BIo 1AL- lab 7 (fruit fly genetics, comp. 2, PCR analysis)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
(vibrio analysis) how do you remove primers, nucleotides, buffer, and taq polymerase from a PCR sample
spin column with silica membrane
DNA binds tightly to silica membrane in the presence of salt
contaminants are washed away using a salt buffer with ethanol
elution: DNA is released from membrane using low salt buffer
(vibrio analysis) describe principles of agarose gel electrophoresis, and how PCR length affects mobility
insert DNA into cathode (negatively charged) and it travels towards anode (pos charge)
DNA sorts into longest —> shortest
(yeast comp. 2) explain wether His- (histidine synthesis mutants) yeast cells would grow on YPD or SD plates
YPD allows all mutant strains to grow
SD (synthetic defined) medium lacks histidine, so strains will not grow unless they complement (they have mutations on different genes)
sterile velvet is used to transfer from YPD to SD plate
define allele, gene, phenotype, genotype, heterozygote, homozygote, hemizygote, recombinant, homologs, independant assortment, recessive, dominant, incomplete dominance
hemizygous is only one copy of a gene present (AY)
homologs- two things that share a common ancestor
true breeding- offspring that have the same traits as their parents
how to determine probabilities of different phenotypes and genotypes in F1 and F2 generations (autosomal AND sex linked)
what alleles are dominant/recessive?
do genes behave as if they are on autosomes or sex chromosomes
do the genes assort independently or are they genetically linked
if genetically linked, how far away are they from eachother
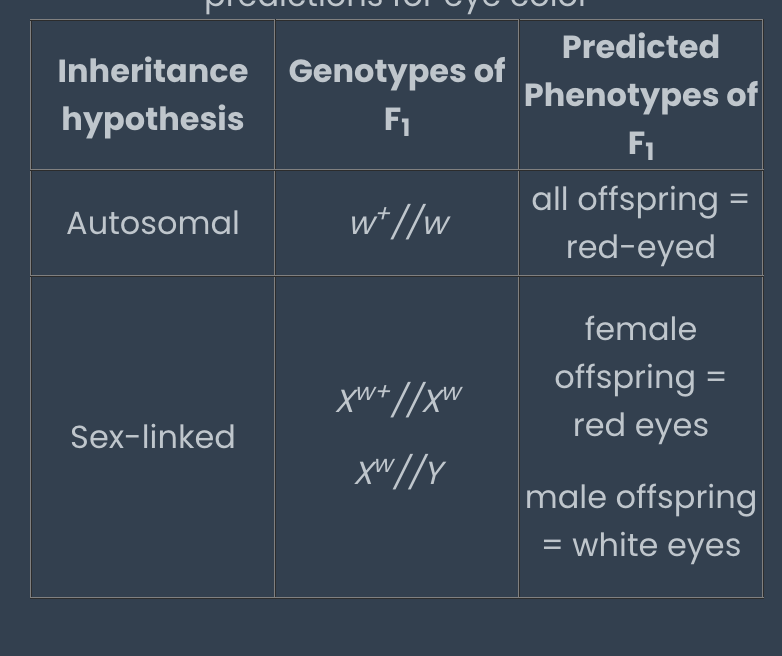
how to draw a genetic map using frequency of recombinants in progeny of a known cross
.When the frequency of recombinant progeny reaches 50%, the genes are considered genetically unlinked: they are either very far apart on the same chromosome or on different chromosomes.
If the frequency of recombinants is less than 50%, we can use this frequency to determine the genetic distance between the two genes.

chi square test
make contingency table and total rows/columns
make null hypothesis that there is no association
expected frequencies: calculate (row total x column total)/grand total
for each cell: (Observed-expected)²/expected
add the results from each cell to get the final X² statistic
use DF (rows-1) x (columns-1) and alpha (0.05) to determine what your X² value should be greater than to REJECT null hypothesis (significant)
genetic notation
The wild-type allele is indicated by the gene name, white or w, followed by the superscript +, e.g., w+.
the double lines represent the two chromosomes in a homologous pair
if 2 different traits are genetically linked, the alleles are written on the same side of the same double lines

hypotheses concerning gene distribution
genes are NOT linked, found on AUTOSOMES
ONE gene is on an autosome the other is on a sex chromosome
genes are genetically linked on either AUTOSOME OR one of the sex chromosomes
what is their map distance if they are linked?
parental vs recombinant gametes
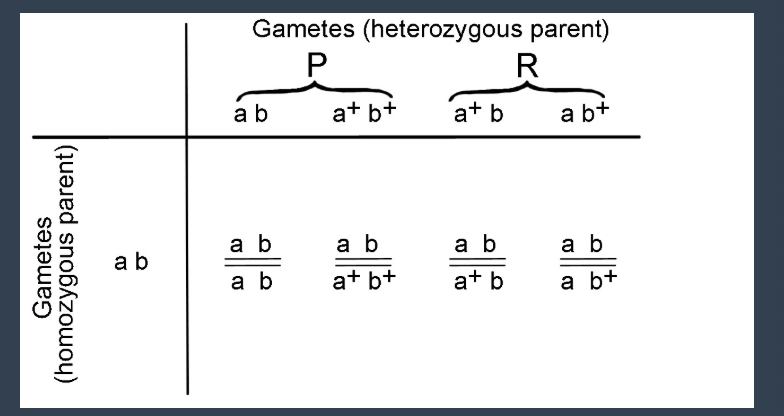
map distance
probability that crossing over will occur between two genes
if it’s less than 50%, the genes are linked by that percentage of map units
determining fly sex
Females are slightly larger and have a larger, lighter-colored abdomen that appears banded. The males have smaller, slightly darker abdomens, especially posteriorly. Males also have a tuft of thick, dark bristles (the sex comb) on each first leg.
