kowluru signal transduction
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
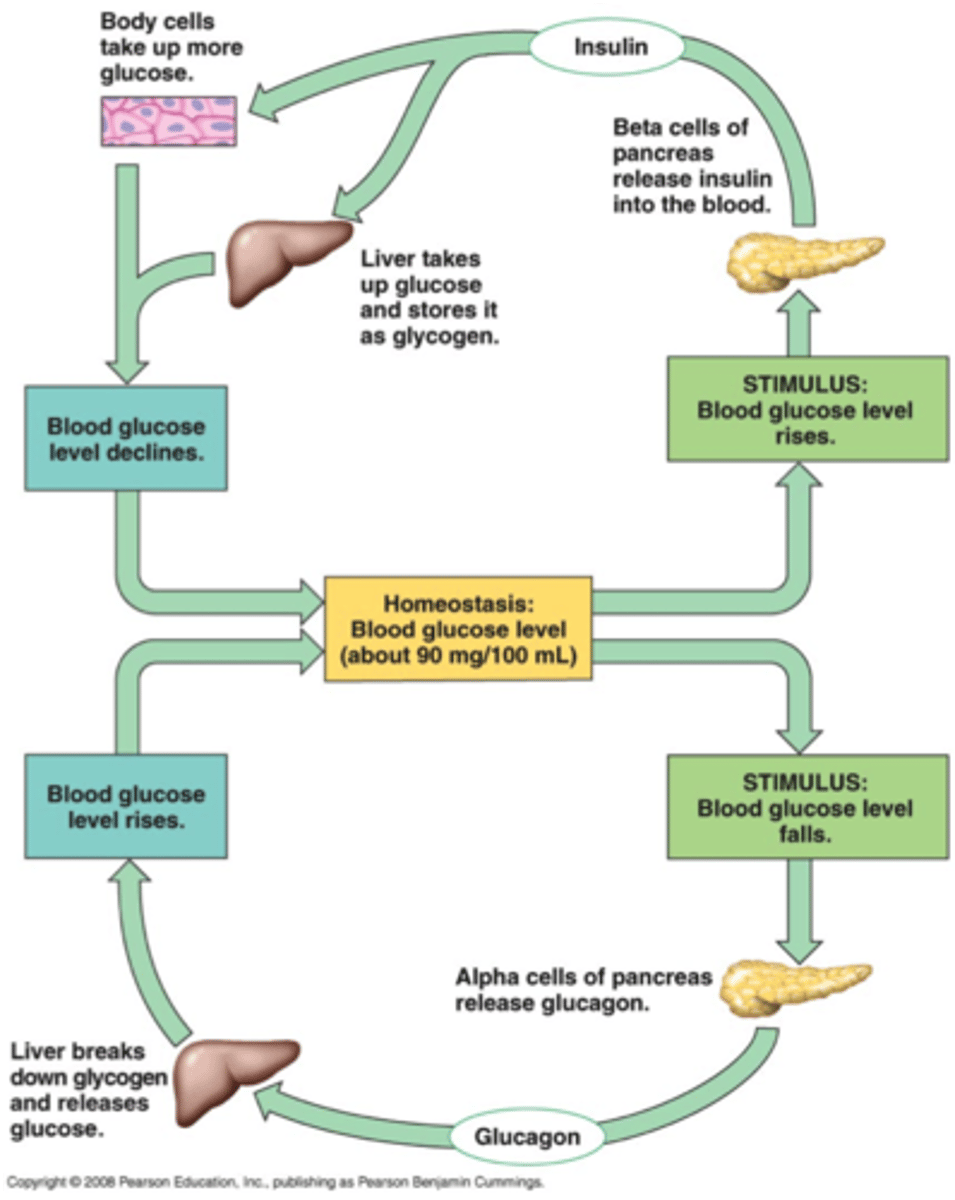
summarize homeostasis of blood glucose
1. low blood glucose-> pancreas alpha cells-> glucagon to liver-> glucose released
2. high blood glucose-> pancreas beta cells-> insulin to fat cells-> glucose taken in
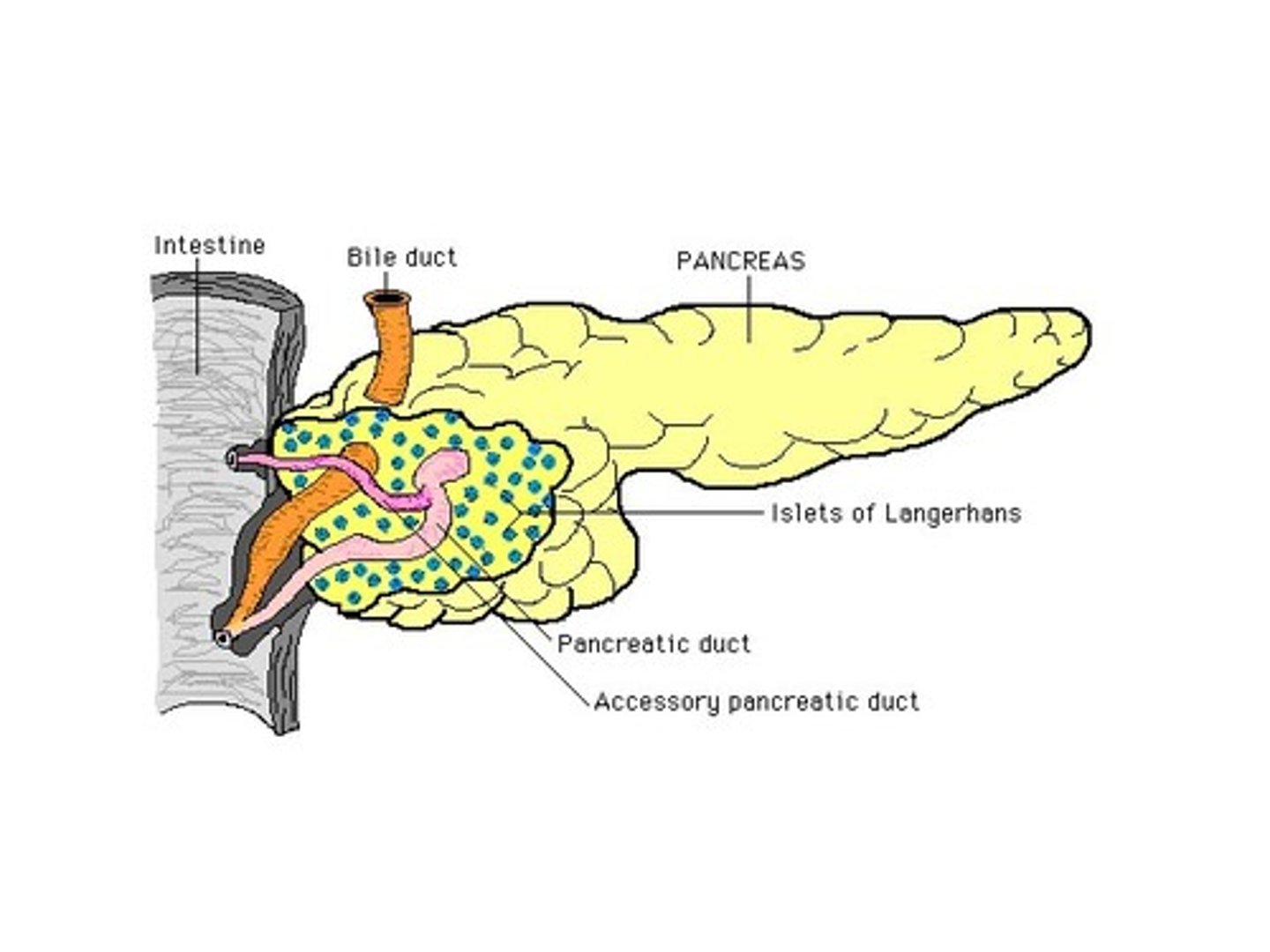
islets of langerhans
areas of pancreatic cells that produce insulin and glucagon
a hormone stain of the islets of langerhans would have what colors? what do they represent?
