Lecture 4: Structure & Function of Molecules #3: Lipids and Proteins
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
9/10/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What are the three different classes of lipids?
Triglycerides
Membrane-forming
Sterols
Examples of Triglycerides
Fats and oils
What forms triglycerides?
A dehydration synthesis
Describe the structure of a triglyceride
Three carbon backbone with fatty acids attached
Fatty acids are long carbon/hydroen chains
Made from two-carbon units so fatty acids are often 16 or 18 carbons but rarely 17
Draw a picture of a triglyceride
Image
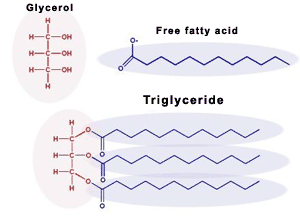
What are the two classes of membrane-forming lipids?
Phospholipids
Galactolipids
Diagram a structural formula, space-filling model, and phospholipid symbol and a fatty acid. Include hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends.
Image
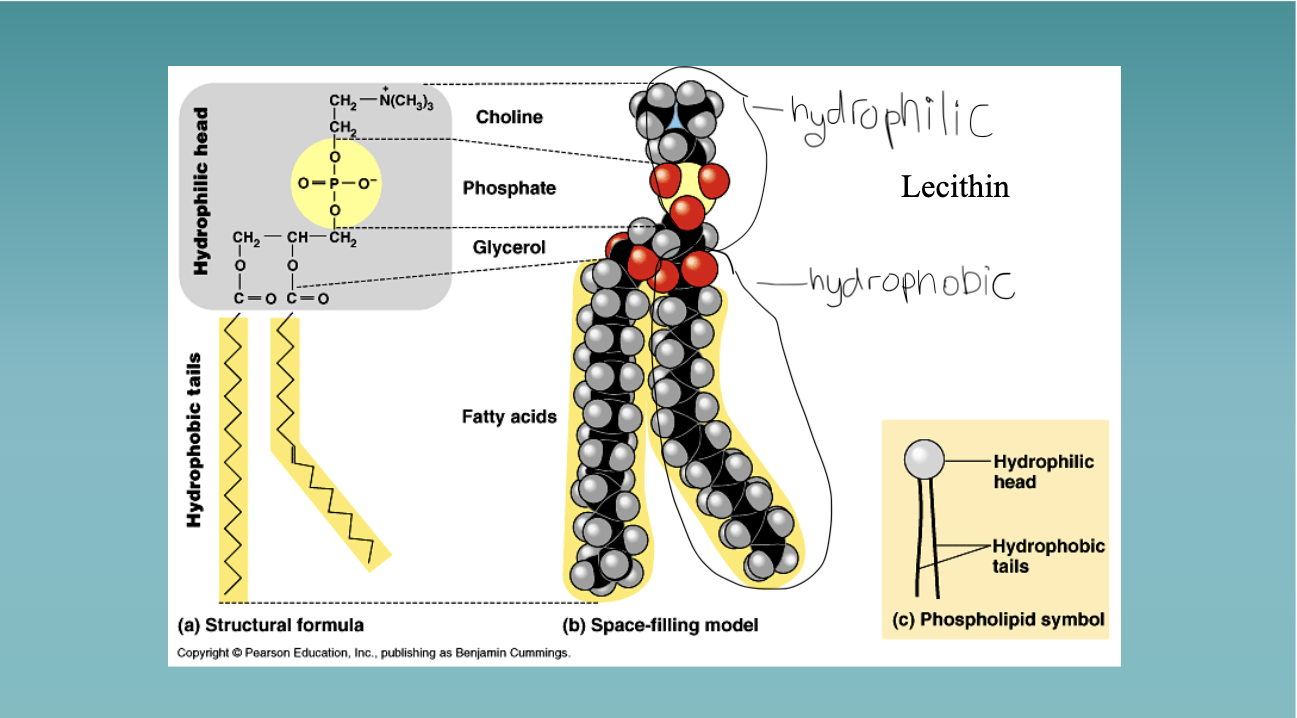
What are micelles and phospholipid bilayers?
