Lab Exam 1
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Brown algae have …
carotenoids
are brown algae multicellular or unicellular
multicellular
Brown algae
Laminaria, SAR
brown algae
postelsia, SAR
Brown Algae
Fucus, SAR
Red Algae
porphyra, Archaeplastida
Red algae
chondrus, archaeplastida
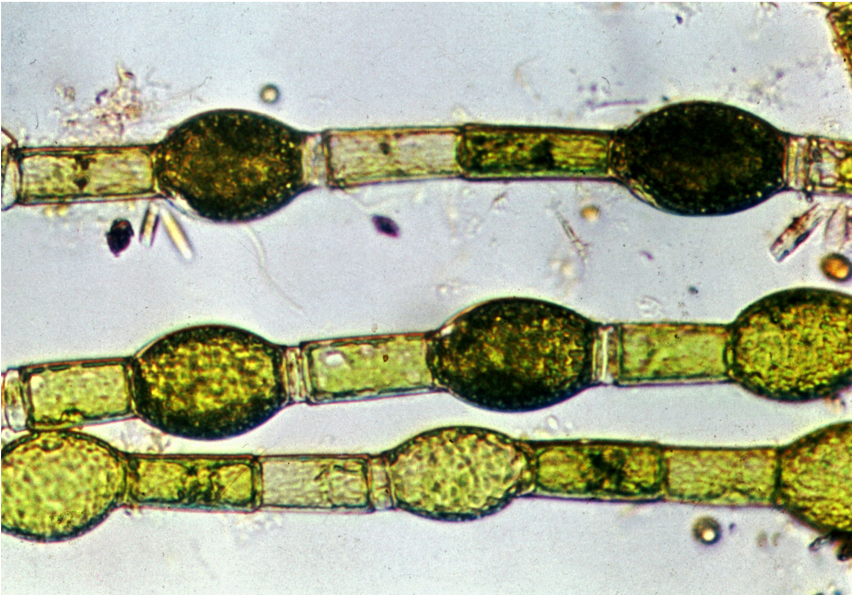
Oedogonium: Archaeplastida
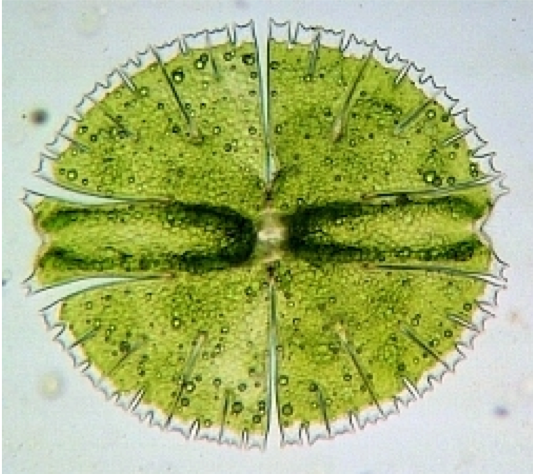
desmid: archaeplastida
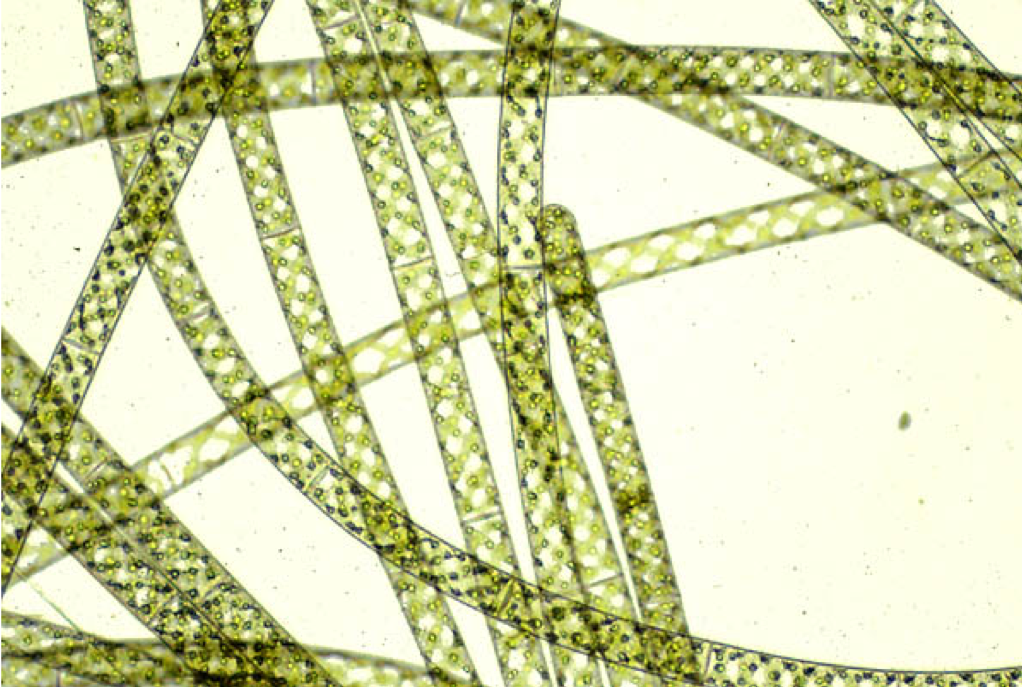
spirogyra: archaeplastida
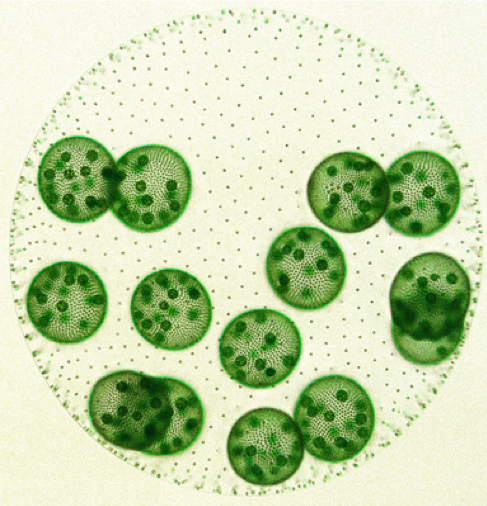
volvox: archaeplastida
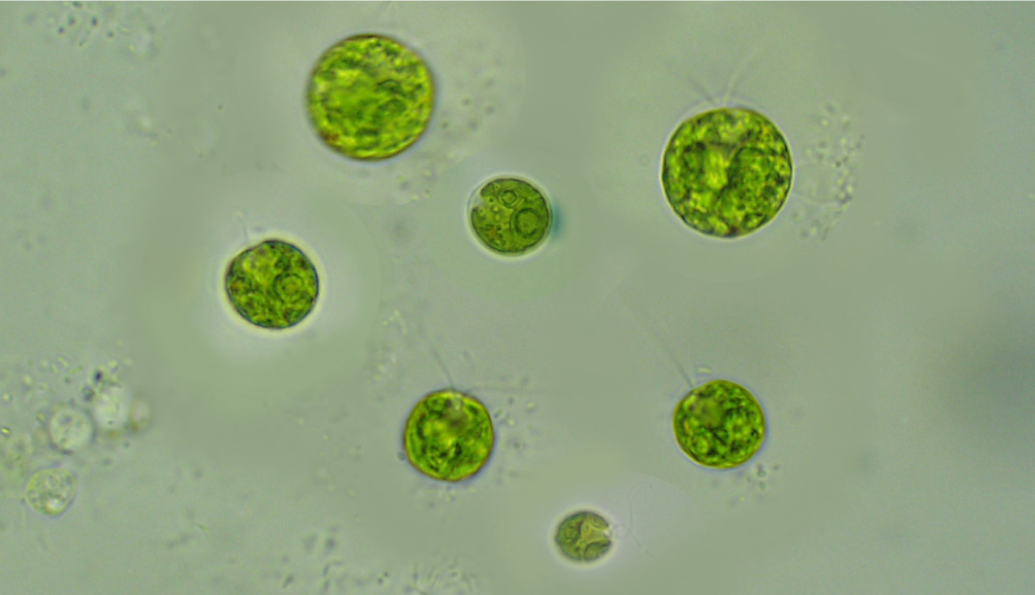
chlamydomonas: archaeplastida
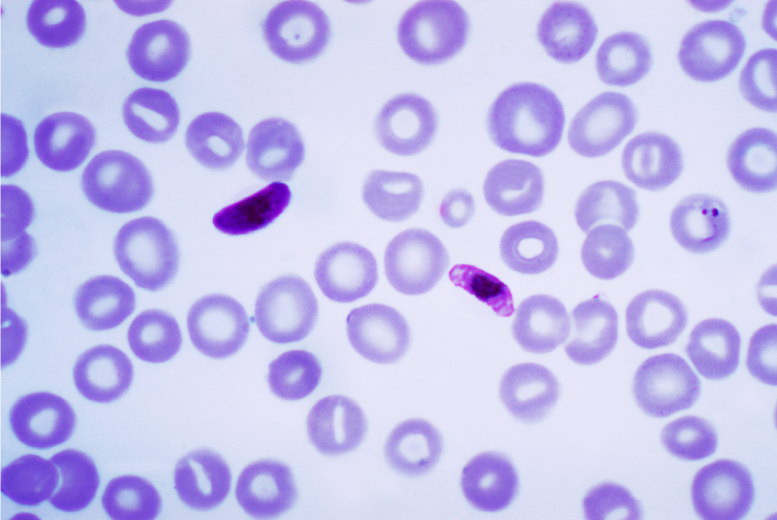
plasmodia: SAR
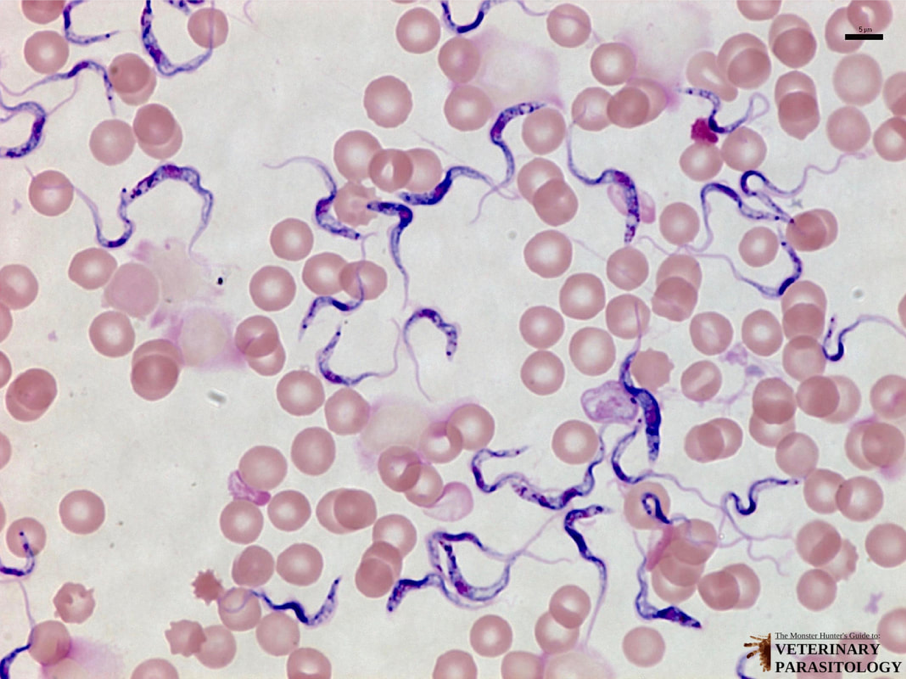
Trypanosoma: Excavata
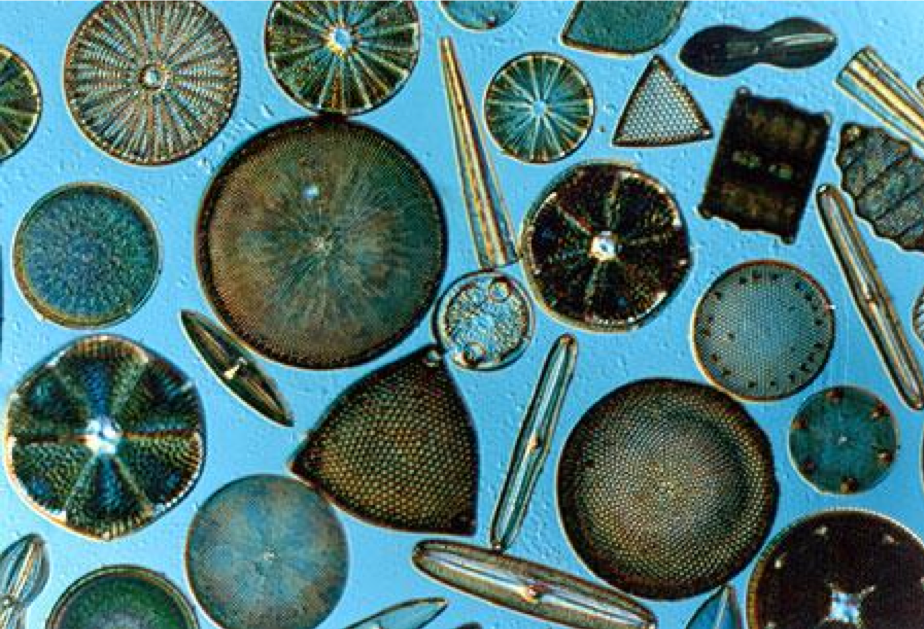

Diatoms: SAR
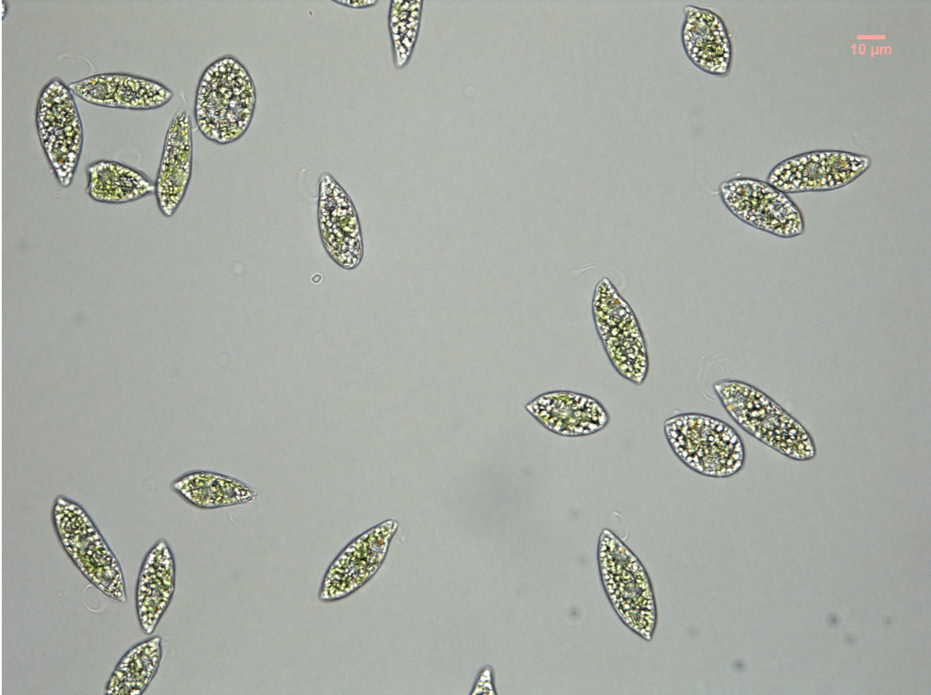
Euglena: excavata
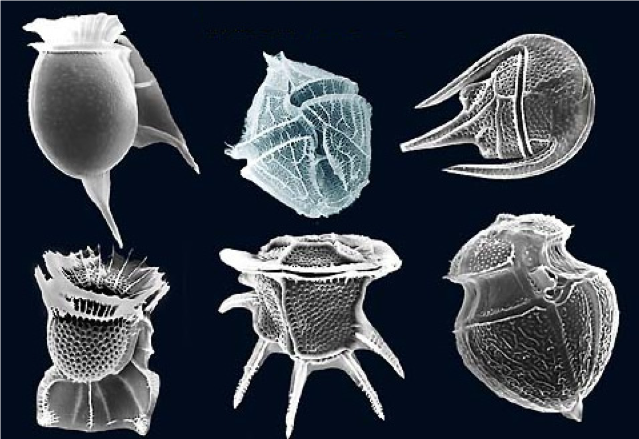
dinoflagellate: SAR
what does the archegonium produce
female gametes
what does the antheridium produce
sperm cells, (male gametes)
