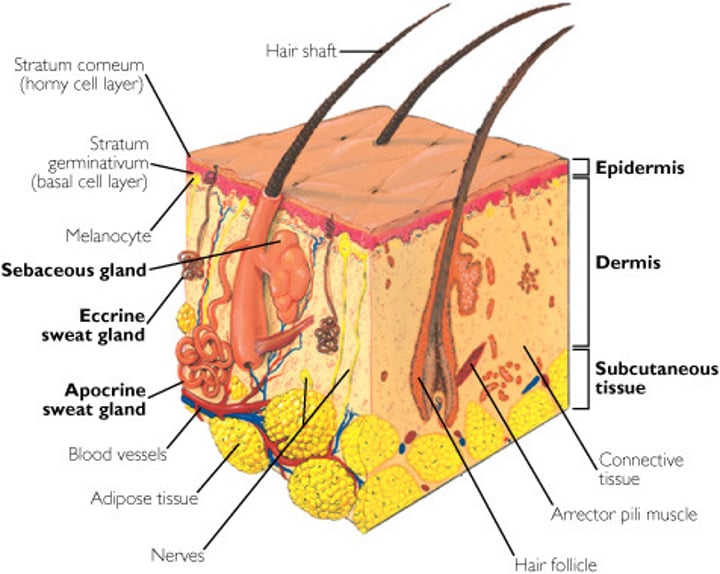
Dermis
-middle layer of skin
-called the true skin.
-Thicker than the epidermis
-Composed of thin papillary layer, and thicker reticular layer.
-Contains nerve endings which process sensory information such as pain, pressure, touch, and temperature.
-contains muscle fibers, hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and blood vessels.
Dermis: Papillary Layer
-Nourishes and supports epidermis
-Thin superficial layer of the dermis
-Forms bumps that project into the epidermis, these are called dermal papilla.
-Composed mainly of loose connective tissue
Dermis: Reticular Layer
-Thick layer of the dermis.
-Composed of dense connective tissue with collagenous fibers
-Contains glands, blood vessels, nerve endings, hair follicles, and the arrector pili muscle.
-Arrector pili muscle is a muscle attached to each hair follicle. When it contracts (from cold or freight) it pulls the hair into a perpendicular position.
Skin color
•Melanin - yellow to reddish-brown to black pigment, responsible for dark skin colors
(Freckles and pigmented moles - result from local accumulations of melanin)
•Carotene - yellow to orange pigment, most obvious in the palms and soles of the feet
•Hemoglobin - reddish pigment responsible for the pinkish hue of the skin
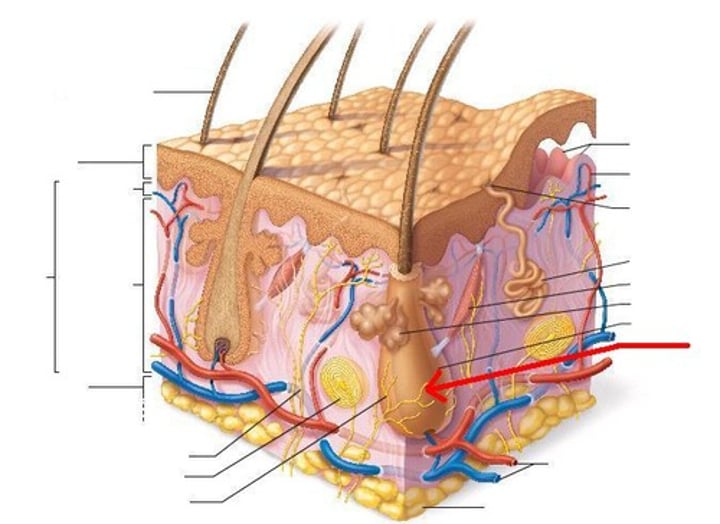
Appendages of the skin
Hair, nails, sweat glands, and oil glands
structure of hair
hair follicle, hair root, hair shaft
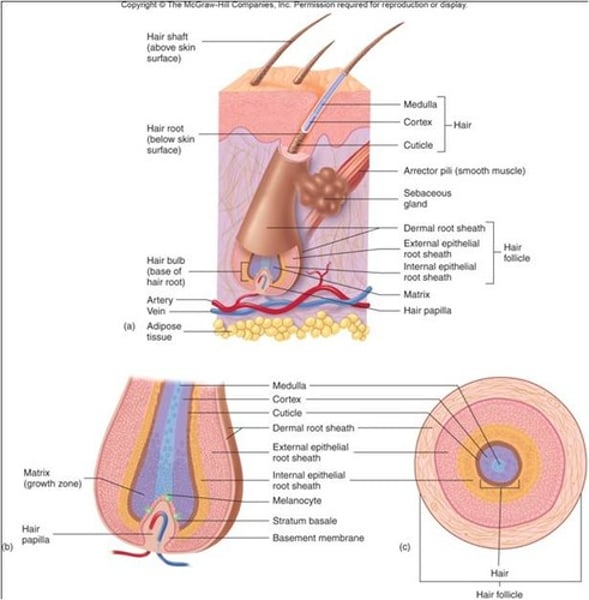
When does a hair start growing?
-when epidermal cells spread down into the dermis to form a tube called hair follicle.
What is the hair root part of?
hair that is hidden in the follicle
Hair shaft
-visible part of the hair. The part that projects out into the surface.
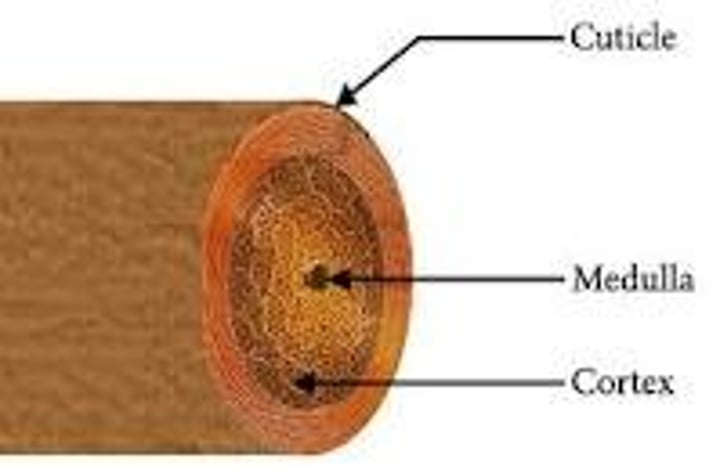
Hair Transparent Cuticle
covers the hair shaft like shingles on a roof, protecting it from the elements and chemicals, and from losing moisture.
hair cortex
-Middle, thickest portion of a hair shaft
-provides most of the hair's weight. It contains melanin (provides color to the hair, stores oils, provides flexibility and elasticity, adds shape to the hair.) -When the cuticle is damaged and exposes the cortex, hair looks dull and dry.
Medulla
a inner hollow core that runs the length of the shaft.
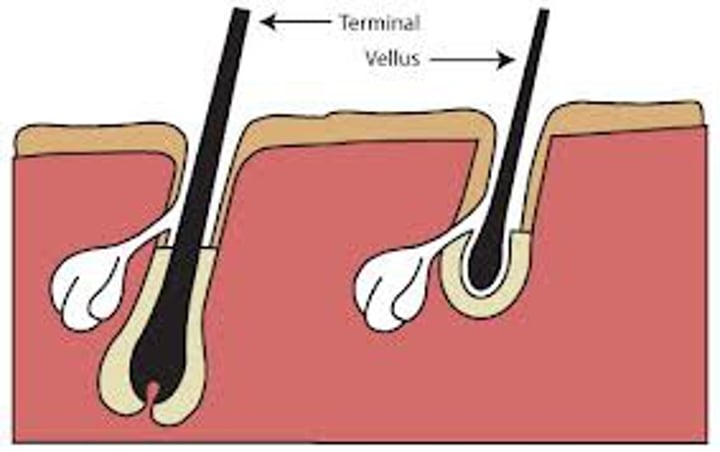
Types of hair
vellus and terminal
Vellus
pale, fine body hair of children and adult females
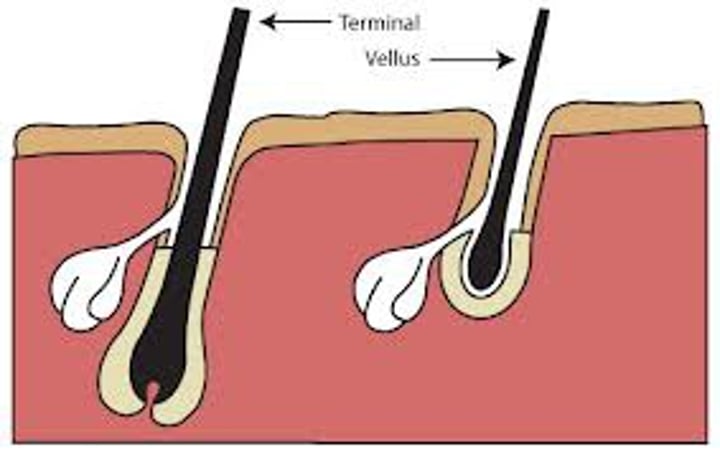
Terminal
coarse, long hair of eyebrows, scalp, axillary, and pubic regions
What are nails made up of?
heavily keratinized epidermal cells.
