COSI 325 Neuroanatomy Pt.2 (brainstem, CN, and blood supply)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What are the three sections that the neural tube divided into?
forebrain
midbrain
hindbrain
What are the two parts of the forebrain?
telencephalon
Diencephalon
What are the two important structures of the diencephalon?
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
What does the thalamus do?
the thalamus is your body's information relay station. All information from your body's senses (except smell) must be processed through your thalamus before being sent to your brain's cerebral cortex for interpretation.
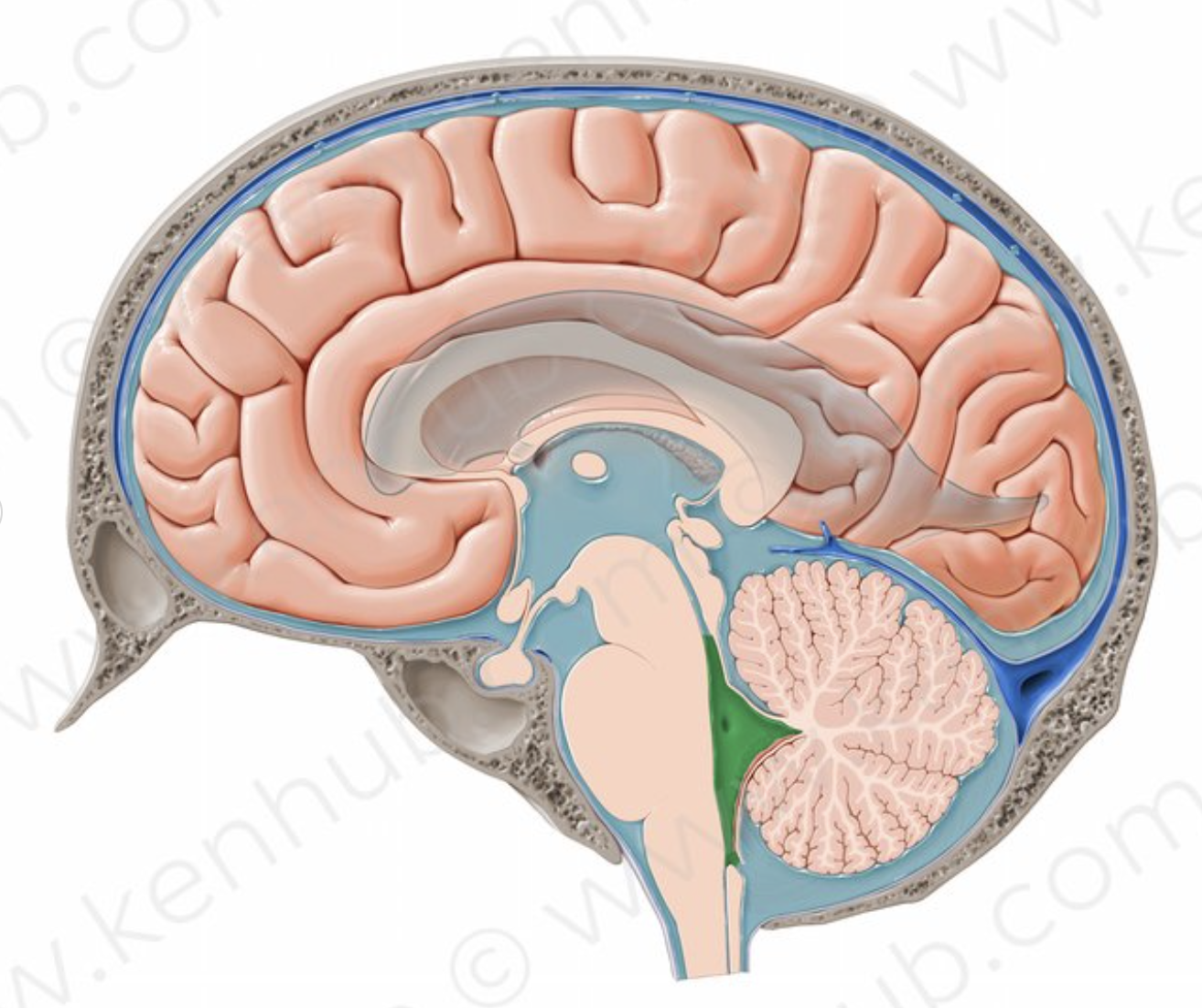
What structure is in green?
4th ventricle
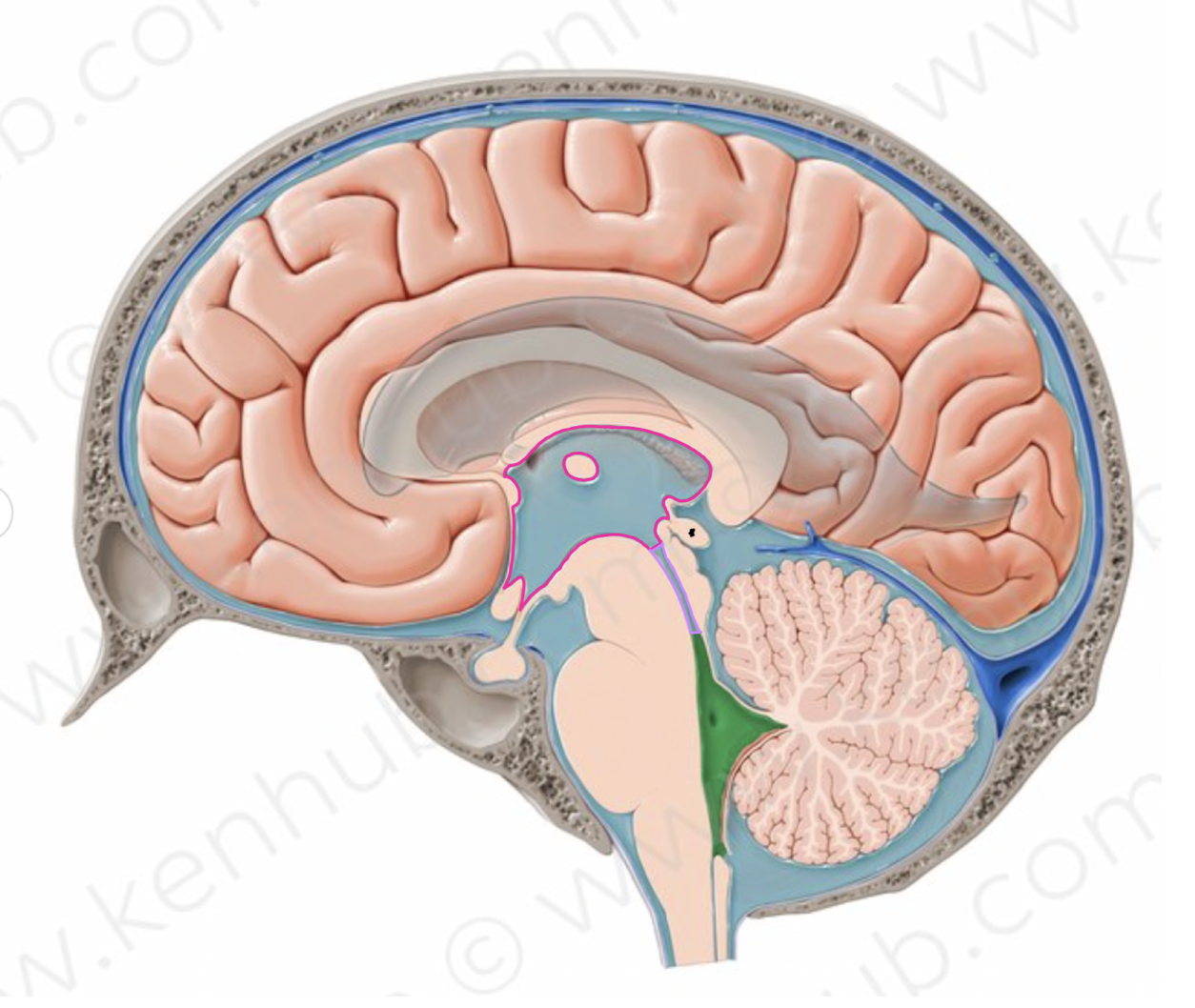
What structure is outlined in pink?