what does the sporophyte individual produce
spores
is the sporophyte haploid or diploid
diploid
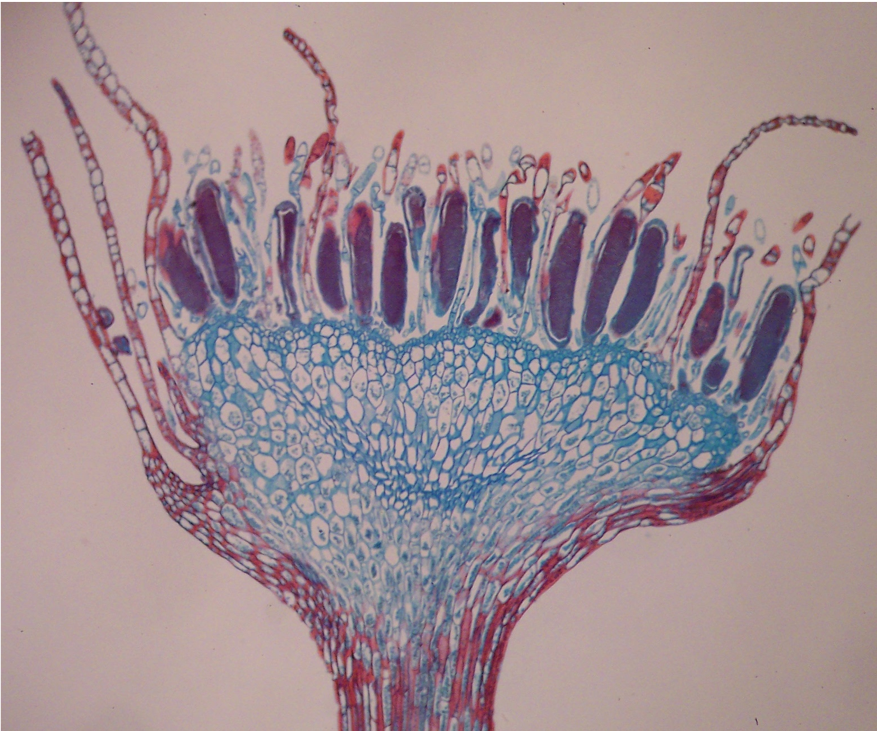
moss antheridia: haploid
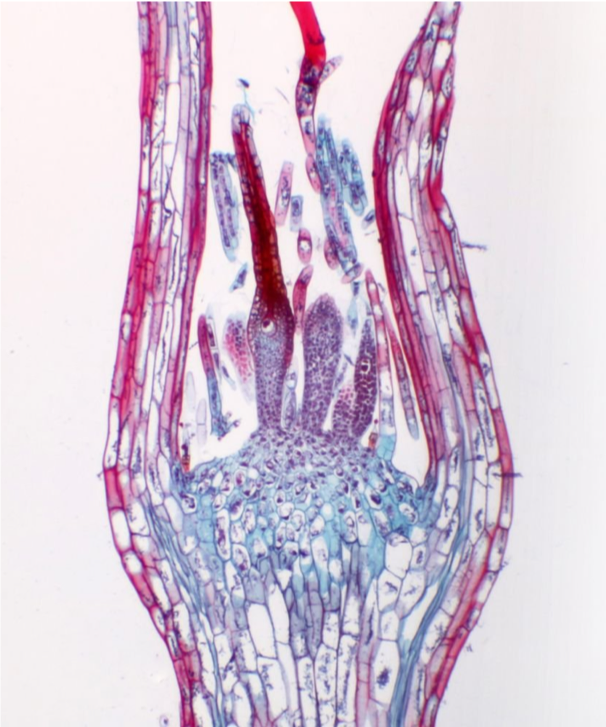
moss archegonia: haploid
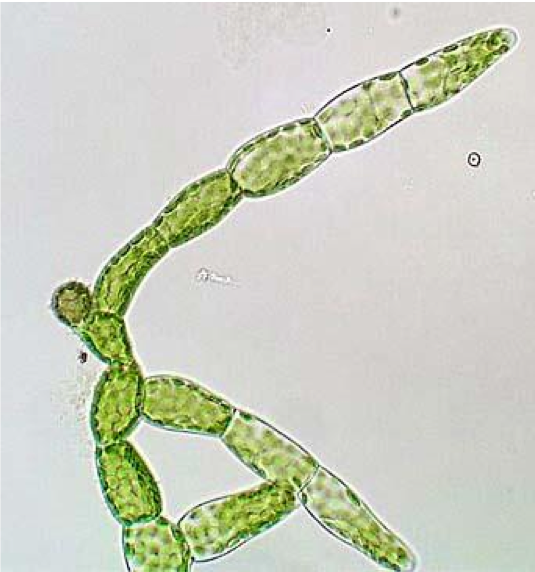
moss protonema: mitosis cycle
which generation, the gametophyte o the sporophyte is dominant in terms of time and size for the fern
sporophyte
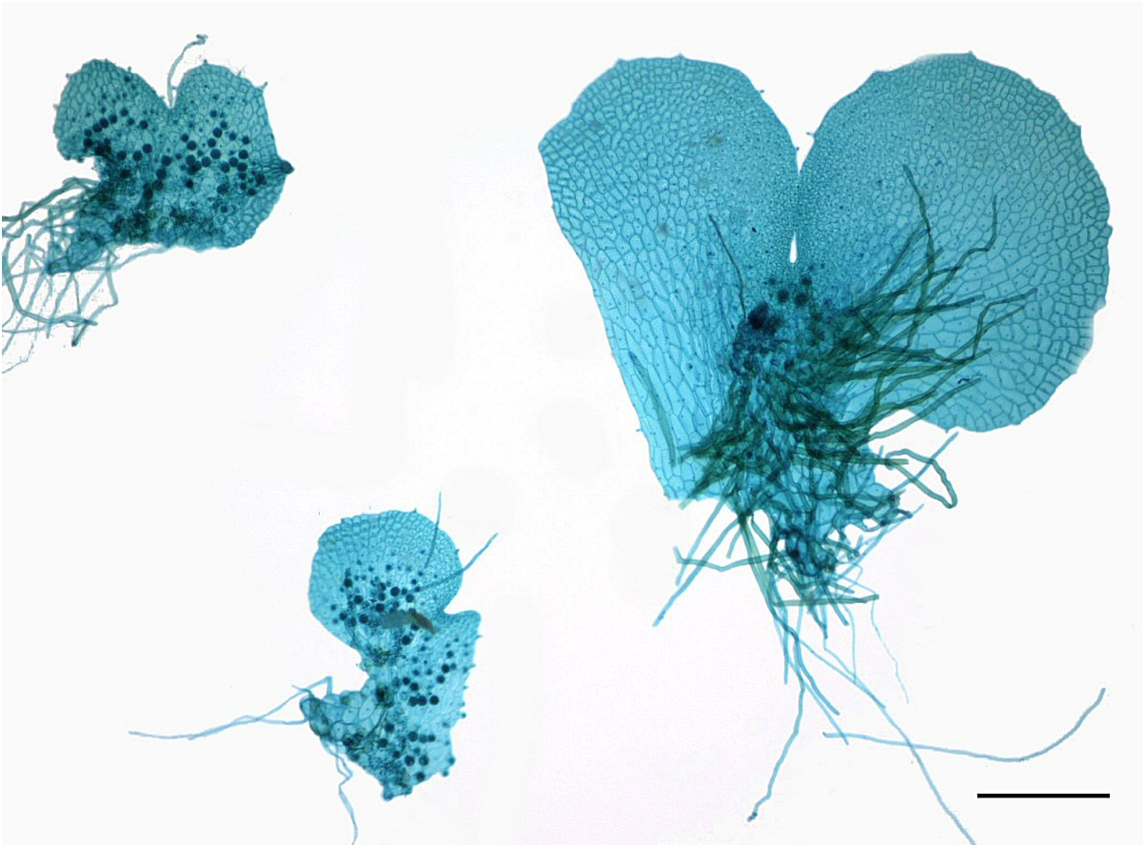
prothallus
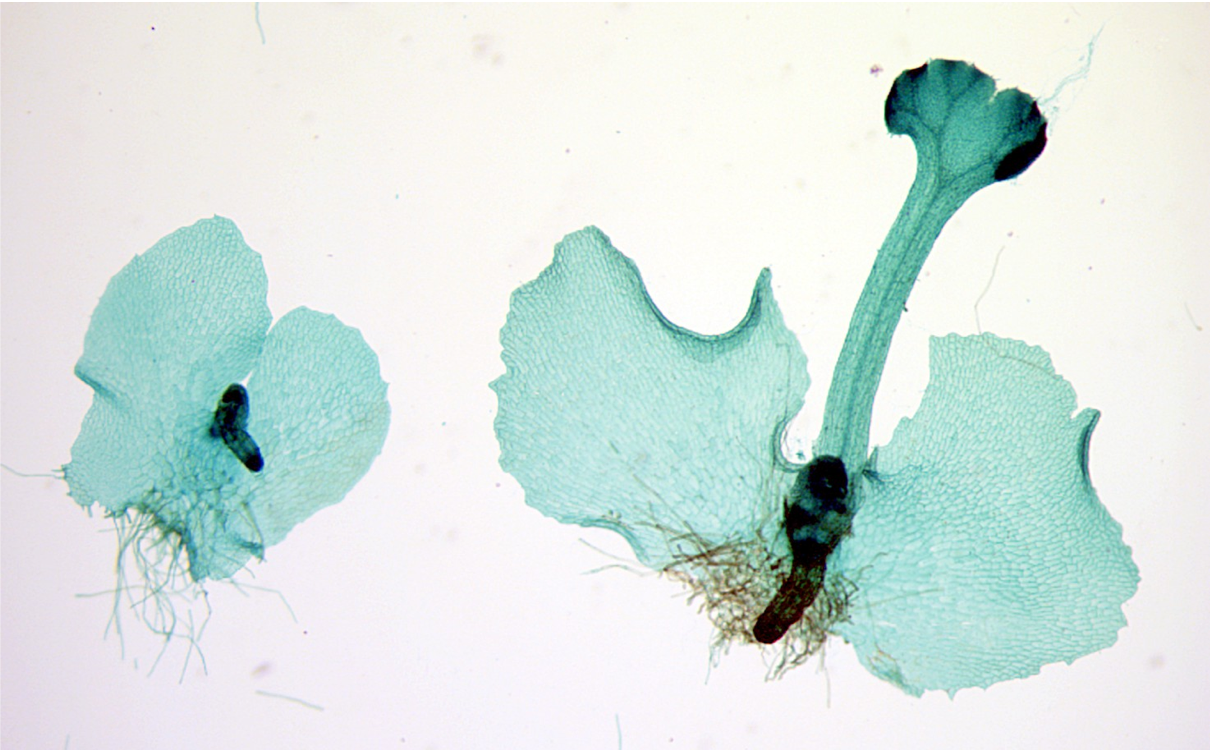
young fern sporophyte
mega
female
micro
male
what is the base of a sporophyll
an egg
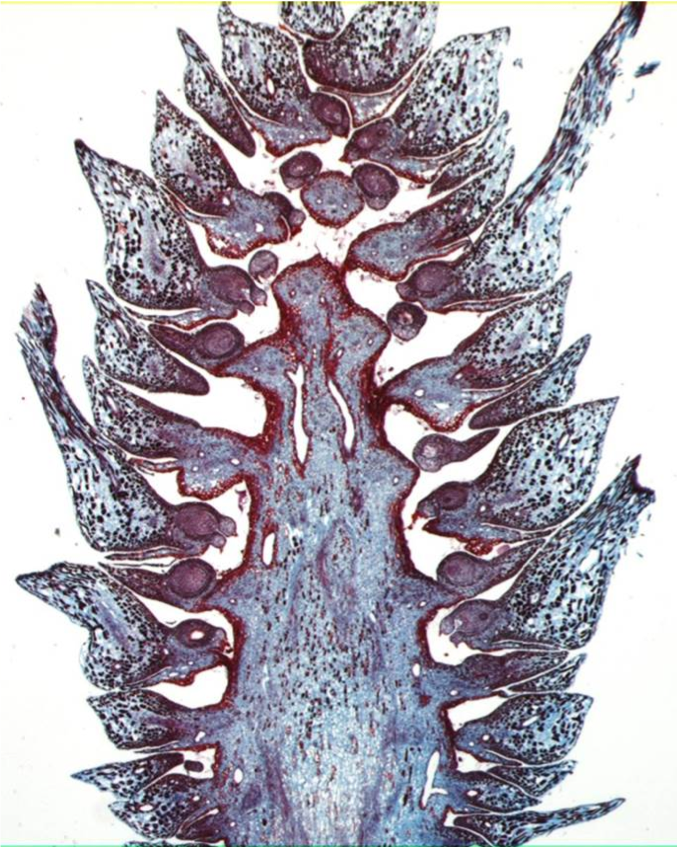
female cone
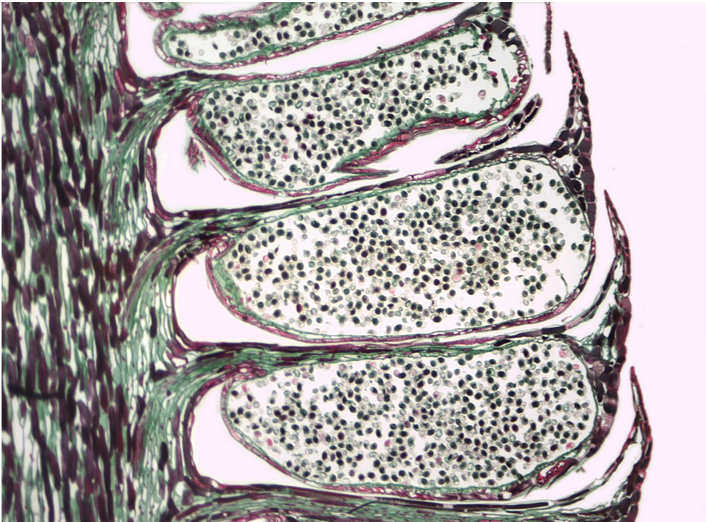
male cone, pictured is pollen grain
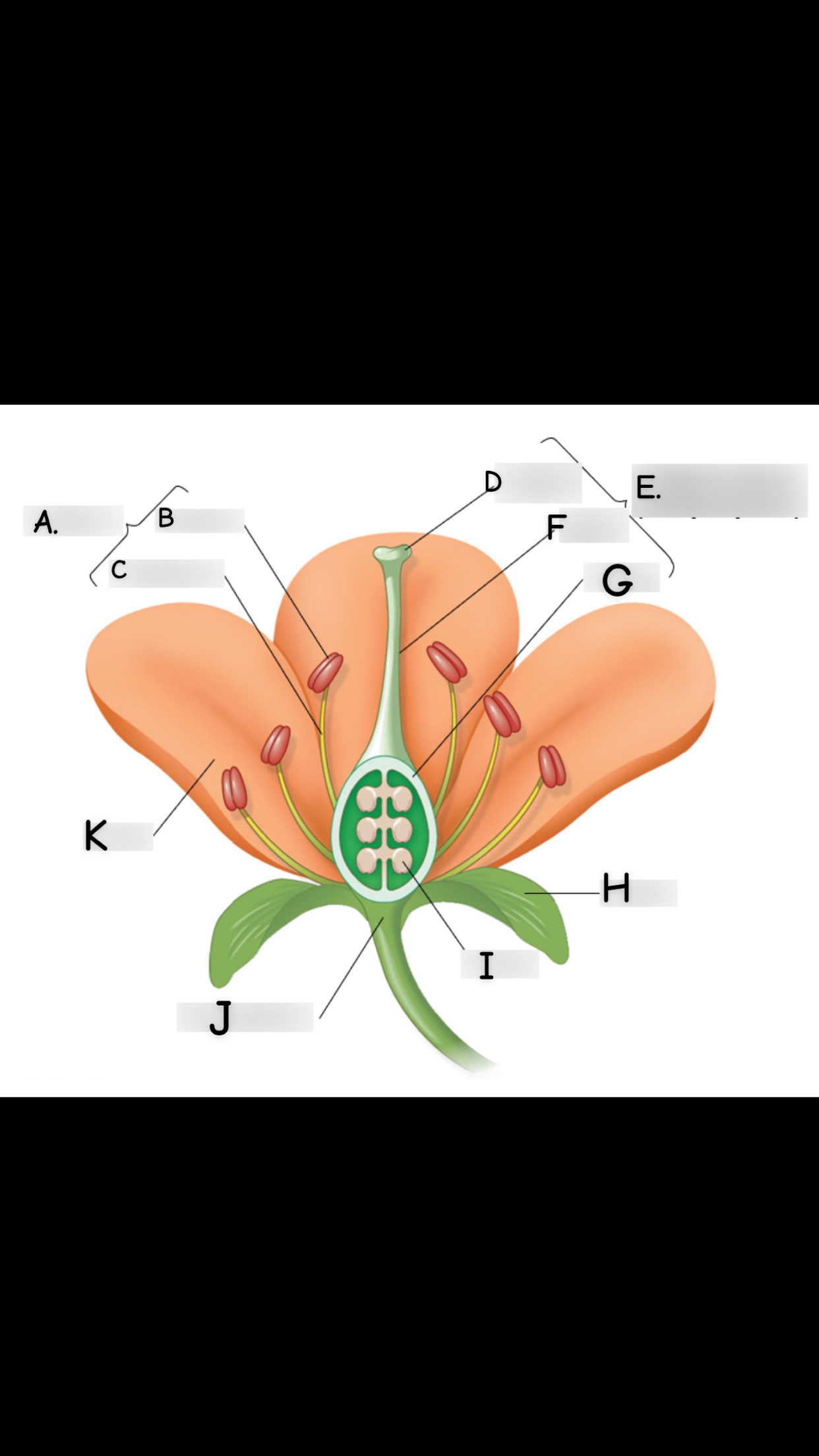
what is A
stamen
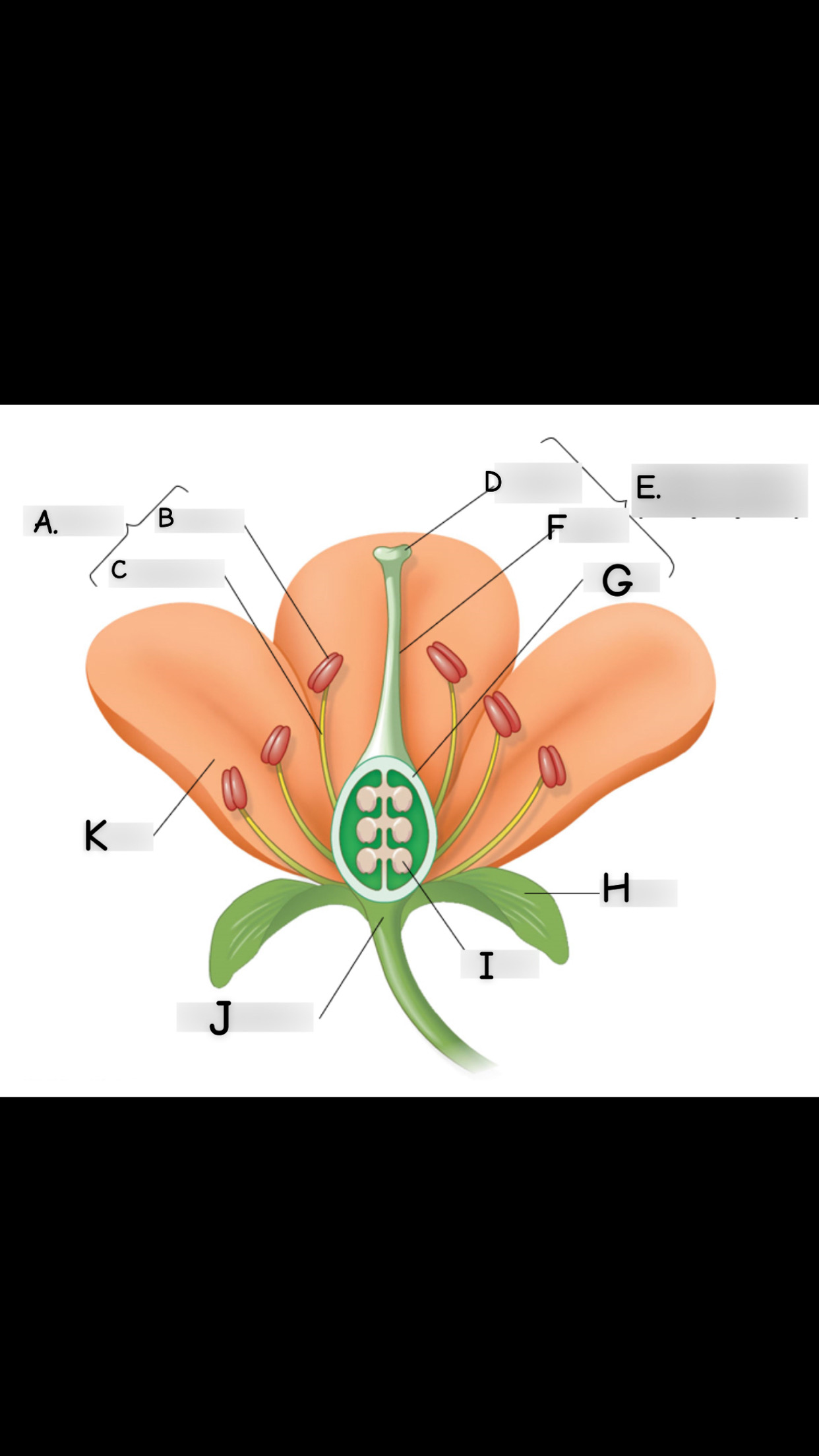
what is B
anther
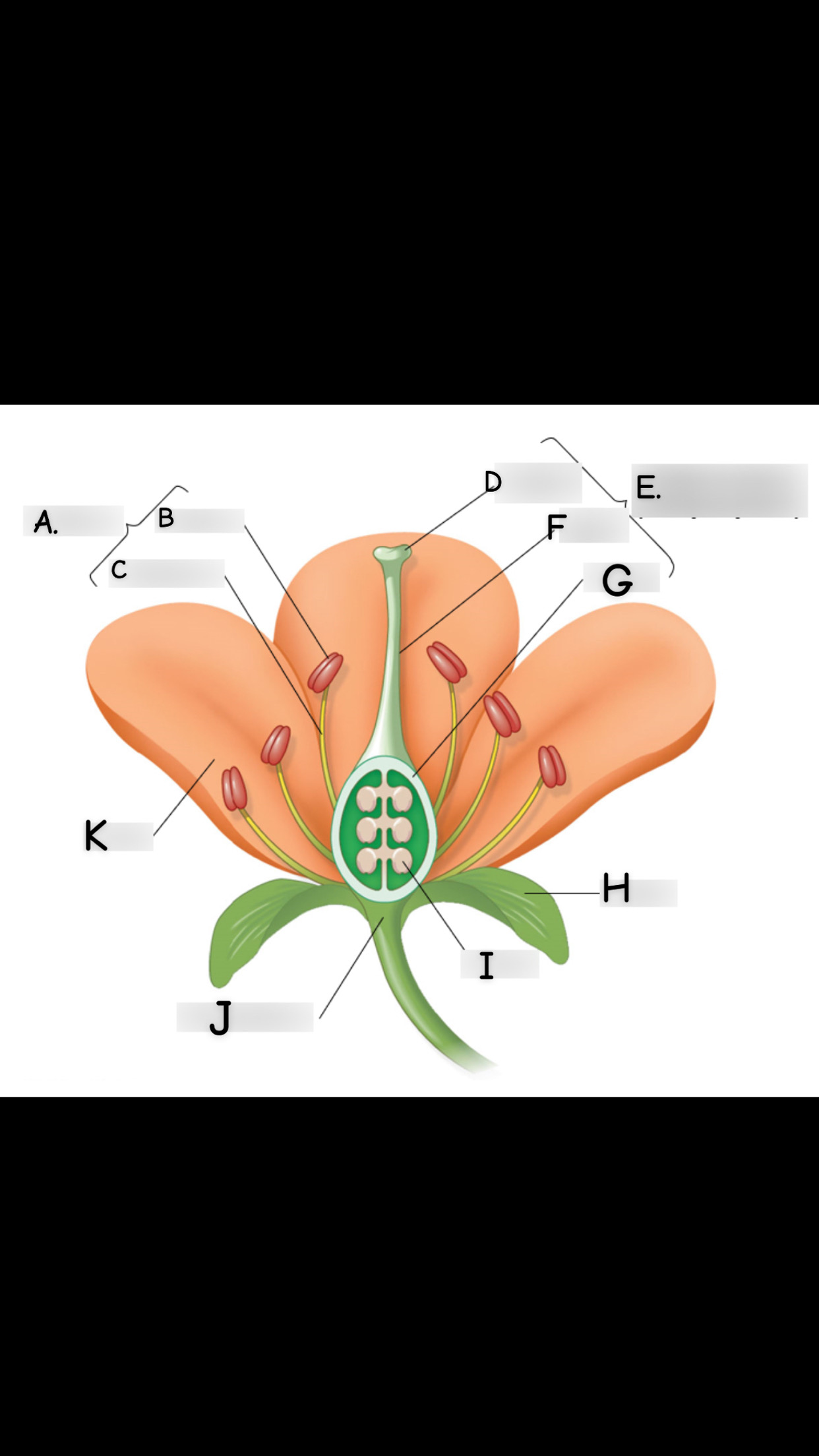
what is C
filament
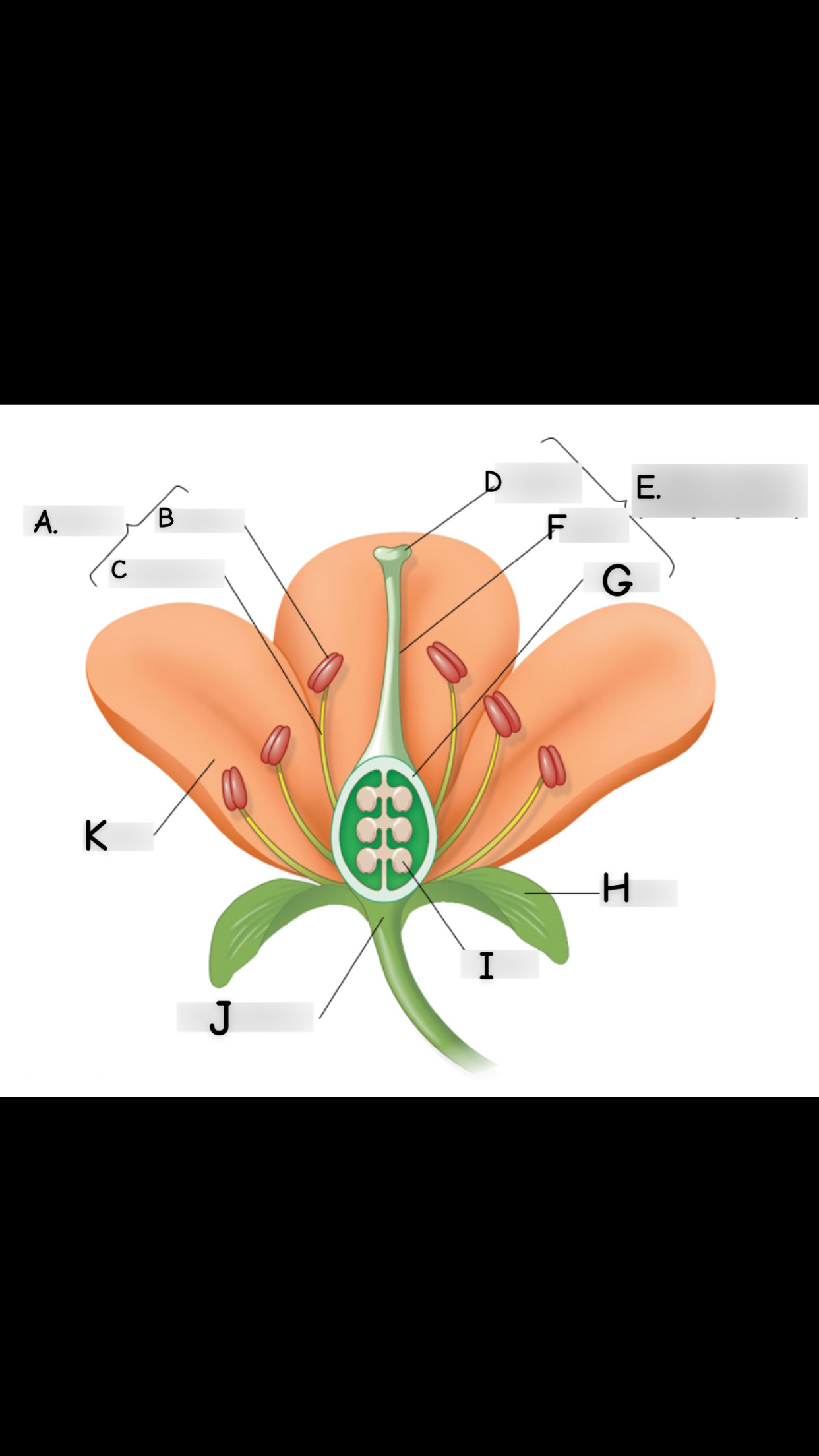
what is D
stigma
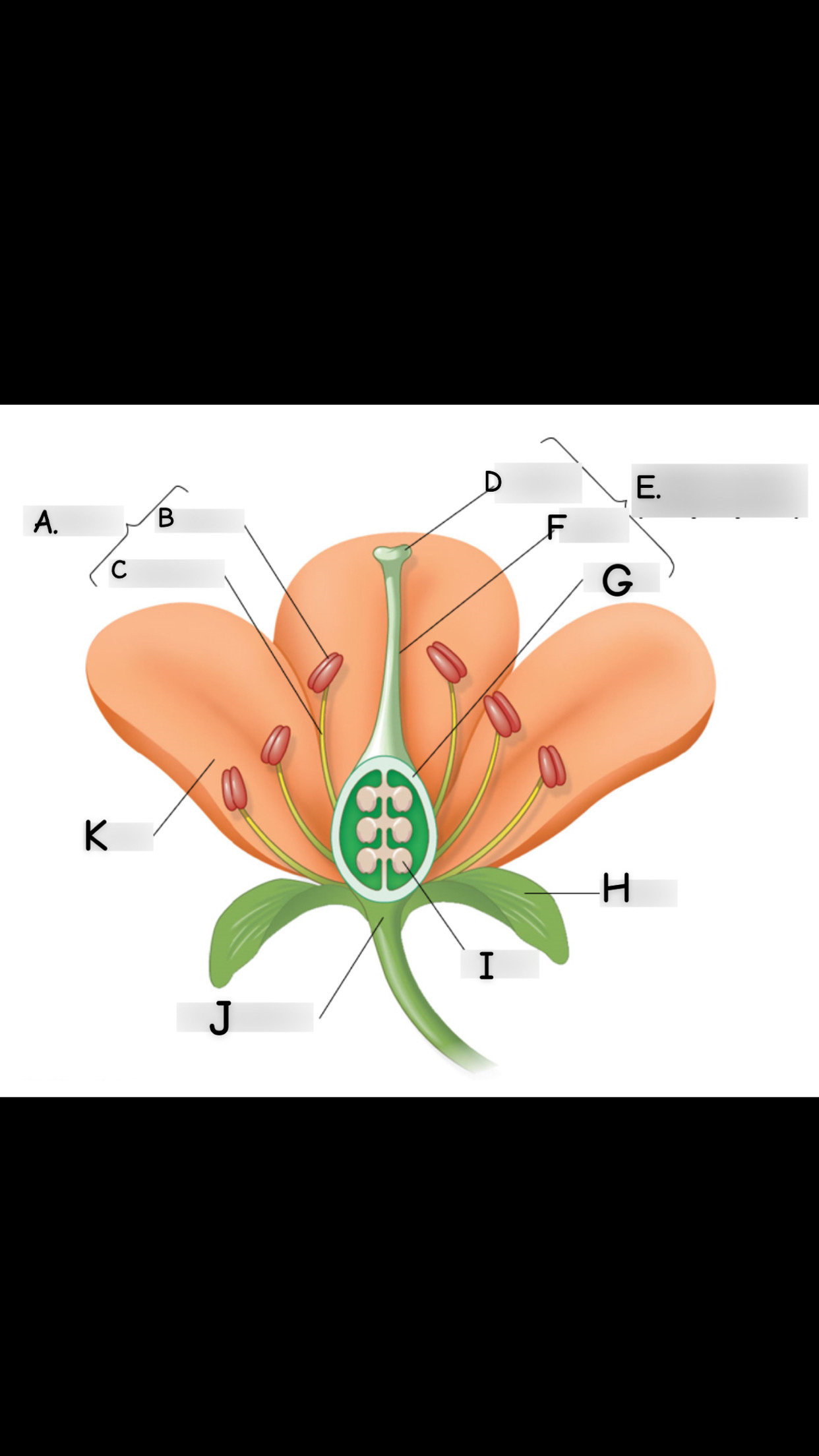
what is E
single carpel
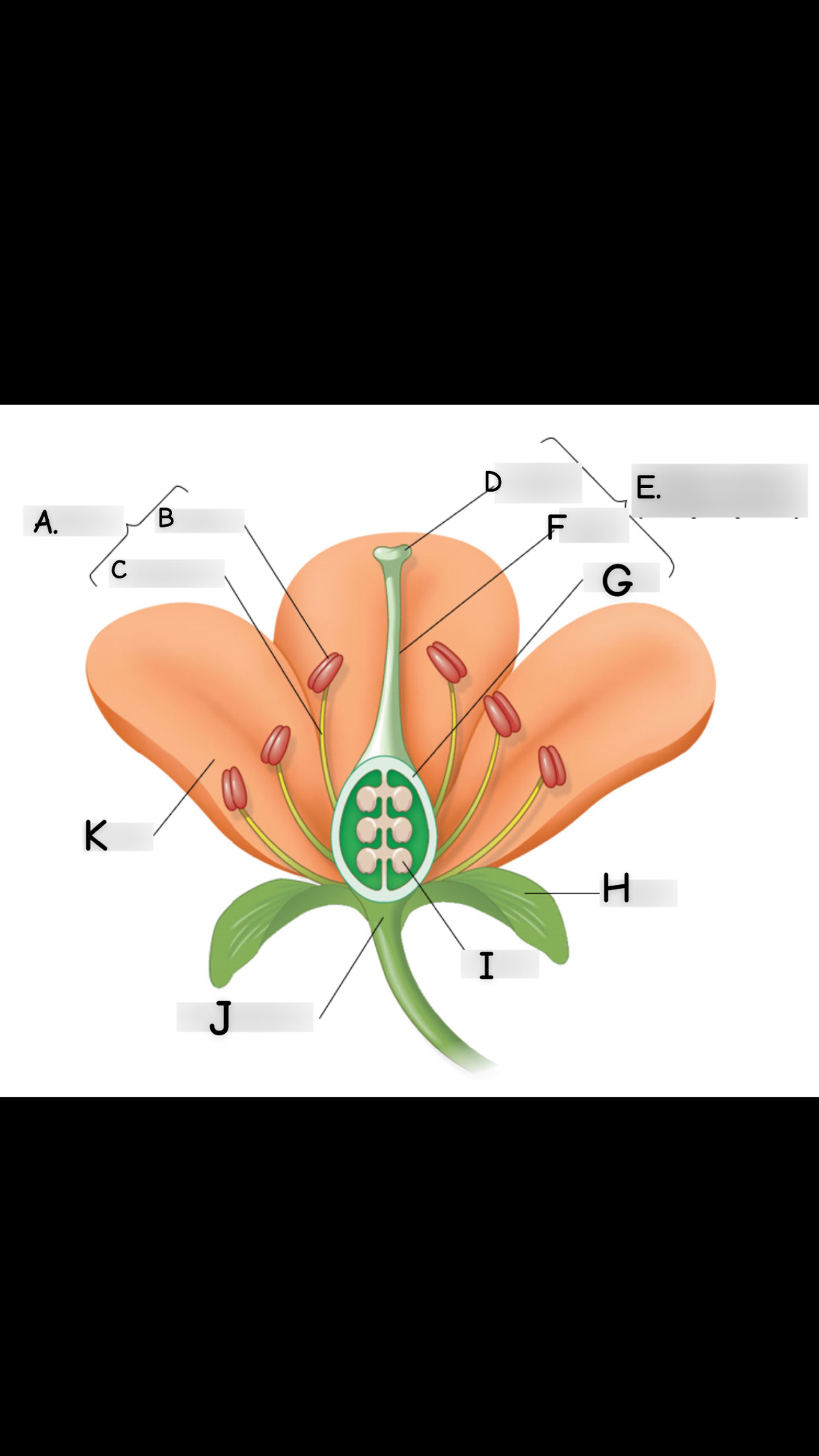