Parts of the nail
-Nail body: the visible part of the nail
-Nail root: the rest of the nail
-Cuticle: the skin border between nail body and root.
-Lunula: the part o nail body nearest the root. It is the crescent-shaped white area.
-Nail bed: it is the area below the nail. It contains blood vessels.
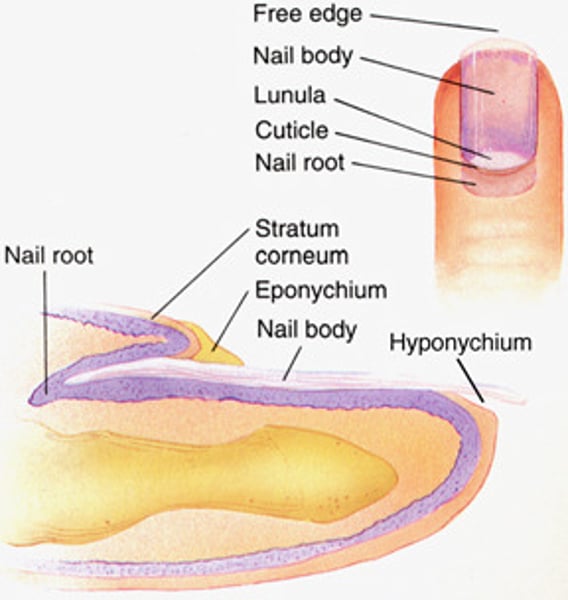
Continual growth of nails is due to...
-mitosis that takes place in the cells underneath the lunula.
- nails grow about 0.5 mm every week
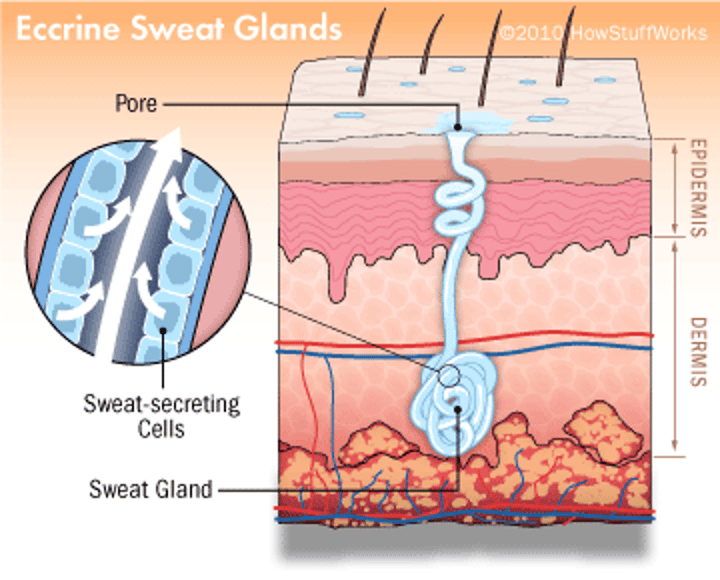
eccrine sweat glands
found in palms, soles of the feet, and forehead
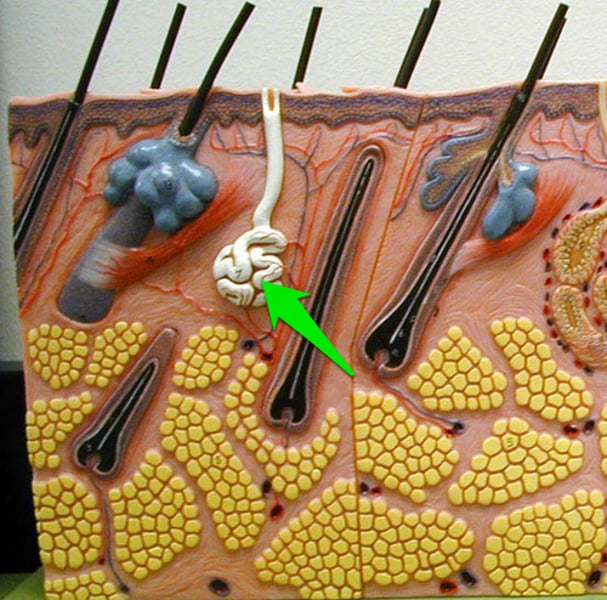
apocrine sweat glands
found in axillary (armpits), areola of breast, and anogenital areas
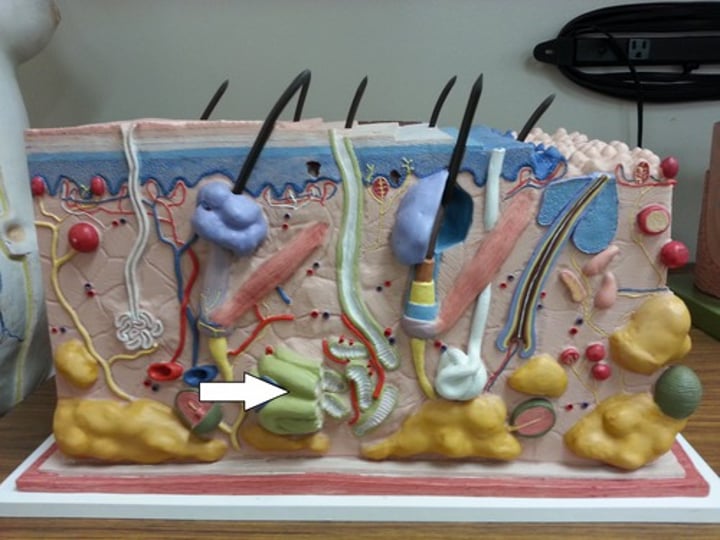
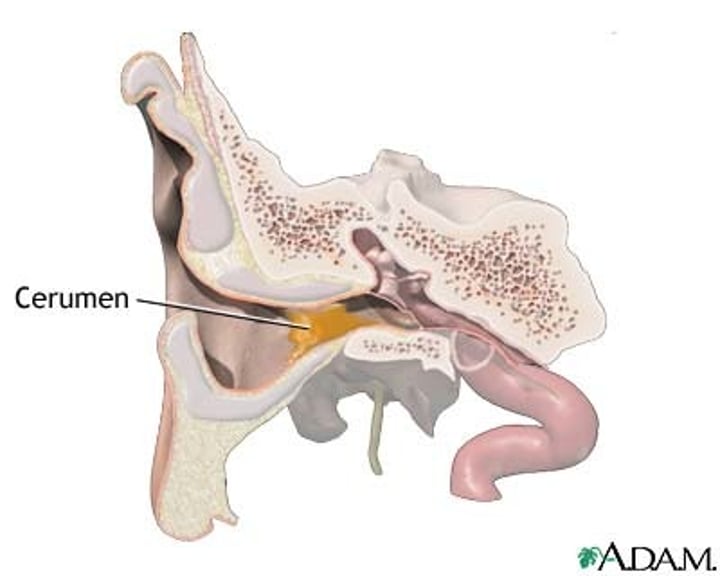
ceruminous glands
modified sweat glands, located in external ear canal, secretes cerumen (earwax) to protect ear from dehydration
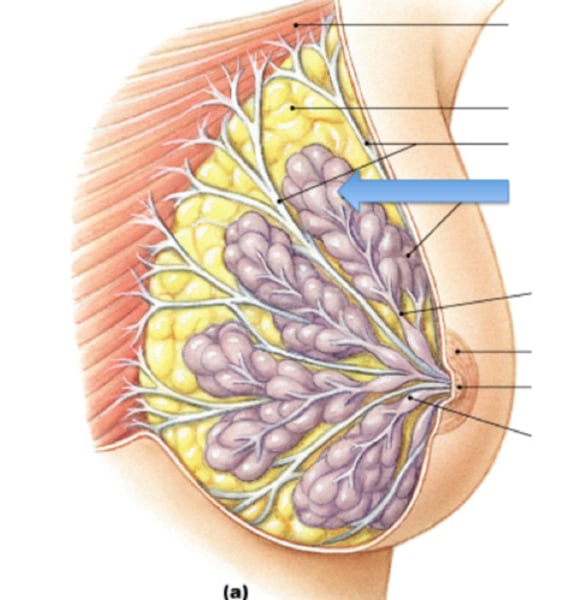
mammary glands
Specialized organs in mammals that produce milk to nourish the young
Eccrine (merocrine) sweat glands:
-Small
-Most numerous
-Distributed over the total body surface (except over the lips, ear canal, glans penis, nail beds)
-Function throughout the life
-Secrete transparent watery liquid
apocrine sweat glands:
-Larger than the Eccrine glands
-Located in a few areas of the body.