third ventricle
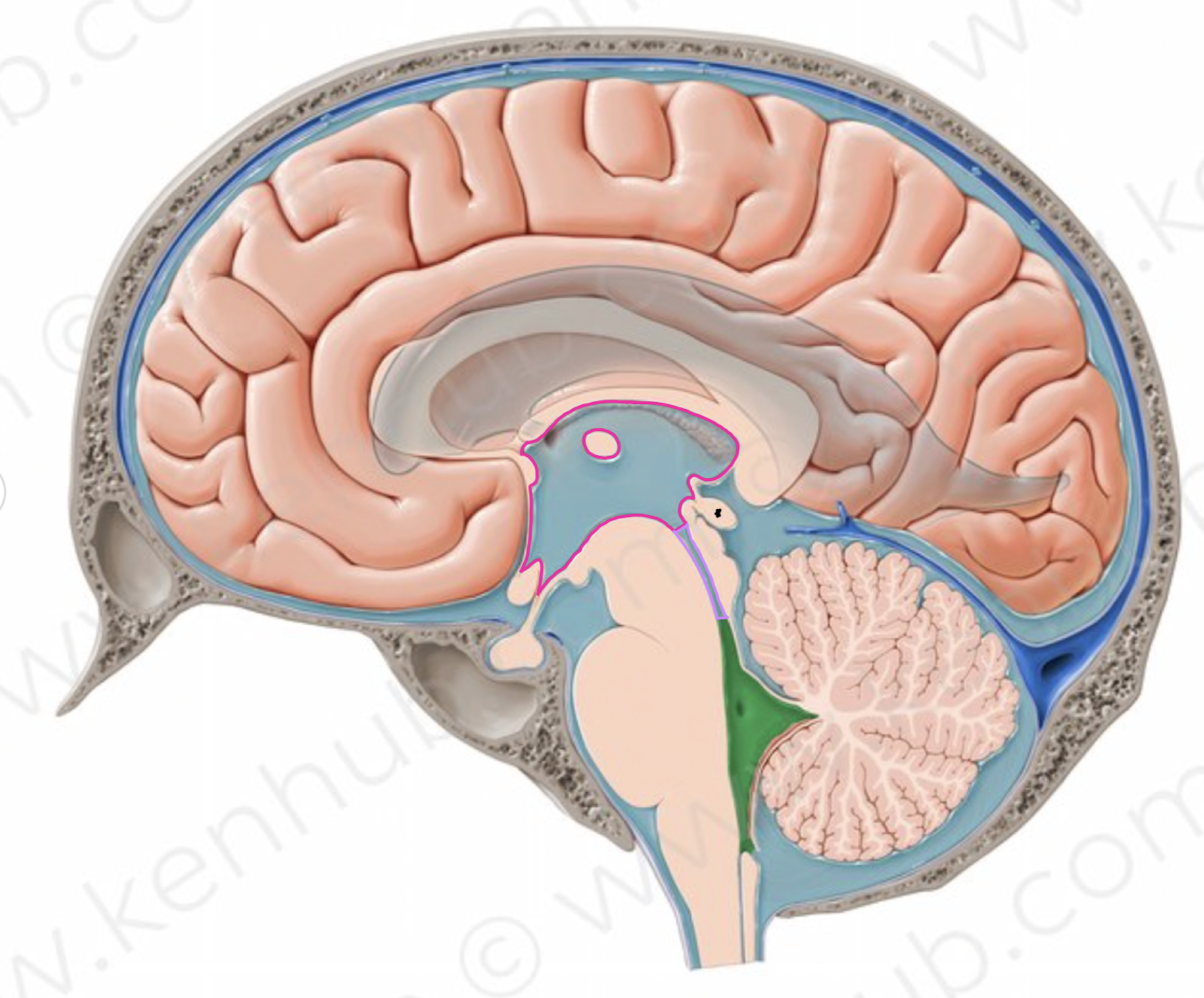
What structure is outlined in purple?
cerebral aqueduct
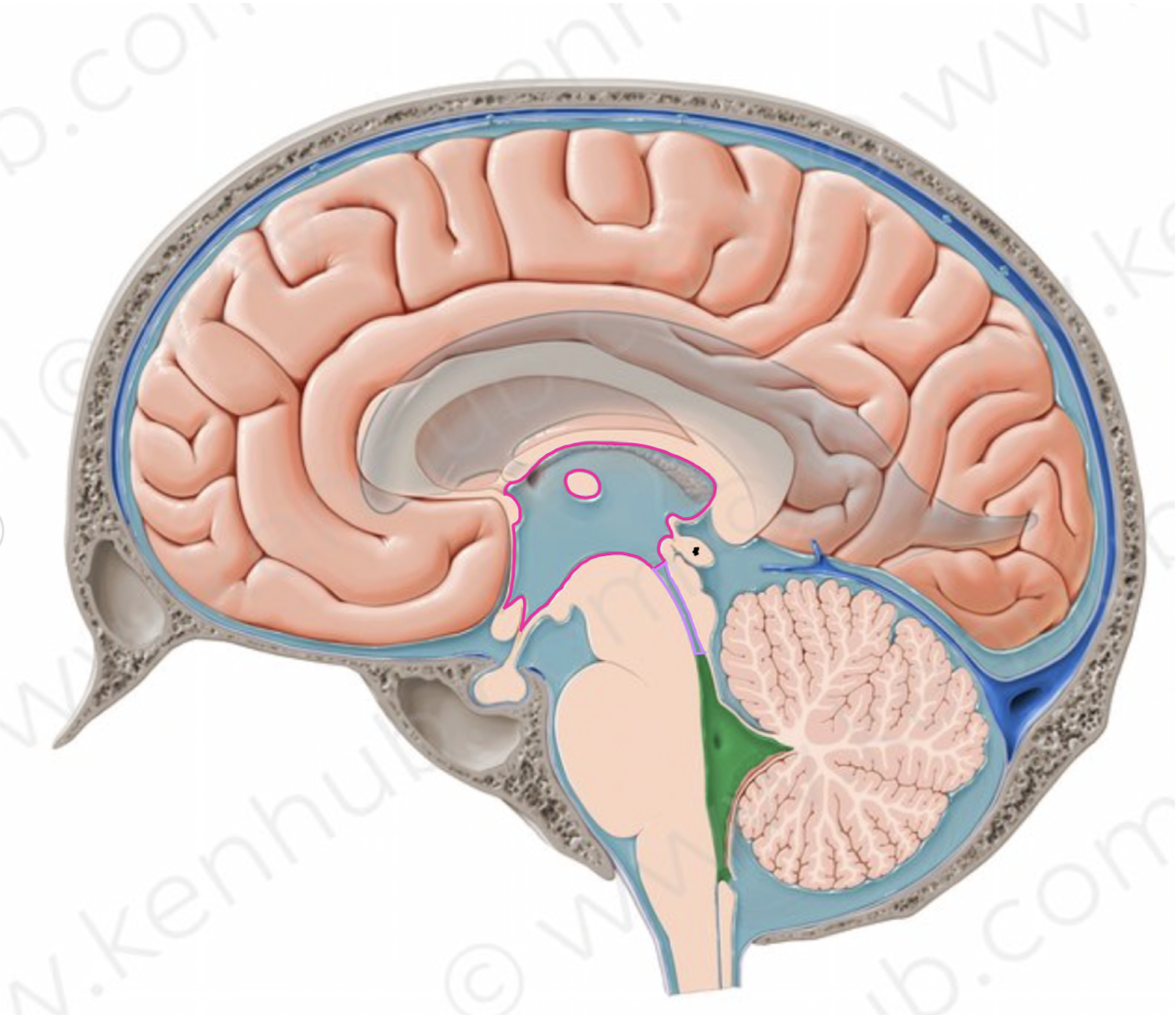
What is the name of the structure labeled with a star?