what is F
style
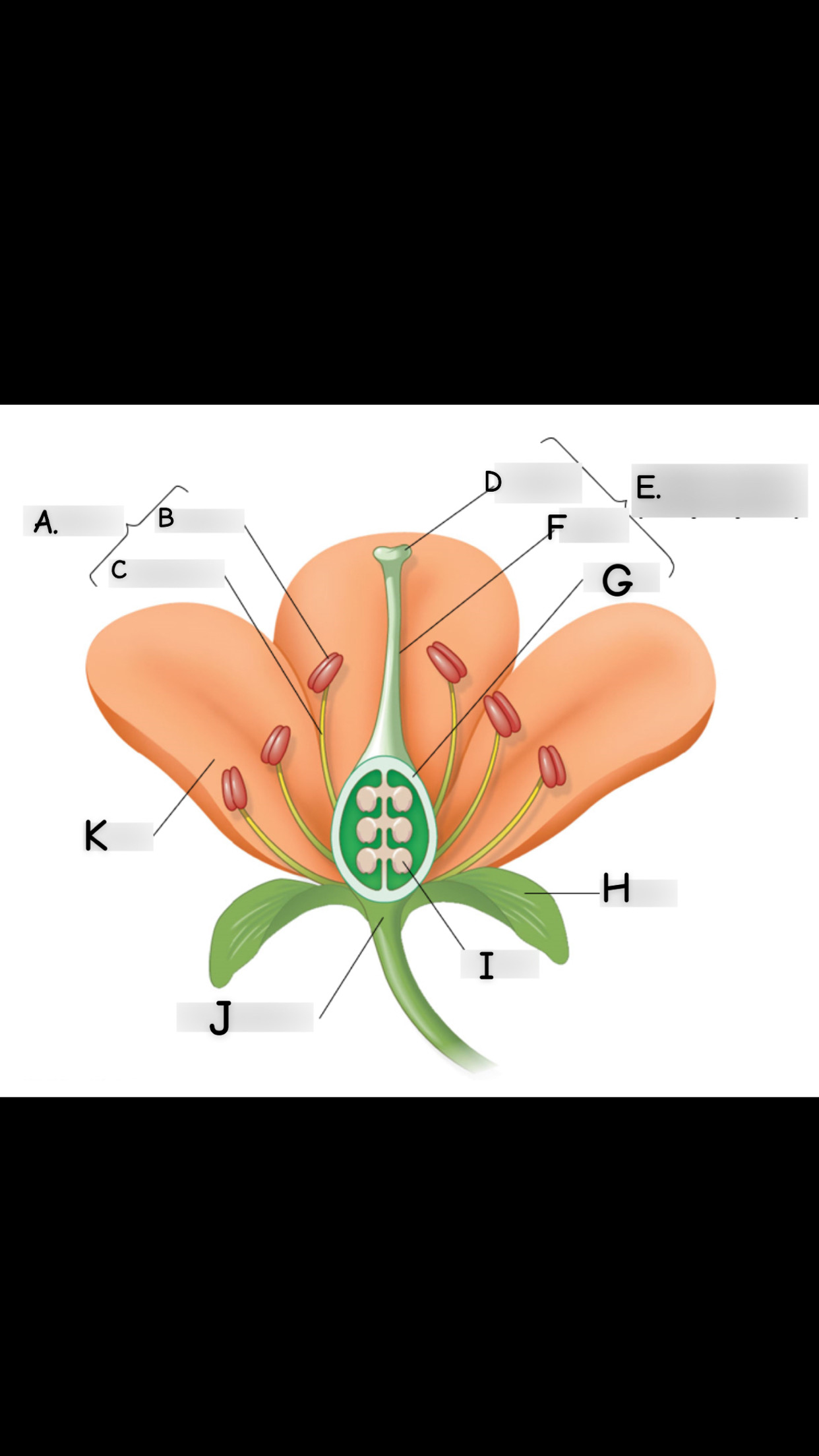
What is G
Ovary
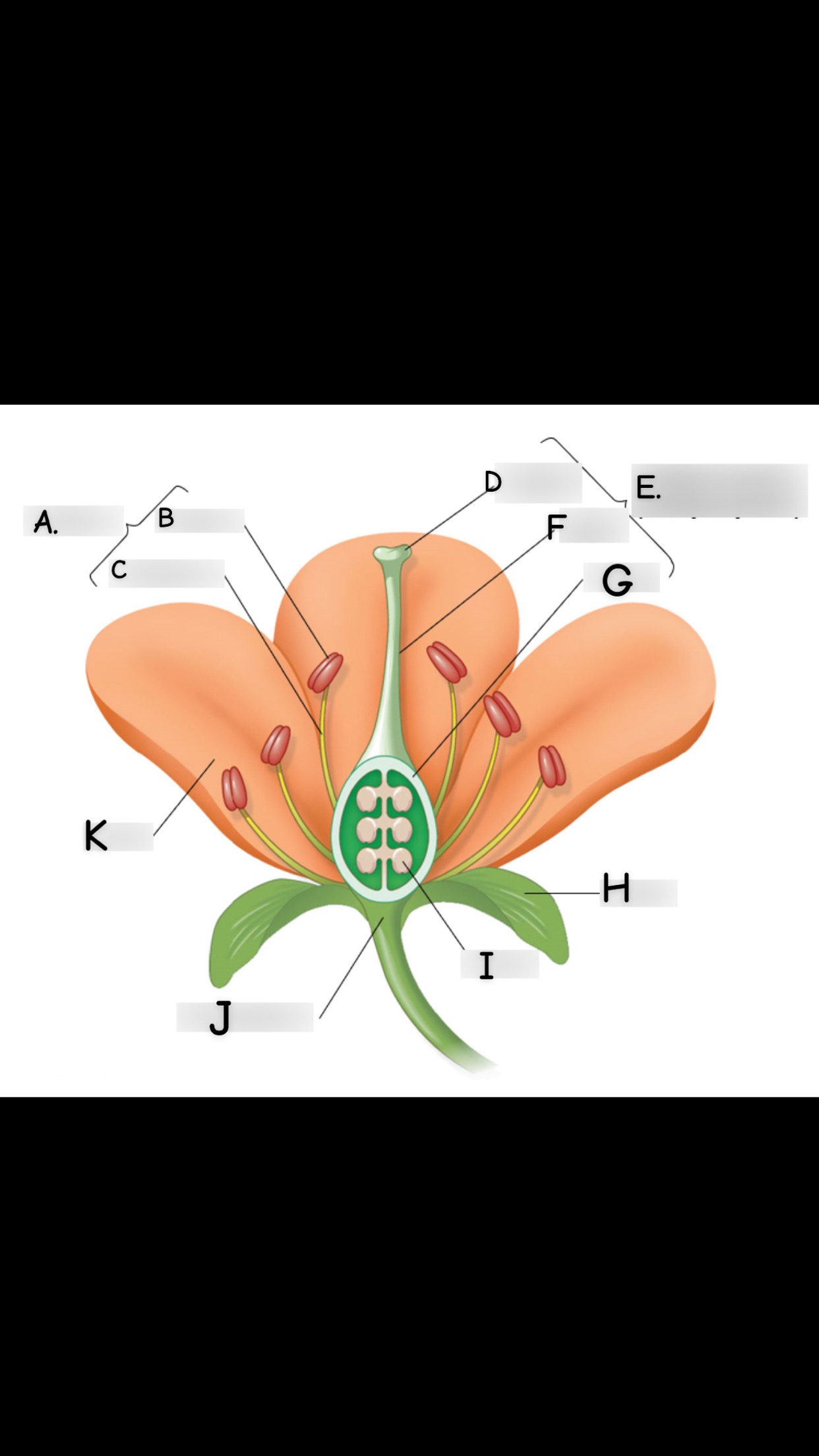
what is H
sepal
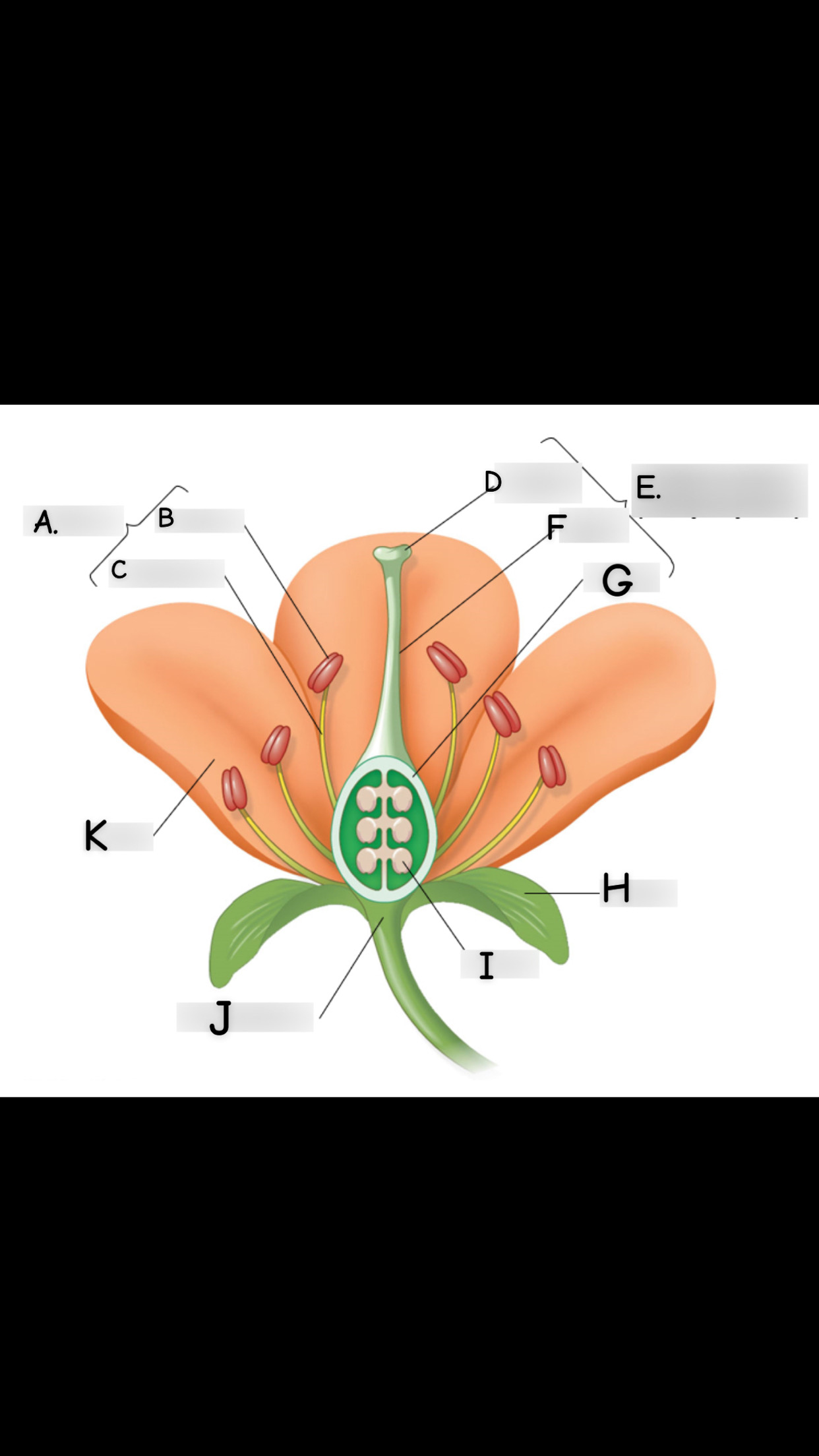
what is I
ovule
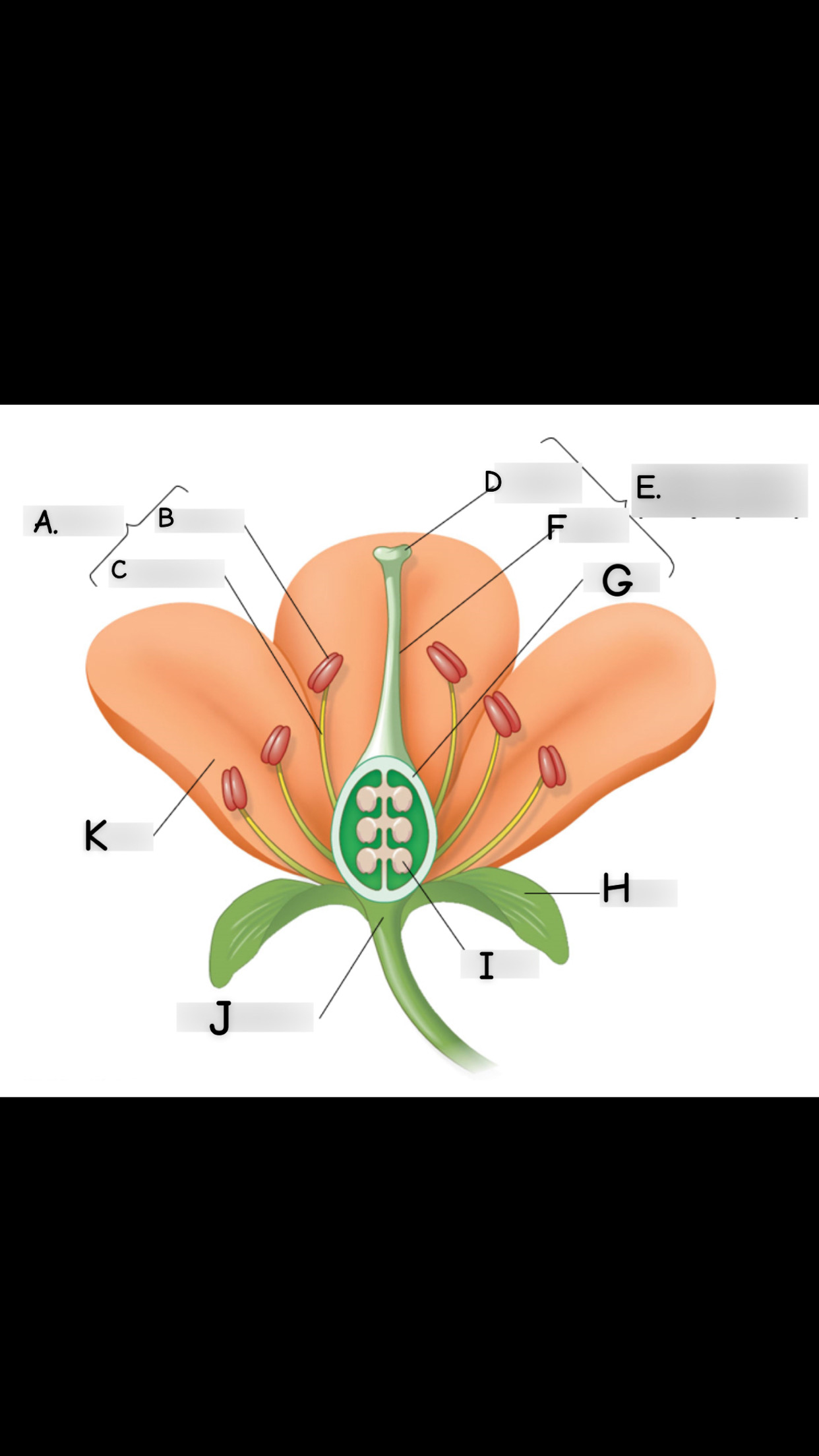
what is J
receptacle
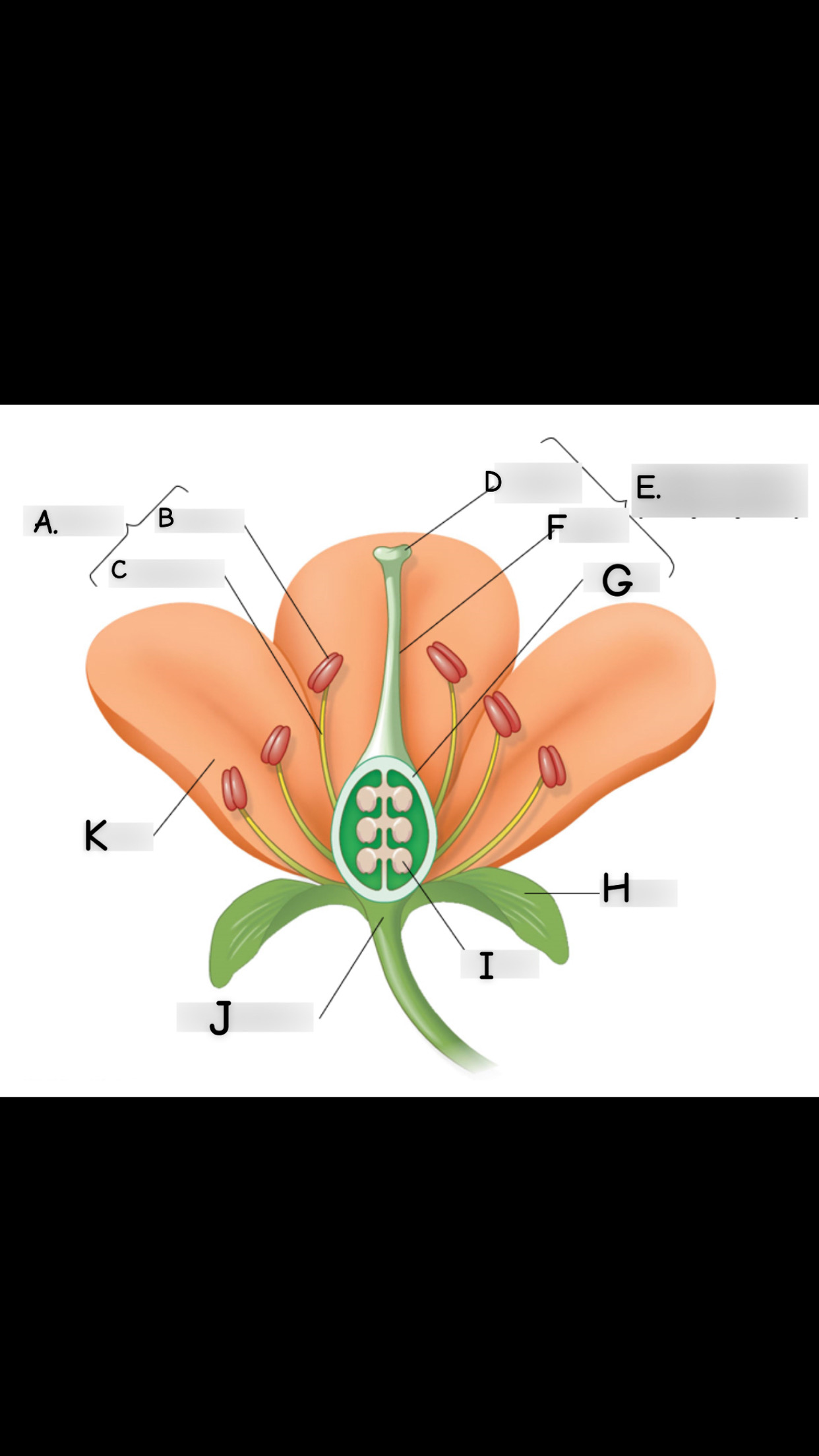
what is K
petal
Embryos: one cotyledon
monocot
leaf venation: veins usually parallel
monocot
stems: vascular tissue scattered
monocot
roots: root stem usually fibrous
monocot
pollen: pollen grain with one opening
monocot
flowers: floral organs usually in multiples of three
monocot
embryos: two cotyledons
eudicot
leaf variation: veins usually netlike
eudicot
stems: vascular tissue usually arranged in ring
eudicot
roots: taproot usually present
eudicot
pollen: pollen grain with three openings
eudicot
flowers: floral organs usually in multiples of four or five
eudicot
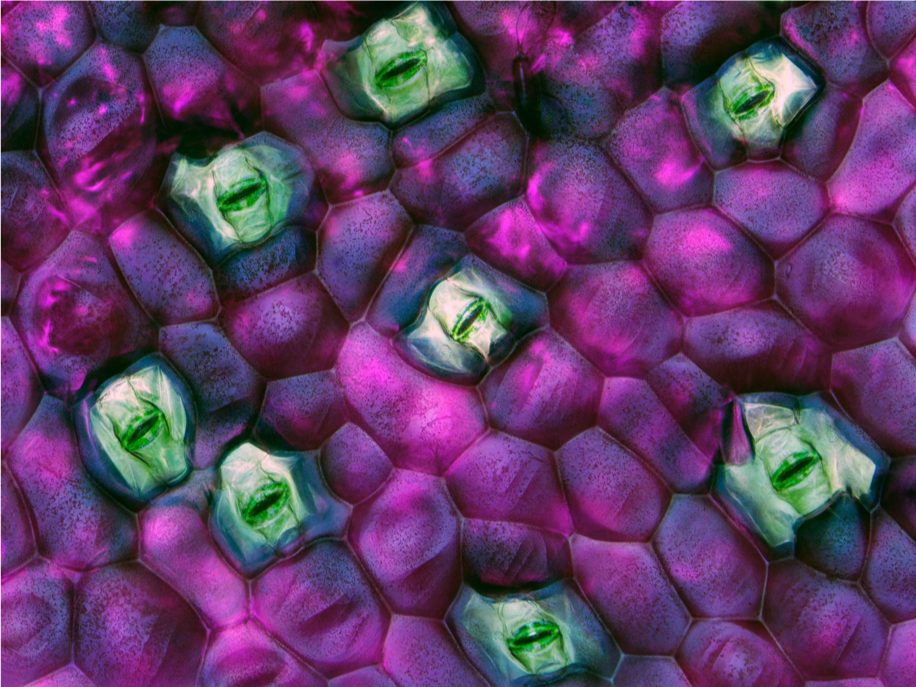

tradescantia, leaf stomata
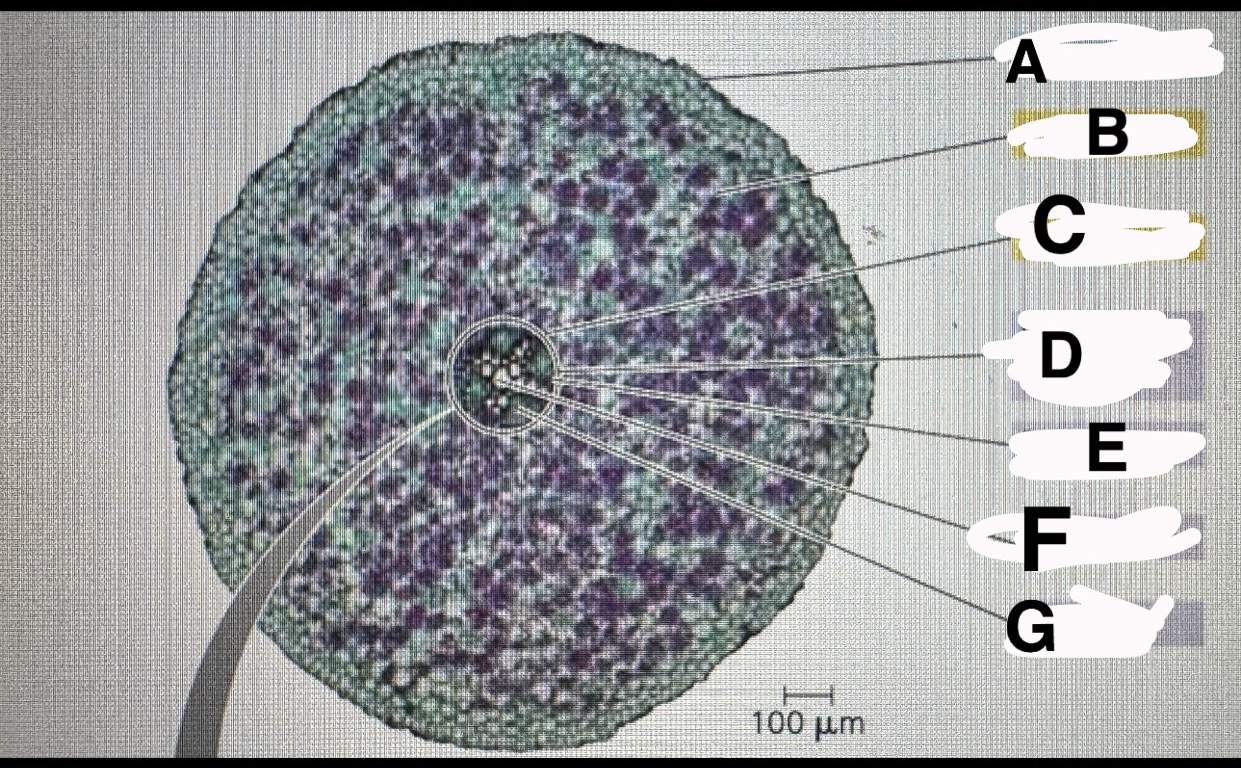
What is A
Eudicot root:epidermis
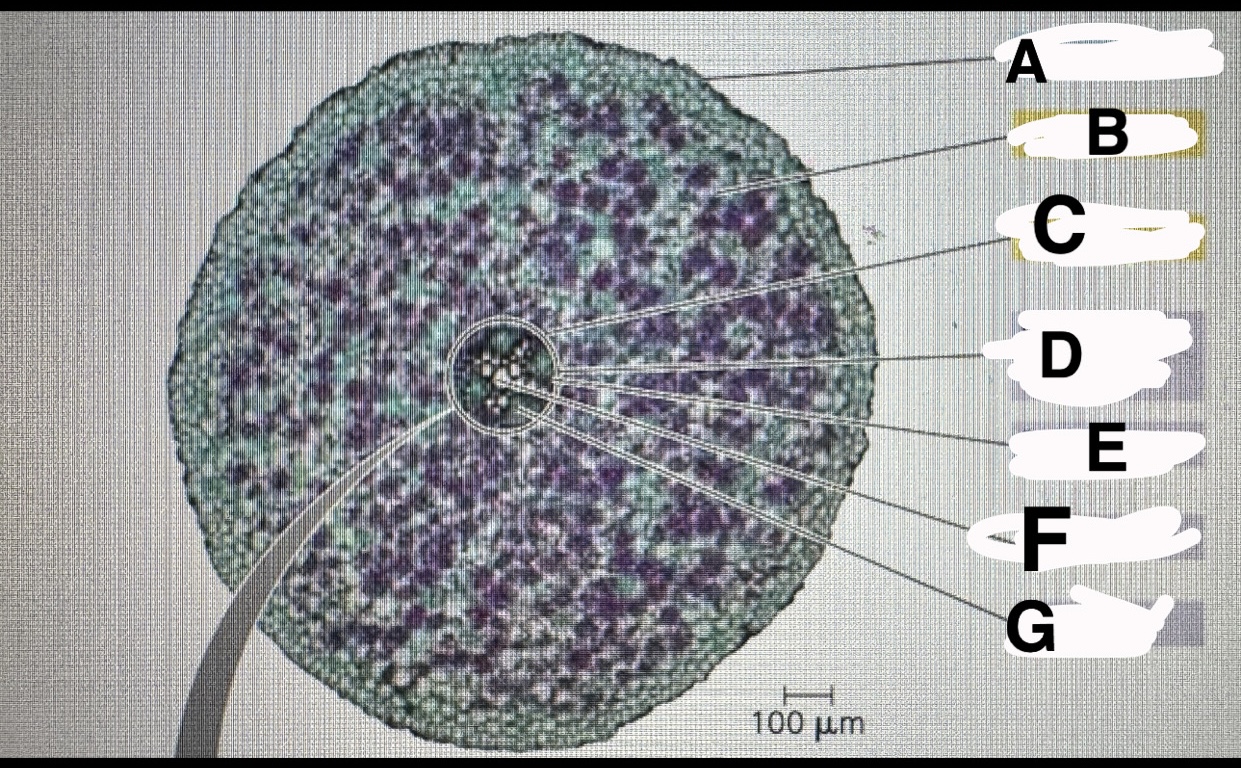
B?