-Connected with hair follicles
-Begin to function at puberty
-Secrete a viscous colored substances that give characteristic odor after interaction with skin bacteria
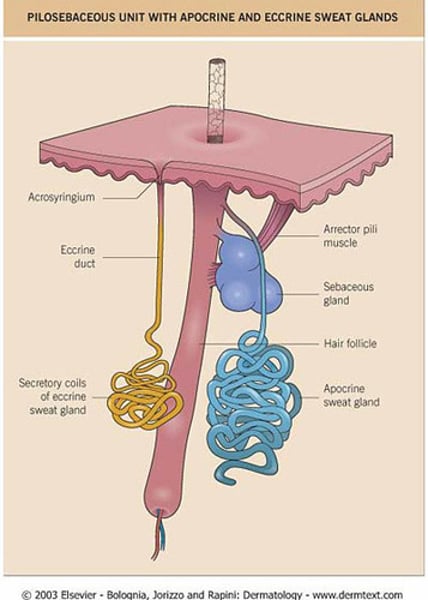
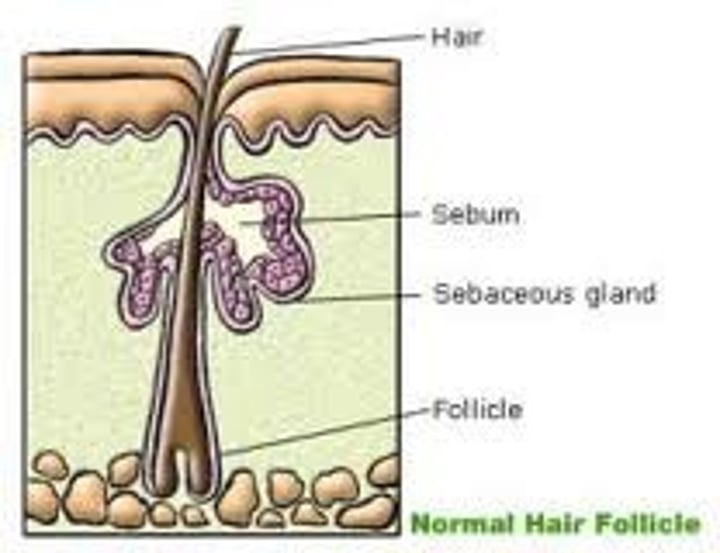
sebaceous glands classified as:
-as holocrine glands because secretions contain cell fragments due to rupture of cell membrane, which lead to oil secretions.
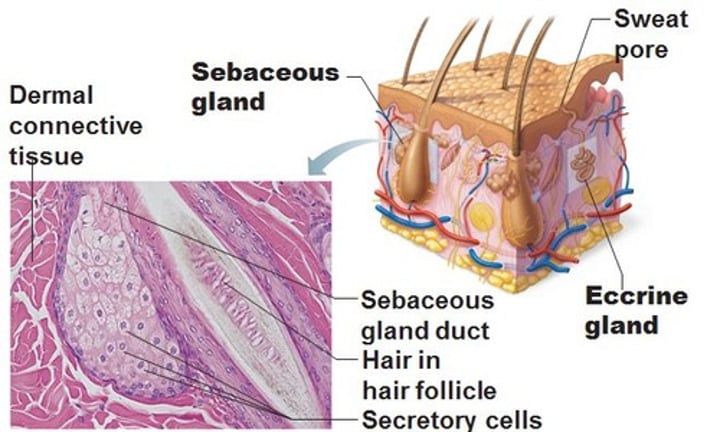
What does sebum do?
-keeps the hair supple & flexible & the skin soft
-prevents excessive water loss from the skin (as mixed with skin keratin).
-contains anti-fungal substances such as waxes & triglycerides that reduce fungal activity.
White pimples are formed by:
-accumulation of sebum in the ducts.
Blackheads are formed by:
Oxidation of accumulated sebum makes it dark & forms it
Examples of specialized sebaceous glands:
-in glans penis, lips, and eyelids.
basal cell carcinoma
Most common & least severe type of skin cancer
•Stratum basale cells proliferate & invade the dermis & hypodermis.
-It is slow growing and do not often metastasize.
-Can be cured by surgical excision in 99% of the cases
squamous cell carcinoma
Type of skin cancer more serious than basal cell carcinoma
•Arises from keratinocytes of stratum spinosum.
-Occur on scalp, ears, and lower lip.
-Grows rapidly and metastasizes if not removed.
-Can be treated by radiation therapy or removed surgically
Melanoma
-The most serious form of skin cancer
-Cancer of melanocytes (most dangerous).
-Treated by wide surgical excision accompanied by immunotherapy.
-Chance of survival is poor if the lesion is over 4 mm thick
ABCD rule
•A: Asymmetry; the two sides of the pigmented area do not match
