Purdue Bio203 Exam 2 Cartes | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
The glenohumeral joint is where the ______ of the scapula meets the humerus
glenoid cavity
Which joint classifications are used to describe how the bone ends of a joint are held together?
Bony, fibrous, synovial or cartilaginous
What holds the bones together in a fibrous joint?
Collagen fibers
A bony immovable joint is called a(n)
Synostosis
The fusion of the right and left mandible into a single mandible bone during fetal development is an example of the formation of what kind of joint?
Synostosis
True or False: Bone joints are formed by ossification of either fibrous or cartilaginous joints
True
Correctly classify the shown joint as fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial (Suture)
fibrous
True or False: The anatomical name of a joint is determined by the manner in which the bone ends are connected at the joint
False
What is another term for a fibrous joint?
Synarthosis
What of the following is produced by embryonic bones fusing seamlessly into one adult bone?
Synostosis
Which class of joints includes sutures and gomphoses?
Fibrous
Which joints are synostosis?
The closure of an epiphyseal plate; The joining of left and right halves of the mandible
Based on structure, the sagittal suture is what type of joint?
Fibrous
What fibrous joint is found in the skull?
Suture
How are individual joints typically named?
Based on the names of the bones involved in the joint
What is a joint in which a hard object, such as a tooth, is held in a bone cavity called?
Gomphosis
All three types of fibrous joints are?
Gomphosis, Suture, Syndesmosis
What is a syndesmosis held together by?
Long collagen fibers
Joints with an interosseous membrane are example of which type of fibrous joint?
Syndesmoses
Where are sutures found?
Only in the skull
Intervertebrated discs comprised of fibrocartilage are found within what type of joints?
Symphyses
What holds the bone ends of an amphiarthrodial joint together?
Cartilage
The epiphyseal plate in a growing bone is an example of what type of joint?
Synchondrosis
A _____ is a type of mobile fibrous joint in which bones are held together by a band of long collagen fibers
syndesmosis
A lubricating fluid that reduces friction between the bones is found where
Synovial joints
True or False, joints containing an interosseous membrane are examples of fibrous joints
True
Because it is a freely moveable joint, a synovial joint is called a what?
Diarthosis joint
A pubic symphysis is an example of which type of joint?
Cartilaginous
What is the type of hyaline cartilage found at the end of bones within a synovial joint called?
Articular cartilage
List the types of cartilaginous joints
Symphyses and synchondroses
The inner layer of a joint capsule that secretes synovial fluid is called the membrane
Synovial
What type of joint is found between the costal cartilage of rib one and the sternum?
Synchondrosis
Which joint is most likely to develop dysfunction due to it's complexity?
Synovial
What comprises the outer layer of a synovial joint capsule?
Fibrous cartilage
What are articular discs, as the one in the temporomandibular joint, made of?
Fibrocartilage
Which structure attaches a muscle to bone?
Tendon
What is the function of synovial fluid?
Lubrication💧
What does a ligament connect?
Bone to another bone
What is the function of a tendon sheath?
Prevent friction
Which are found in a joint capsule?
Fibrous cartilage/ Synovial membrane/ Fibrous capsule
Which structure is found between the bones of the temporomandibular joint?
Fibrocartilage pad
A lever that would produce more speed or distance than the force exerted on it
A lever with mechanical advantage of less than 1.0
Tendons can serve which of the following functions?
Attaches muscle to bone/ stabilize a joint
In a musculoskeletal lever system, what force does the muscle contraction provide?
Effort
A strip of tough collagenous tissue attaching a bone to another bone is called a
Ligament
What are the fibrous sacs filled with synovial fluid found in areas where friction from tendons occurs called?
Bursae
A synovial joint cavity is enclosed by which of the following?
Joint capsule
Within a musculoskeletal lever system, what is the fulcrum?
Joints
Within a lever system, what is the resistance arm?
The portion of the lever from the fulcrum to the point of resistance
True of False: The tone of an opposing muscle can represent resistance in a musculoskeletal lever system
True
What is a bursa wrapped around a tendon called?
Tendon sheath
What compromises the outer layer of a synovial joint capsule?
Fibrous capsule
If a lever's mechanical advantage is 1.0 or greater, what is true?
The lever produces more force (but less speed or distance) than the force exerted on it
What are the three factors that can represent resistance in a musculoskeletal lever system?
The weight of a limb/ the object being moved/ the opposing muscle tension
Extension of the arm at the elbow is an example of what type of lever system?
First class lever
What describes a second class lever?
The resistance is located between the fulcrum and effort
What describes a third class lever?