pineal gland
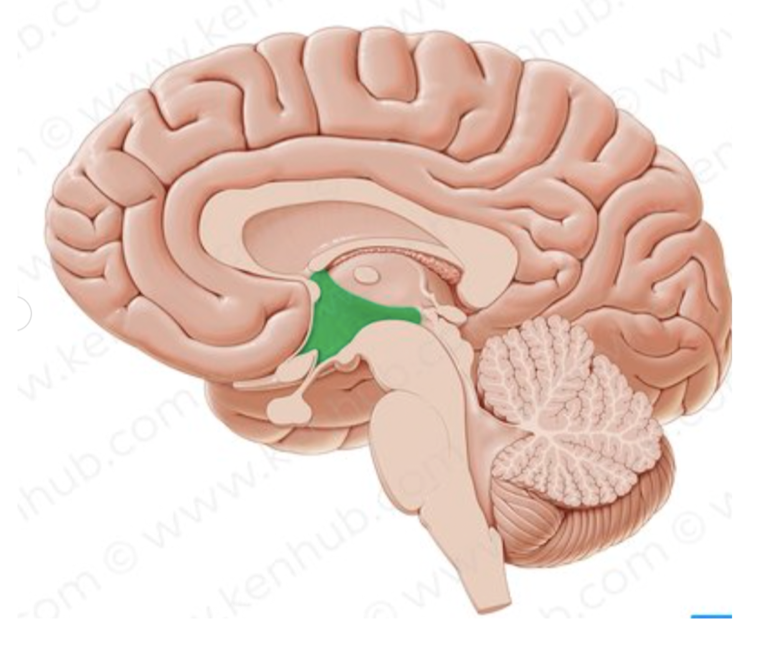
What structure is in green?
Hypothalamus
What does the hypothalamus do?
regulates body temperature
when someone is actively dying it is the fist to go —> person will experience fevers and chills
What are habenula nuclei?
These are nuclei found in the posterior thalamus
they regulate serotonin (happy) and dopamine (move)
What two parts make up that hind brain?
pons
medulla oblongata
How does the brainstem communicate with the cerebellum?
Via peduncles
connect each section of the brainstem to the cerebellum
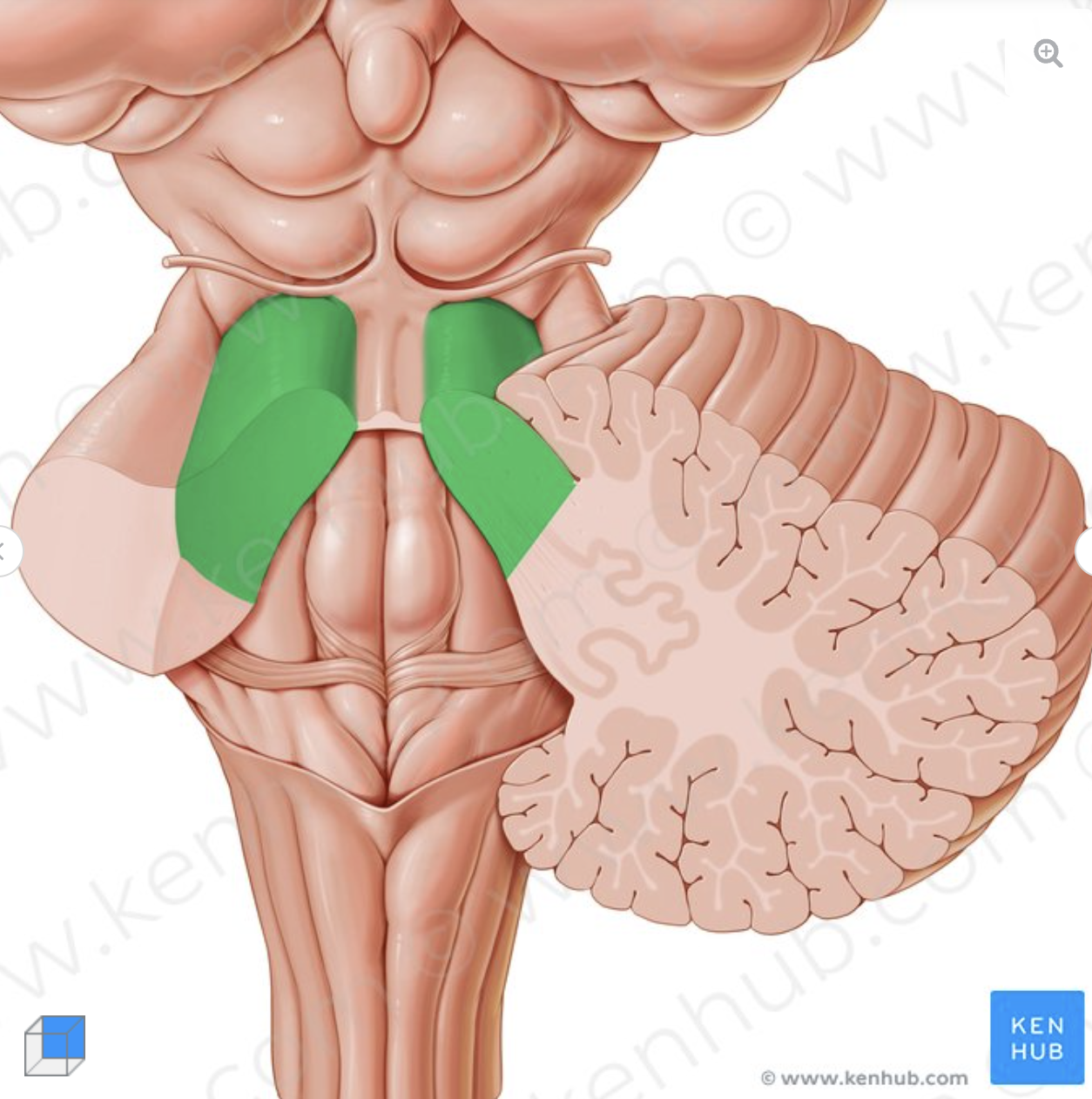
What is the structure in green?