green= beta cells-> insulin (60%= majority)
blue= alpha cells-> glucagon
pink= delta cells-> somatostatin
which cells of the pancreas form the majority of the islets of langerhans and what do they secrete
beta cells (60%)= insulin
summarize how insulin is released from beta cells
1. glucose lands on GLUT2= enters beta cell
2. metabolism
3. increased ATP/ADP ratio [AND GPCR activation-> Ip3-> calcium]
4. ATP causes K channel to close (K cannot leave)
5. membrane depolarization (more +)
6. Voltage dependent calcium channel opens (VDCC)
7. Ca2+ rushes in
8. increased Ca promotes insulin granule exocytosis
![<p>1. glucose lands on GLUT2= enters beta cell</p><p>2. metabolism</p><p>3. increased ATP/ADP ratio [AND GPCR activation-> Ip3-> calcium]</p><p>4. ATP causes K channel to close (K cannot leave)</p><p>5. membrane depolarization (more +)</p><p>6. Voltage dependent calcium channel opens (VDCC)</p><p>7. Ca2+ rushes in</p><p>8. increased Ca promotes insulin granule exocytosis</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e49ed423-f239-49e6-9263-7608f3b3ac85.jpg)
insulin is stored as ______ in ________ cells
granules; beta
what prevents movement of insulin granules to membrane under basal conditions? what stops these barriers?
cytoskeleton (ex: F-actin); glucose stimulus disrupts these barriers
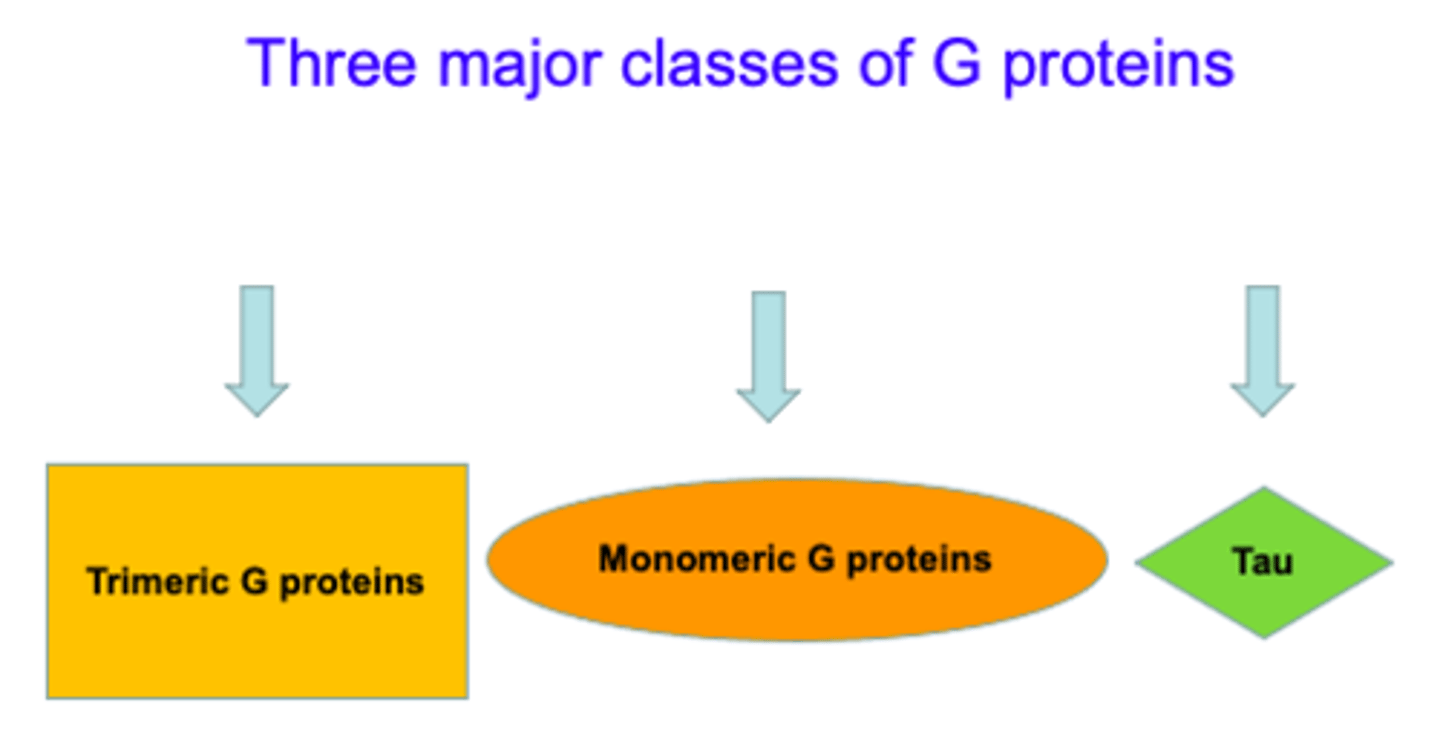
3 major classes of G proteins
1. Trimeric= alpha, beta, gamma
2. Monomeric= single subunit; cytoskeletal reorganization
3. Tau= less studied, protein biosynthesis
t/f: all G proteins bind to GTP
true
GTP-bound form is ________
GDP-bound form is _________
gtp= active
gdp= inactive
inhibitory vs stimulatory G protein on cAMP
inhibitory decreases cAMP
stimulatory increases cAMP via adenylyl cyclase
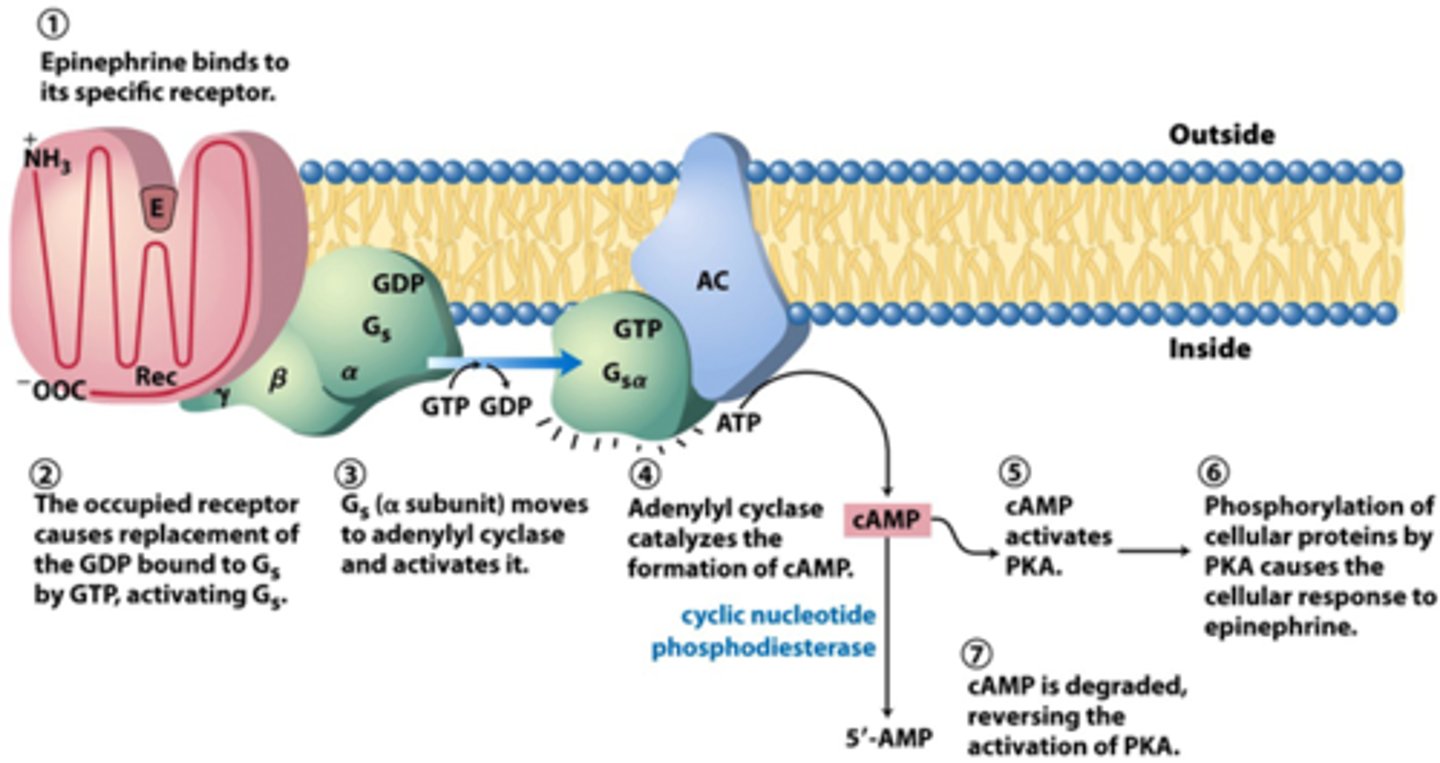