The effort is located between the fulcrum and the resistance
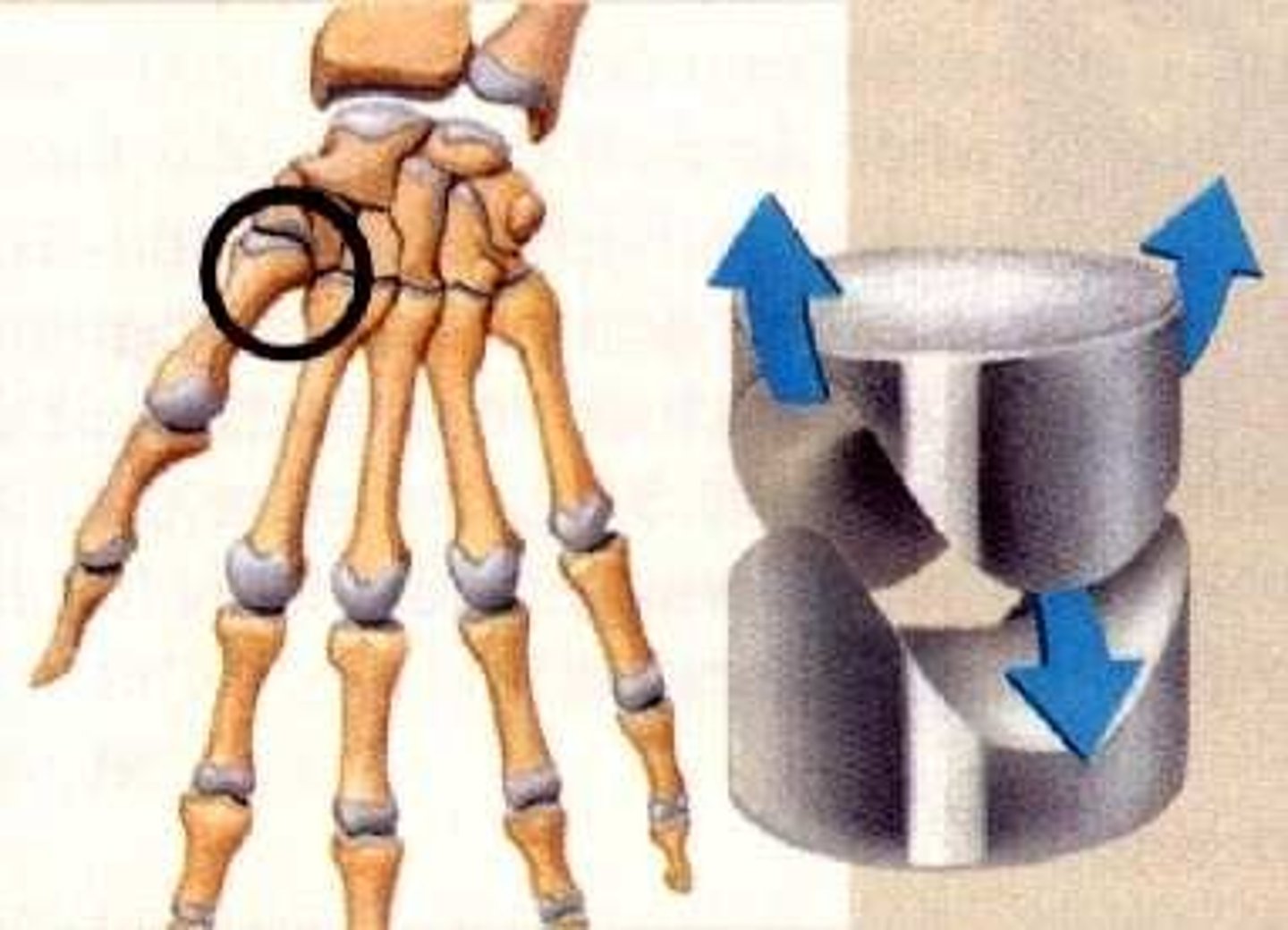
Trapeziometacarpal Joint is a?
Saddle joint