Superior cerebellar peduncle
connects midbrain to the cerebellum
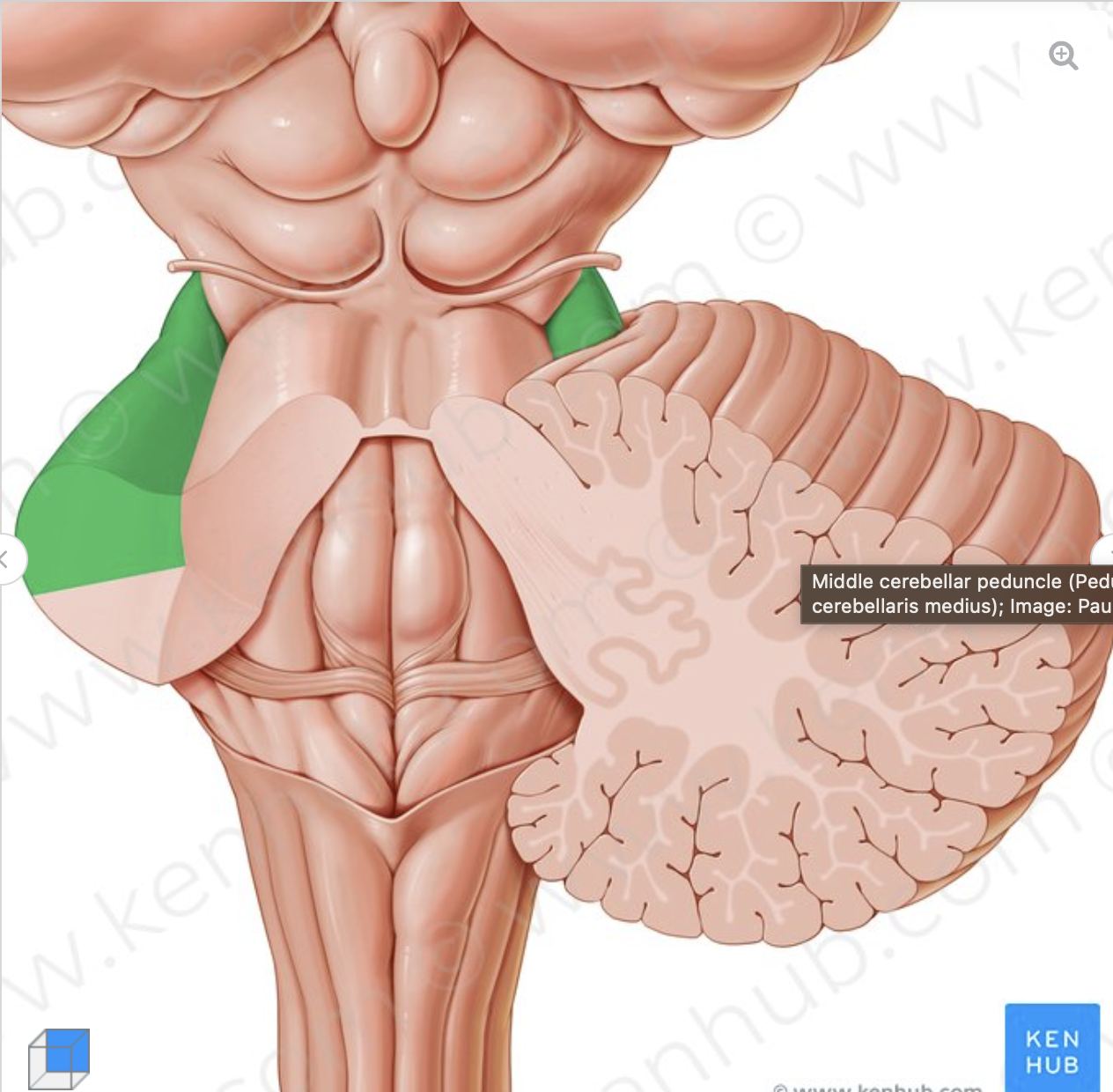
What is the structure in green?
middle cerebellar peduncle
connects pons to the cerebellum
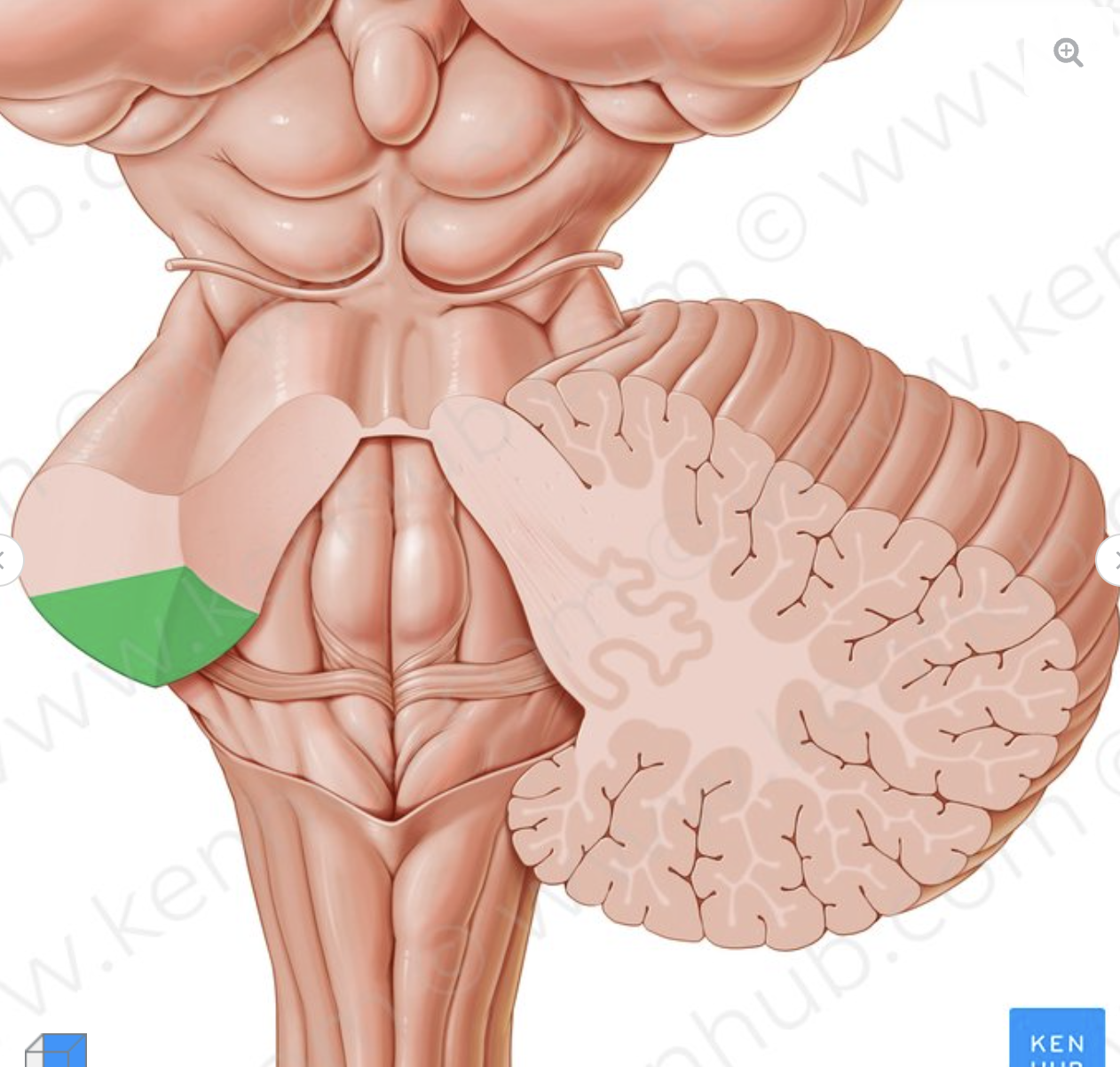
What is the structure in green?
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
connects the medulla oblongata to the cerebellum
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
fine-motor movements
What is ataxia?
stroke to the cerebellum
drunk syndrome
slurred speech (sounds drunk)
unable to perform fine motor movements
What are the three divisions of the midbrain? (superior to inferior)
tectum
tegmentum
crus
What two things are found in tectum of the midbrain? What are their functions
Superior colliculus
visual reflex (like auditory reflex in the inferior colliculus)
Pretectal nuclei
pupillary light refelex
What are the six things found in the tegmentum of the midbrain?
