CHM 104 Exam 4
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Organic Chem, Biochem, and Nuclear Chem
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Organic Chem - main molecules and bonding
Carbon - 4 bonds, 0 lone pairs
Hydrogen - 1 bond, 0 lone pairs
Nitrogen - 3 bonds, 1 lone piars
Oxygen - 2 bonds, 2 lone pairs
building blocks of biological systems
structural isomers
same formula, different arragement of bonds
geometric isomers
same formula, same arrangement of bonds, different orientation of bonds in the same space - around a double bond (cis and trans)
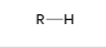
alkane
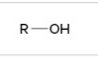
alcohol
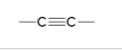
alkyne
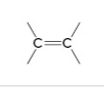
alkene
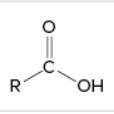
carboxylic acid
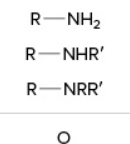
amine (1, 2, 3)
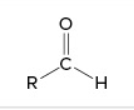
aldehyde
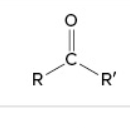
ketone
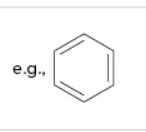
aromatic
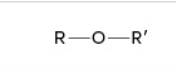
ether
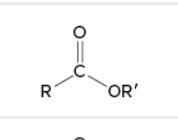
ester
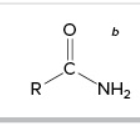
amide
optical isomers (enantiomers)
mirror images not superimposable , important in biological chemistry
chirality
must have 4 different groups bonded - property of non superimposable images
polarimetry
measure rotation of the plane polarized light (only way to distinguish 2 enantiomers)
carboxylic acid acidity + amine basicity
to produce 1 H+ ion and charge carboxylic acid
amines - weak organic base - + water
to produce 1 OH- and amine of higher property
condensation
2 smaller molecules join —> larger molecule and H2O
hydrolysis
H2O reacts with larger molecule break —> 2 smaller molecules
carboxylic acid + amine (condensation)
amide and H2O (CNOH form) and (CONH break)
amide + h2O (acid catalyzed) (hydrolysis)
carboxylic acid and amine (CONH form) (CNOH break)
carb condensation - alcohol and alcohol (acid catalyze)
ether and H2O
carb hydrolysis- ether + H2O
alchol and alcohol
carboxylic acid + alcohol acid cat. - condens
ester and H2O (C-OR formed and C-OH broken)
**hydrolysis carboxylic acid (acid base cat.)
carboxylic acid and ester
biological nutrients
proteins, carbohydrates, fats
protein purpose
building materials, large structures
muscles, skin, hair, nails, organ tissue
enzymes blood cells
protein polymer and monomer
amino acid and polypeptides
amino acids differ by
polar, nonpolar, acidity, basicity, size, and shape
amino acids in humans
20 different
vary in order
structural and functional diversity
2 pKa values for amino acid
cationic amino - protenated form (low pH)
→ deprotenate once (neutral)
anionic amino acid - pka2 proton off amoniu (basic)
are amino acids chiral? isomers?
YES
peptide bonding
between oh of carboxylic acid group and H of amide to for peptide bond
N and C terminus
protein amide
amino acid condensation
amide
protein amide bond
peptide bond
polypeptide formation
protein
small molecule
beta sheets+ribbons polypeptides or R groups
primary structure
polypeptide chain
secondary structure
alpha helix/beta pleated sheets (h bonds stabilize)
helix w/ R pendant groups
polar and non polar sides based on R groups
beta w/ pendant R groups
tertiary structure
all aspects of how secondary bundles
quaternary structure
more than 1 tertiary structure
protein in body
9 are in body 11 are eaten
protein assembly
condensation joins amides ie to make enzymes and tissue
disassembly
hydrolysis break samides aka food protein digestion —> amino acids —> liver —> reassembly in cells