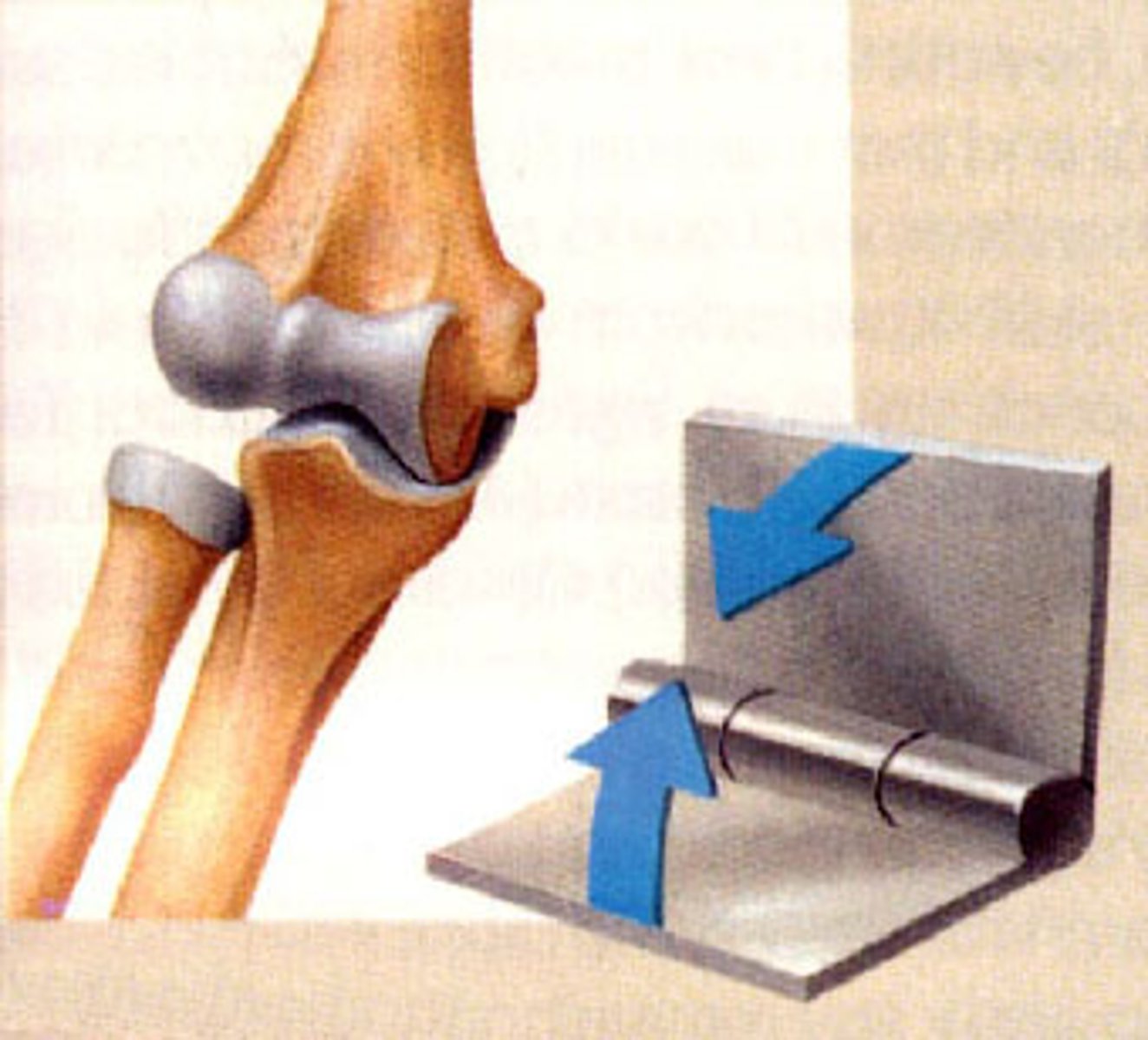
Ulnar-humeral joint is a?
Hinge joint
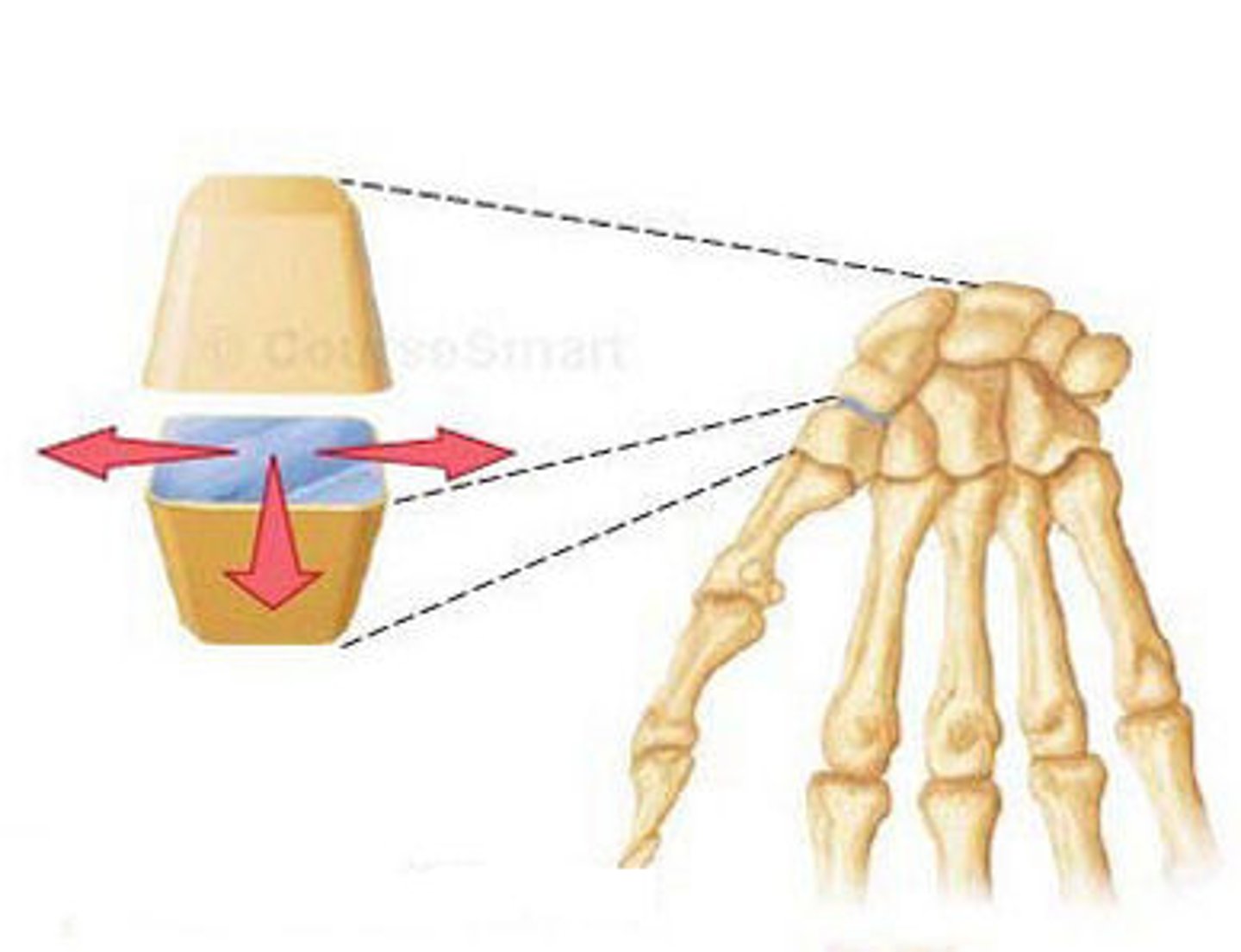
A joint between carpal bones is a ?