Cerebral Aqueduct
periaqueductal grey matter
medial longitudinal fasiculus (MLF)
Motor Nuclei of CN III Oculomotor
Parasympathetic Branch of CN III Oculomotor
Pars compacts of the substantia nigra
What runs through the cerebral aqueduct?
cerebral spinal fluid
what is the function of the periaqueductal grey matter?
provides cushion to the cerebral aqueduct
what does the medial longitudinal fasiculus (MLF) do?
assists with eye and head movement
What are the two parts that make up the substantia nigra?
pars compacts
pars reticulata
What is the function of the pars compacts section of the substantia nigra?
this is where dopamine is made
when there is an issue with this structure —> parkinsons disease
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter made in your brain. It plays a role as a “reward center” and in many body functions, including memory, movement, motivation, mood, attention and more
What is the function of the pars reticulata section of the substantia nigra?
this is where GABA is made
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter
problems in this section can lead to anxiety and depression
Benzodiazepines —> used to treat anxiety and depression by causing an uptake in GABA production within this area
What are the two parts of the oculomotor cranial nerve?
motor nuclei of CN VIII
Parasympathetic branch of CN VIII
What are the two tracts found in the crus of the midbrain>
Corticospinal tract
corticobulbar tract
What is the corticospinal tract responsible for?
The corticospinal tract controls primary motor activity for the somatic motor system from the neck to the feet. It is the major spinal pathway involved in voluntary movements.
What is the corticobulbar tract responsible for?
Corticobulbar tract carries upper motor neuron input to motor nuclei of trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, and hypoglossal nerves. The motor component of trigeminal nerves supplies muscles of mastication. The facial nerve supplies the muscles of facial expression.
what are the two divisions of the pons?
tegmental
basilar
what are the 4 things found in the tegmental portion of the pons?
Vestibular nucleus
dorsal cochlear nuclei
tenitis
assists in localization
ventral cochlear nuclei
speech processing
medial lemniscus
What type of nuclei are found in the basilar portion of the pons?
pontine nuclei
travel contrallaterally
The reticular formation is a region in the pons involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle and filtering incoming stimuli to discriminate irrelevant background stimuli
Where is the middle cerebellar peduncle connected in the pons?
basilar portion
What nuclei are found in the medulla? (superior to inferior)
Posterior cochlear nuclei
Anterior cochlear nuclei
hypoglossal nuclei
dorsal accessory olivary nuclei
principle olivary nuclei
medial accessory olivary nuclei
CN I (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN I
Olfactory
Cerebrum
S
Smell
CN II (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN II
Optic
Cerebrum
S
Vision
CN III (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN III
Oculomotor
Midbrain
M
Pupilary light refelex + looking up
CN IV (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN IV
trochlear
midbrain
M
Looking down and in
CN V (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN V
Trigeminal
pons
B
sensation of face + muscles of chewing
CN VI (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN VI
Abducens
Pons
M
Look laterally
CN VII (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN VII
Facial
Pons
B
Muscles of facial expression + most of taste
CN VIII (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN VIII
Vestibularcochlear
Pons
S
Hearing + vestibulation
CN IX (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN IX
Glossopharyngeus
medulla
B
swallowing muscles
CN X (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN X
Vagus
Medulla
B
heart rate regulation, blood pressure, laryngeal muscles (airway closure)
CN XI (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN XI
Accessory
Medulla + Spinal Cord
M
Neck and shoulder muscles
CN XII (Name, Location of nuclei, S/M/B, Function)
CN XII
Hypoglossal
Medulla
M
Tongue muscles
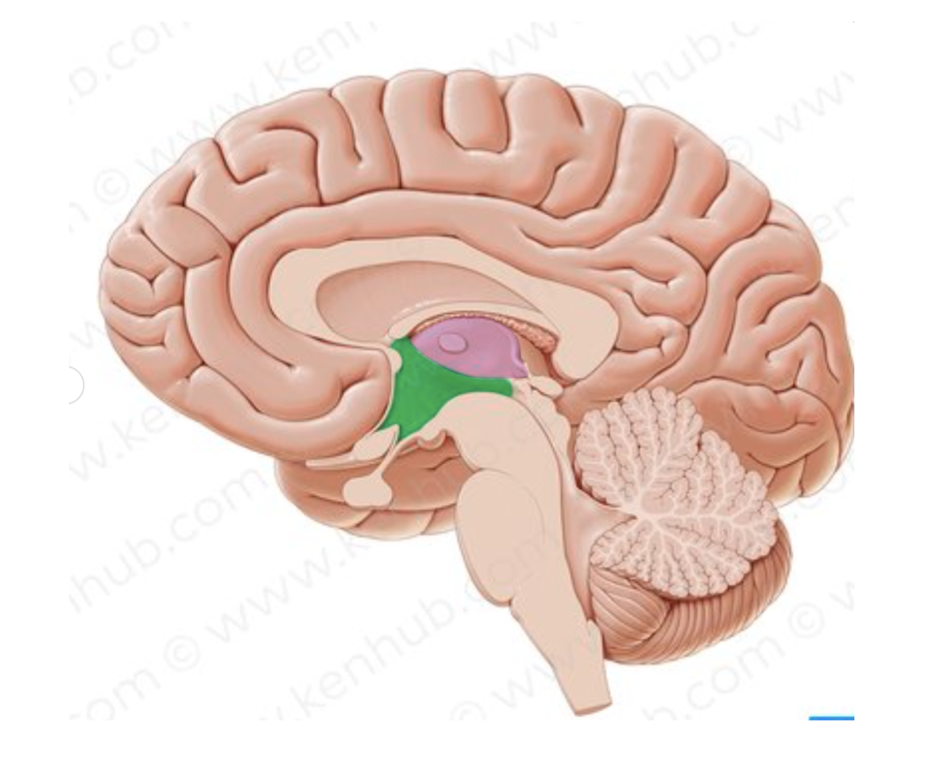
What is the name of the structure in in pink?
thalamus
Where does do all the arteries run through?
the subarachnoid space
What are the two artery systems?
Vertebral system
carotid system
What is the vertebral system?
aka the posterior system
comes from the subclavian system of the heart
supplies blood supply to pons, medulla, cerebellum, occipital lobe
where do the paired vertebral arteries travel through?
they travel through the transverse foramen and magnum foramen
what do the paired vertebral arteries come together to form?
basilar artery
What artery supplies the two branches that come together to form the anterior spinal artery?
the vertebral arteries
What are the 4 arteries that can be found in the cerebellum?