A way of organization
Draw a diagram of a micelle and a phospholipid bilayer showing how hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions stabilize these structures
Image
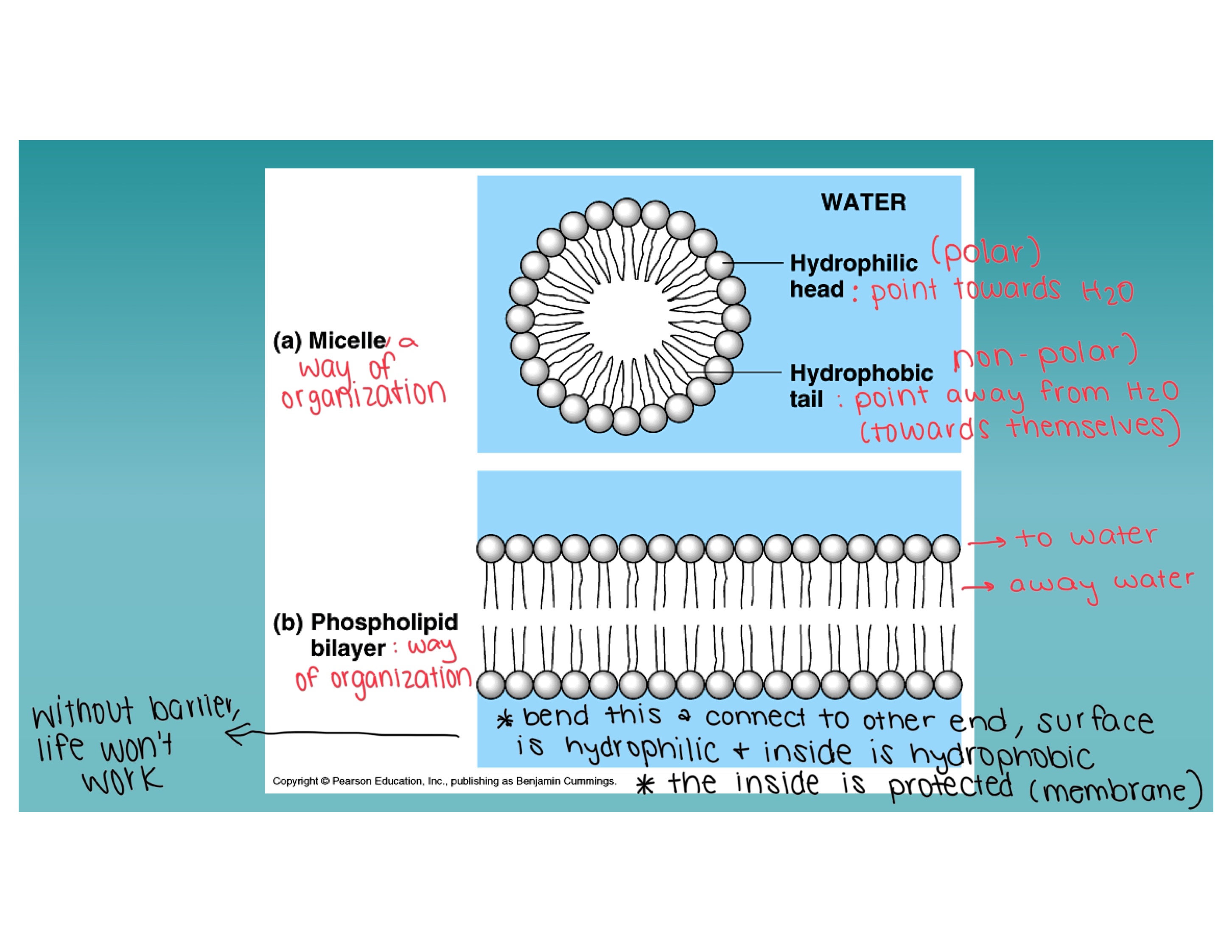
Examples of sterols in plants and animals
Plants: stigmasterol
Animals: cholesterol
Sterols main functions (3) in membranes:
Stiffen (fine tune how flexible membrane is)
Maintains fluidity (prevents fatty acids crystalizing)
Localized “special” regions (rafts)
Be able to identify a sterol lipid.