Plane joint
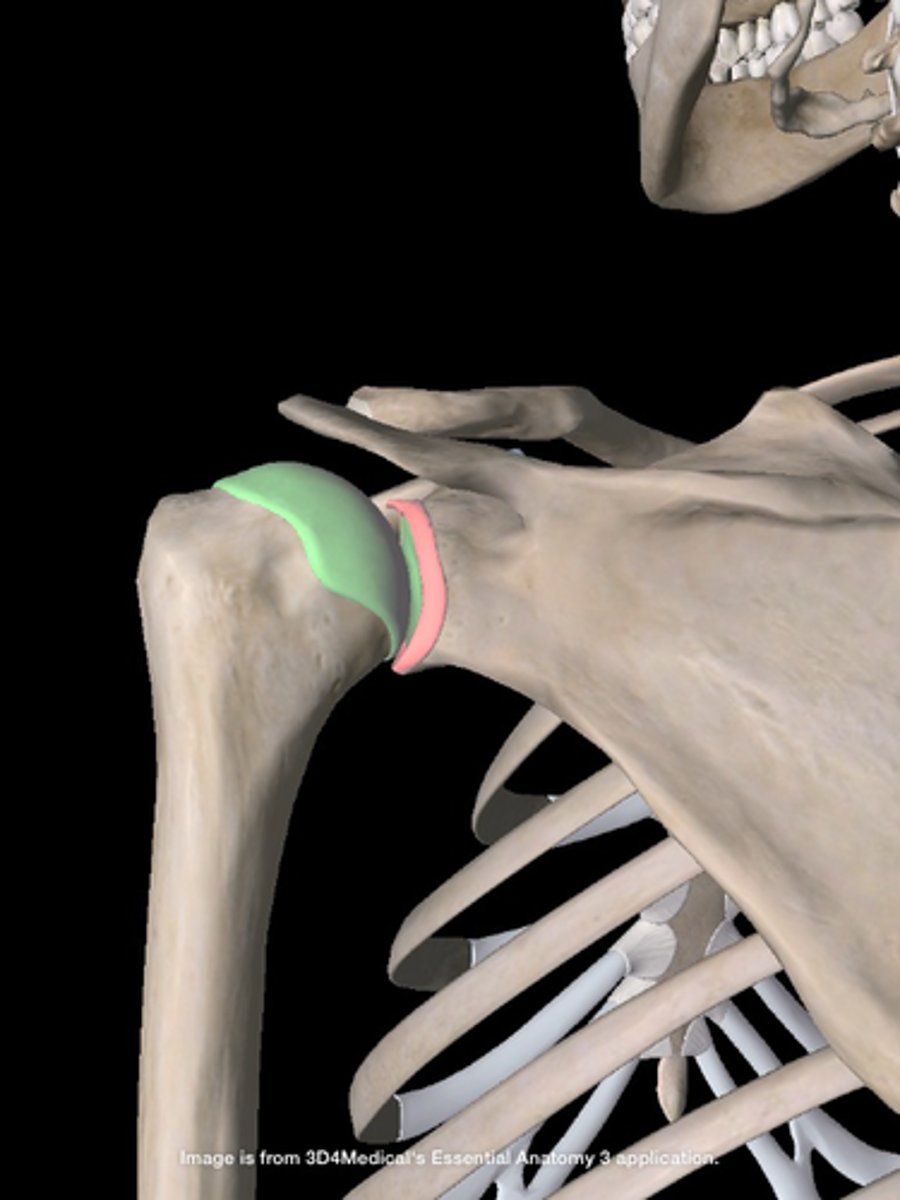
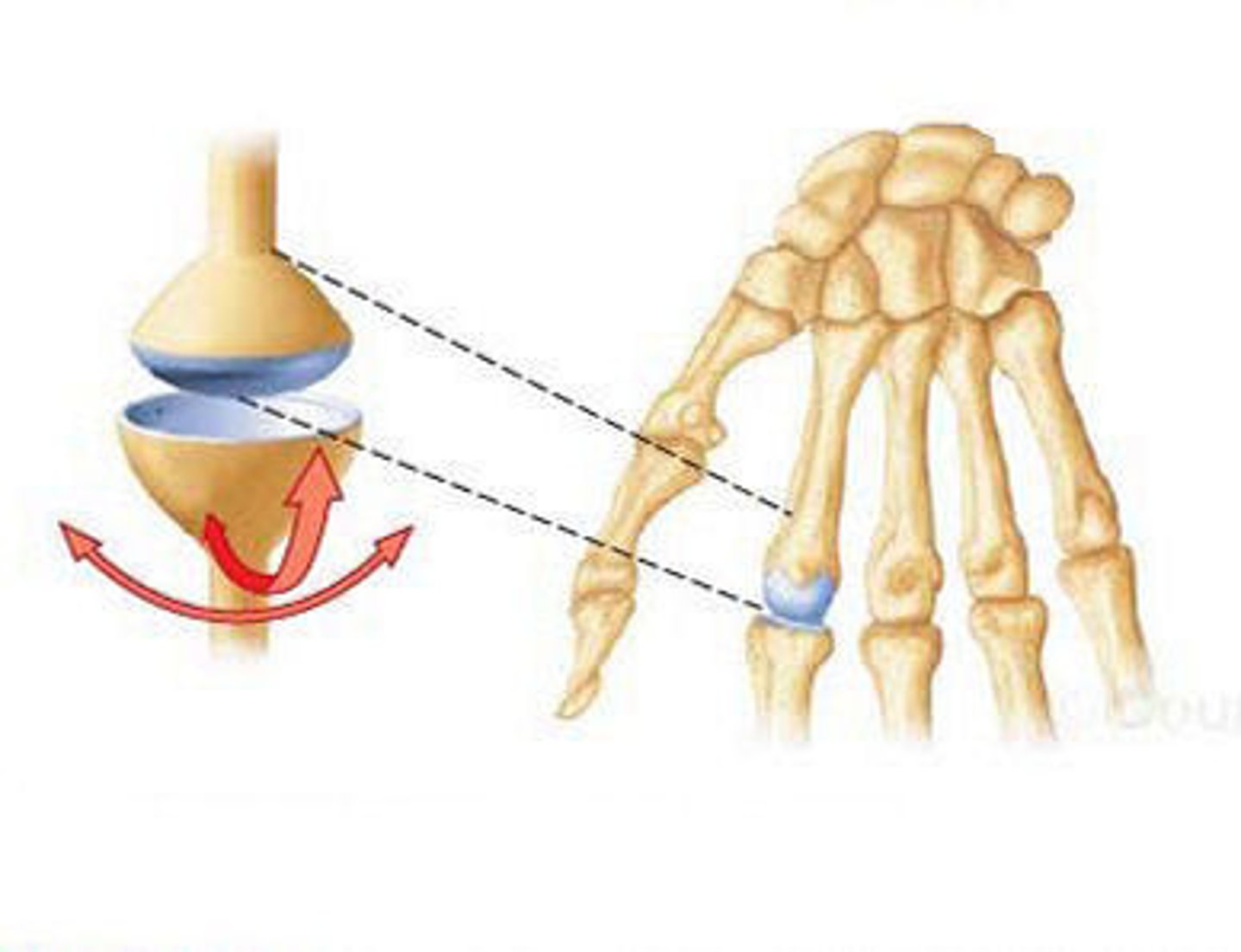