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
superior cerebellar artery
labyrinthine artery
What are the small arteries that come off the basilar artery?
pontine branches
these supply blood to the pons
what does the basilar artery go on to form?
it splits into two branches
posterior cerebral arteries
where do the vertebral arteries come together to form the basilar artery?
pontomedullary junction
What are the two spinal arteries? What portion of the spine does it supply?
posterior spinal artery
posterior 1/3 of the spinal cord
anterior spinal artery
supplies the anterior 2/3 of the spinal cord
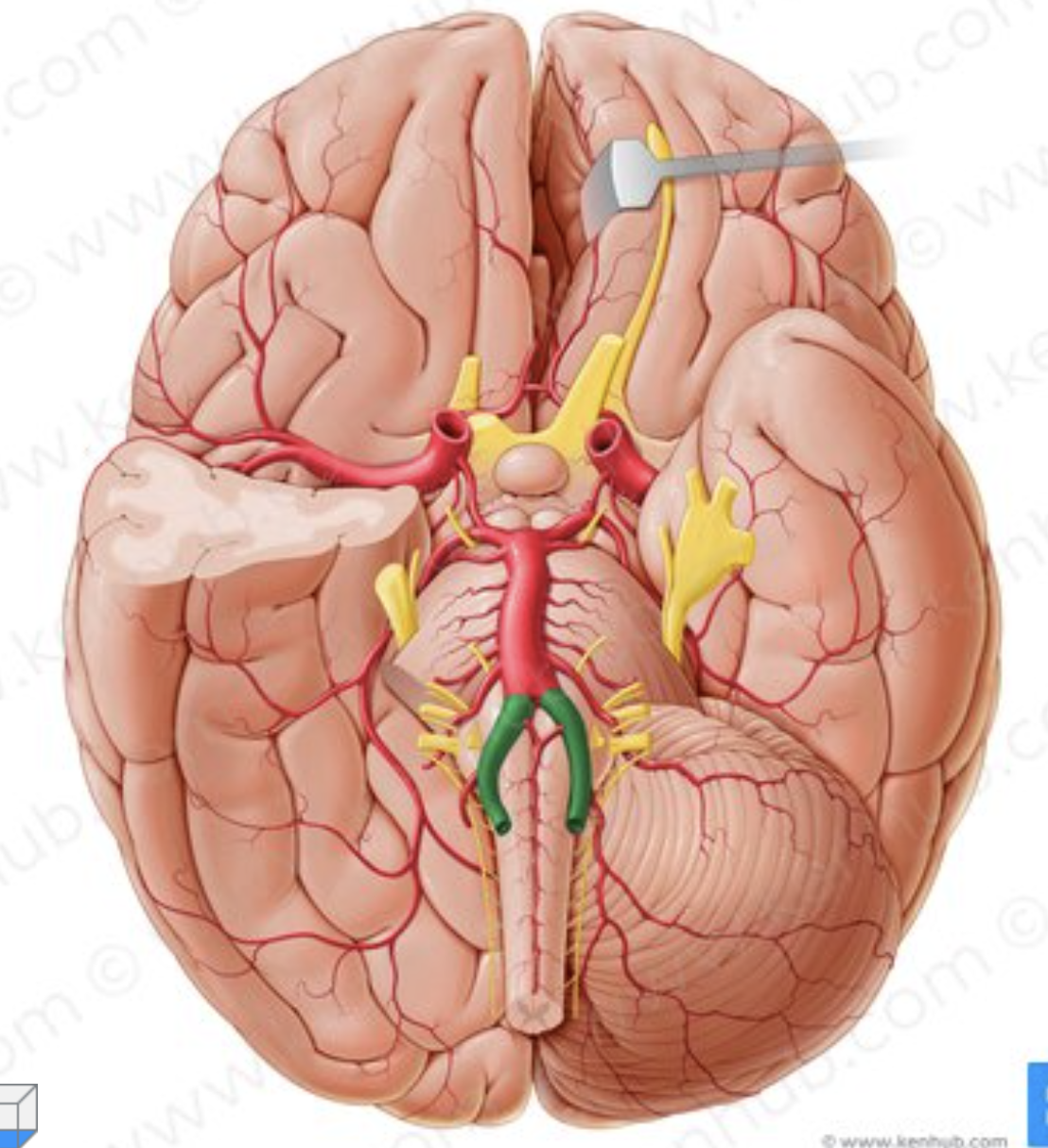
What artery is in green?
Vertebral arteries
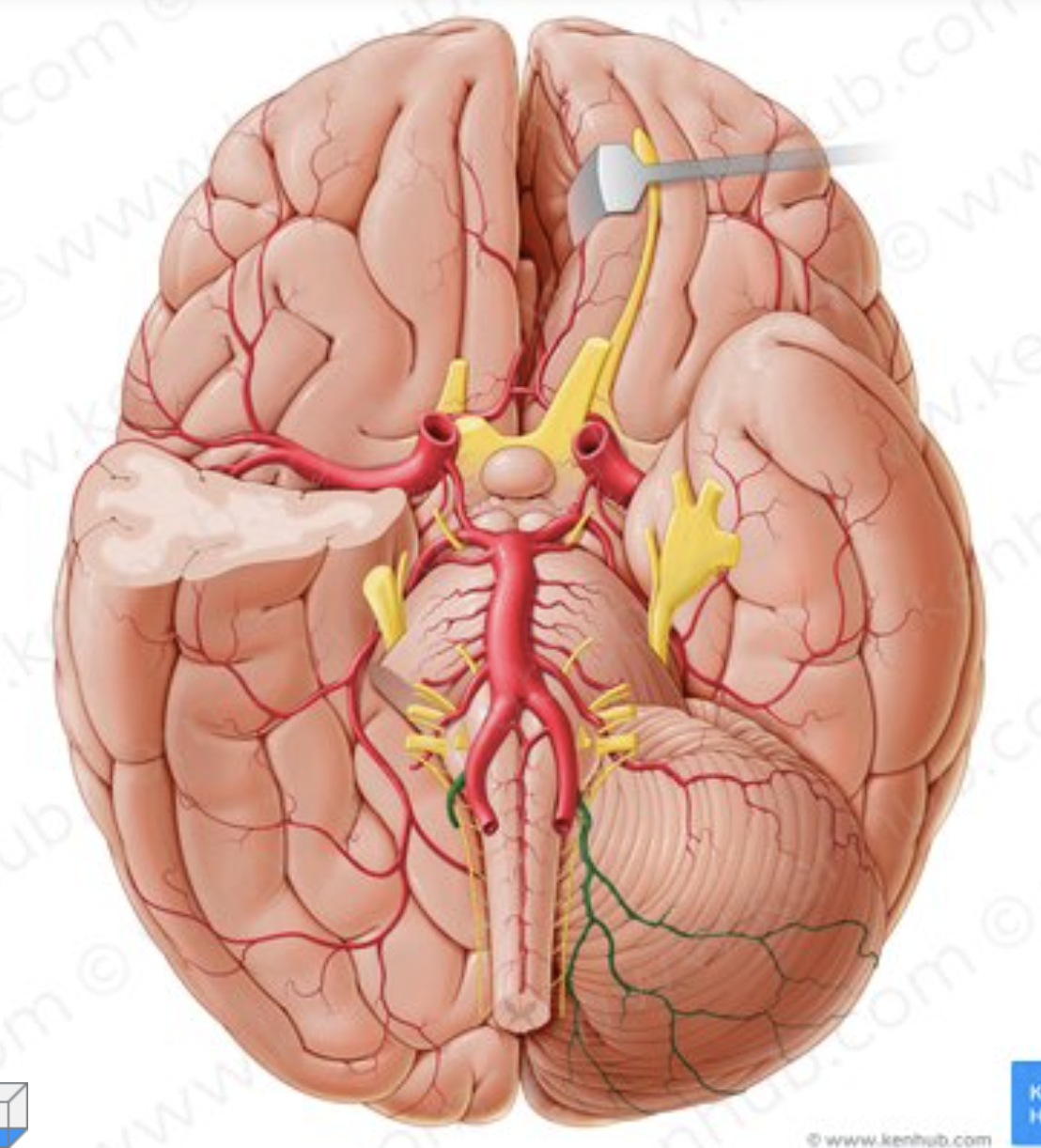
What is the name of the artery in green?