Eudicot root:cortex
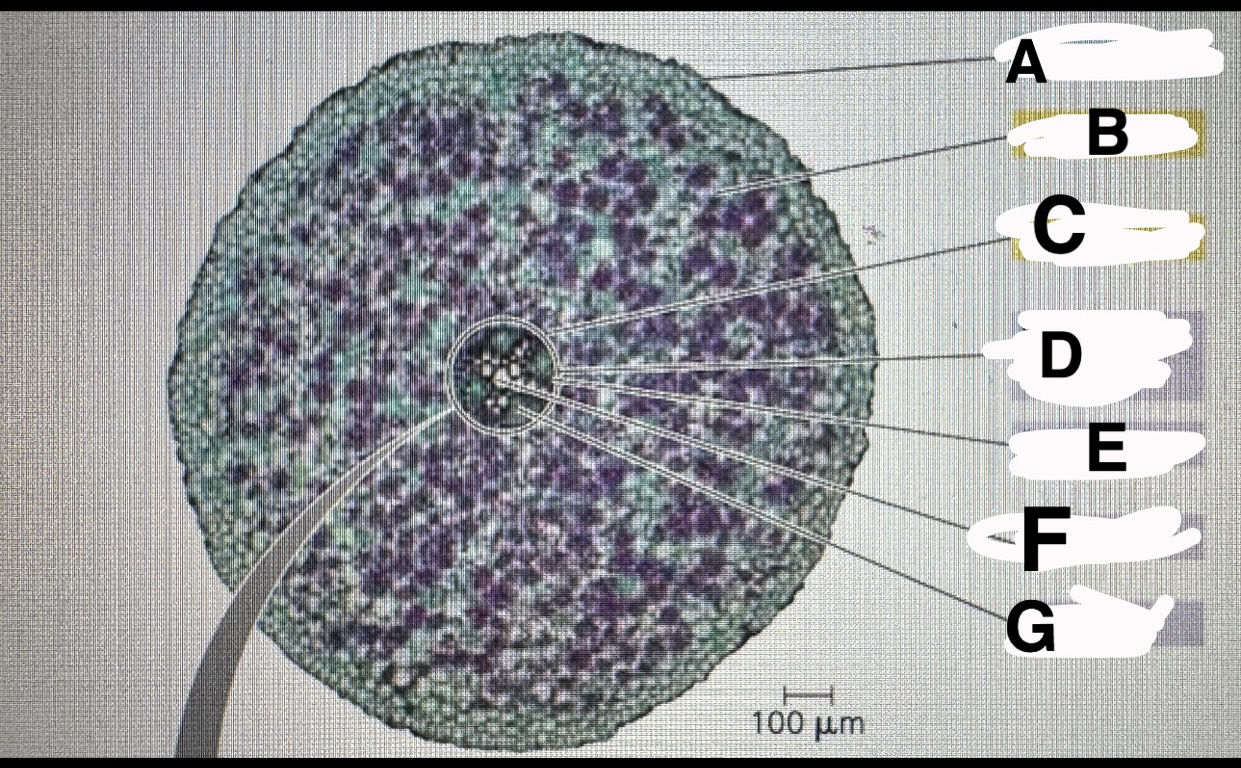
C?
Eudicot root:endodermis
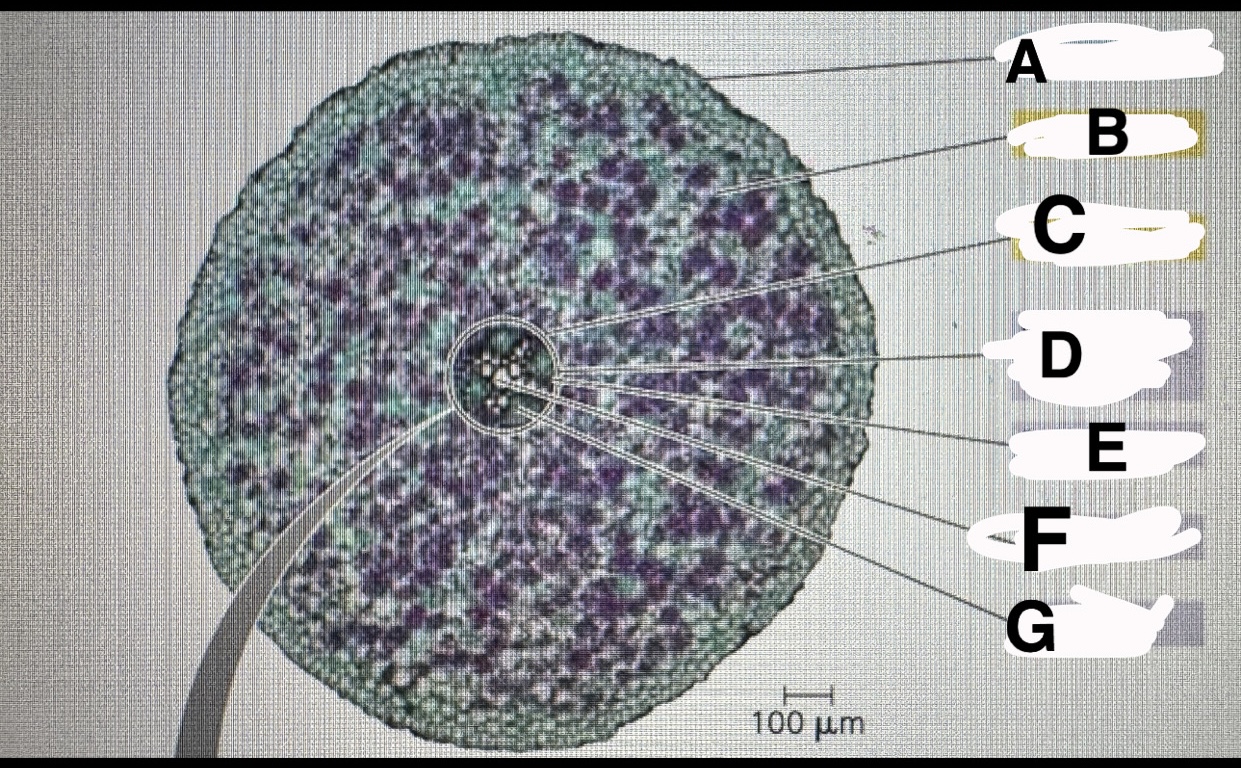
D?
Eudicot root:vascular cylinder
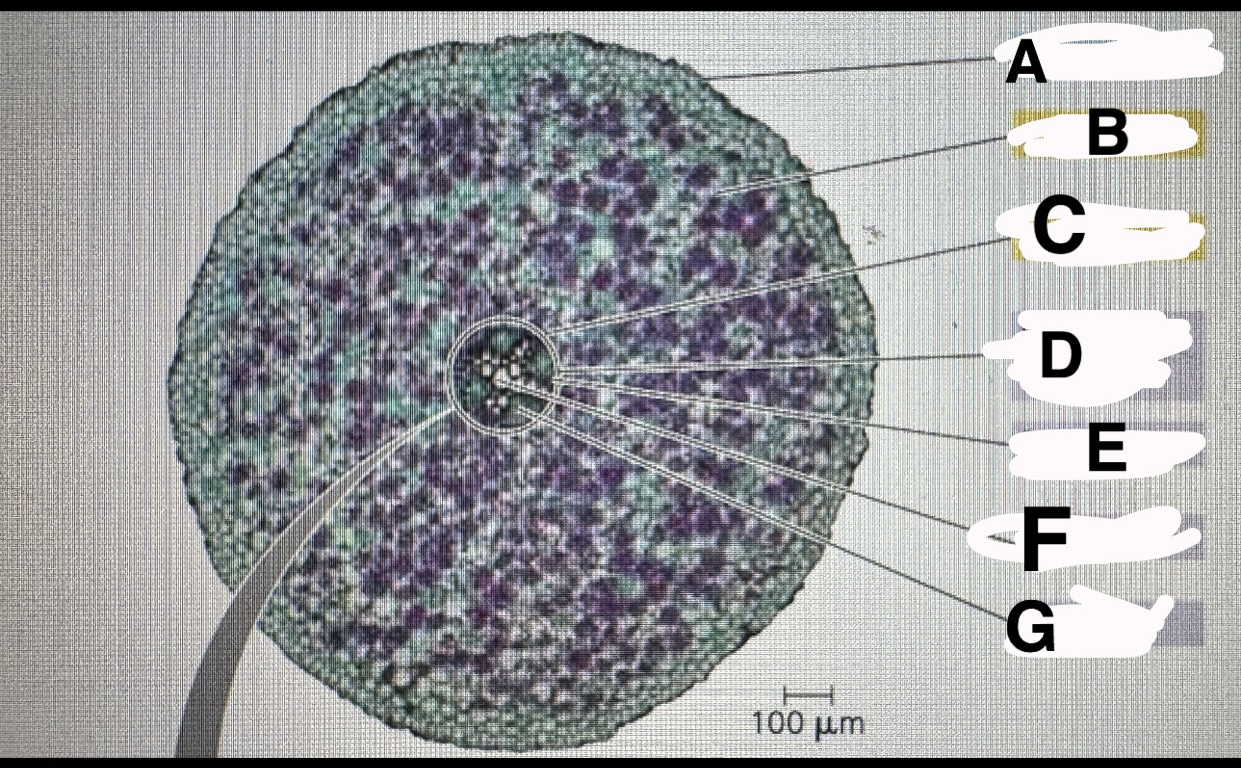
E?
Eudicot root: pericycle
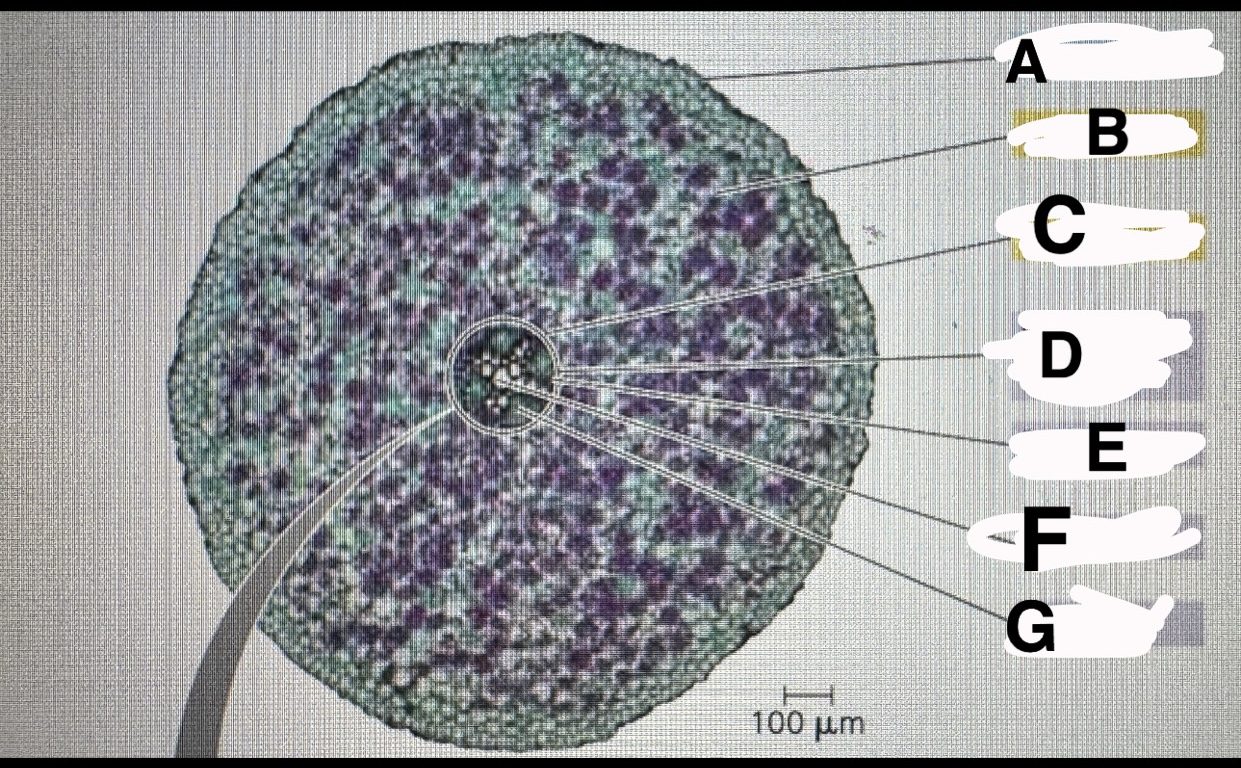
F?
Eudicot root:xylem
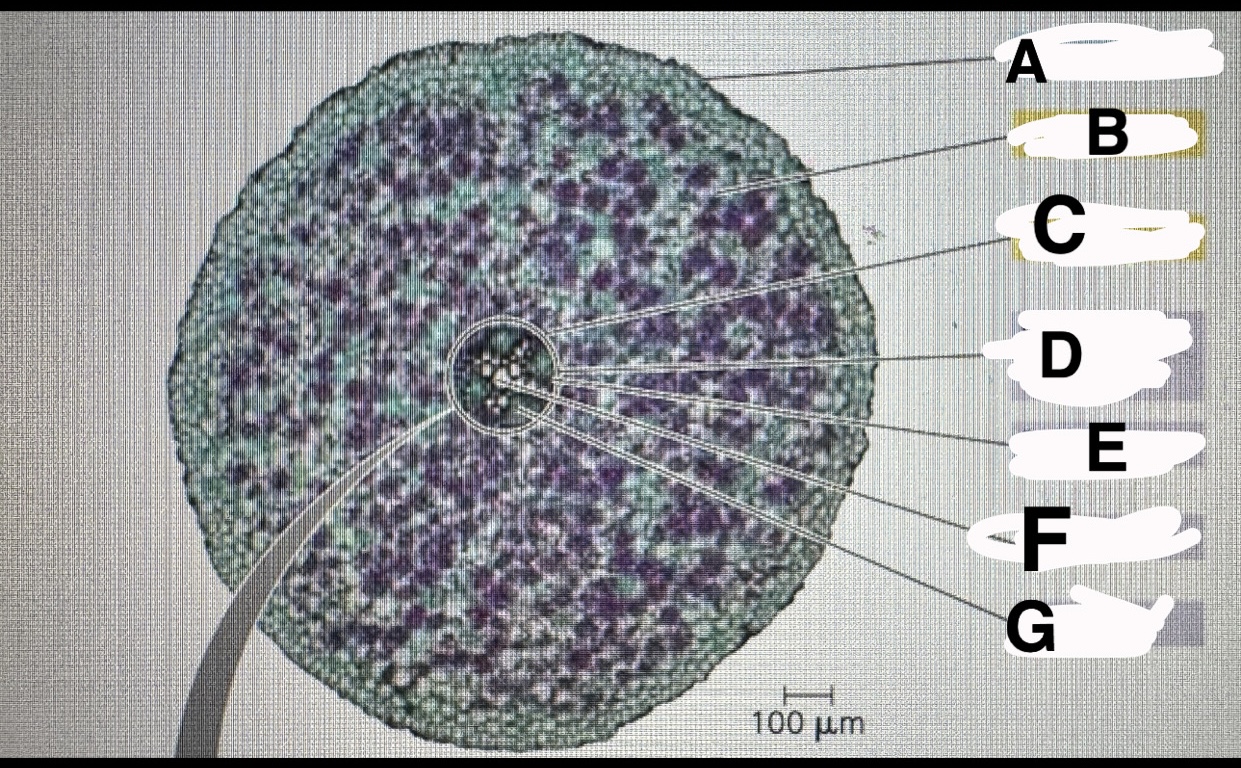
G?
Eudicot root: phloem
A?
monocot root: epidermis
B?
monocot root:cortex
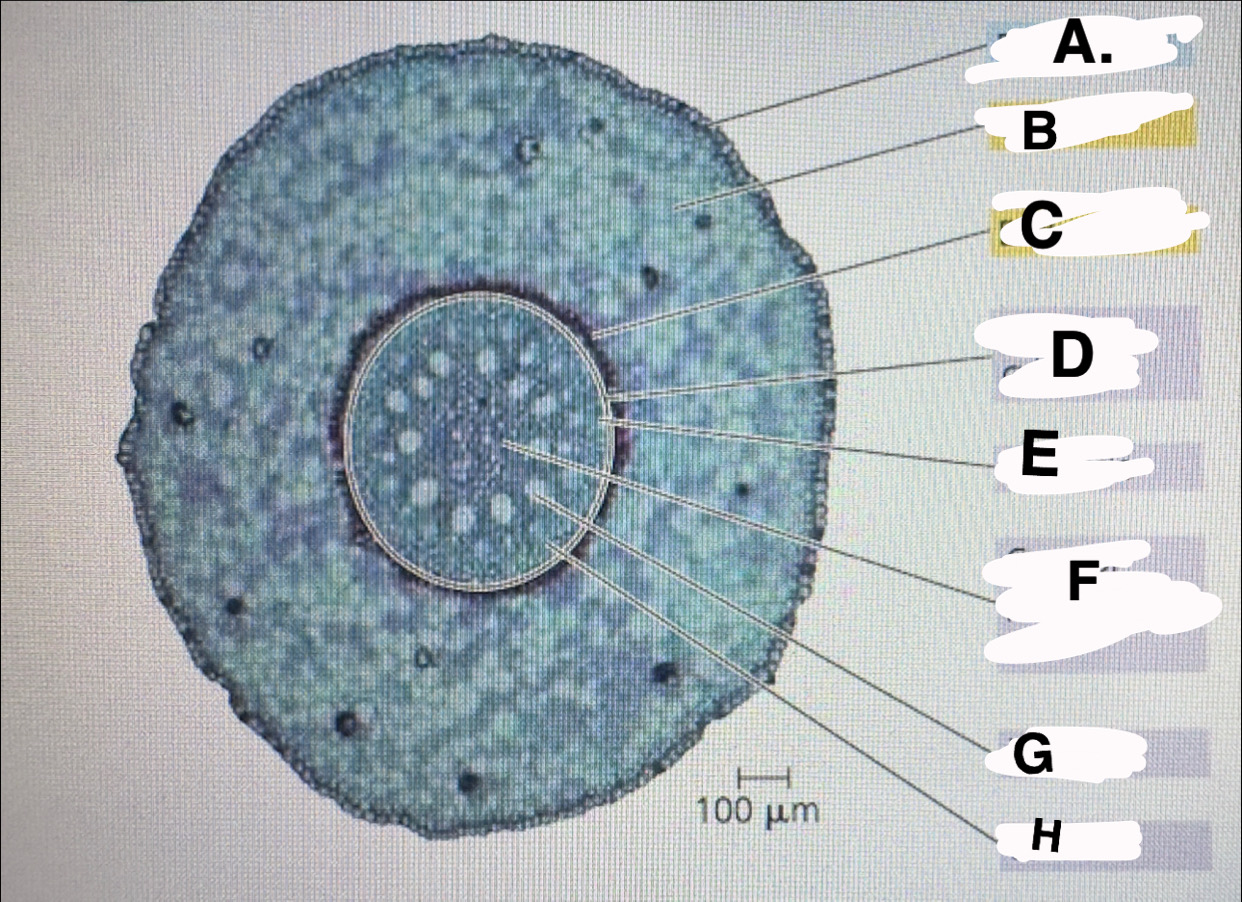
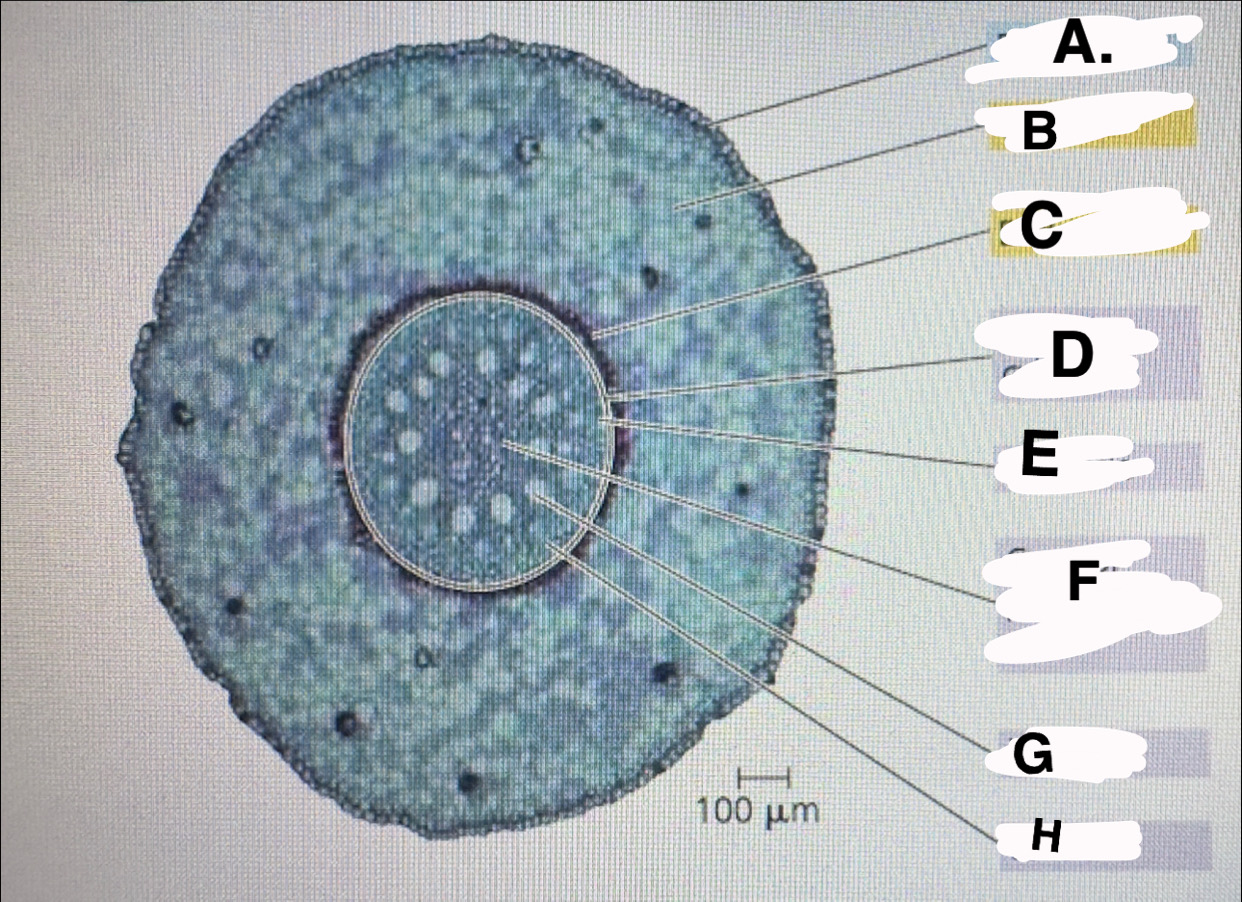
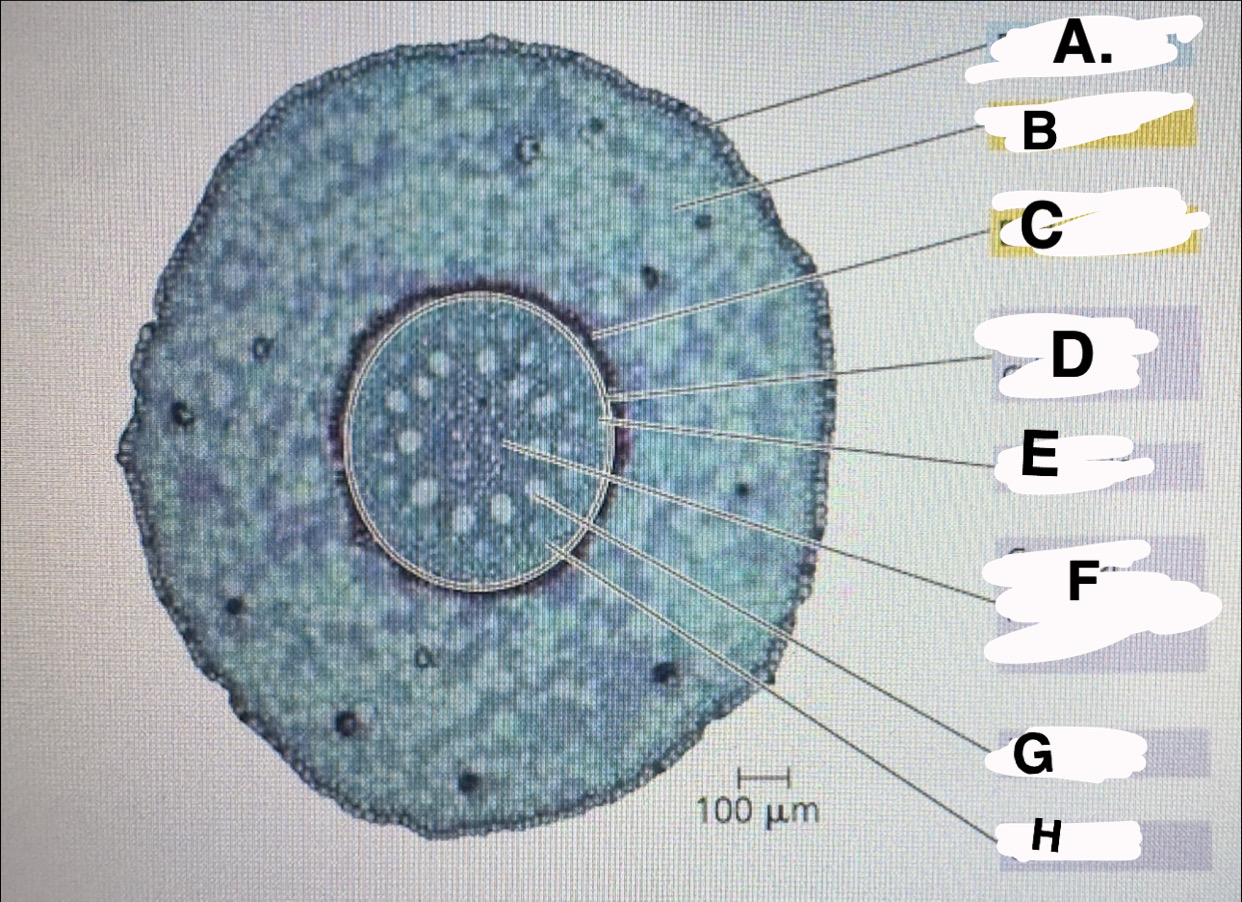
c?