Glenohumeral joint is a?
Ball-and-socket joint
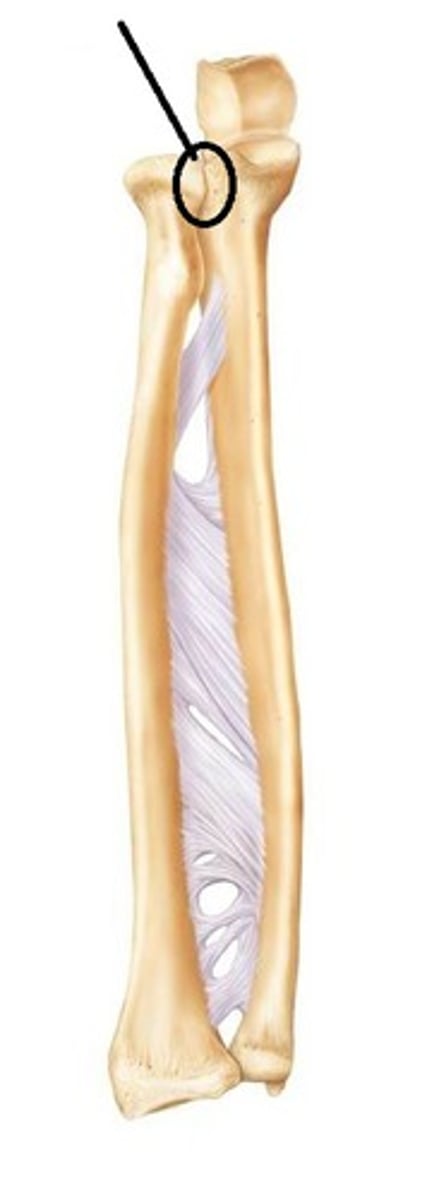
Radioulnar joint is a?