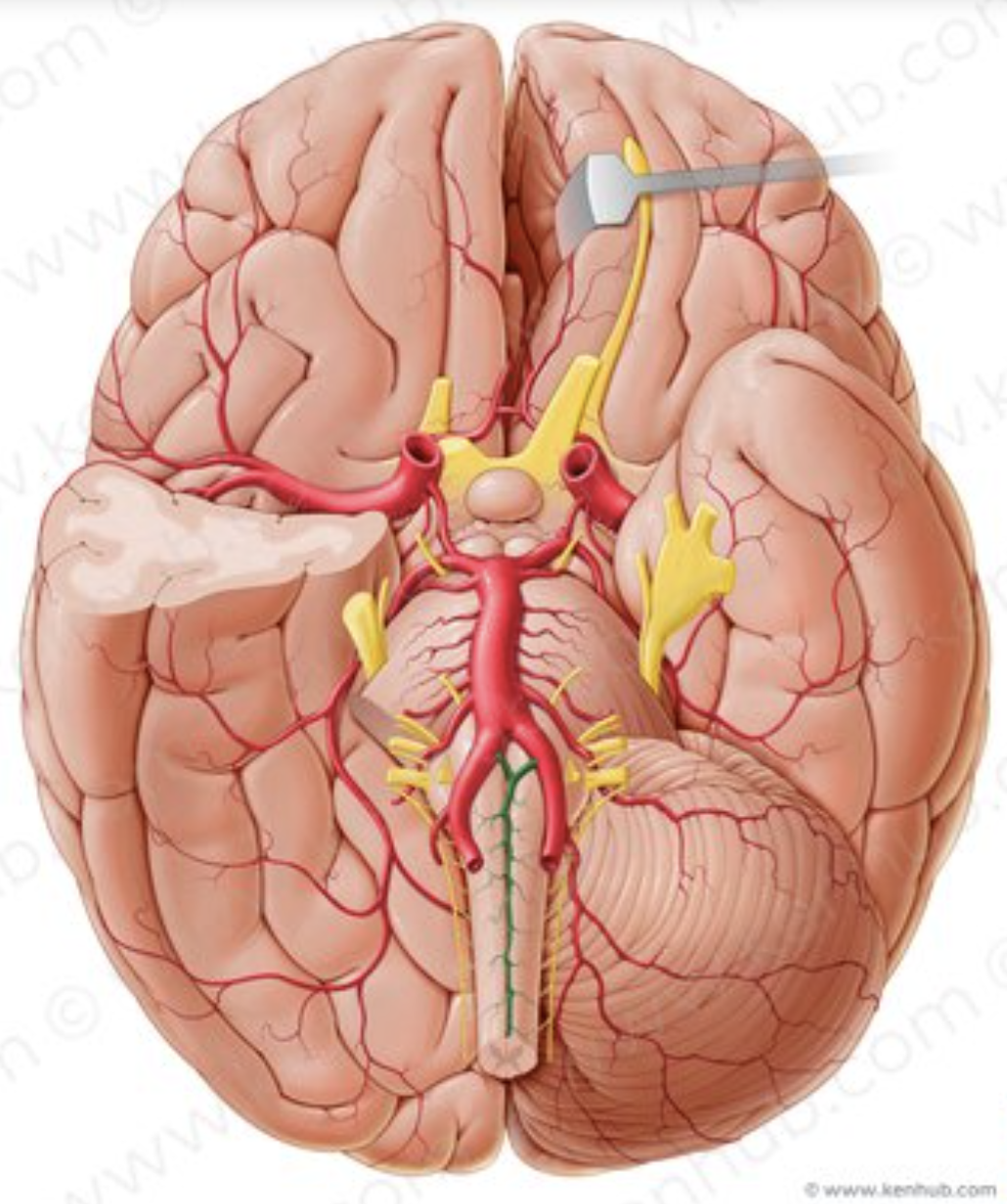
What is the name of the artery in green?
anterior spinal artery
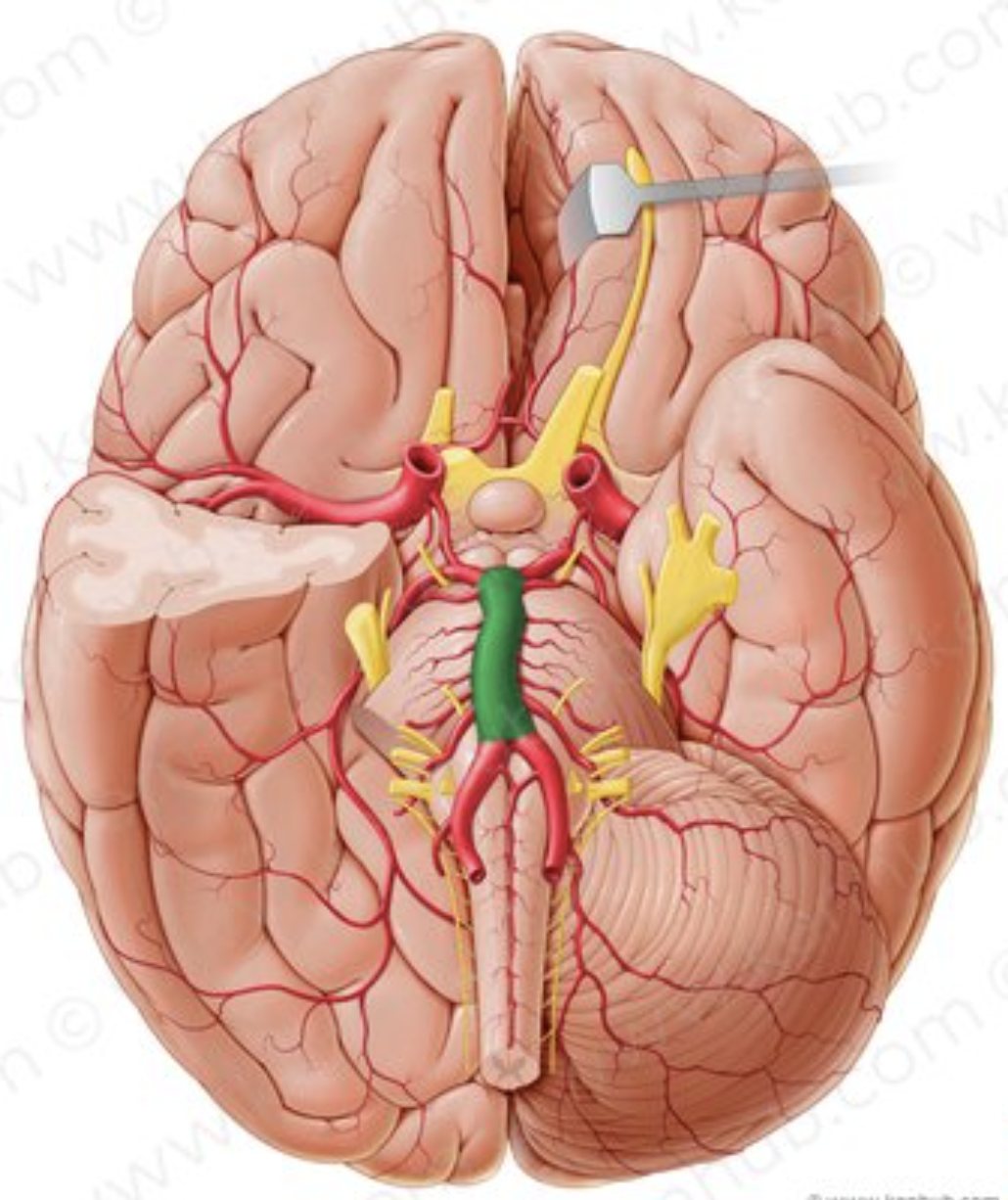
What is the name of the artery in green?