t/f: under basal conditions, the heterotrimeric G protein stays as a complex, with the alpha subunit only dissociating upon activation
true; alpha dissociates when bound to GTP
the alpha subunit is active when it is bound to
GTP
which enzymes hydrolyzes GTP back to GDP
GTPase
t/f: both alpha and beta/gamma can activate effectors
true
small molecular mass G proteins role
- single subunits (20-25kDa)
- several classes that have many functions : cytoskeletal remodeling, vesicle fusion, docking
ex: Ras, Rho, Rac1
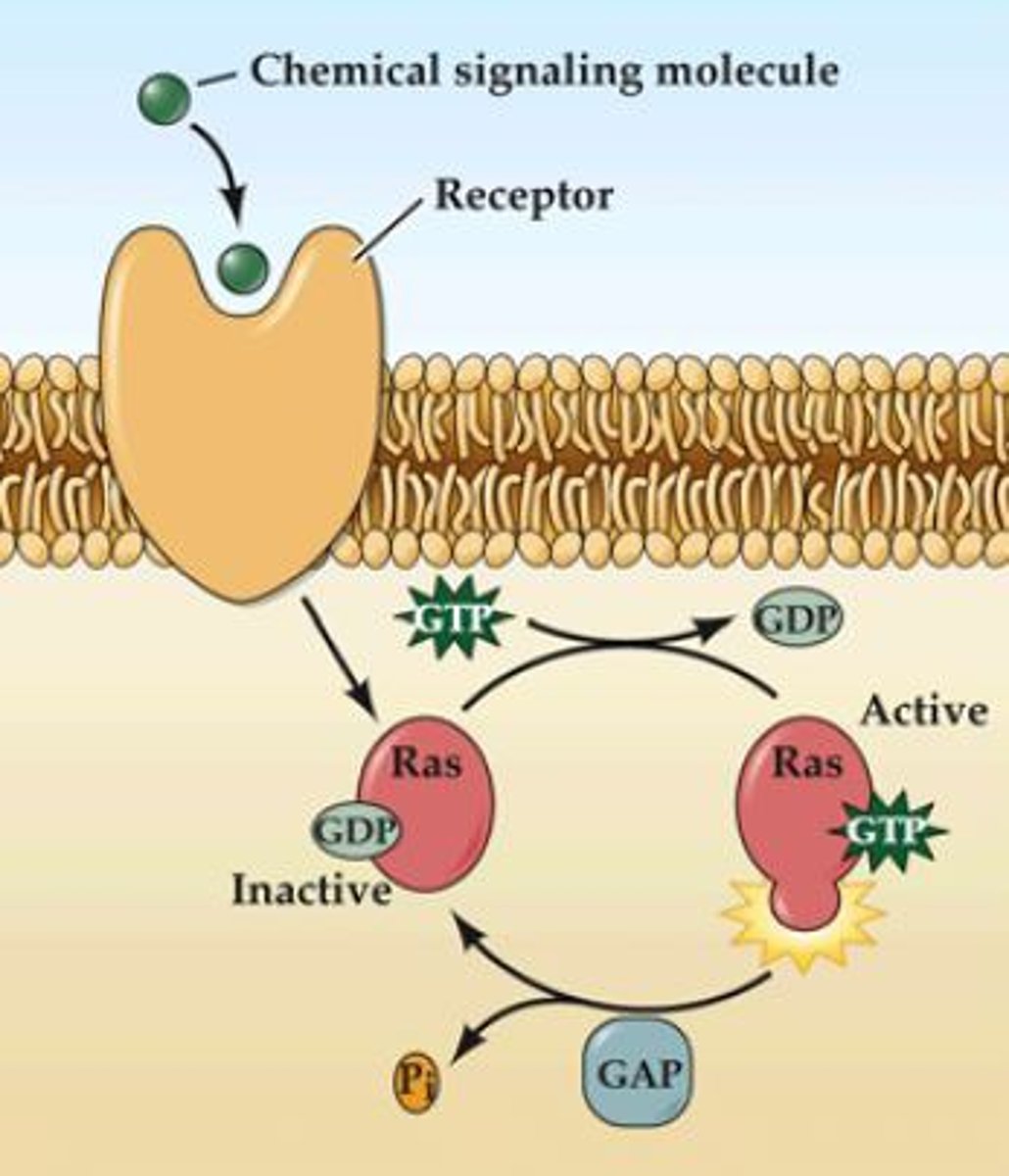
small G protein activation and deactivation
Gprotein + GDI (GDP dissociation inhibitor) = INACTIVE/GDP
->GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factors): makes G-protein ACTIVE/GTP
->GAP= GTPase-activating protein= deactivates back to G + GDI
G-protein + GDI=
GEF=
GAP=
involved in small G protein activation/deactivation
GDI= GDP dissociation inhibitor= INACTIVE