monocot root:endodermis
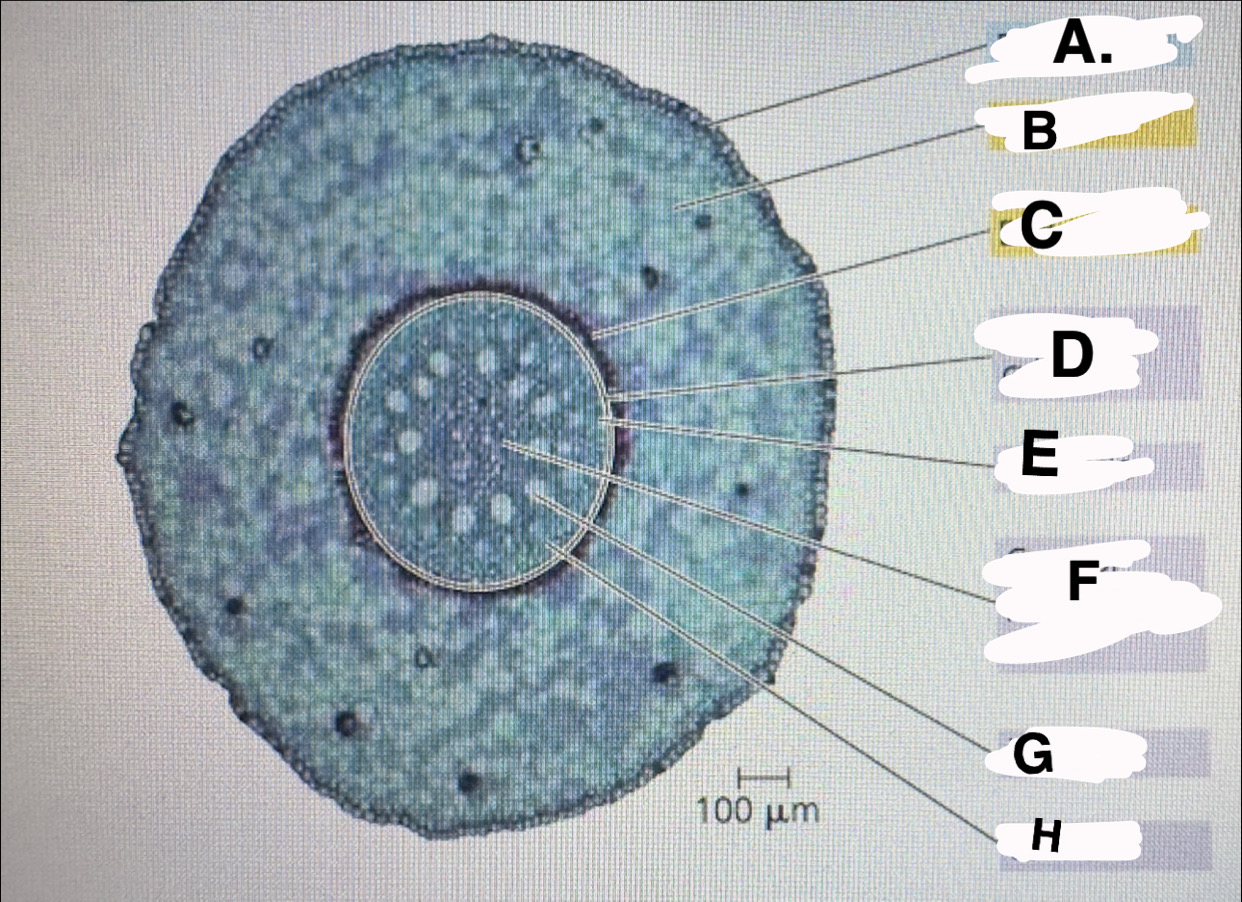
d?
monocot root:vascular cylinder
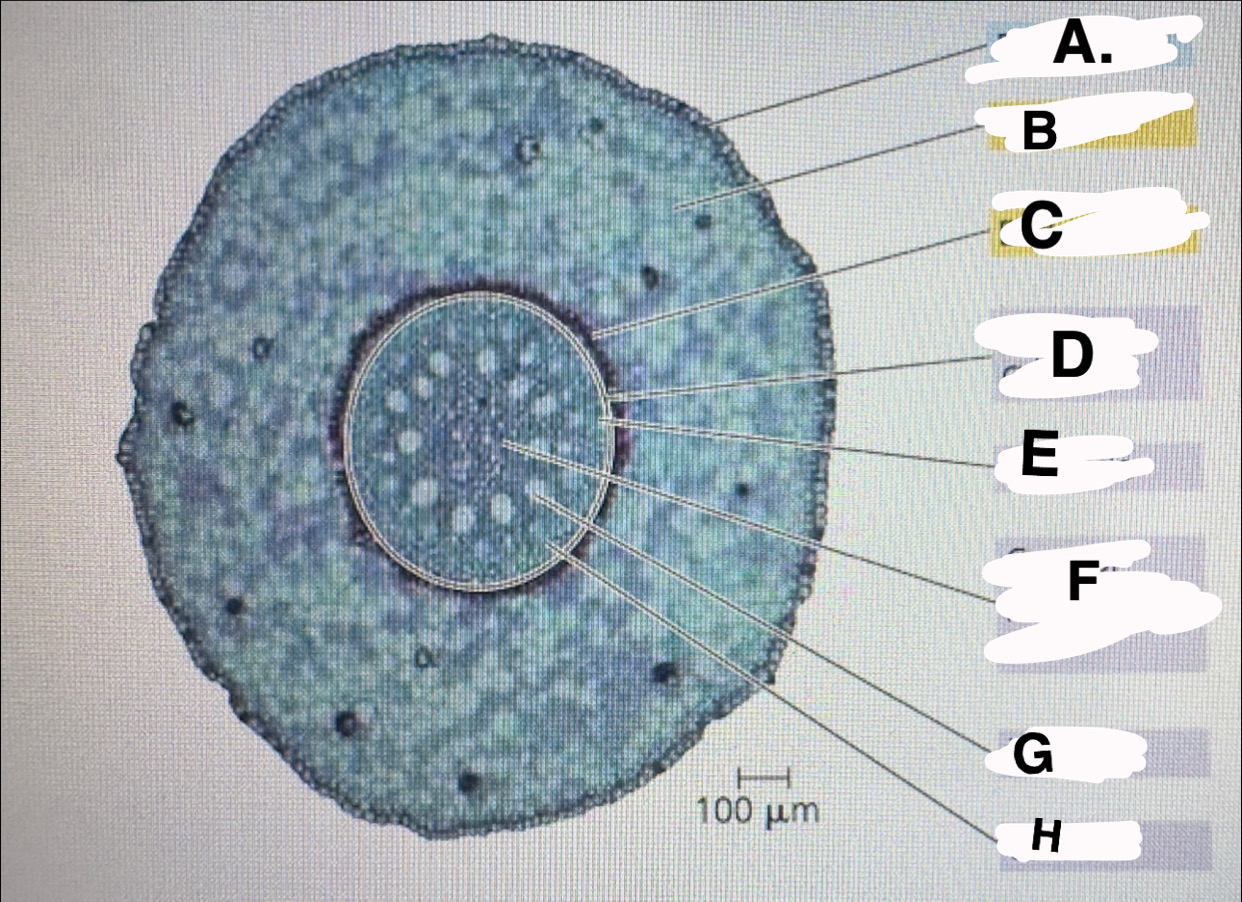
E?
monocot root:pericycle
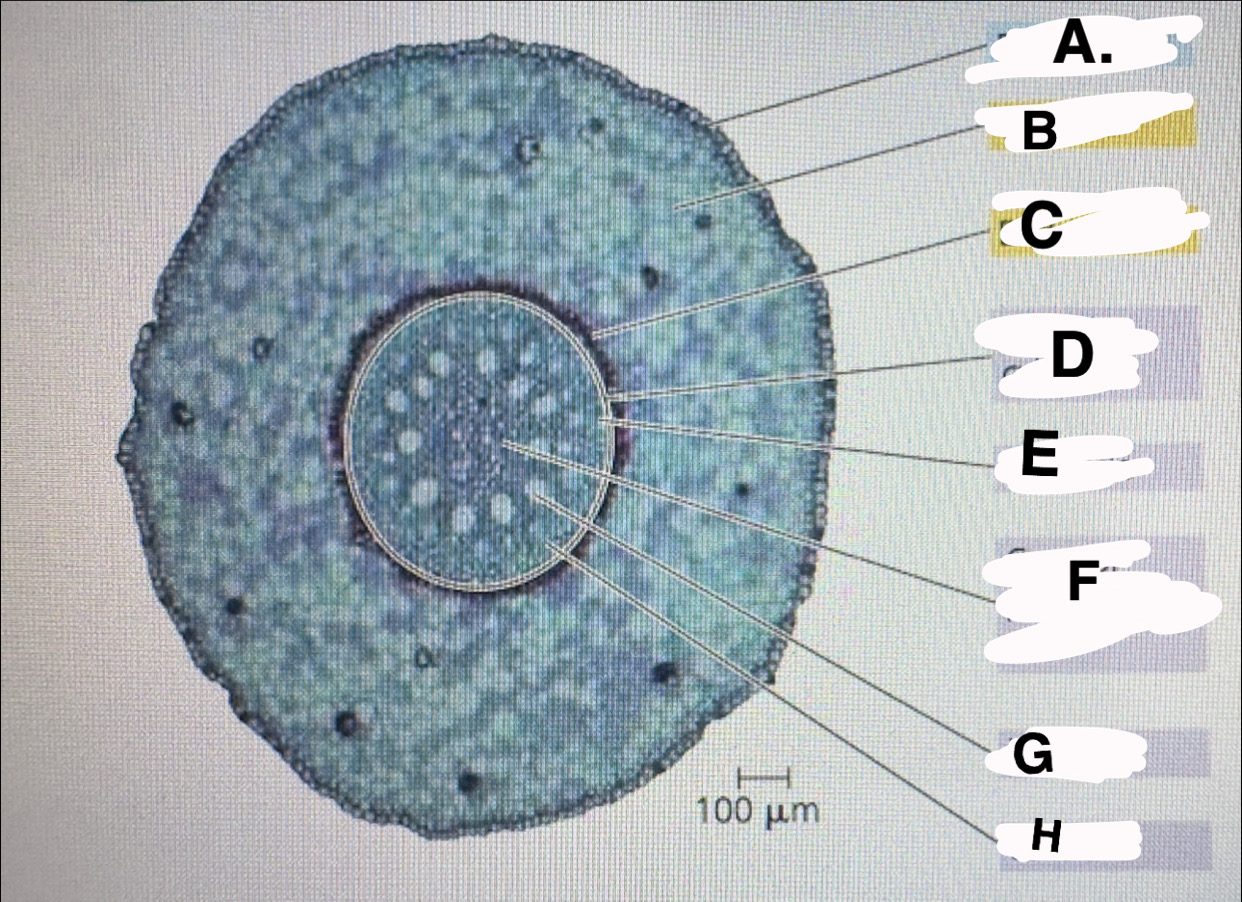
F?
monocot root: core of parenchyma
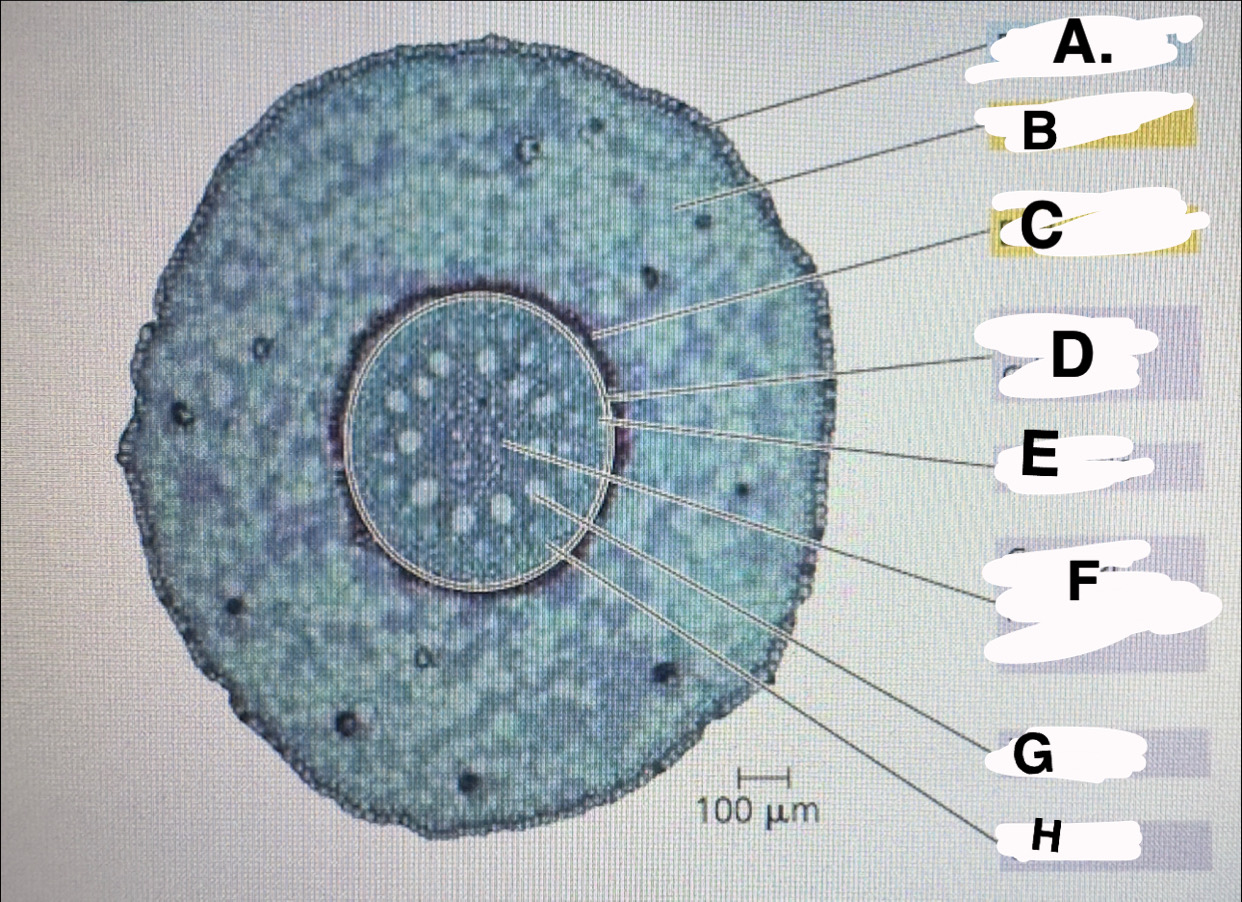
G
monocot root: xylem
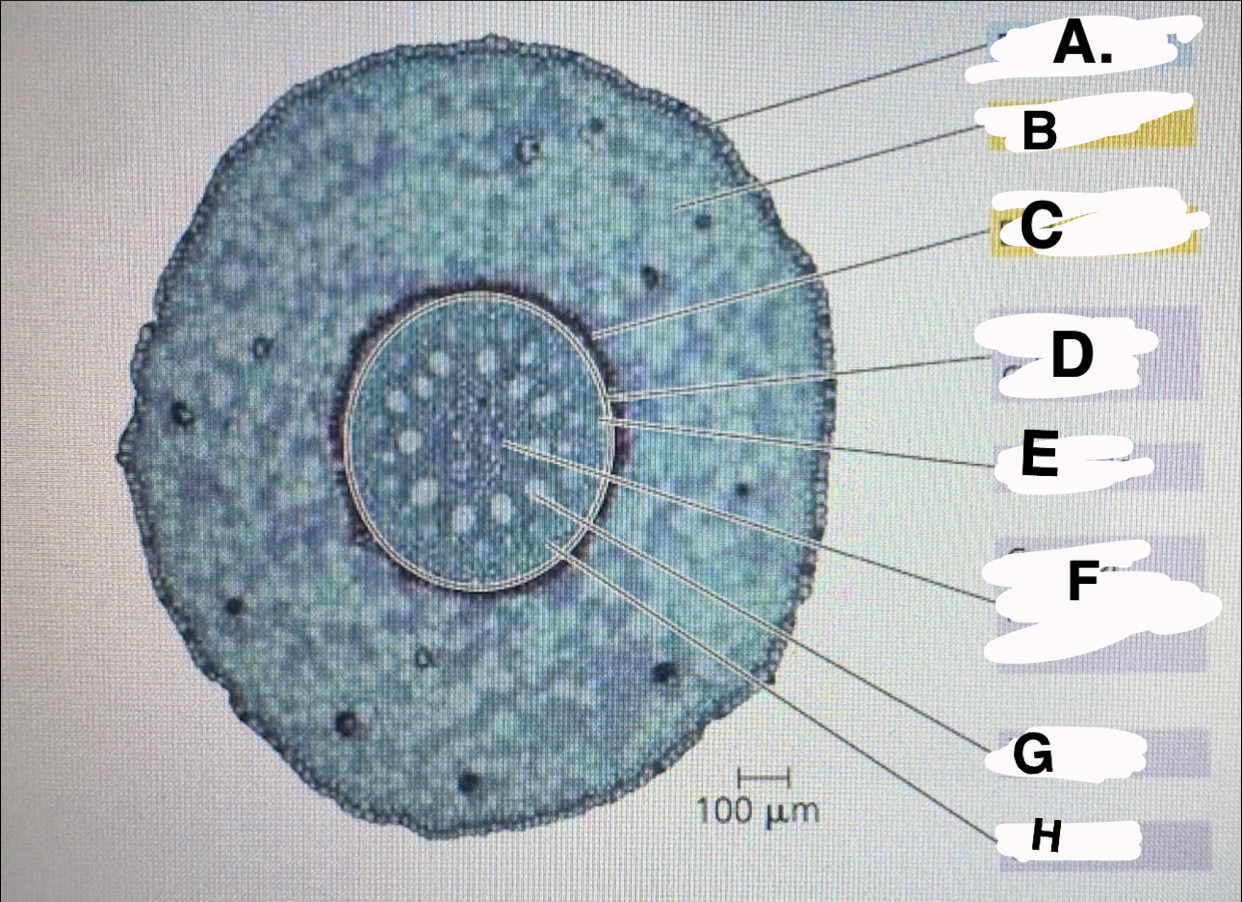
H
monocot root:phloem
what does phloem look like?
tinier dots outside of the xylem
what does xylem look like?
bigger circles surrounded by phloem
describe palasade
packed tightly
describe spongey
open, saggy look
describe stomates
spongey side since gases move here
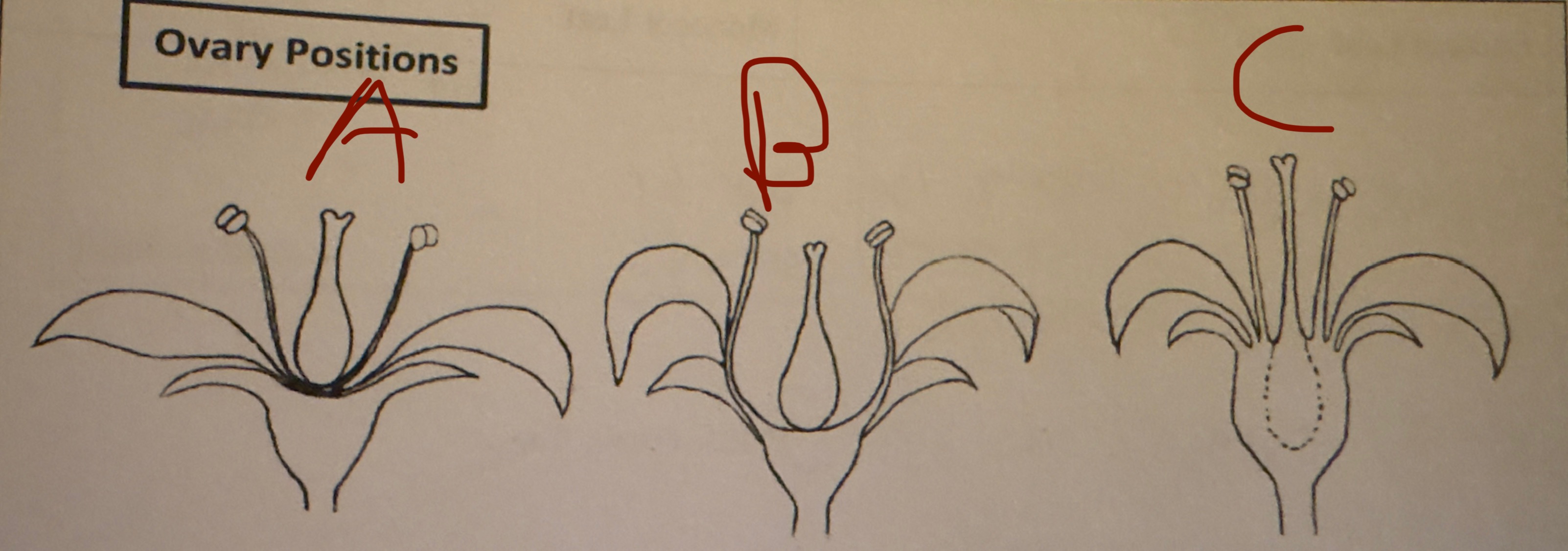
A?