Image
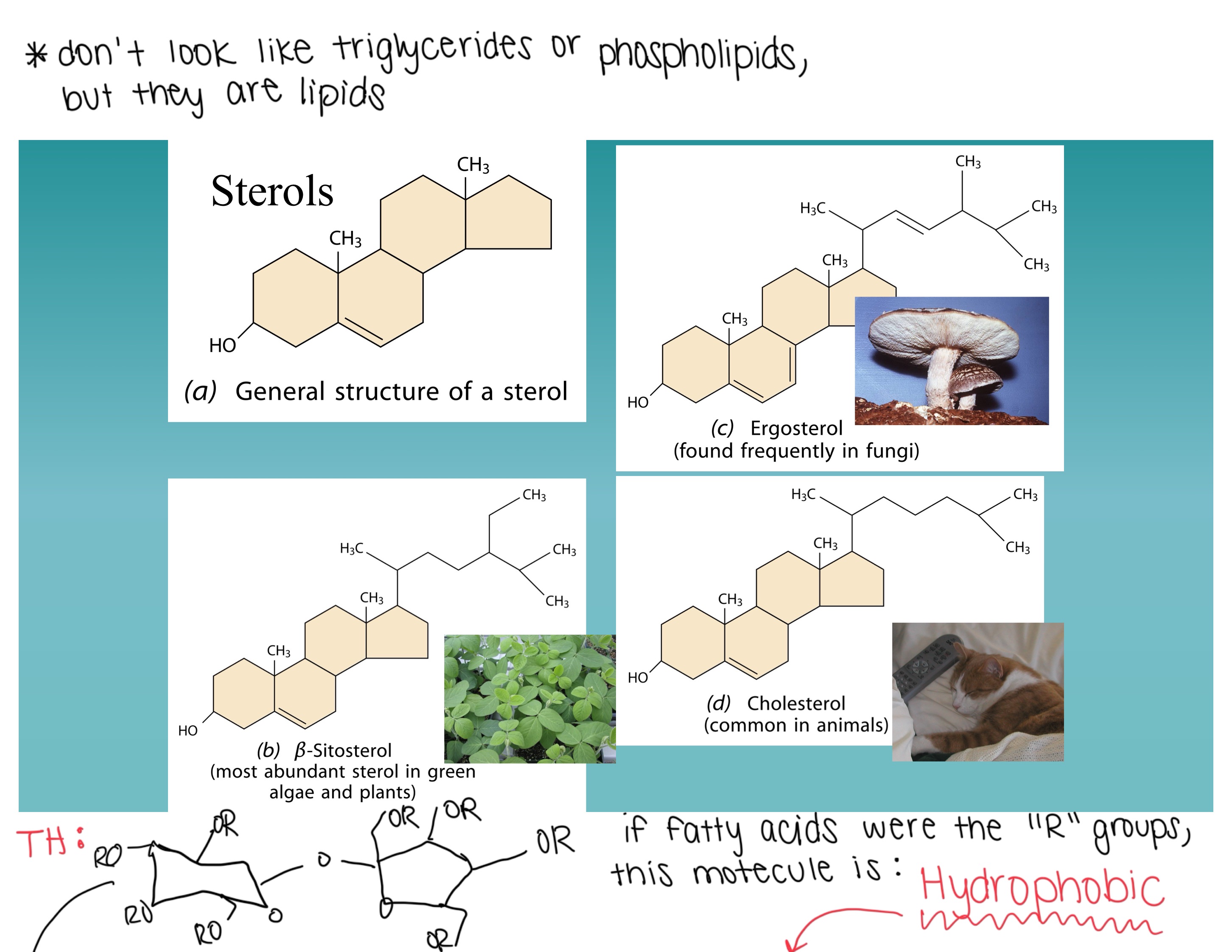
What is Olestra?
Sucrose with a-8 fatty acids
In a short version, what do proteins do?
They build tiny “machines”
What is a very important factor with proteins?