GEF= guanine nucleotide exchange factors (MAKES ACTIVE)
GAP= GTPase activating protein (MAKES INACTIVE)
t/f: activation of small G proteins follows the same steps as the trimeric G proteins
false. small G protein involves GEFs, GAP, GDI
t/f: heterotrimeric G proteins are not anchored to the membrane and are allowed to float through the cytoplasm
false. they are anchored to the membrane via lipids
which post-translational modification steps assist in G protein lipid anchoring
alpha subunit= myristylation (N-terminus) and palmitoylation (cysteine)
gamma subunit= prenylation (C-terminus)
*note beta is attached to gamma which is attached to membrane
t/f: G protein lipid anchoring is a post-translational step
true
effects of lipidation of G-proteins (lipid anchoring)
1. increase hydrophobicity= translocation to membrane
2. increase interactions btwn proteins and receptors
3. increase association btwn subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma)
phospholipase C
enzymes that hydrolyzes phospholipids on the membrane; activated by GTP-alpha
cleaves PIP2 into DAG and IP3
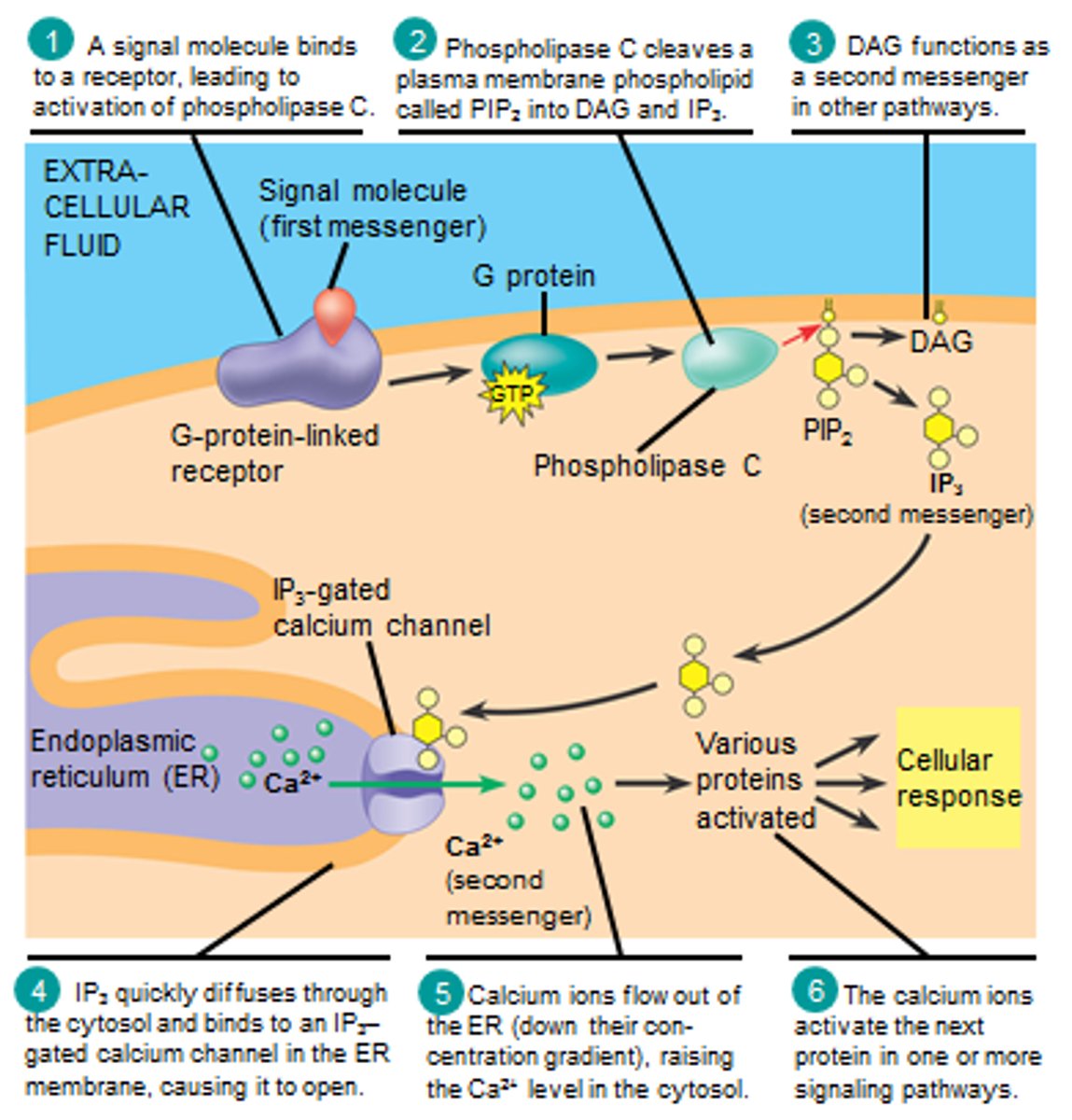
PIP2 is a phospholipid cleaved by __________ into ____________
phospholipase C: DAG and IP3
DAG
diacylglycerol
stays in membrane (hydrophobic); activates protein kinase C
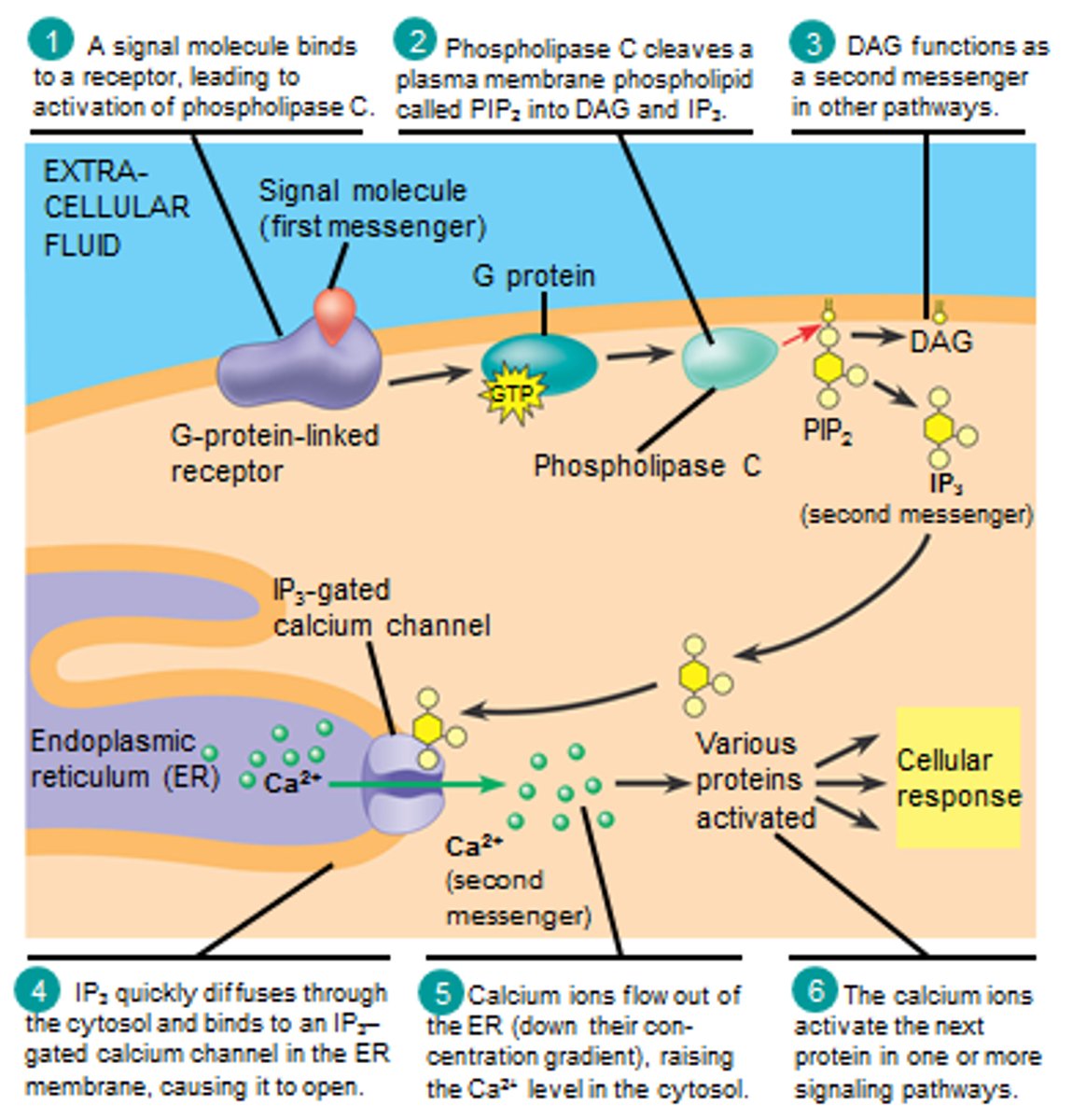
IP3
inositol triphosphate
hydrophilic; promotes calcium release
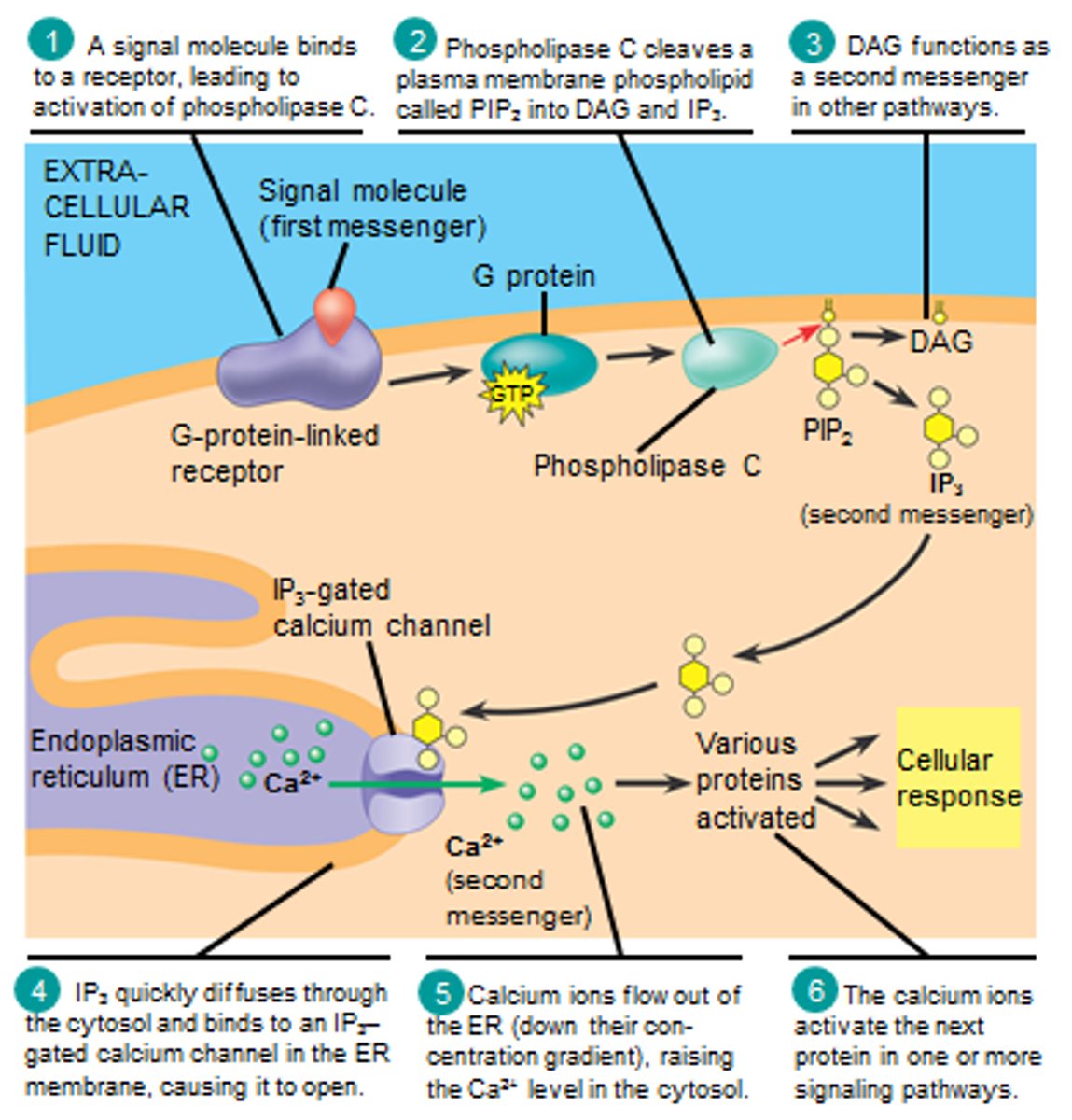
t/f: DAG is a hydrophilic molecule that forms upon PIP2 cleavage and leads to increased calcium
false. that is IP3. DAG stays in membrane (hydrophobic) and activates protein kinase c
upon PIP2 cleavage and IP3 formation, what does IP3 do?
lands on IP3 gated calcium channels, releasing calcium from the ER
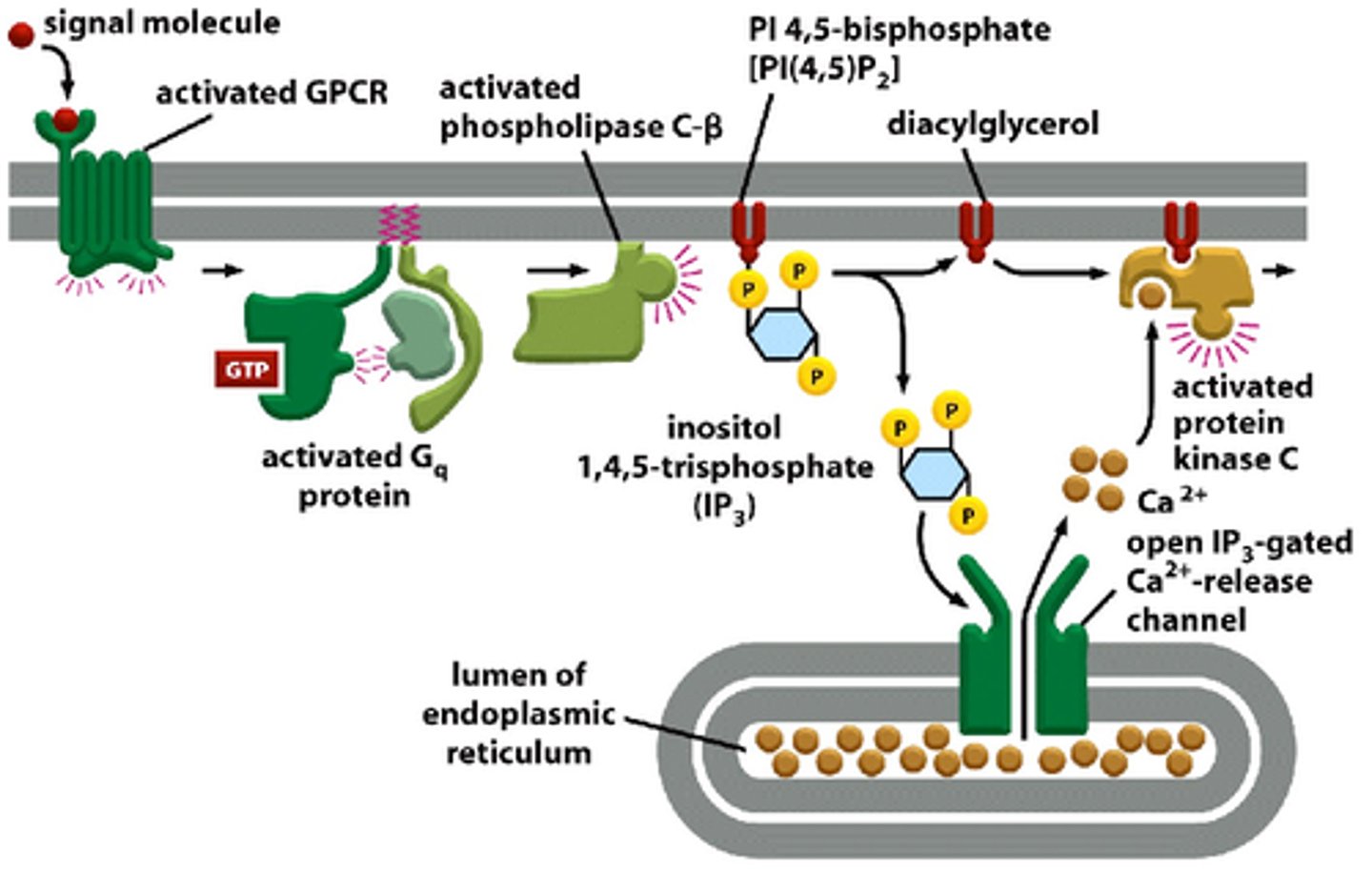
DAG is hydro_____ while IP3 is hydro_____. where do they reside?