Pivot joint

Metacarpophalangeal joint is a?
Condylar joint
When one is standing in anatomical position, joints are said to be in what position?
Zero position
The arrow A indicates a movement called? Raising of bicep
Flexion
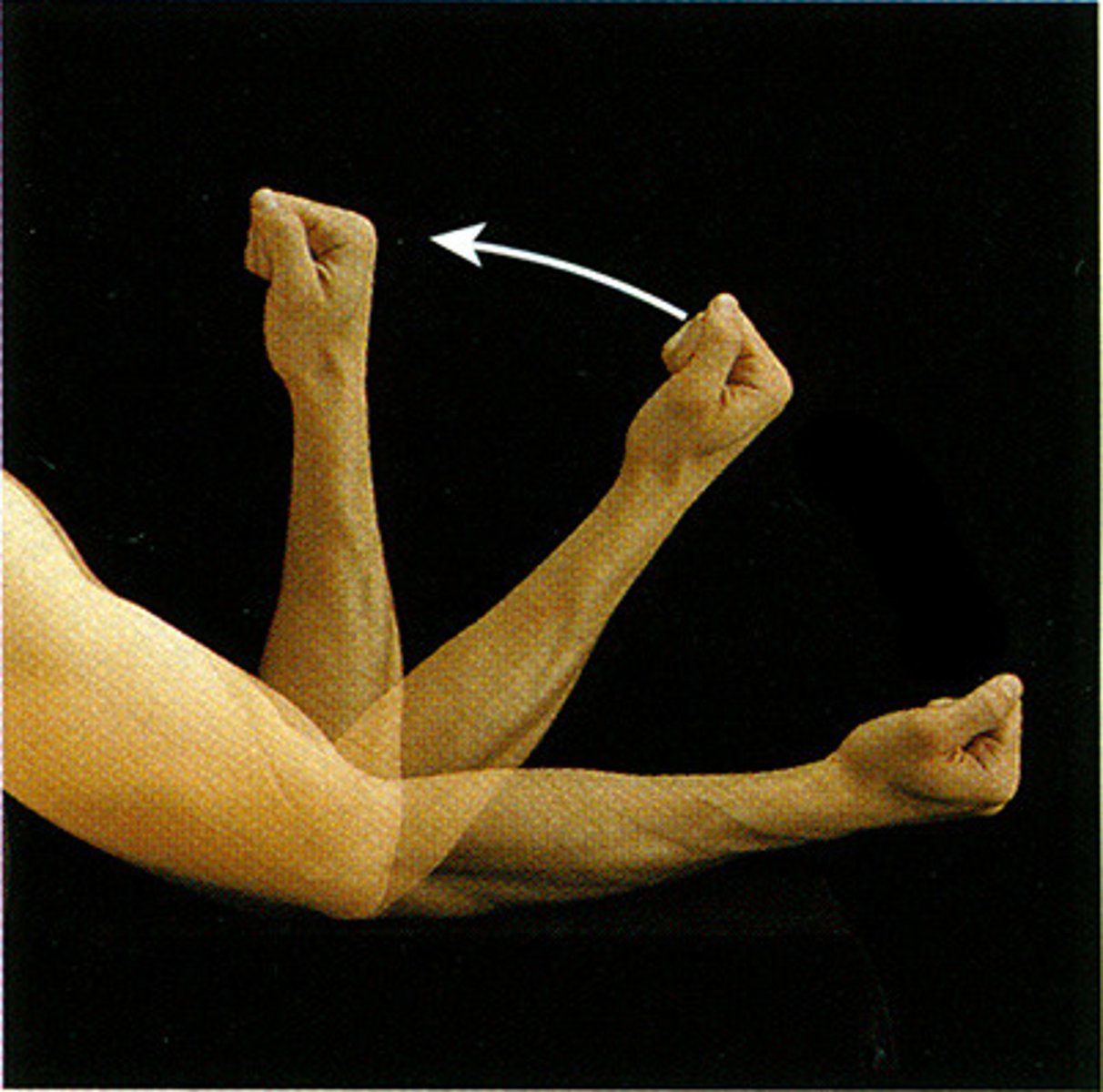
A joint that is extended beyond zero position is said to be what?
Hyperextended
What is moving a body part in the frontal plane away from the midline of the body called?
Abduction
Which movement lowers a body part vertically in the frontal plane?
Depression
Extending a joint beyond the zero position is always an abnormal movement?
False
In which movement does a bone spin on its longitudinal axis?
Rotation
Which two characteristics describe adduction?
A movement towards the midline of the body/ A movement along the frontal plane
Rotation of the bent upper limb of the shoulder, bringing the forearm towards the midline of the body is an example of?