•B: Border is irregular and exhibits indentations
•C: Color (pigmented area) is black, brown, tan, and sometimes red or blue
•D: Diameter is larger than 6 mm (size of a pencil eraser)
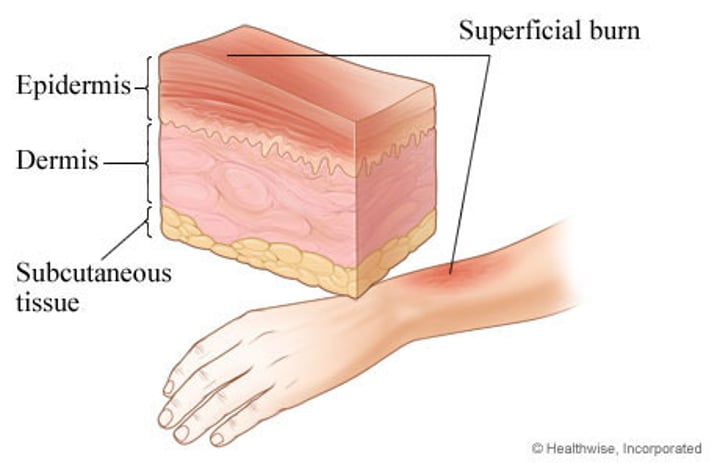
first degree burn
•only the epidermis is damaged
•Symptoms include localized redness, swelling, and pain
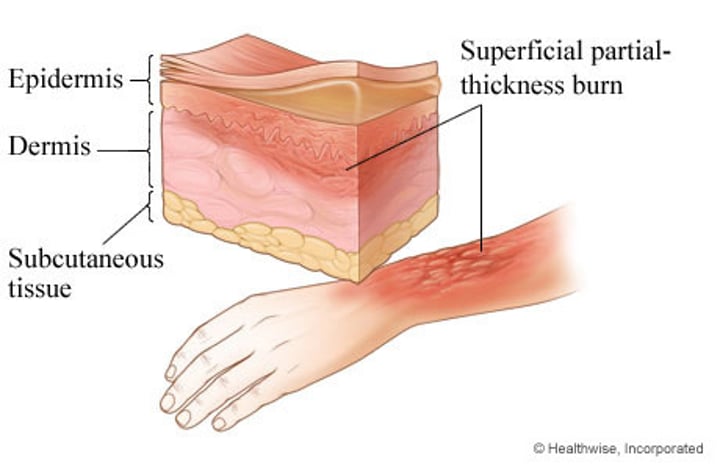
second degree burn
•the epidermis & upper regions of dermis damaged
•Symptoms mimic first degree burns, but blisters also appear
third degree burn
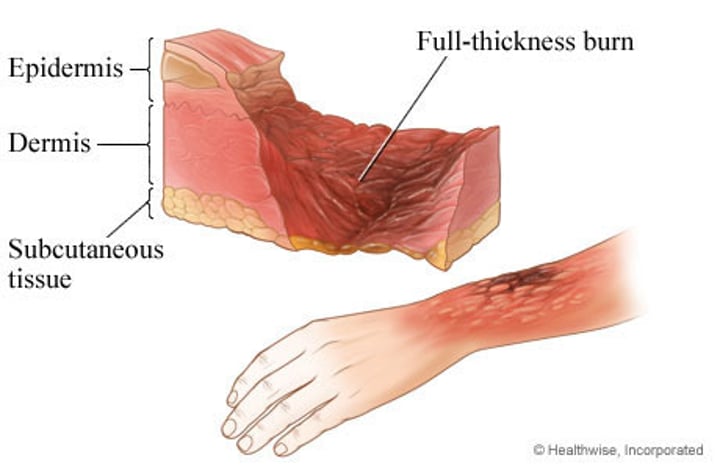
•involve entire thickness of the skin
•Burned area appears gray-white, cherry red, or black, & there is no initial edema nor pain (since nerve endings are destroyed)
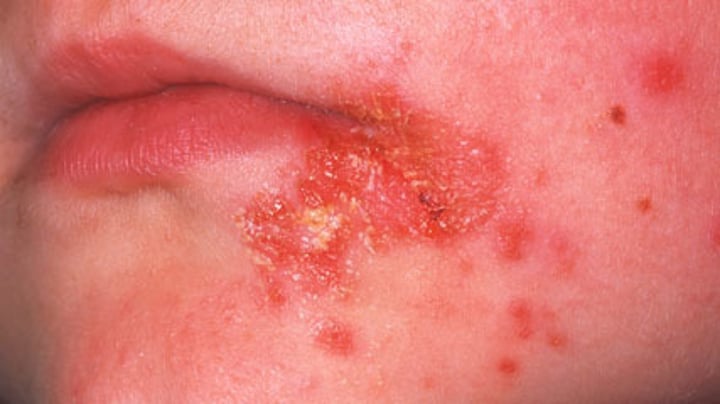
Impetigo
•Small blisters containing pus; easily rupture to form a thick, yellowish crust; usually affects children
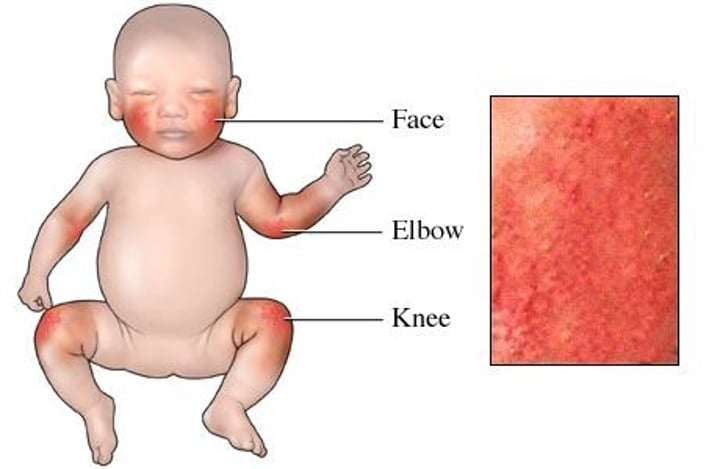
eczema
•Inflammatory conditions of the skin caused by allergy, infection, poor circulation, or exposure to chemical or environmental factors
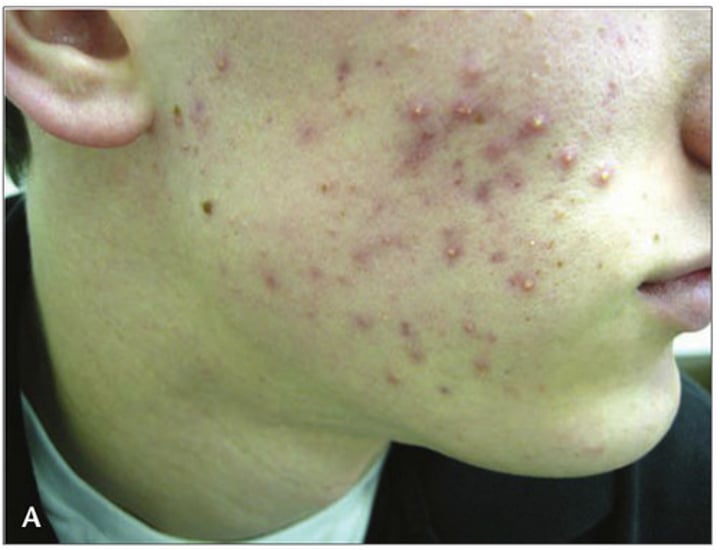
acne
•the occurrence of inflamed/infected sebaceous glands in the skin; (condition characterized by red pimples on the face, prevalent chiefly among teenagers.)
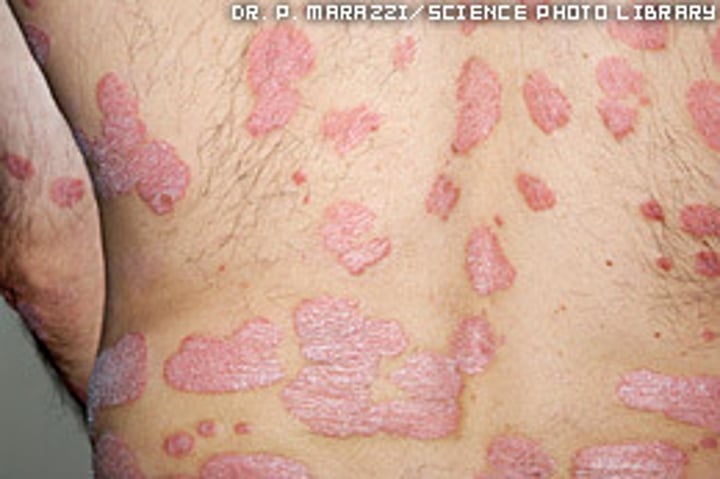
Psoriasis
•Chronic skin disease characterized by thicker-than-normal epidermal layer (stratum corneum) that sloughs to produce large, silvery scales; bleeding may occur if the scales are scraped away
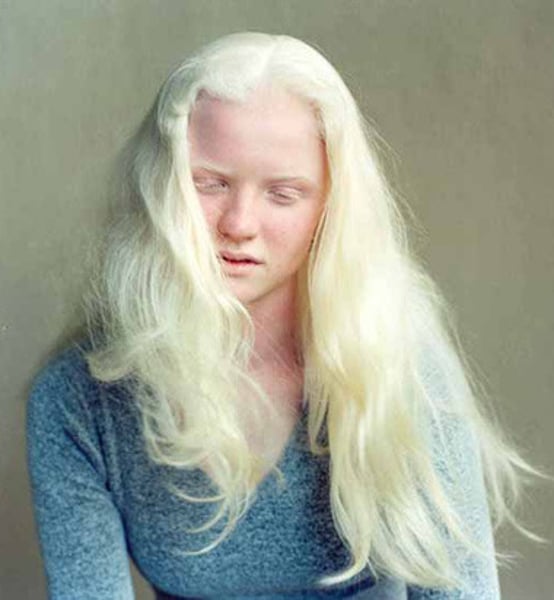
Albinism
•recessive genetic trait that results from an inability to produce tyrosinase. -result is a deficiency/an absence of pigment in the skin, the hair, & the irises of the eyes.