DAG= hydrophobic (stay in plasma membrane)
IP3= hydrophilic (cytosol)
t/f: cAMP, cGMP, and calcium are all hydrophilic second messengers
true. all soluble in cytosol
what does DAG activate
protein kinase C
what does cAMP activate?
protein kinase A
functions of cAMP
1. intracellular second messenger
2. regulate ion channels
3. activate protein kinase A
4. regulate guanine nucleotide exchange factors
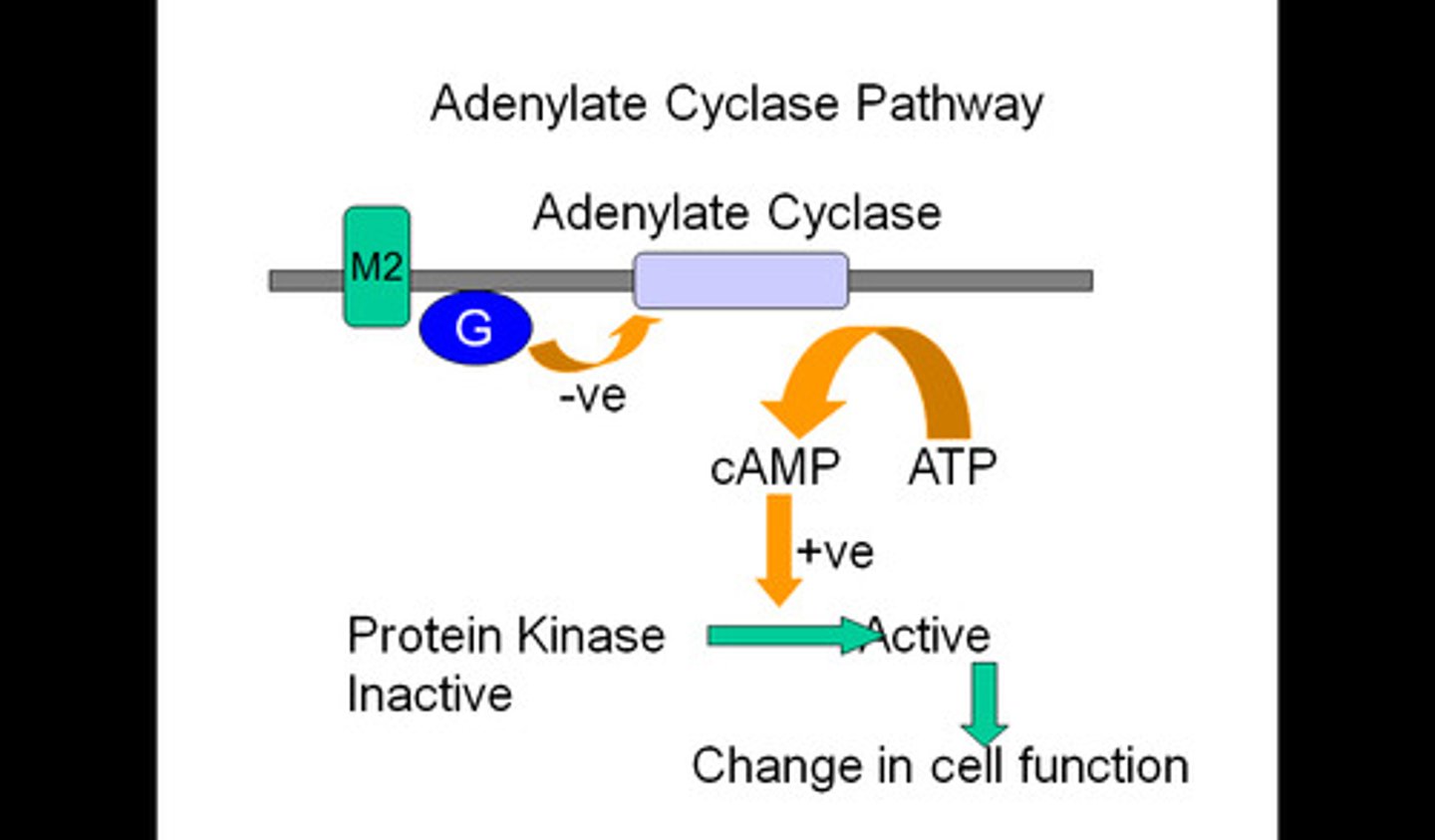
adenylate cyclase equation
ATP-> cAMP + PPi (makes cAMP)
phosphodiesterase equation
cAMP + H2O -> AMP (inactive)
which enzyme makes cAMP? breaks?
makes: adenylate cyclase
breaks: phosphodiesterase
protein kinase vs protein phosphatase
kinase: phosphorylates OH of serine, threonine, tyrosine to make ACTIVE protein
phosphatase: removes phosphate
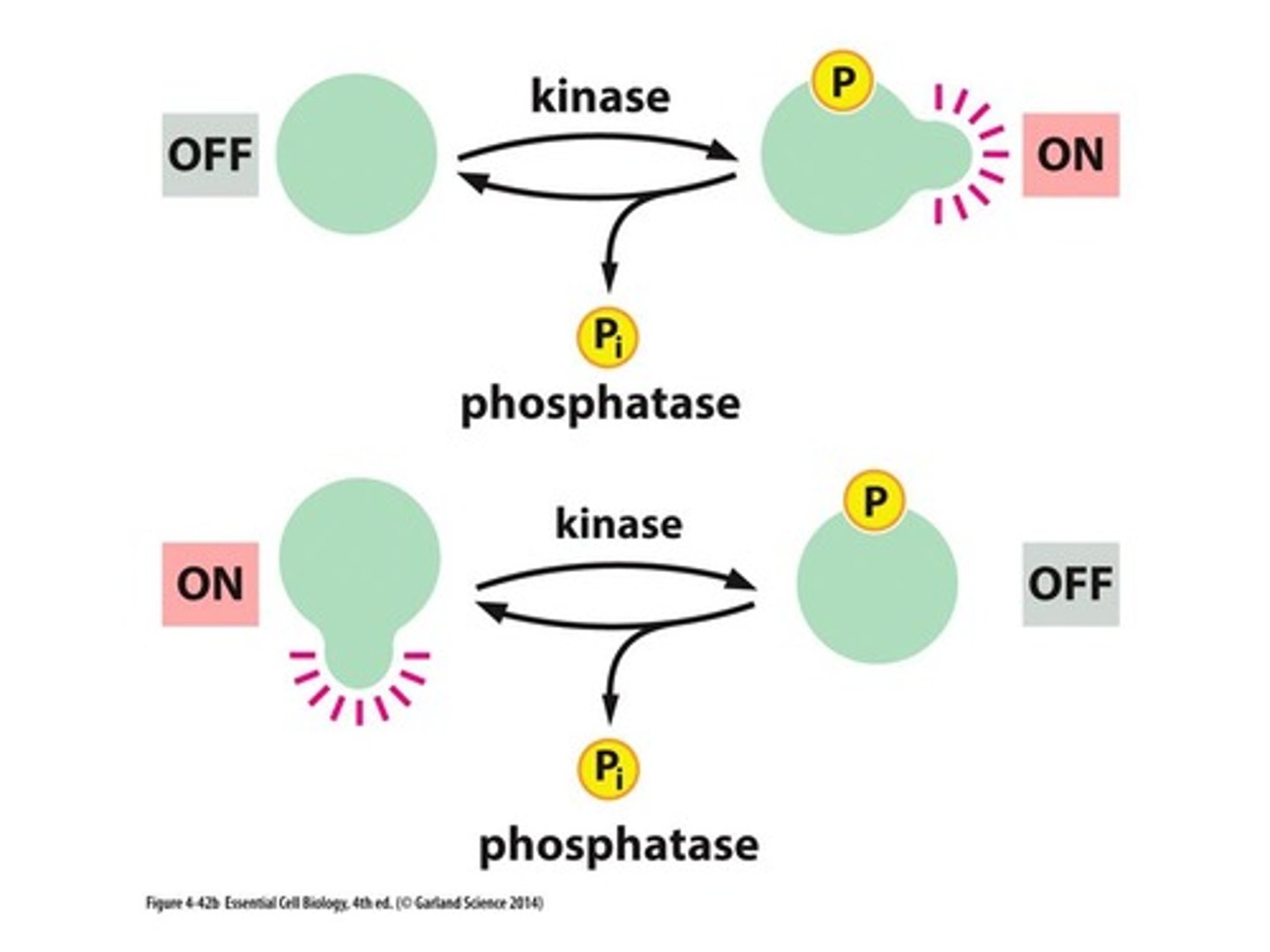
how does protein kinase add a phosphate group
phosphorylates OH group of amino acids (serine, threonine, tyrosine)
nearly ________ protein kinases are encoded in the human genome
500
t/f: the activity of protein kinases and phosphatases regulate enzyme activity by activation and inactivation