Medial rotation
A movement that turns the palm forward or upward is called?
Supination
Which of the following describes elevation?
A bone raised vertically
What are two characteristics of protraction?
Movement along the transverse plane/ an anterior movement of the bone
What movement is the arrow indicating? Circular arm motion
Circumduction
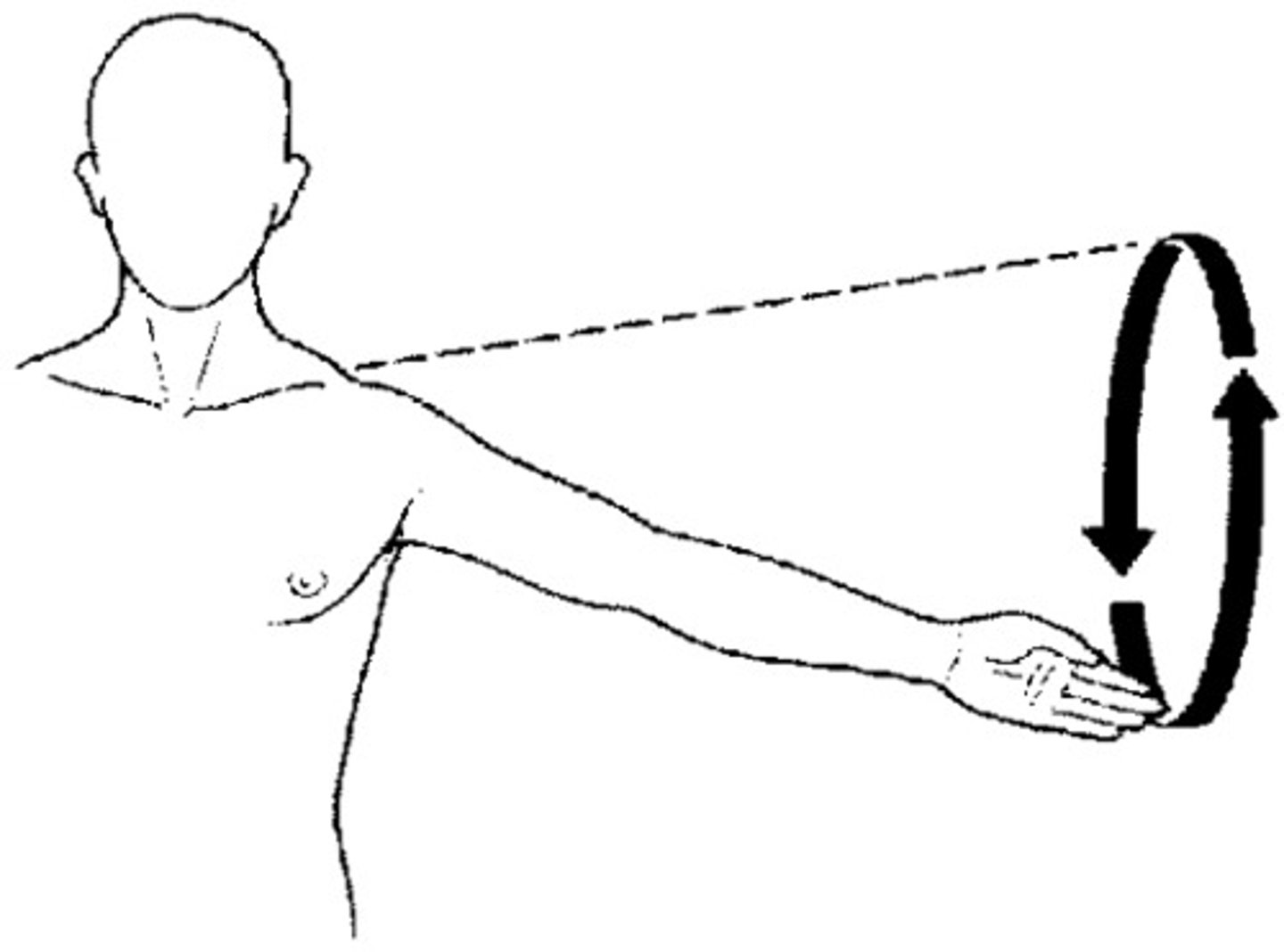
True or false: Ulnar flexion tilts the hand laterally at the wrist?