Hypogynous
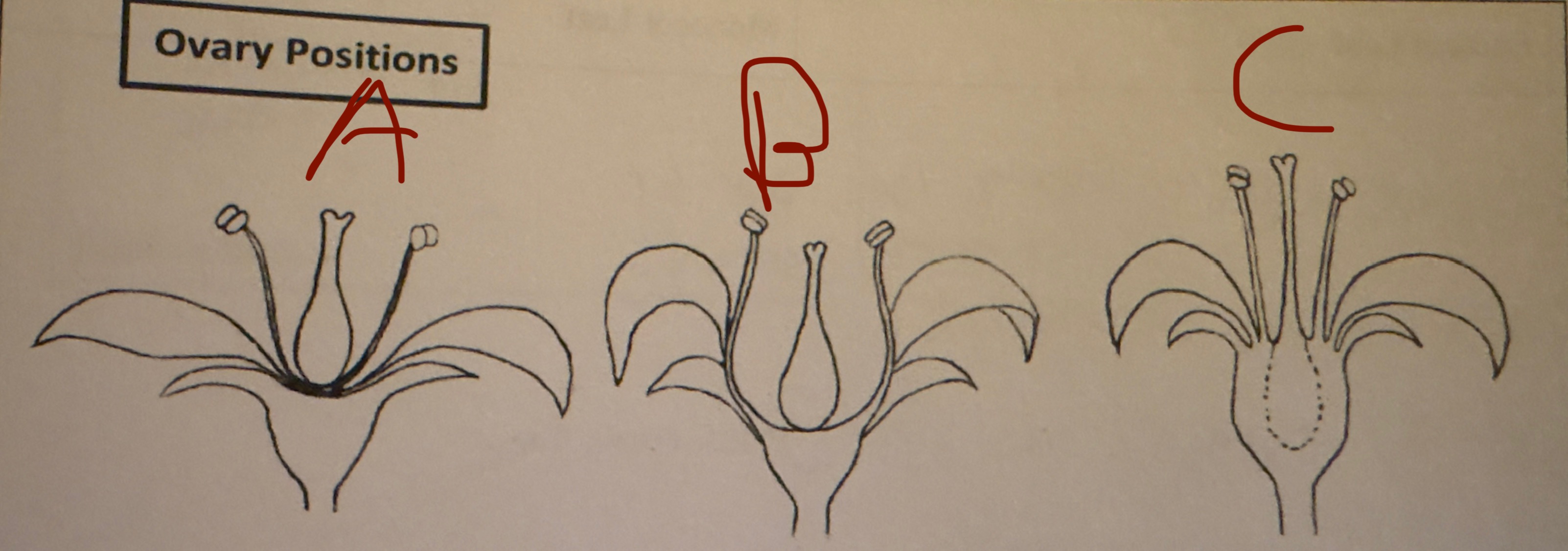
B?
perigynous
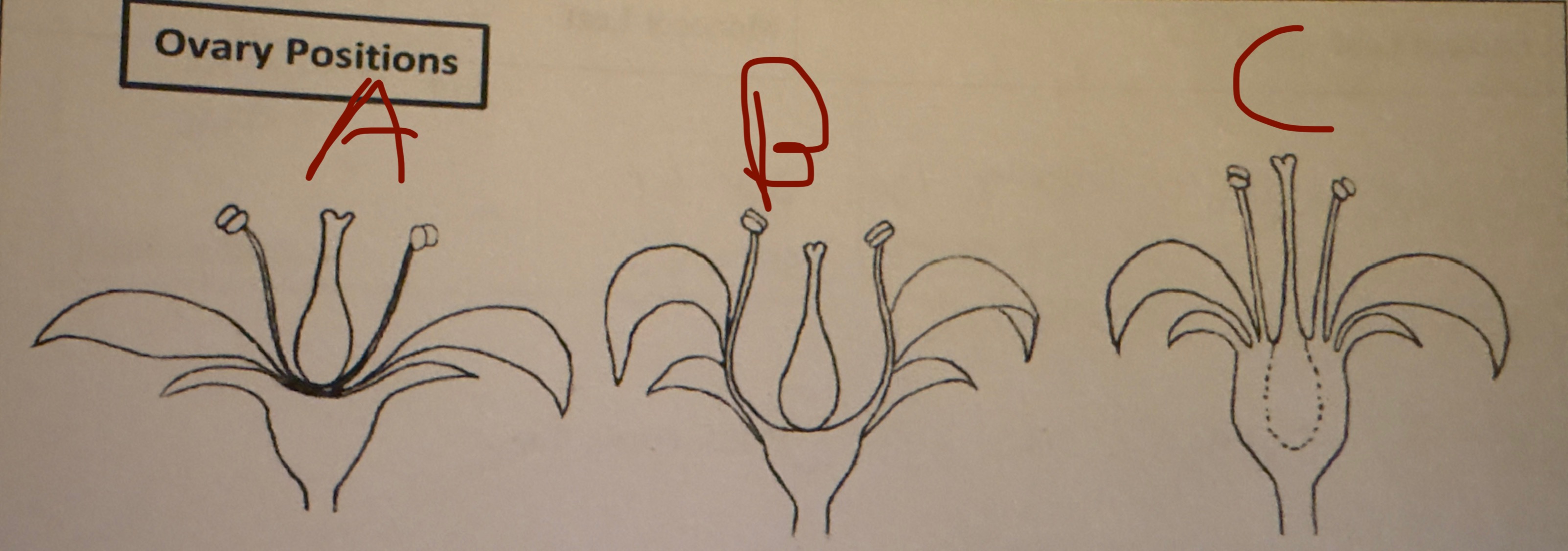
C?
epigynous
increase in length
primary growth
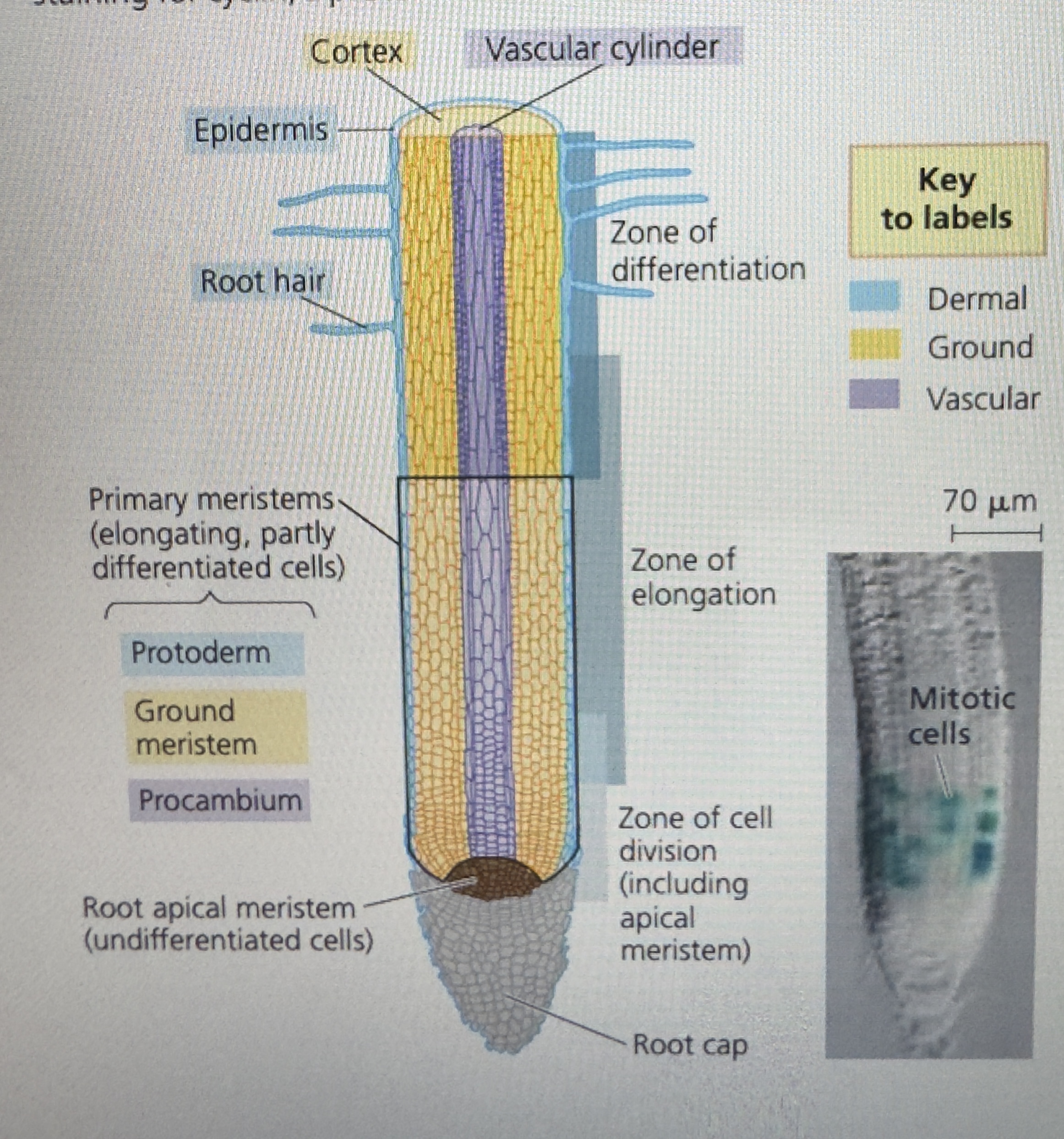
be familiar with where apical meristem is
process of mitosis, root growing tip
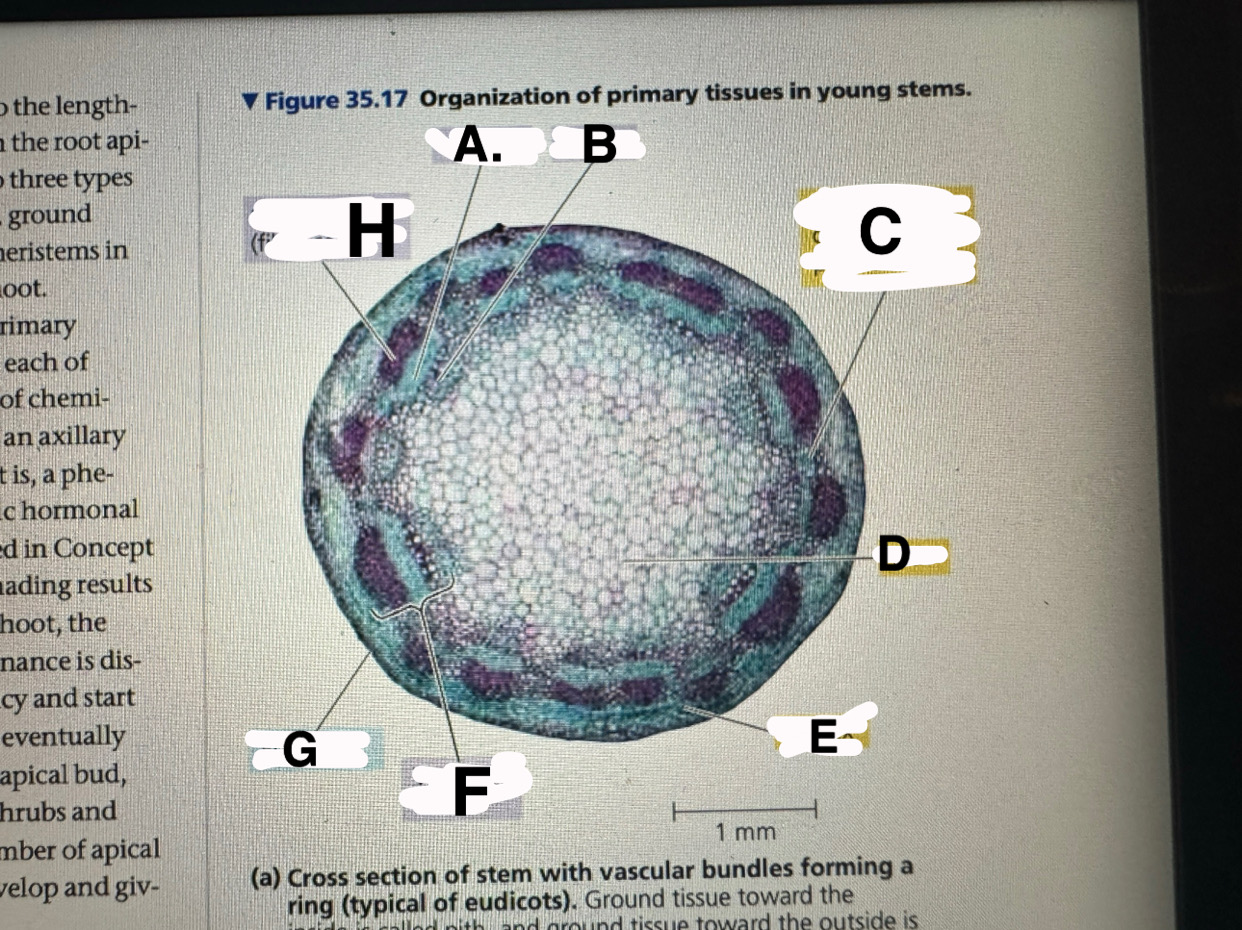
A?
eudicot stem: phloem
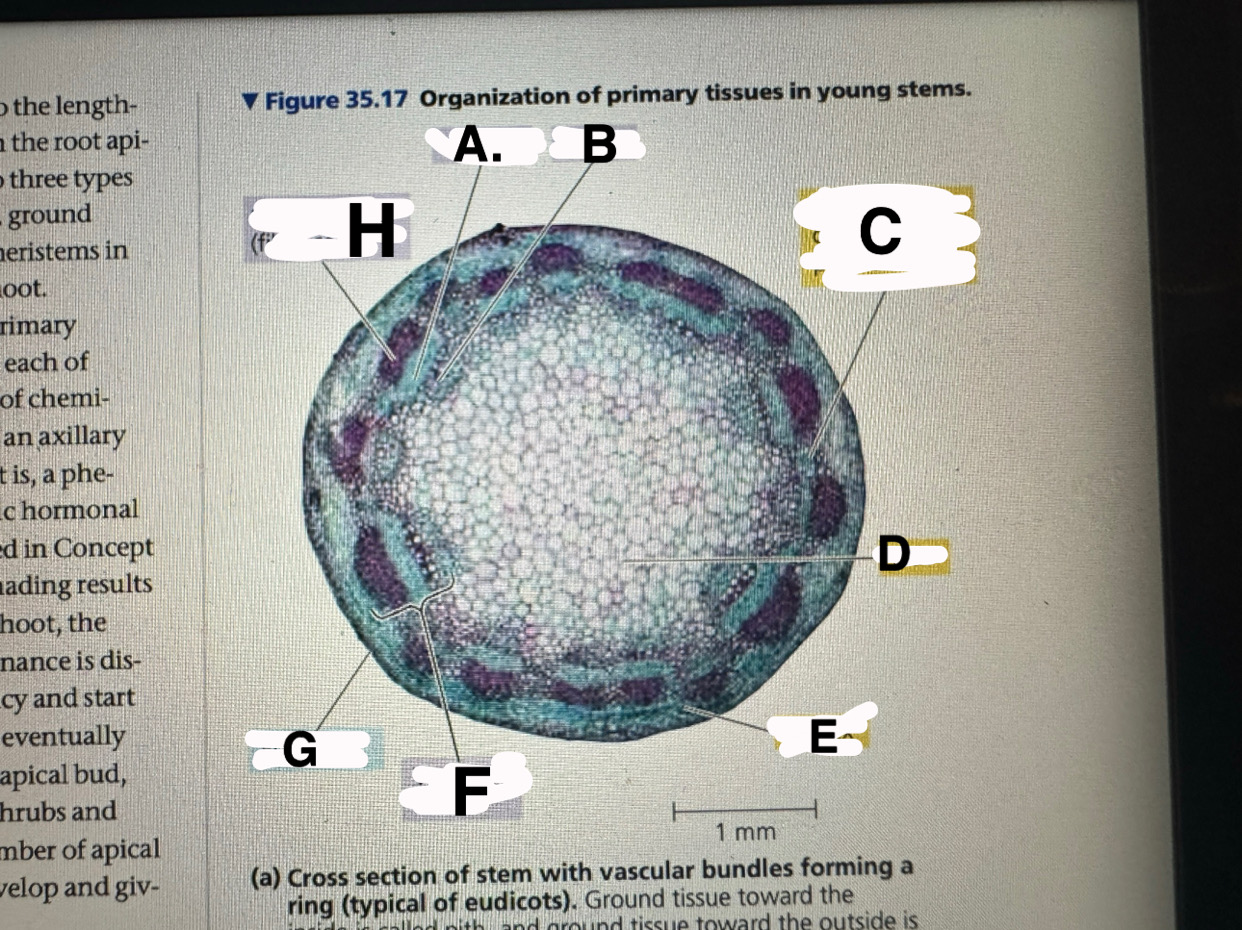
B?
eudicot stem: XYLEM
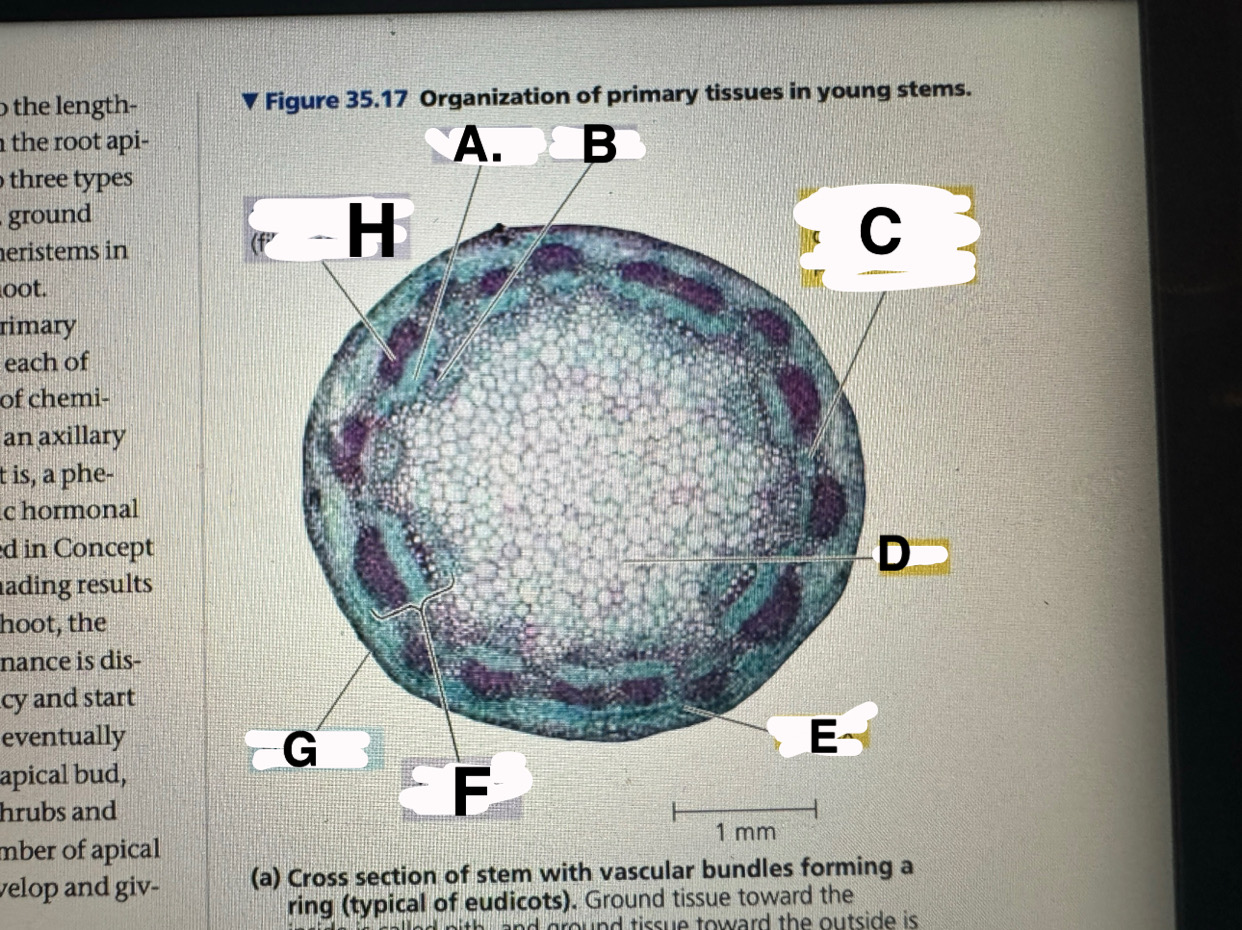
c?