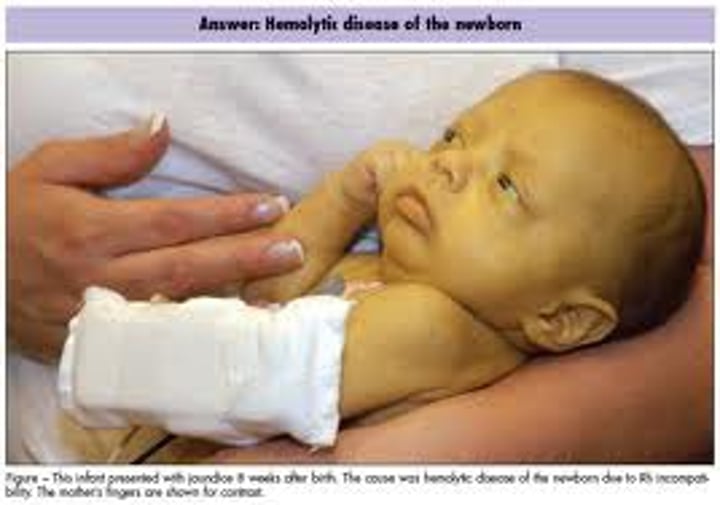
jaundice
•caused by a buildup of bilirubin (a waste material) in the blood
-An inflamed liver or obstructed bile duct can lead to this
-Symptoms include a yellow tinge to the skin and whites of the eyes, dark urine, and itchiness
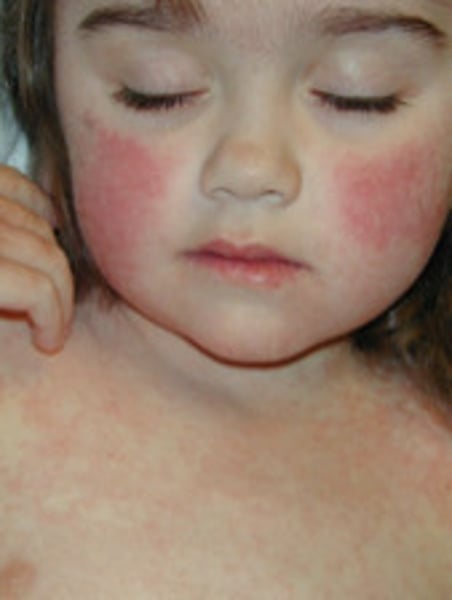
erythema
skin turns a reddish hue when the amount of blood flowing through the skin increases
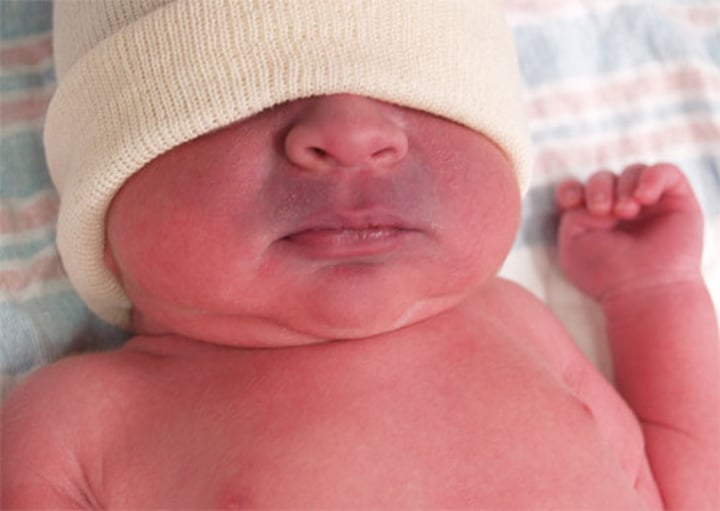
cyanosis
skin turns bluish due to A decrease in blood flow thus in blood oxygen content, as occurs in shock, can make the skin appear pale
The skeletal system is made up of two major types of connective tissue:
1- Bone of the skeleton (~206 bones)
2- Cartilages, ligaments and other connective tissues that stabilize and connect
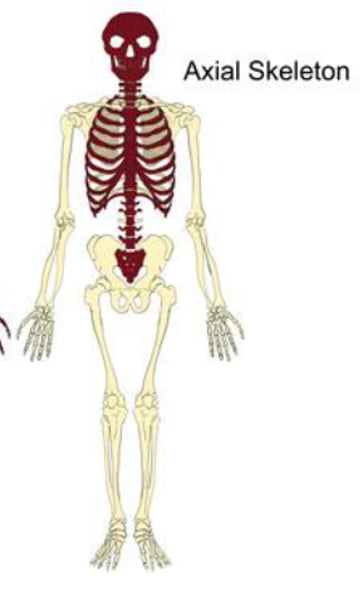
How many bones does the axial skeleton consist of?
80 bones.
-It consists of the skull, vertebral column (spine), ribs & sternum (chest bone).
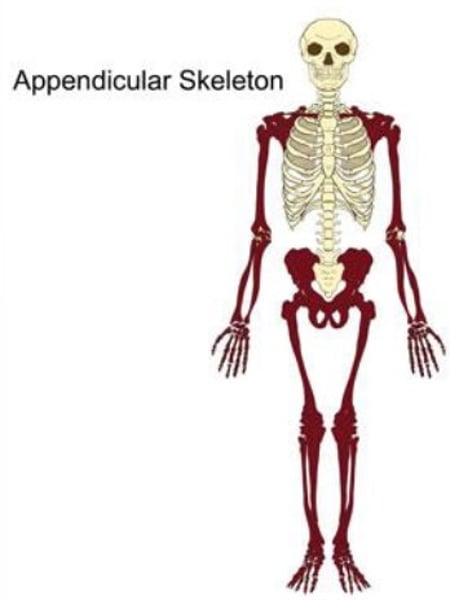
How many bones does the appendicular skeleton consist of?
126 bones.
-It consists of the shoulder or pectoral girdle, arms, hands, pelvic girdle, legs, & feet.
Functions of the skeletal system: SUPPORT:
-Bones: form the body's framework, well suited for bearing weight & they are the major supports of organs.
-Cartilages: provides firm yet flexible support (nose, ear, trachea). Ligaments are strong fibrous tissue bands that hold bones together.
Functions of the skeletal system: PROTECTION:
forms bony cavities which protect organs
Functions of the skeletal system: MOVEMENT:
forms levers for muscle action.
Functions of the skeletal system: MINERAL STORAGE:
calcium & phosphorus depot (place for storage)
Functions of the skeletal system: HEMATOPOIESIS:
production of blood cells.
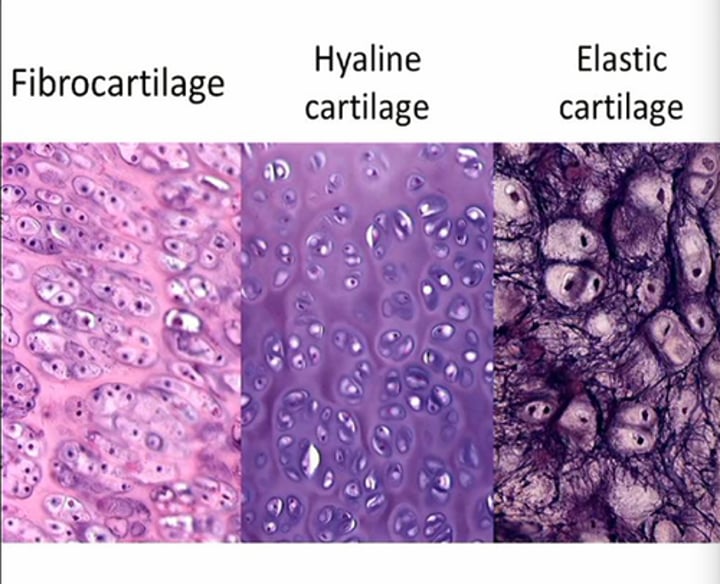
Types of cartilage
•Hyaline (most closely associated with bones), fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
Most bones start as
Hyaline cartilage
What happens during bone formation?
•hyaline chondroblasts secrete (produce) a matrix during which the chondroblasts differentiate into chondrocytes.
-The matrix is rich in collagen (provides strength) and proteoglycan (makes cartilage resilient by trapping water).
Cartilage growth by:
-appositional (chondroblasts add new cartilages)
-interstitial (chondrocytes in center of tissue divide and add more matrix between existing cells).
Long Bones
-bones of the upper & lower arms & legs as well as the metacarpals & metatarsals.