Shape
Chemical definition of a protein
A polymer of amino acids
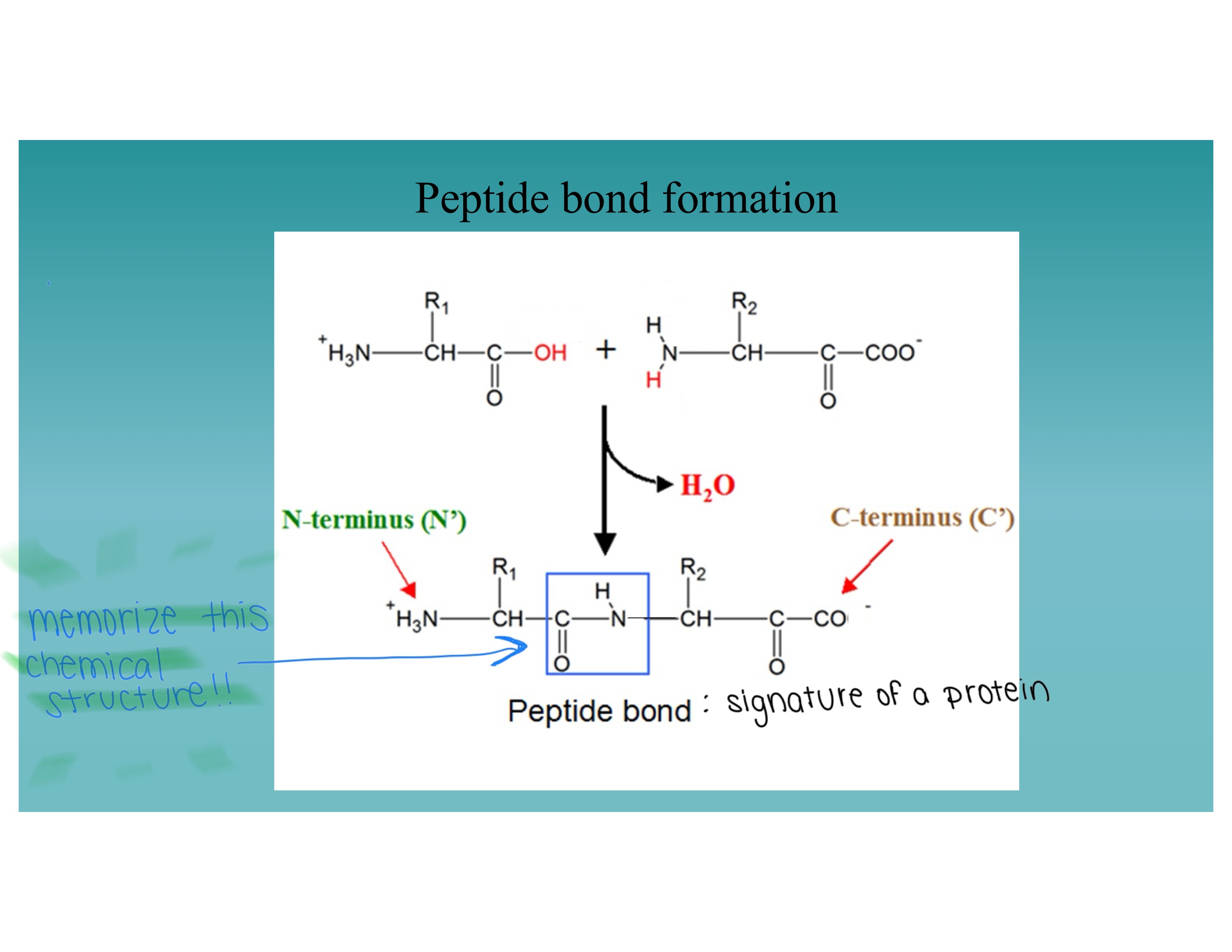
What bond links amino acids together in a protein?
A peptide bond
How is the peptide bond in proteins formed?
By removal of water in a dehydration synthesis reaction (condensation reaction), where the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another, releasing water and creating a covalent amide bond.
What is the opposite reaction of a dehydration synthesis reaction?
Hydrolysis reaction
What do the properties of proteins depend on?
Depend on which amino acids are used and in what order (order of amino acids is important)
How many amino acids are used in proteins (in all organisms)?