eudicot stem: ground tissue connecting pith to cortex
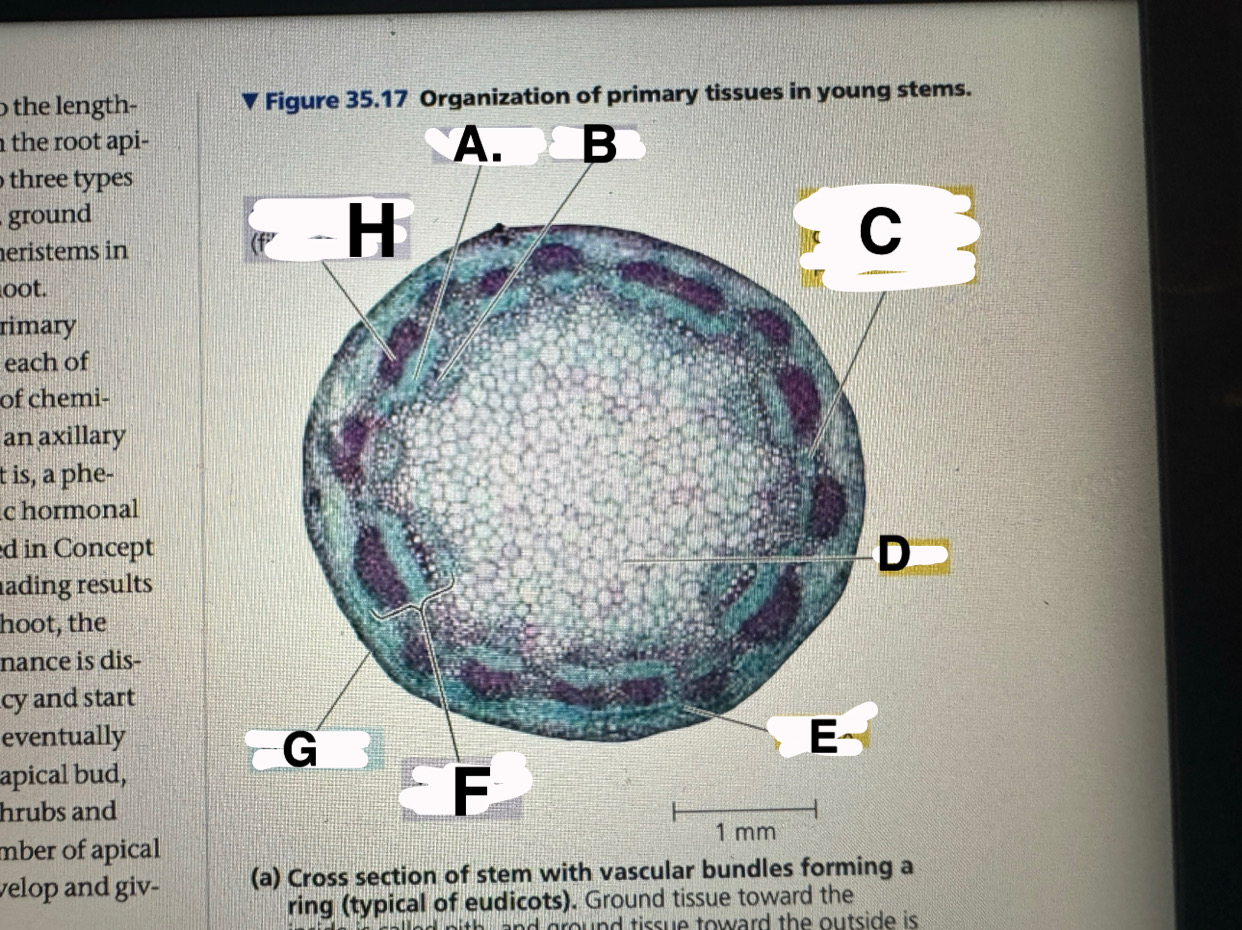
d
eudicot stem: pith
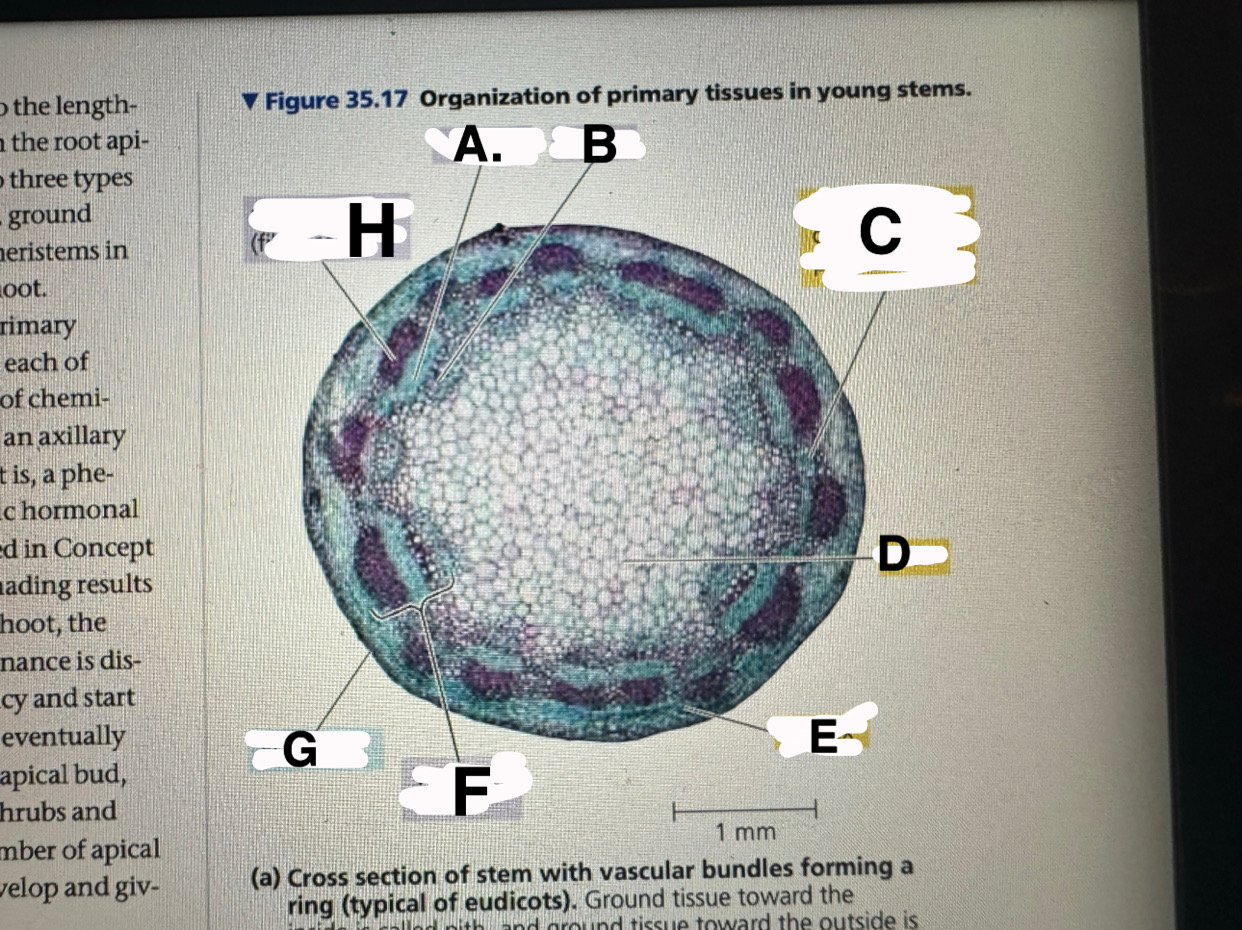
e
eudicot stem: cortex
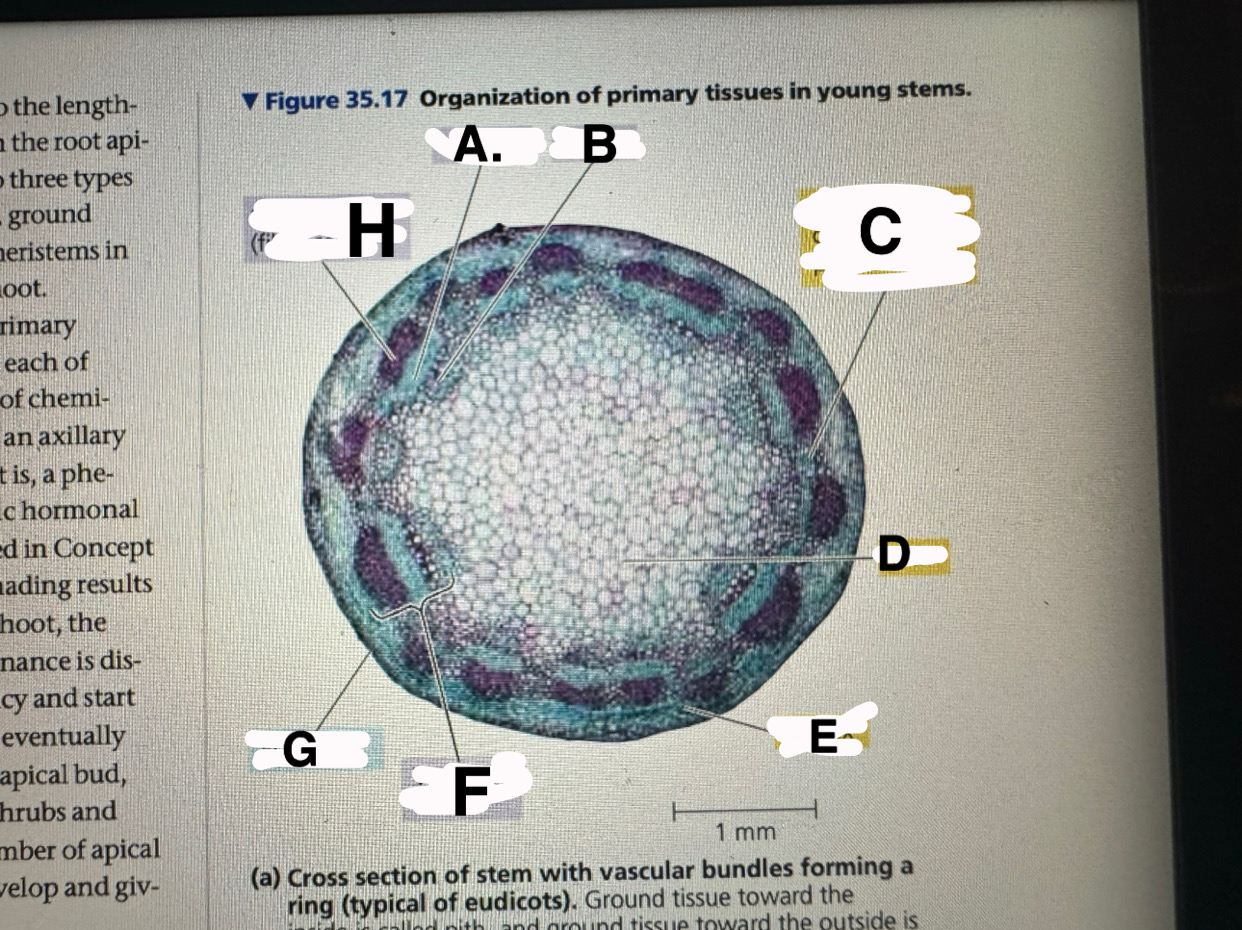
f
eudicot stem: vascular bundle
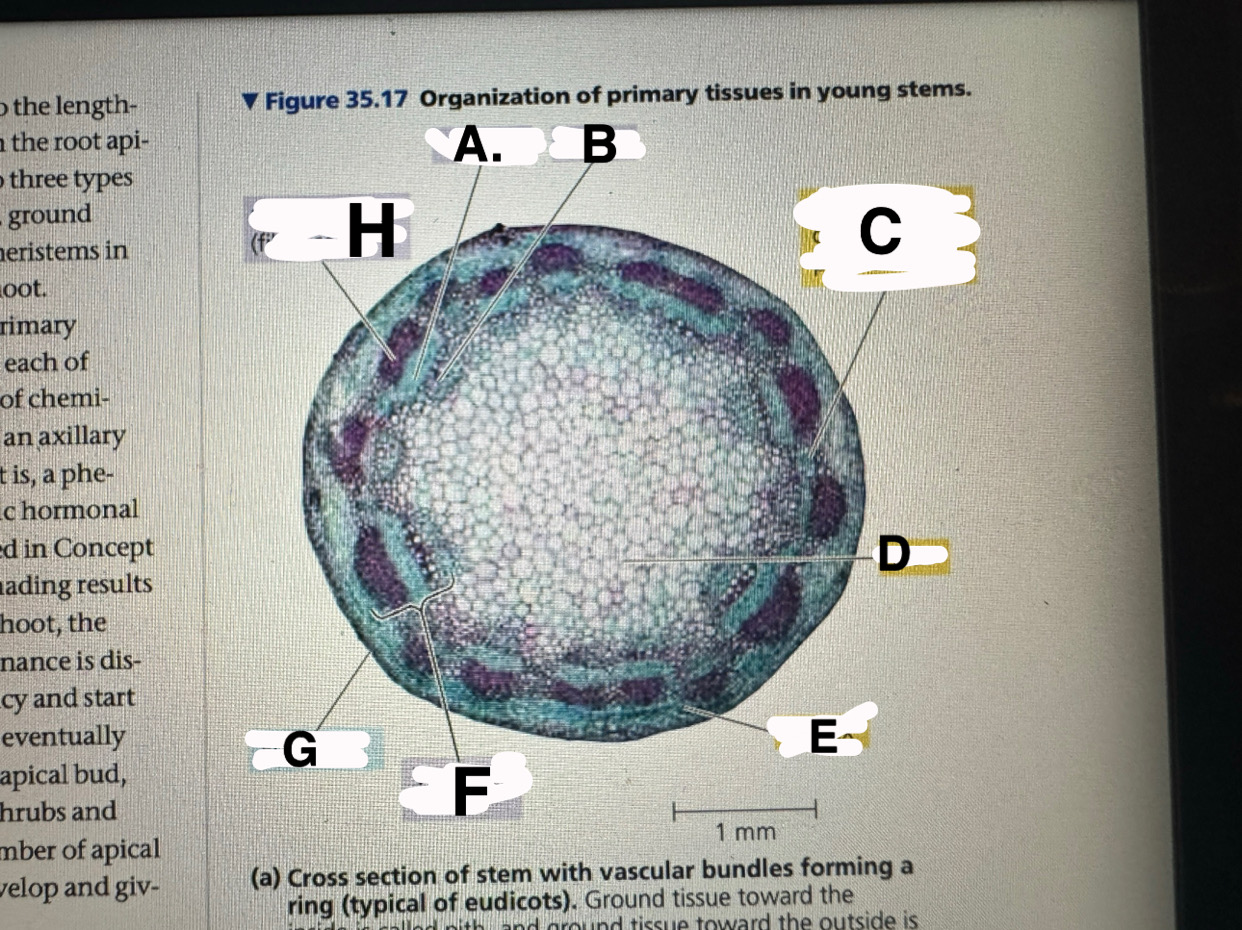
g
eucicot stem: epidermis
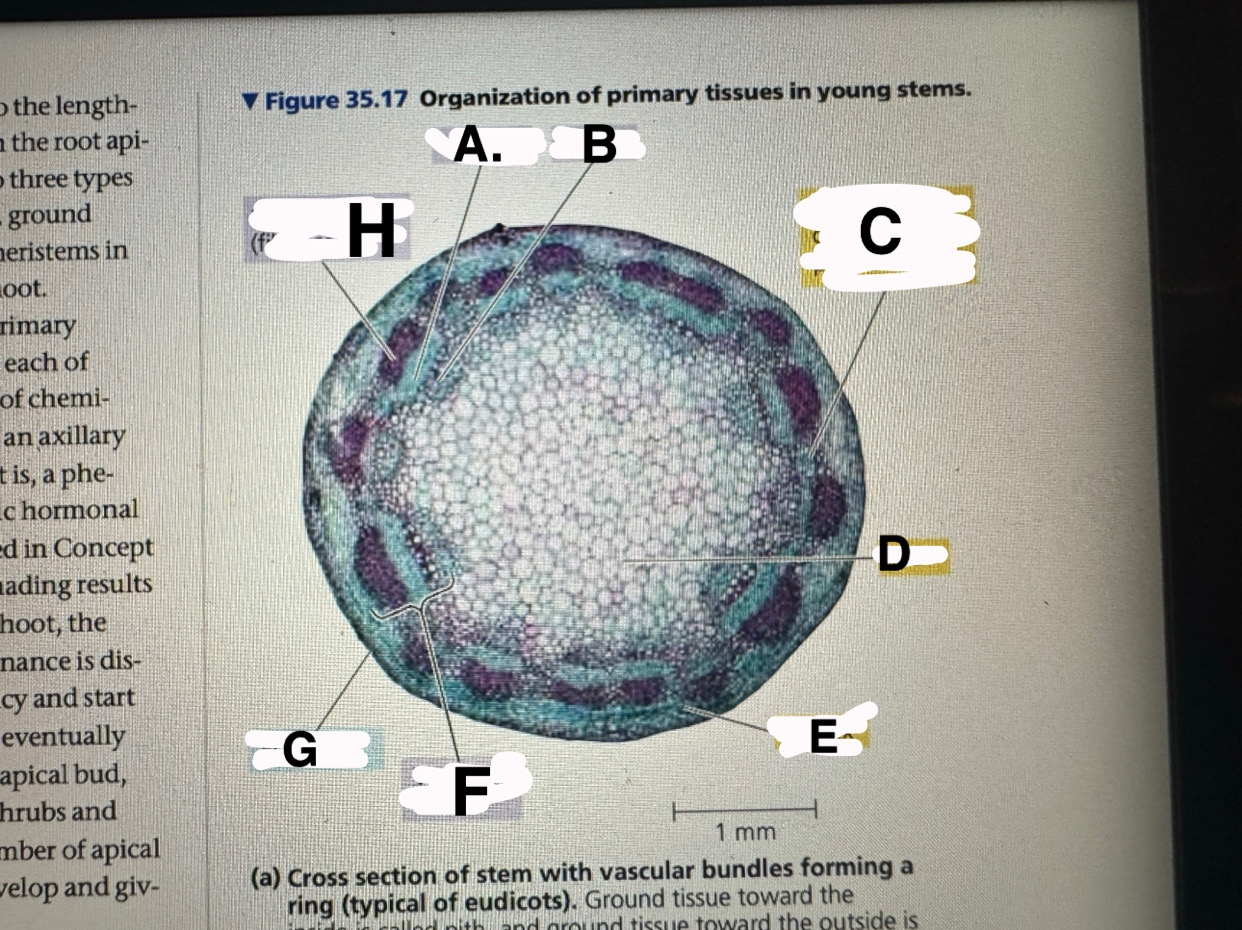
h
eudicot stem: fiber cells
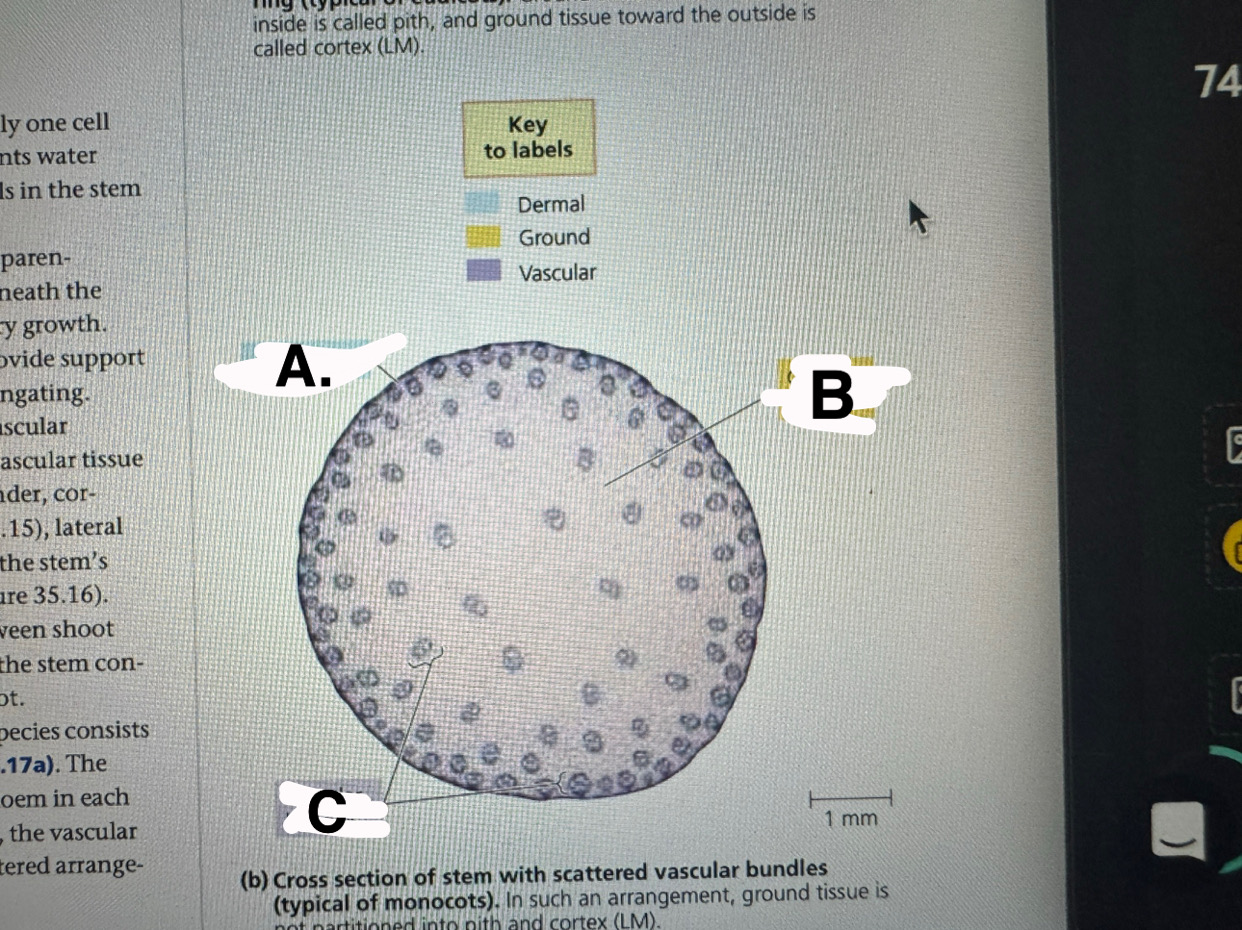
a
monocot stem: epidermis
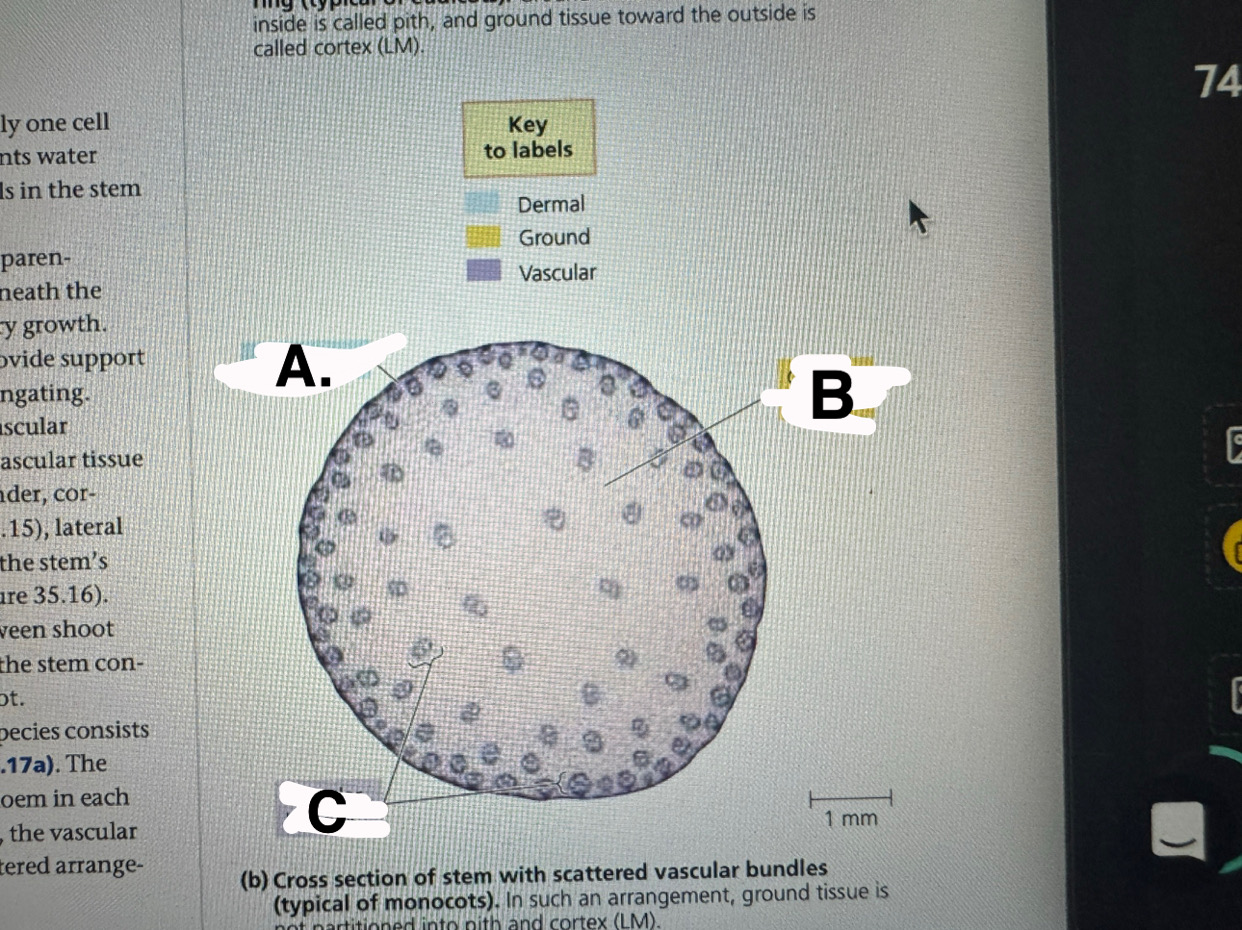
b
monocot stem: ground tissue
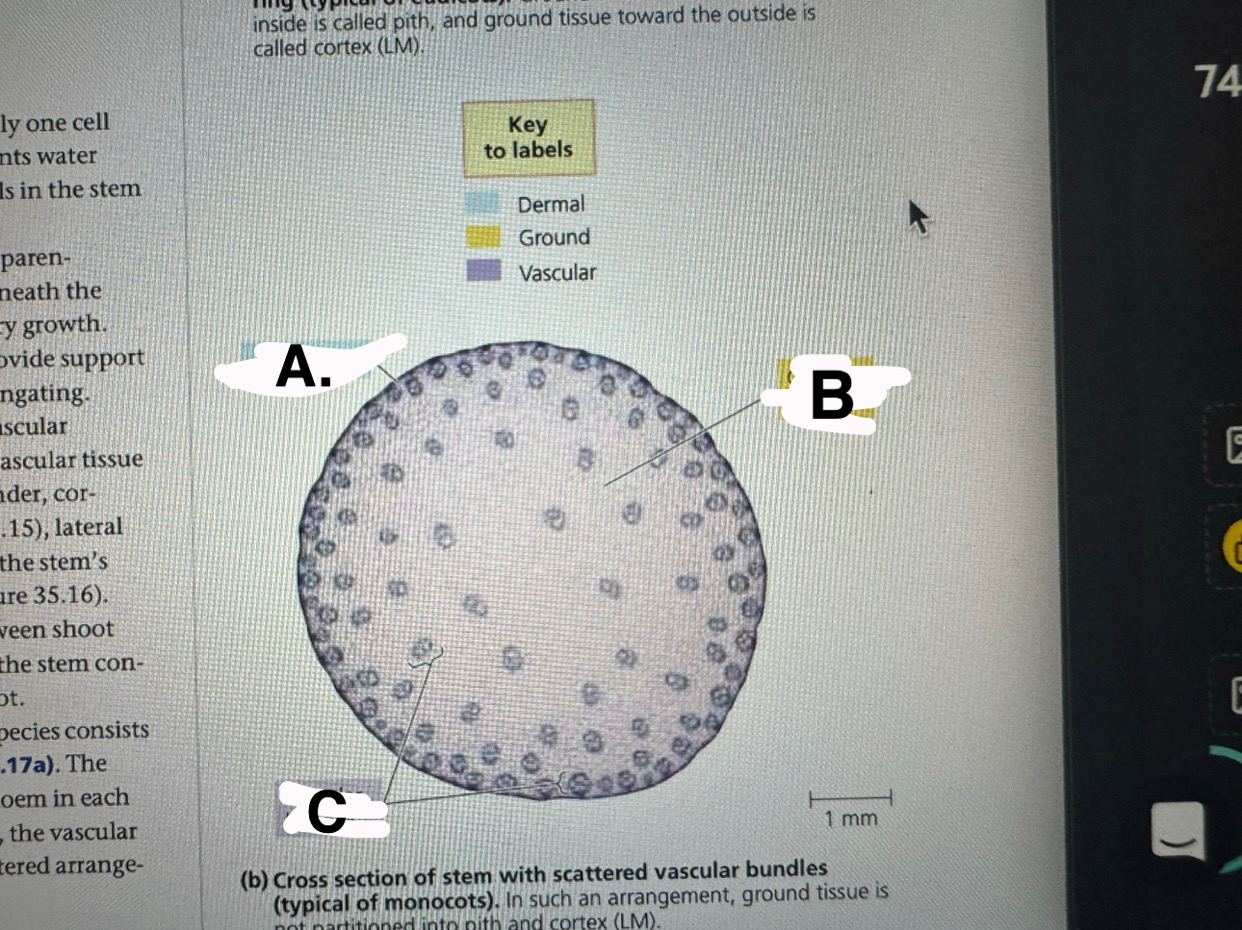
c
monocot stem:vascular bundles