-Ex: femur (thigh), tibia (larger shin), fibula (smaller shin bone), humerus (upper arm), radius (larger forearm), ulna (smaller forearm), hand and finger bones (metacarpals), and feet and toe bones (metatarsals)
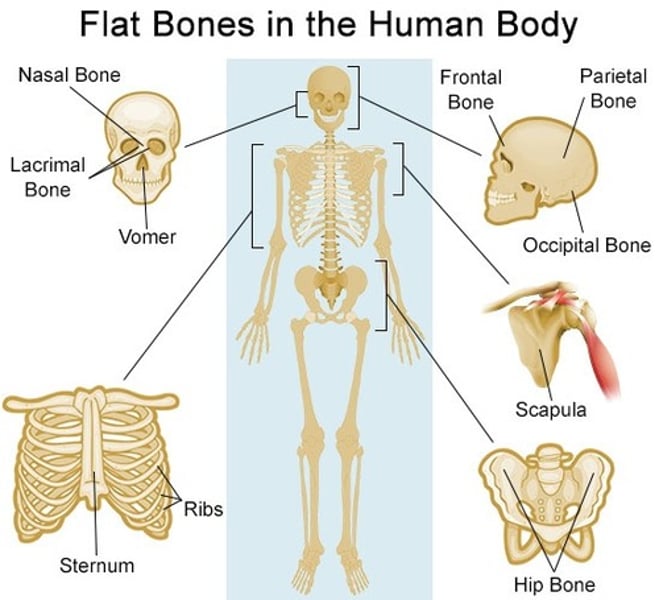
Flat bones
sternum, ribs, scapulae, cranium
Short bones
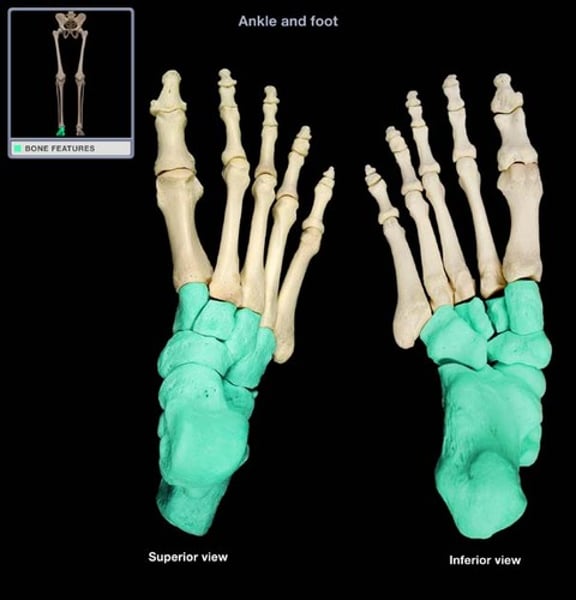
carpals (wrist) and tarsals (ankle)
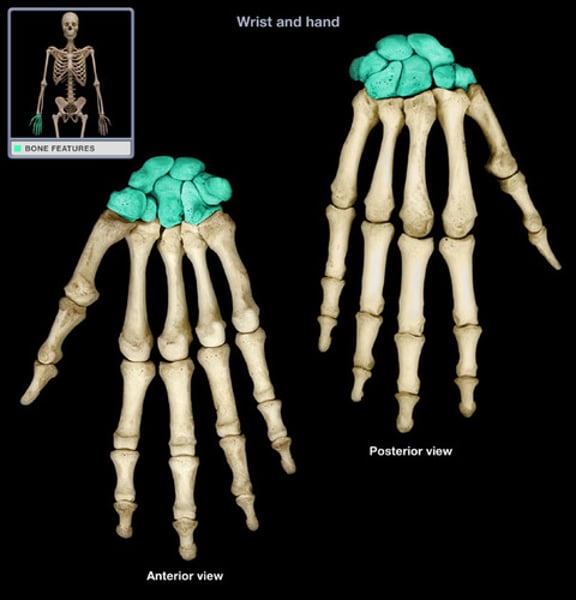
Carpal bones
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
Tarsal bones
calcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular, and cuneiforms (lateral, intermediate, and medial)
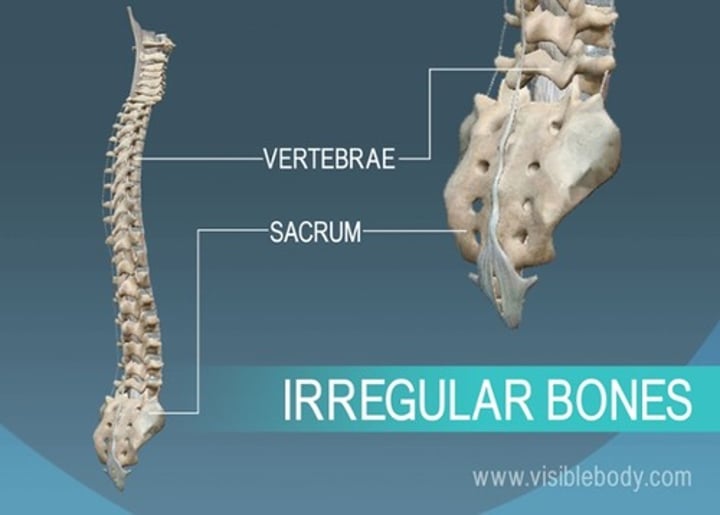
irregular bones
vertebrae and pelvis
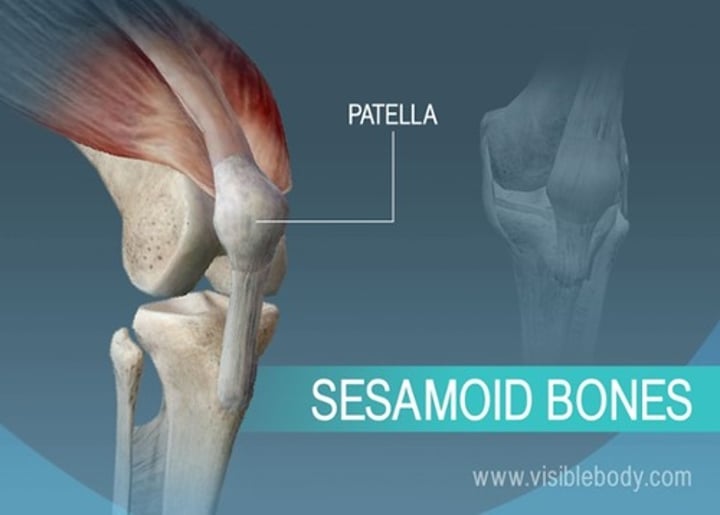
sesamoid bones
round bones found near joints (e.g., the patella)
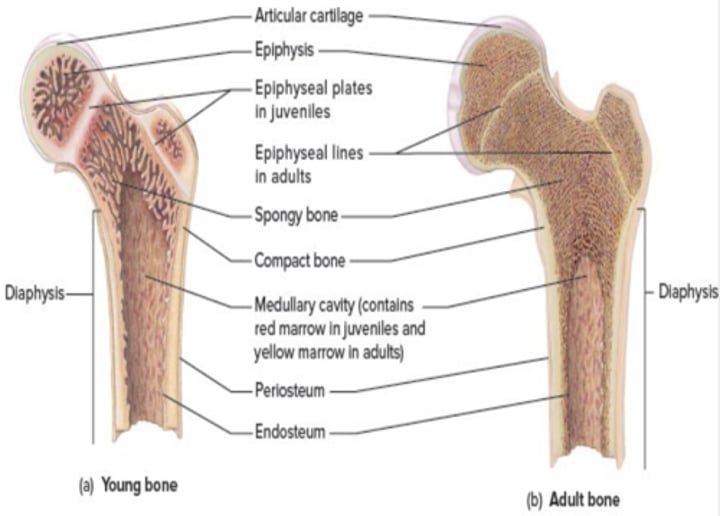
a typical long bone includes:
-Diaphysis (the bone shaft)
- Epiphyses (the growing ends)
-Medullary (Marrow) cavity: filled with red or yellow marrow.
-Periosteum: covers bone.
-Endosteum: lines bone
-Epiphyseal plate: Hyaline cartilage between epi and diaphysis- Responsible for bone growth.
Types of bone tissue
compact bone and spongy bone
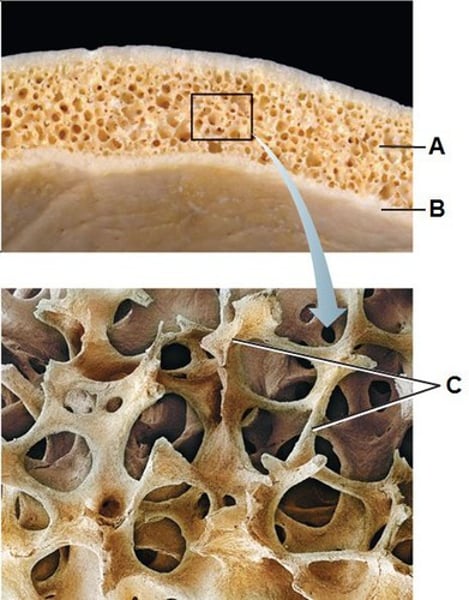
Compact bone
-dense bone found in the shaft (diaphysis) of long bones and as outer layer of all bones.
spongy bone
Layer of bone tissue that has many small spaces and is found just inside the layer of compact bone.
bone extracellular matrix
-Bone tissue has a matrix containing inorganic materials (65%) and organic fibers (35%).