False
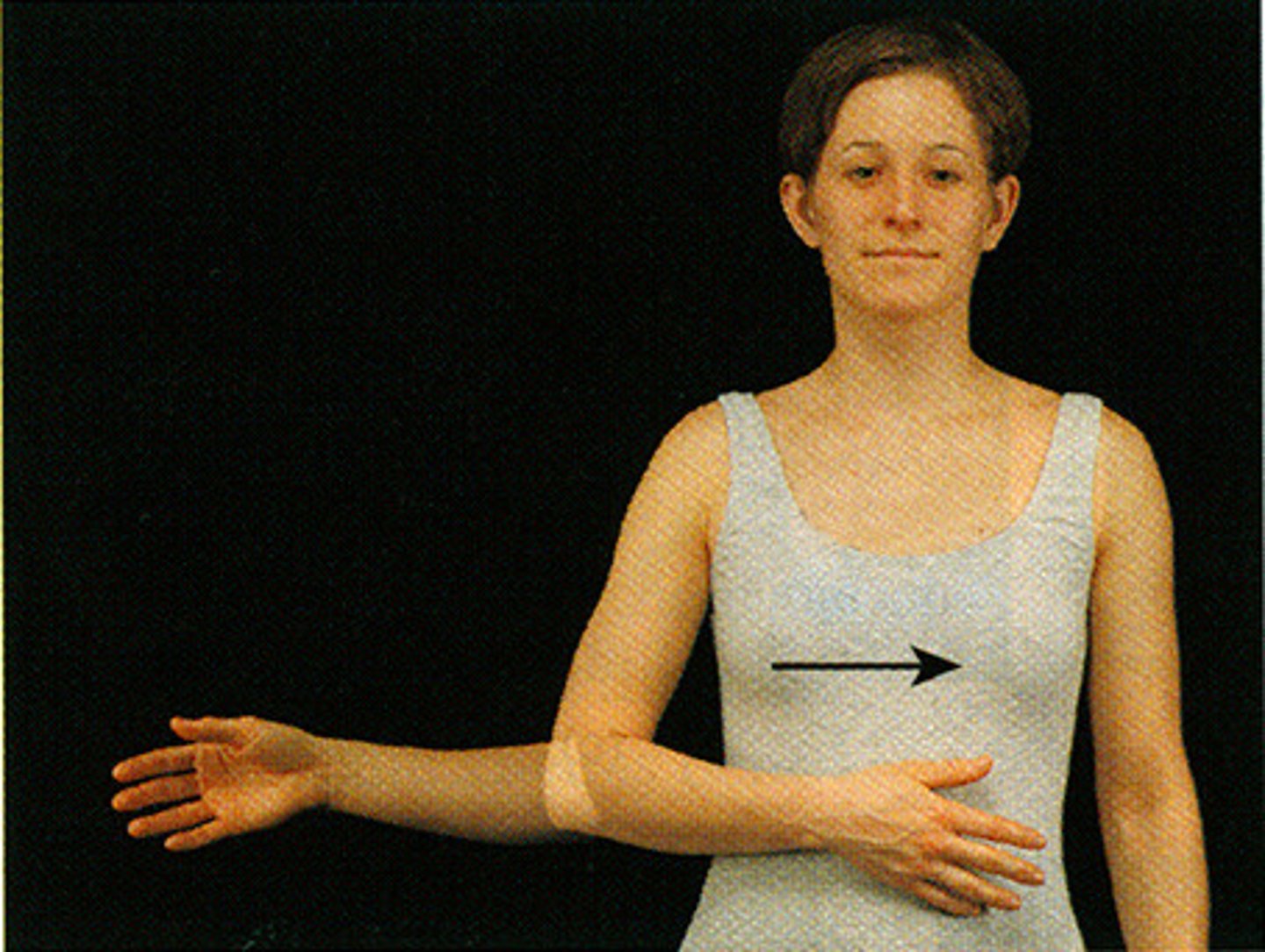
Identify the movement indicated by the arrow (arm inwards)
Medial rotation
What is the movement of toes downward, as when jumping or stepping on a gas pedal called?
Plantar flexion
Which describes pronation?
Turning the palm posteriorly
_______ of the foot turns the sole of the foot laterally
Eversion
Reaching forward to open a door involves which action of the shoulder joint?
Protraction
What factors allow the shoulder to have a wide range of motion?
loose joint capsule and shallow joint cavity
What are the four important muscles that help stabilize the shoulder joint?
Infraspinatus, subscapularis, teres minor, supraspinatus
Tilting the hand medially while in anatomical position is called what?
Ulnar felxion
What is the movement of the foot upwards, as when walking on your heels called?
Dorsiflexion
The tendons of which muscles form the rotator cuff?
Supraspinatus, infraspinatu, teres minor, subscapularis
What is turning the sole of the foot medially called?
Inverison
What are the two articulations of the elbow joint?
Humeroradial/humeroulnar
The ______ joint is the articulation between the arm and shoulder, also known as the shoulder joint?
Glenohumeral
The proximal radioulnar joint ______part of the hinge action at the elbow joint
is not
In addition to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus, what other muscles stabilize the shorter joint?
Teres minor, biceps brachii, subscapularis
Which joint is the most complex diarthrosis in the body?
Knee joint
The joint capsule of the knee encloses which aspects of the knee joint?
Lateral and posterior
What are the two primary stabilizing structures of the knee?
Tendon of the semimembranosus/ tendon of the quadriceps femoris
What are the menisci of the knee composed of?
Fibrocartilage
Which is a superficial ligament located on the medial surface of the knee?
Tibial collateral ligament
True or false: In terms of structure, the knee is no more complicated than either the hip or ankle joints
False
Which knee ligament prevents posterior movement of the tibia?
Posterior cruciate ligament
Which aspect of the knee is not covered by the joint capsule
Anterior