true
which molecule does protein kinase remove a phosphate from in order to add to an amino acid
ATP-> ADP
how is protein kinase C activated and what does it do
activated by DAG, calcium, TPA; it is a kinase so it phosphorylates OH on amino acids

what activates protein kinase A? what does it do?
cAMP; phosphorylates enzymes
which molecule can activate protein kinase C without G protein stimulation
TPA= tissue plasminogen activator (goes right through membrane)
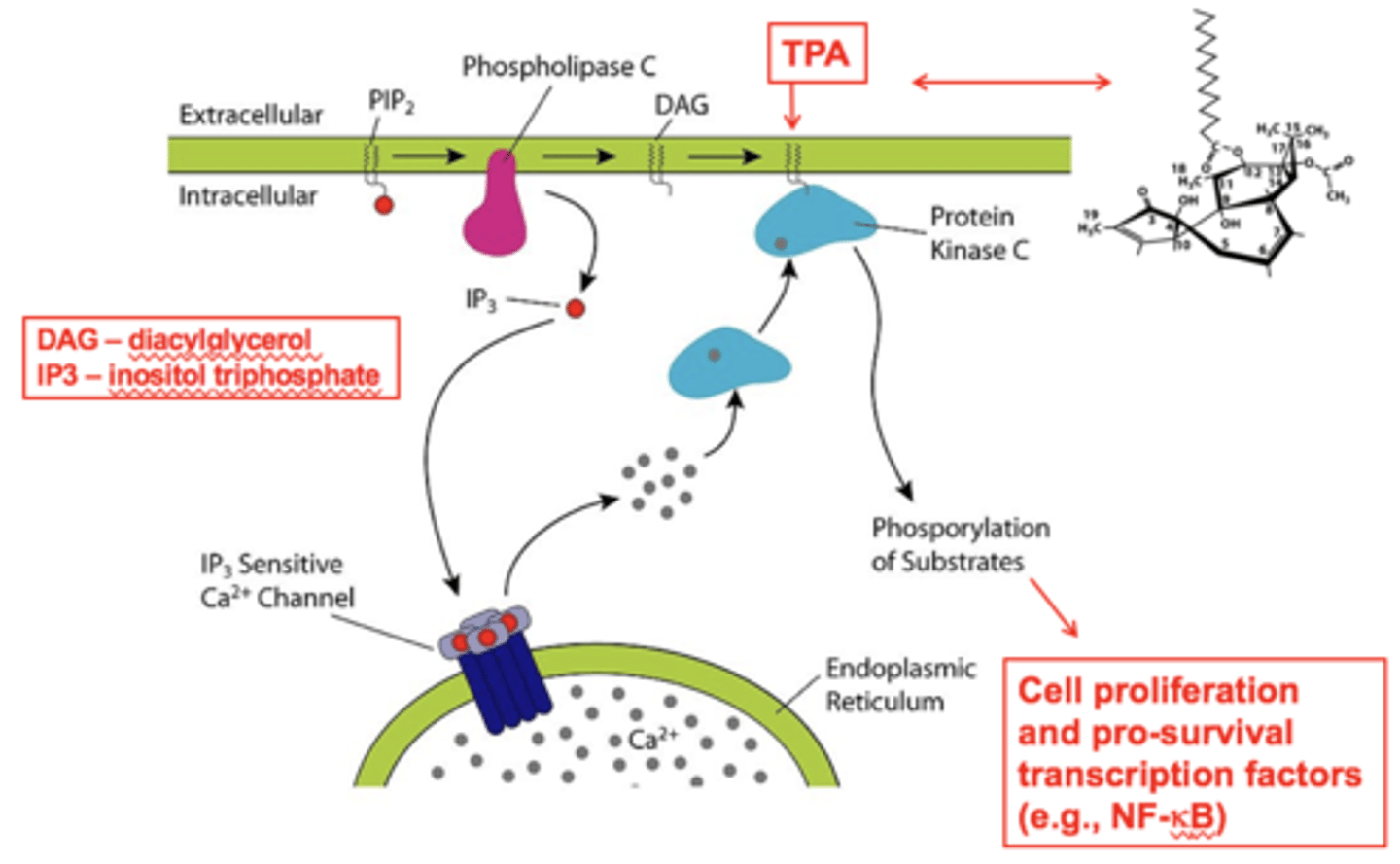
_____________ are the antagonists of protein kinases
protein phosphatases
t/f: phosphatases can activate a protein through dephosphorylation or they can dampen the effects of kinases
true
summarize GTP cell signaling transduction (big overview)
1. ligand lands on GPCR
2. alpha subunit+GTP dissociate
3. activates phospholipase C: PIP2-> DAG and IP3
-DAG [along w calcium, TPA] activates protein kinase C
-IP3 promotes calcium release
3. activates adenylate cyclase: ATP-> cAMP
-cAMP activates protein kinase A