-The inorganic matrix provides rigidity and hardness to bone and it is composed of hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate)
-The organic collagen fibers give a bone its strength and resistance to stress.
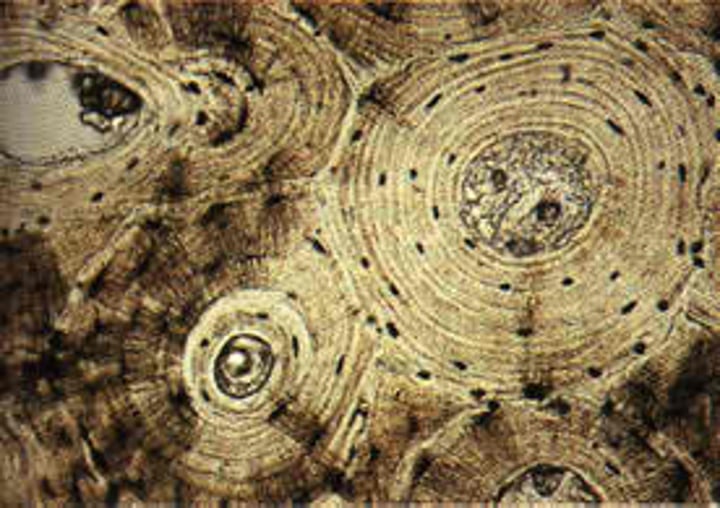
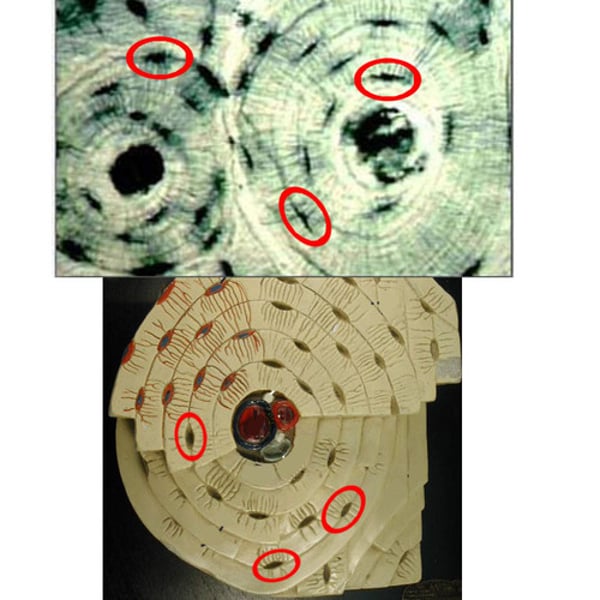
Osteon (Haversian system)
structural unit of compact bone
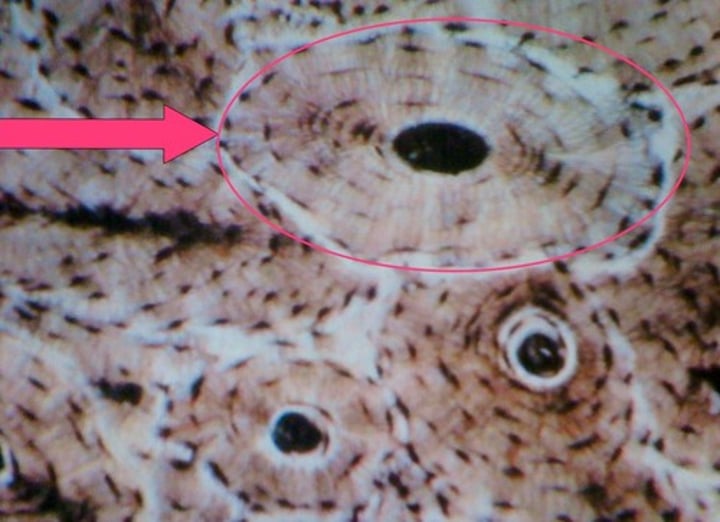
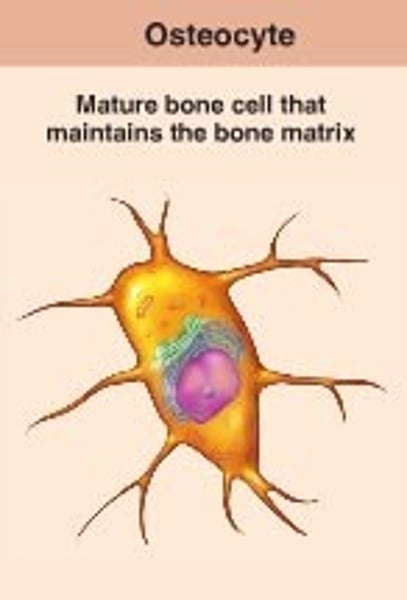
Osteocytes
-bone cells that arrange around a central canal filling the lacunae
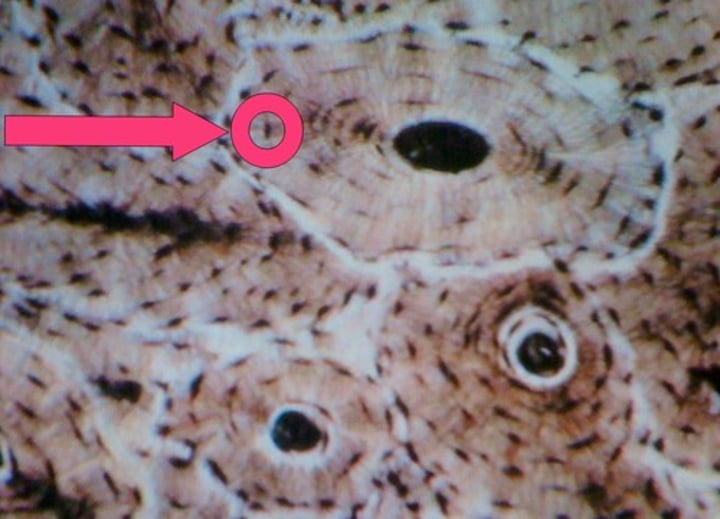
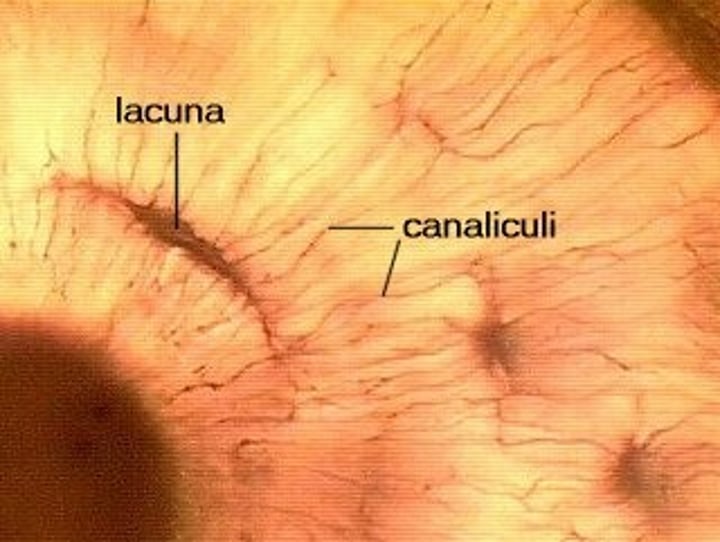
Lacunae
cavities around the central canal
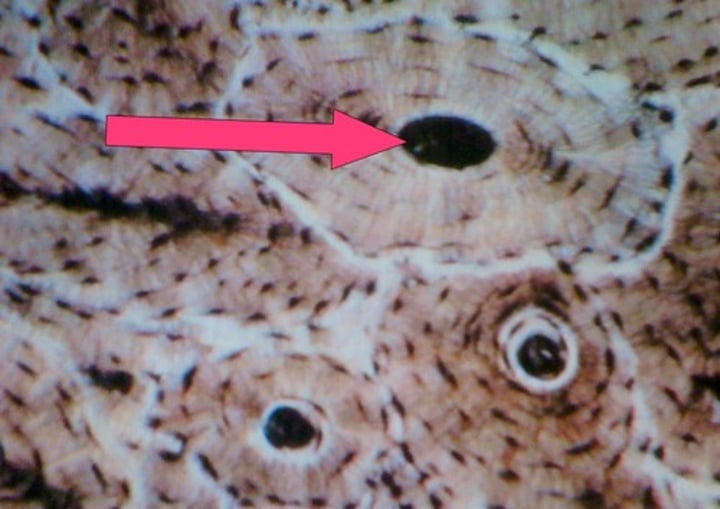
central canal (haversian canal)
-in the center of each osteon. It contains blood vessels.