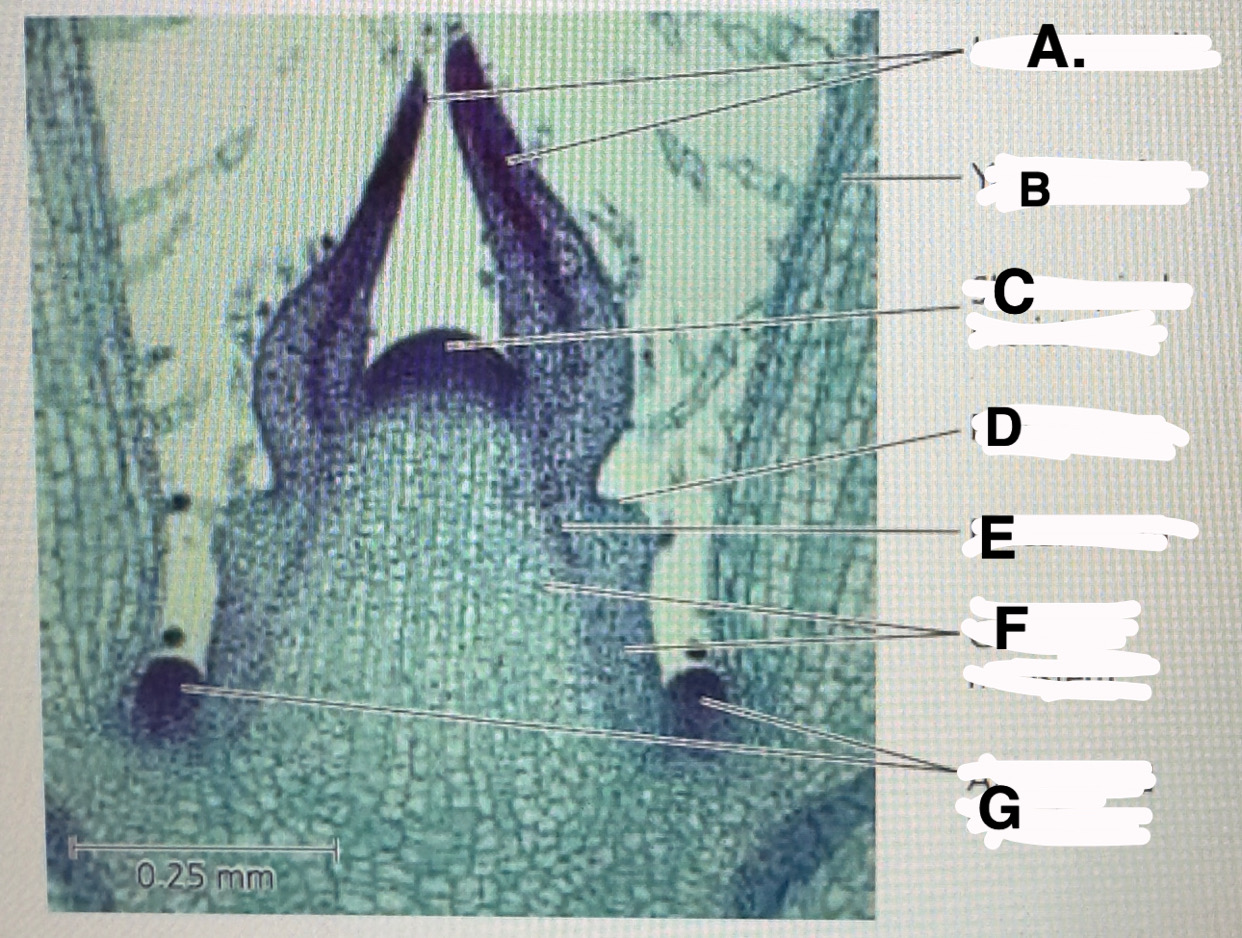
a
Stem shoot growing tip: leaf primodia
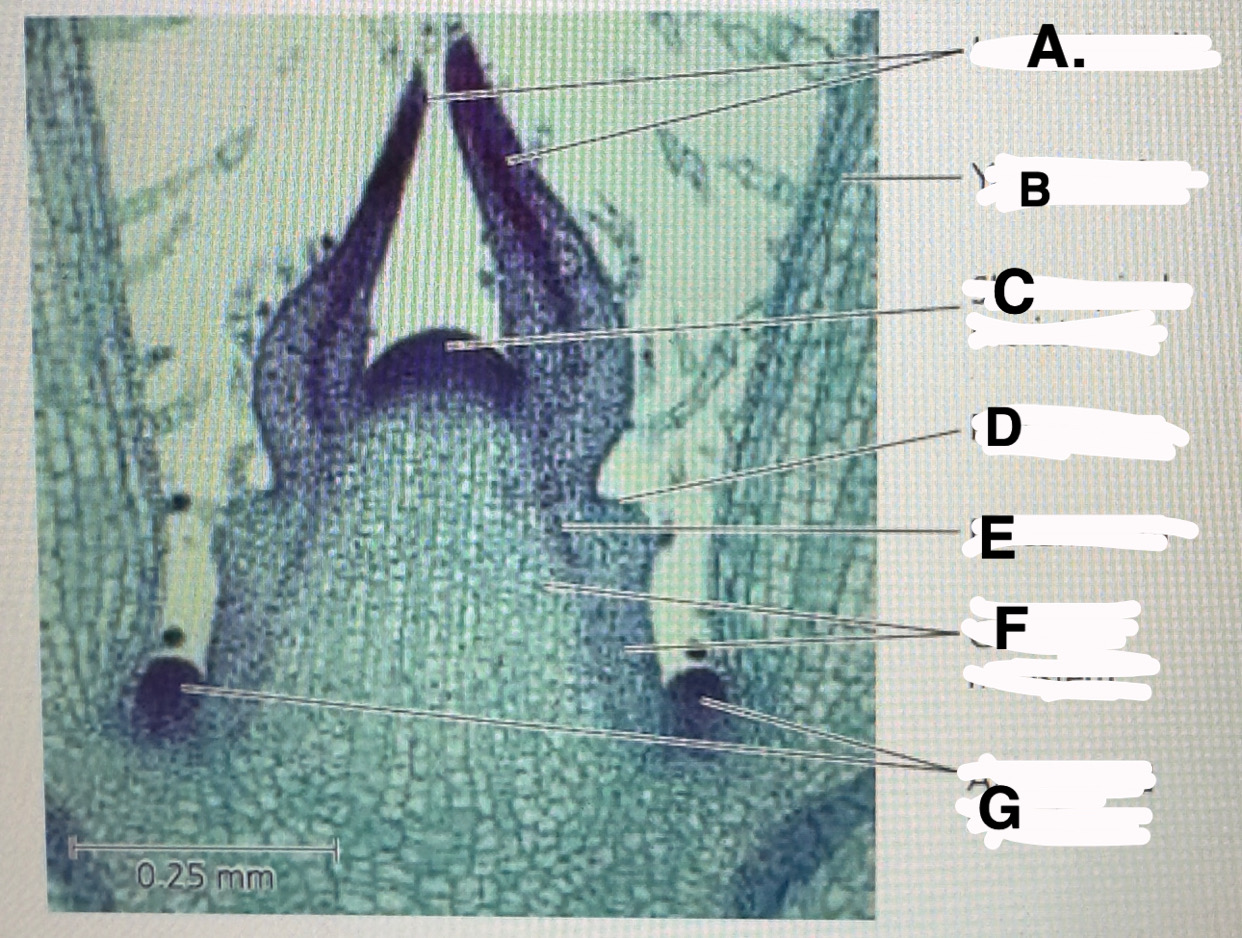
b
Stem shoot growing tip: young leaf
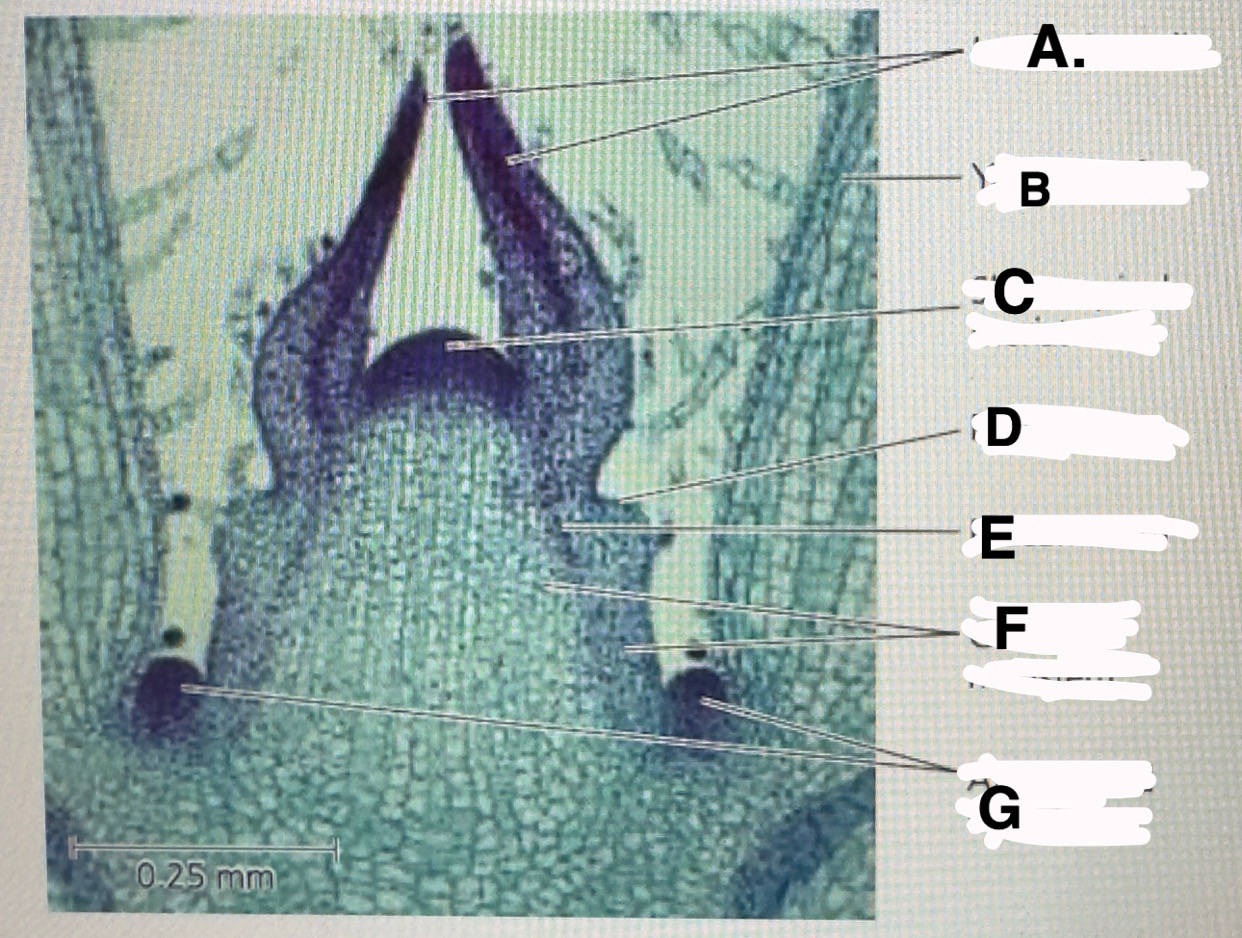
c!! important
Stem shoot growing tip: shoot apical meristem
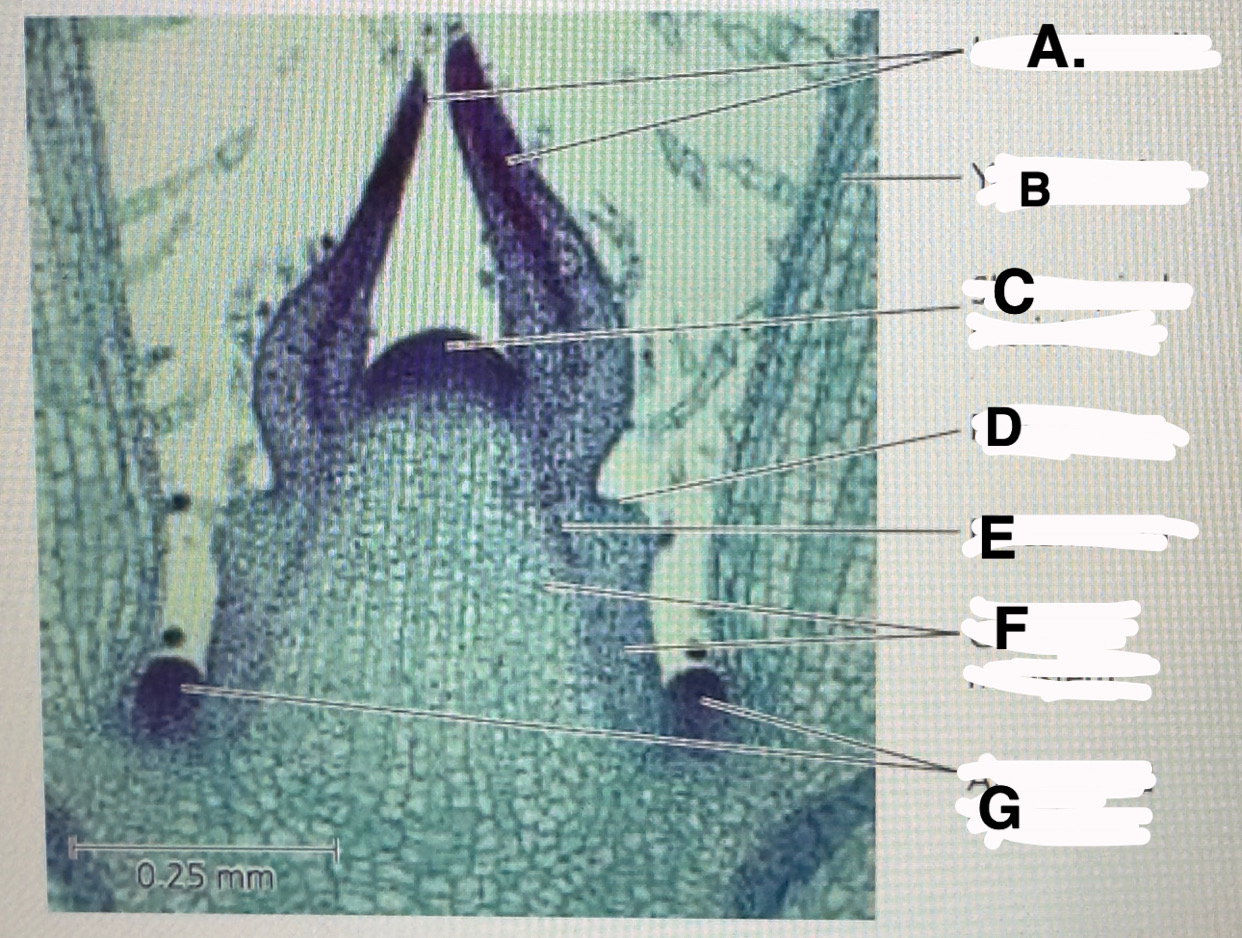
d
Stem shoot growing tip: protoderm
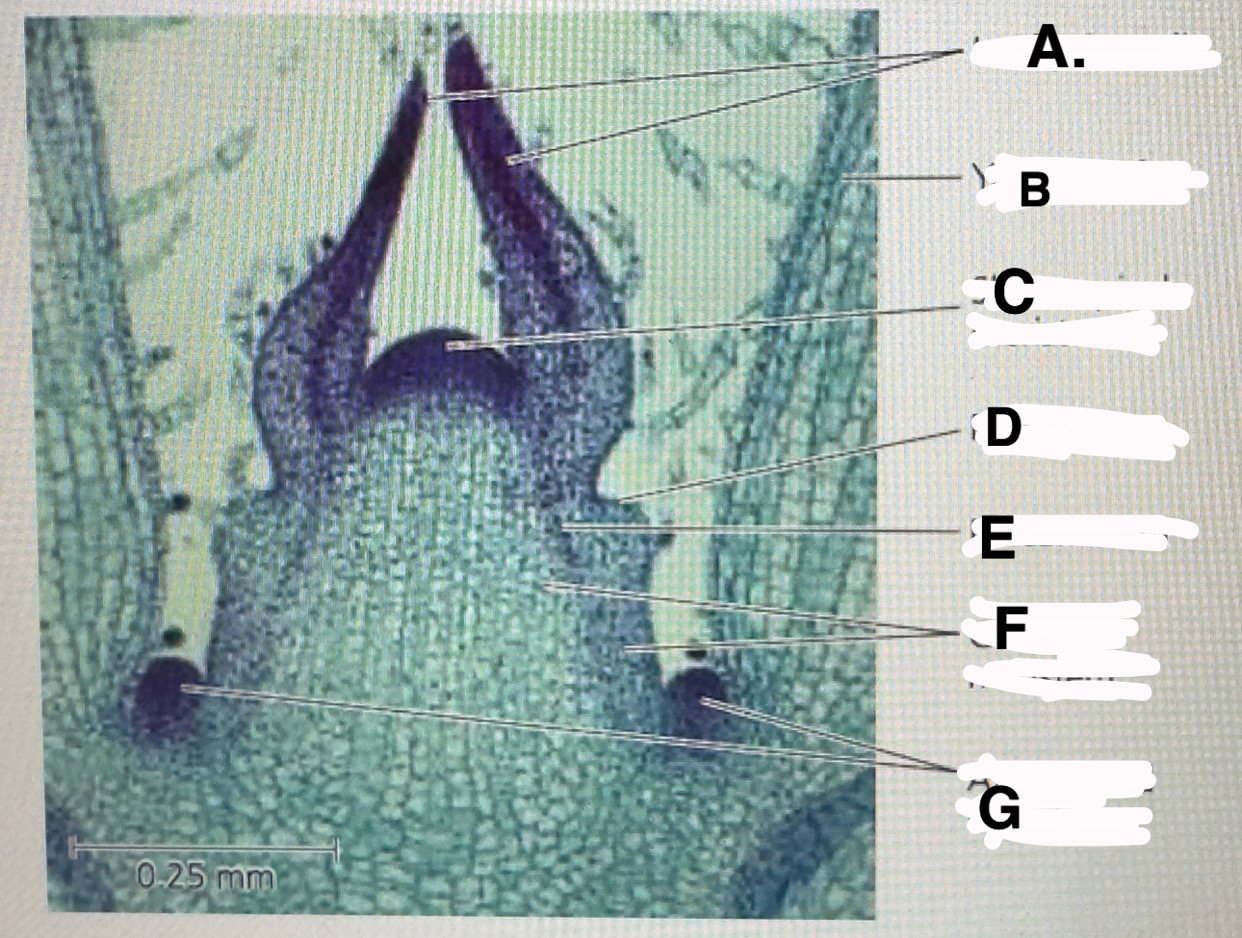
e
Stem shoot growing tip: procambium
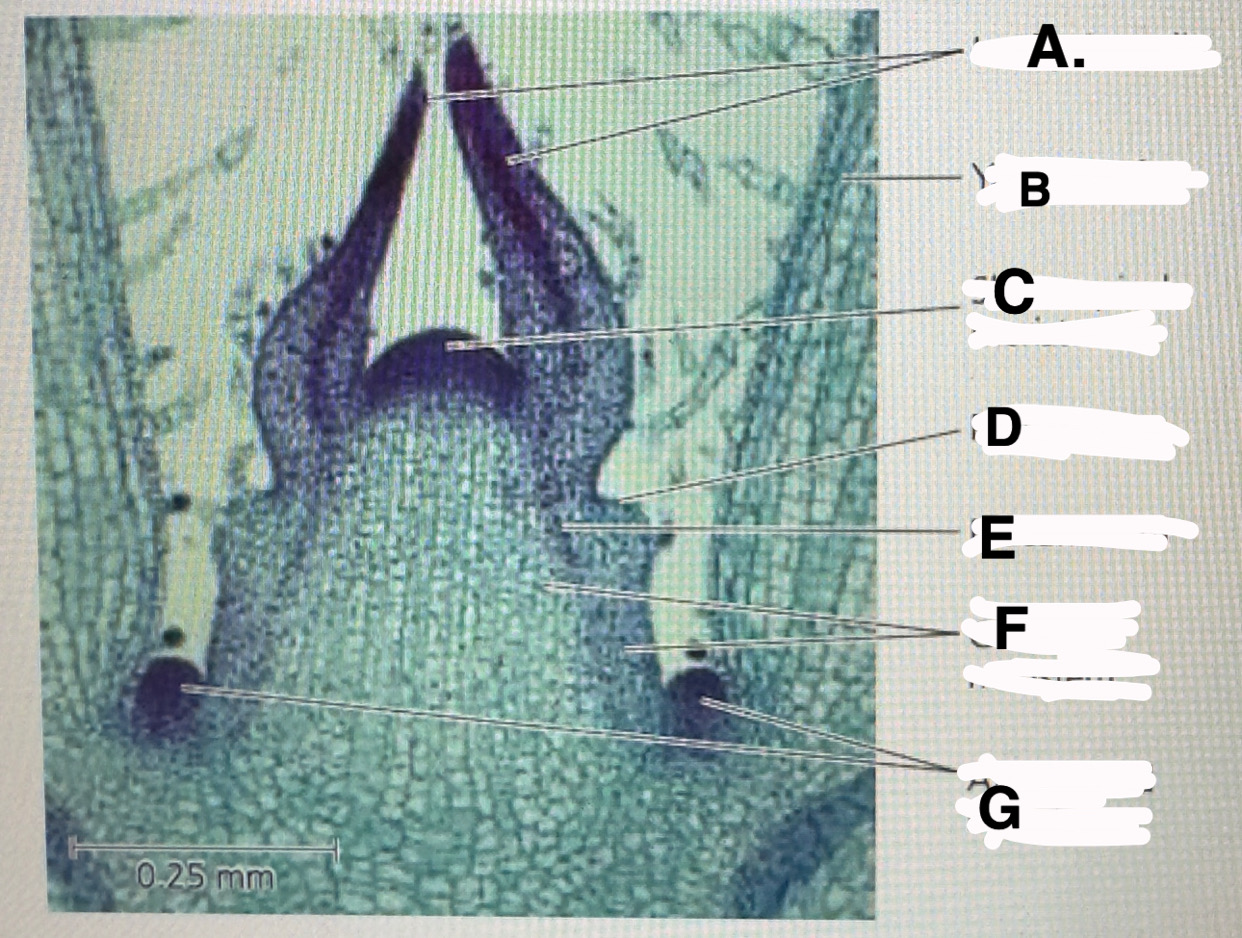
f
Stem shoot growing tip: ground meristem
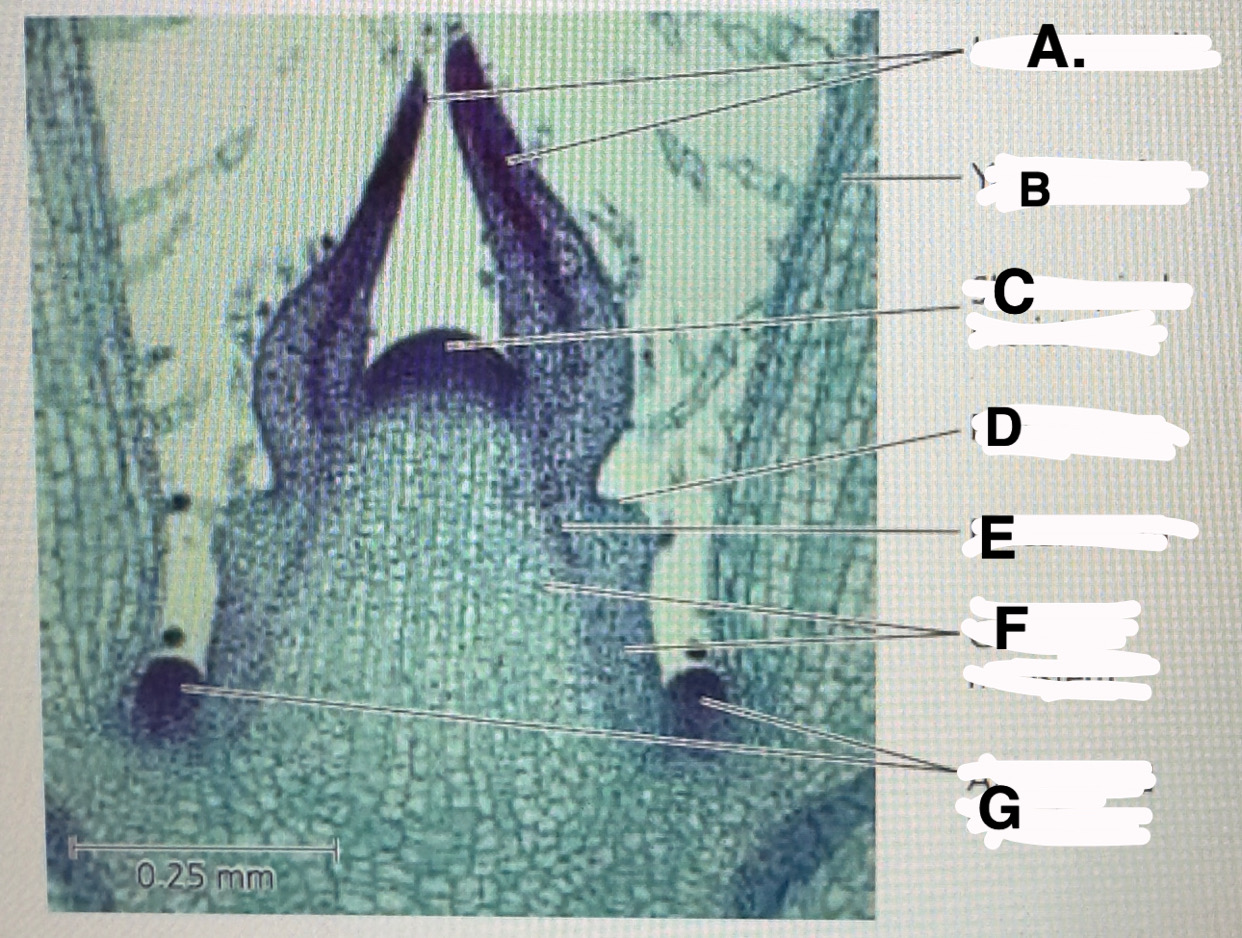
g
Stem shoot growing tip: axillary bud meristems