20 amino acids
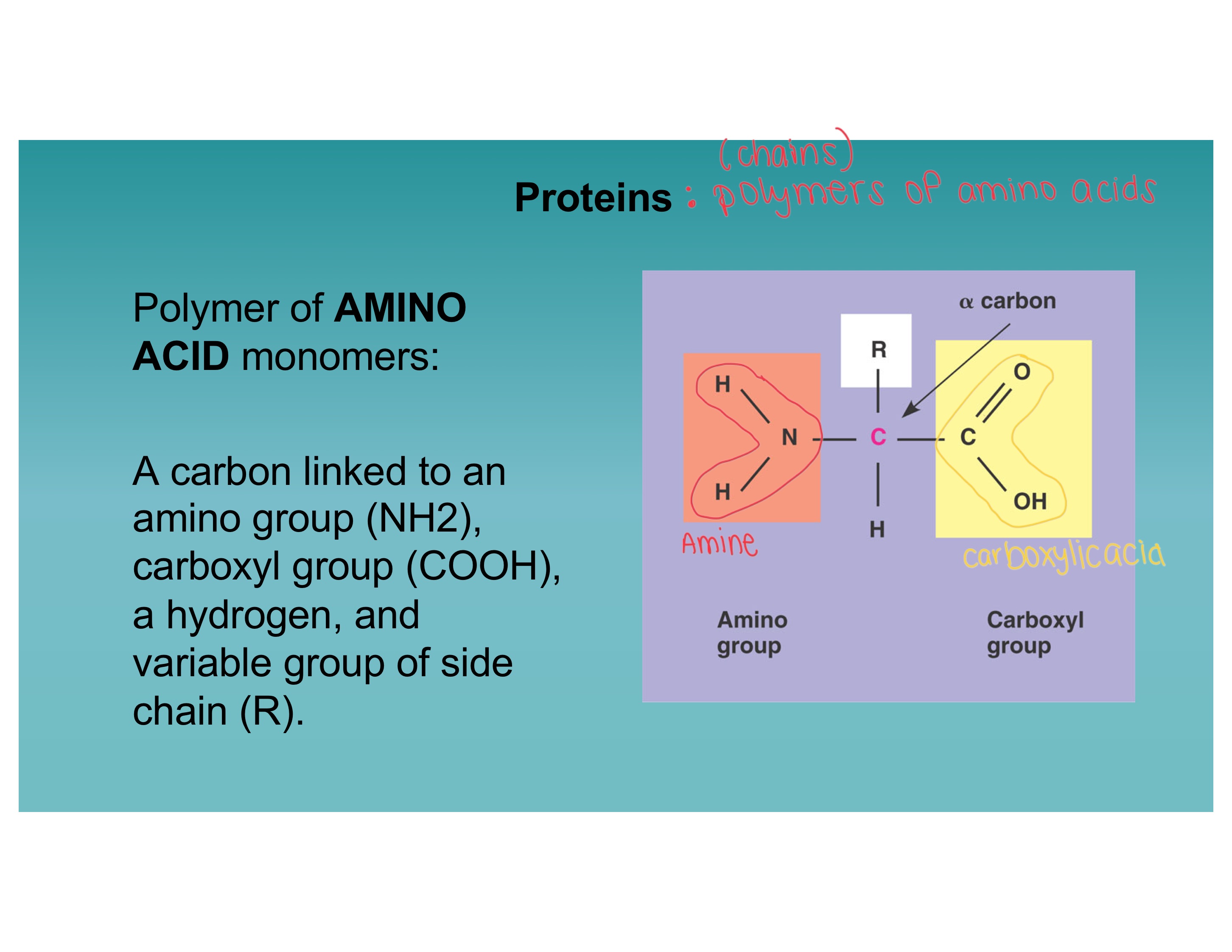
Describe the structure of a protein
Carbon linked to an amino group (NH2), Carboxyl group (COOH), a hydrogen, and variable group of side chain (R)
Be able to identify a protein
Image
Show the chemical structure of a peptide bond formation
Image
How many non-polar (hydrophobic) amino acids are there?
9 amino acids
How many polar (hydrophilic) amino acids are there?
6 amino acids
How many electrically charged amino acids are there?
5 amino acids
2 Acidic
3 Basic
Fill in the blanks: ______ is ______ into _____ that is ________ into _________
DNA is transcribed into RNA that is translated into protein
Explain why biological membranes contain other lipids, such as sterols, in addition to phospholipids
Because different lipids perform essential functions. Other lipids help in functions such as modulating membrane fluidity and permeability (cholesterol), creating specialized regions (lipid rafts) and serving as signaling molecules (phosphates)
Define amino acid
Organic compound that serves as the building block of proteins. Essential for growth, repair, and metabolism
Define polar/non-polar
Polar molecules have an uneven distribution of electrons, creating a positive and negative end (dipole)
Non-polar molecules have an even distribution of electrons, where any bond dipoles cancel out, resulting in a non-net dipole
Define side chain
A variable chemical group attached to the central alpha-carbon of an amino group (also known as the “R” group)
Define peptide bond
A covalent chemical bond that links two amino acids together to form a polypeptide chain, which is the foundation for proteins
Define protein
Complex organic compounds composed of amino acids, which are linked together in long chains
Define cholesterol
A waxy, sterol-type lipid found in all animal cells (essential component of cell membranes; maintains their structure and fluidity)
Define lipid
Fats and “fat-like” substances
Define transcription
the process of copying genetic information from a segment of DNA into a complementary molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA)
Define translation
the process where a cell reads the genetic information carried by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and uses it to synthesize a specific sequence of amino acids, forming a polypeptide chain that will then fold into a functional protein