Canaliculi
-tiny canals between lamellae.
Types of bone cells
osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts
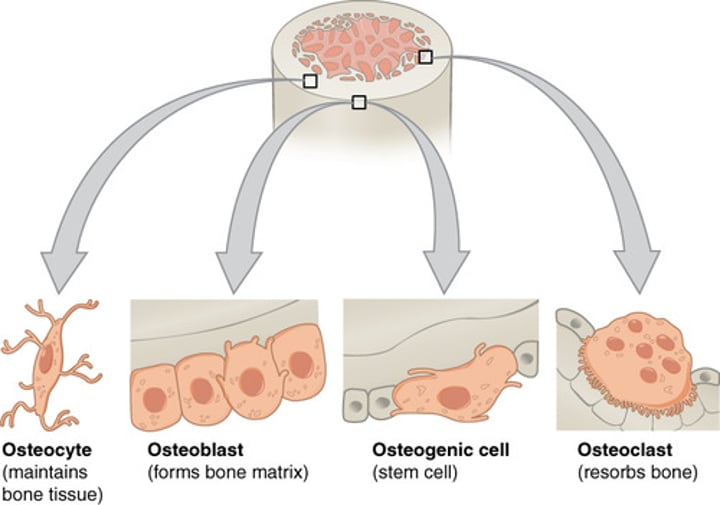
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells which secrete (produces) the osteoid (specialized organic matrix) and then calcify it.
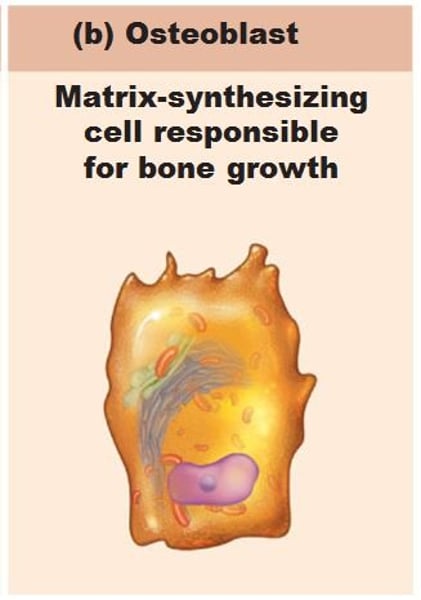
Osteocytes
-mature bone cells, perform maintenance.
-Octeocytes form from osteoblasts once the later have secreted enough matrix Just like hyaline chondrocytes formation.
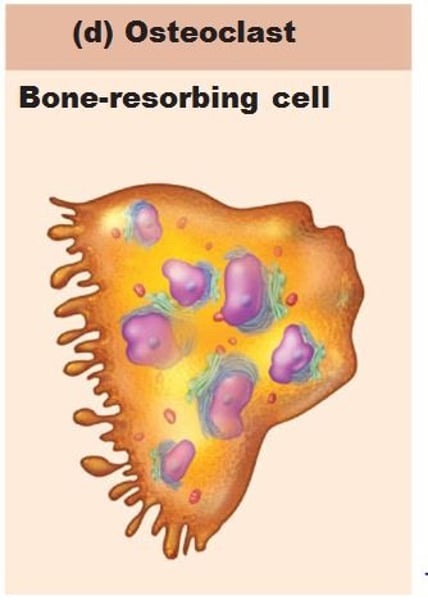
osteoclasts
responsible for bone resorption (bone breakdown) and active erosion of bone minerals.
connective tissue develops embryologically from
mesenchymal cells.
-some mesenchymal cells become stem cells, some of which replicate and become more specialized cell types.
-osteochondral progenitor cells are stem cells that can become osteoblasts or chondroblasts. they are located in the inner layer of the perichondrium and in layers of connective tissue that cover bone.
development of bone
ossification (osteogenesis) & calcification
Ossification (osteogenesis)
-formation of bone
•Ossification occurs in appositional growth on the surface of previously existing materials, either bone or cartilage.
intramembranous ossification
•Bones formed within fibrous membrane. Few flat bones
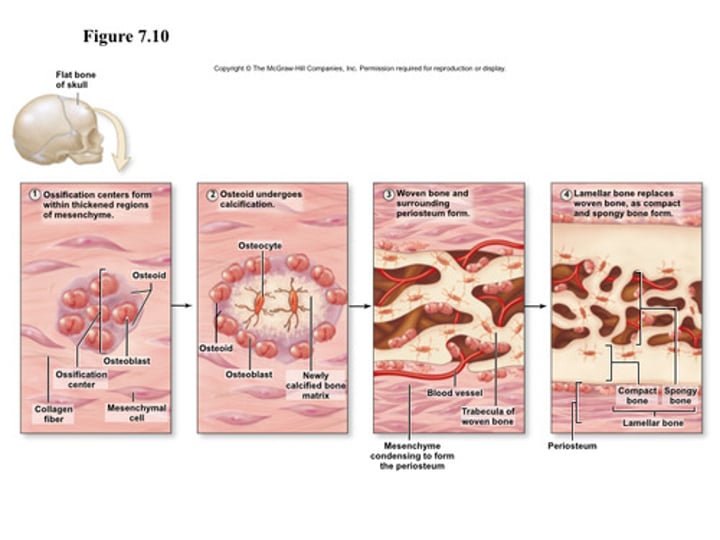
endochondral ossification
•conversion of cartilage into bone. Most bones.
Calcification
depositing calcium salts within tissues
bone growth
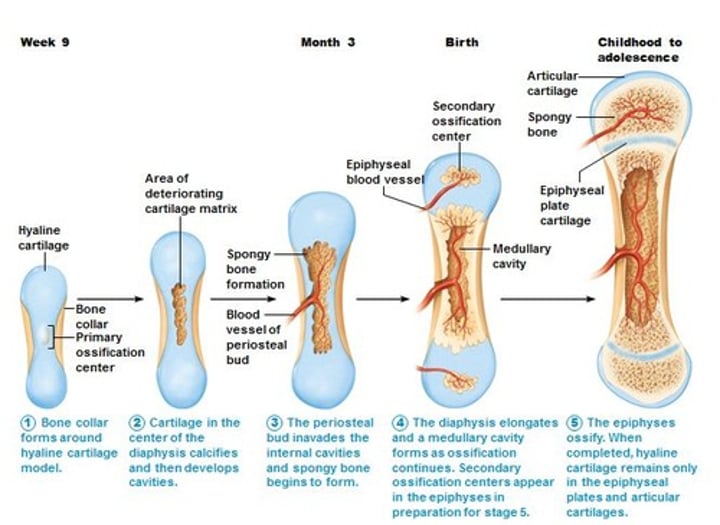
growth in length
Long bones grow by creating new cartilage in the epiphyseal plate. The epiphyseal plate is organized into five zones
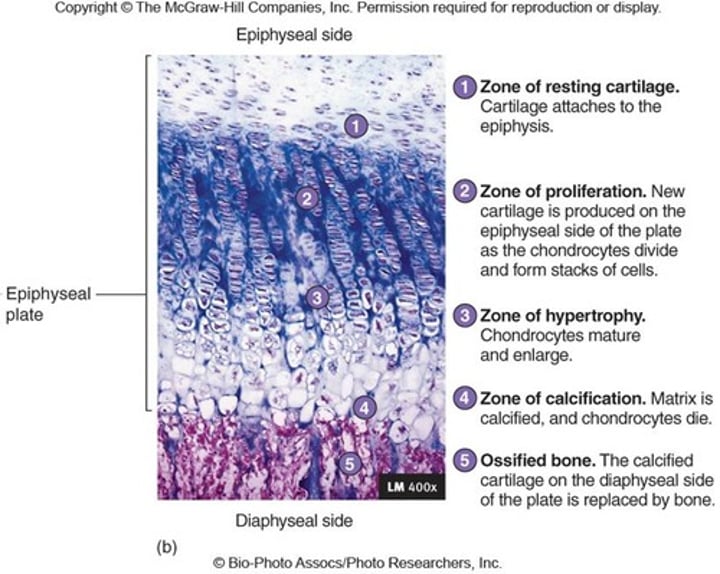
zone of resting cartilage
nearest the epiphysis and contains slowly dividing chondrocytes