Basilar artery
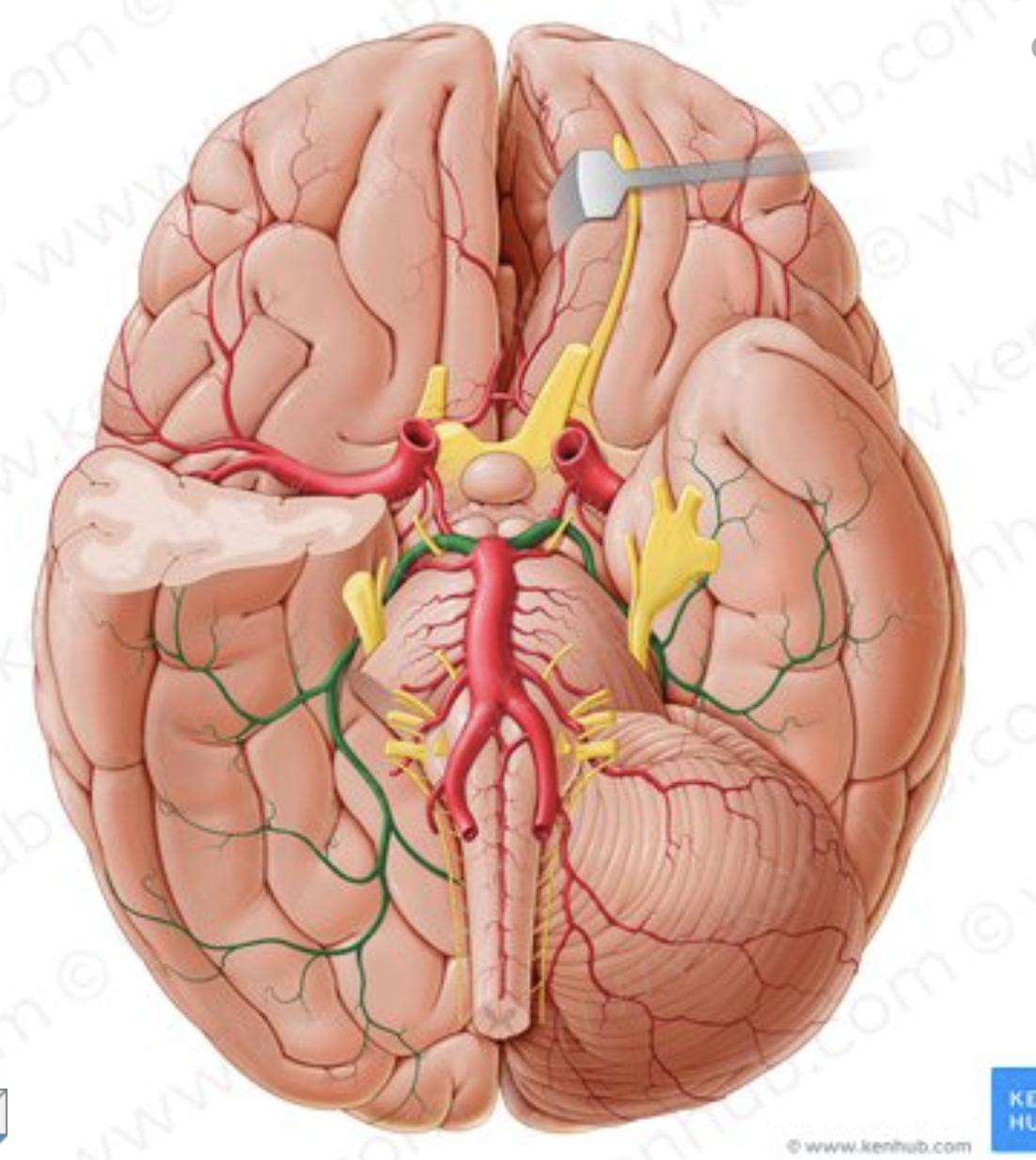
What is the name of the artery in green?
Posterior cerebral artery
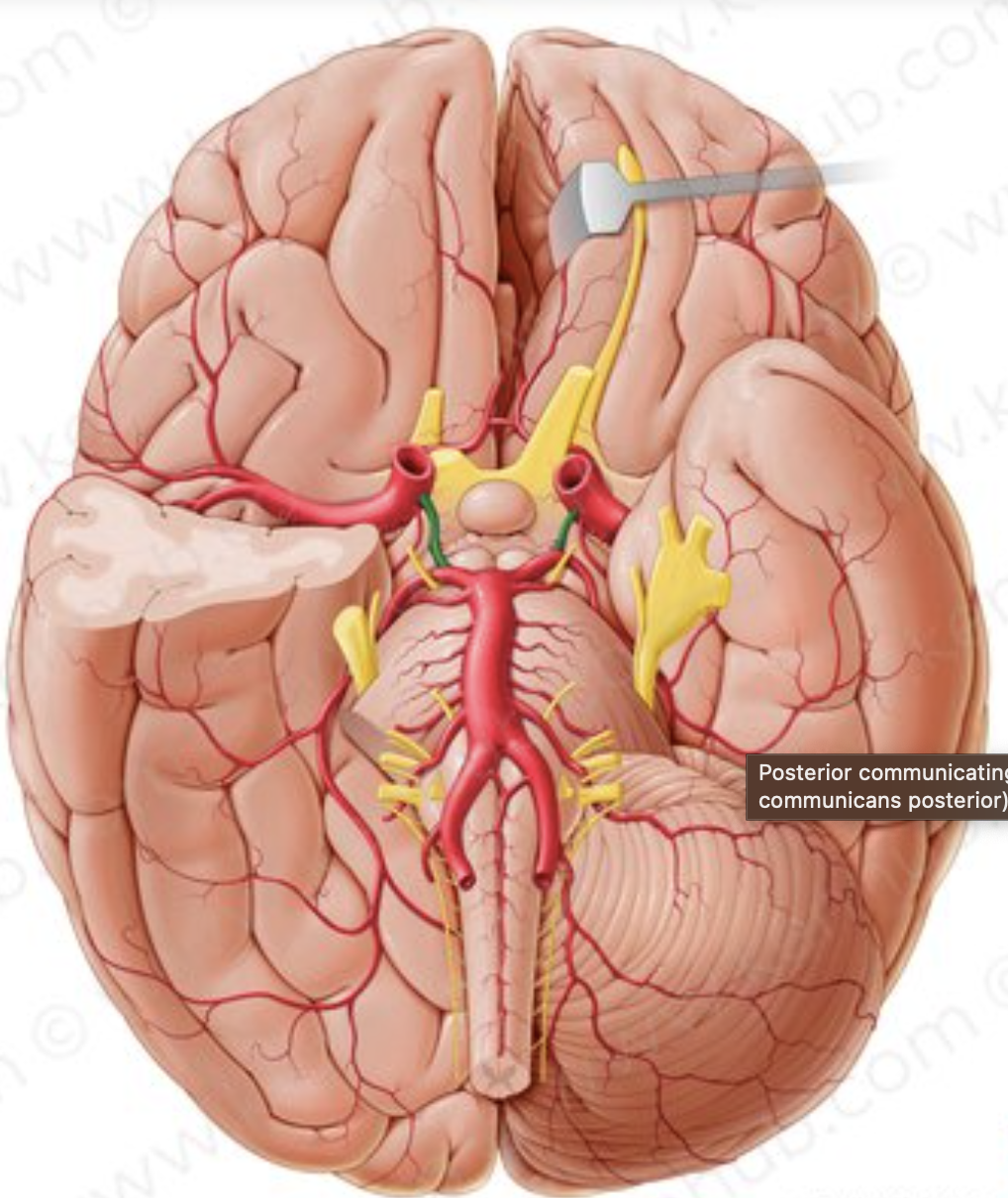
What is the name of the artery in green?
posterior communicating artery
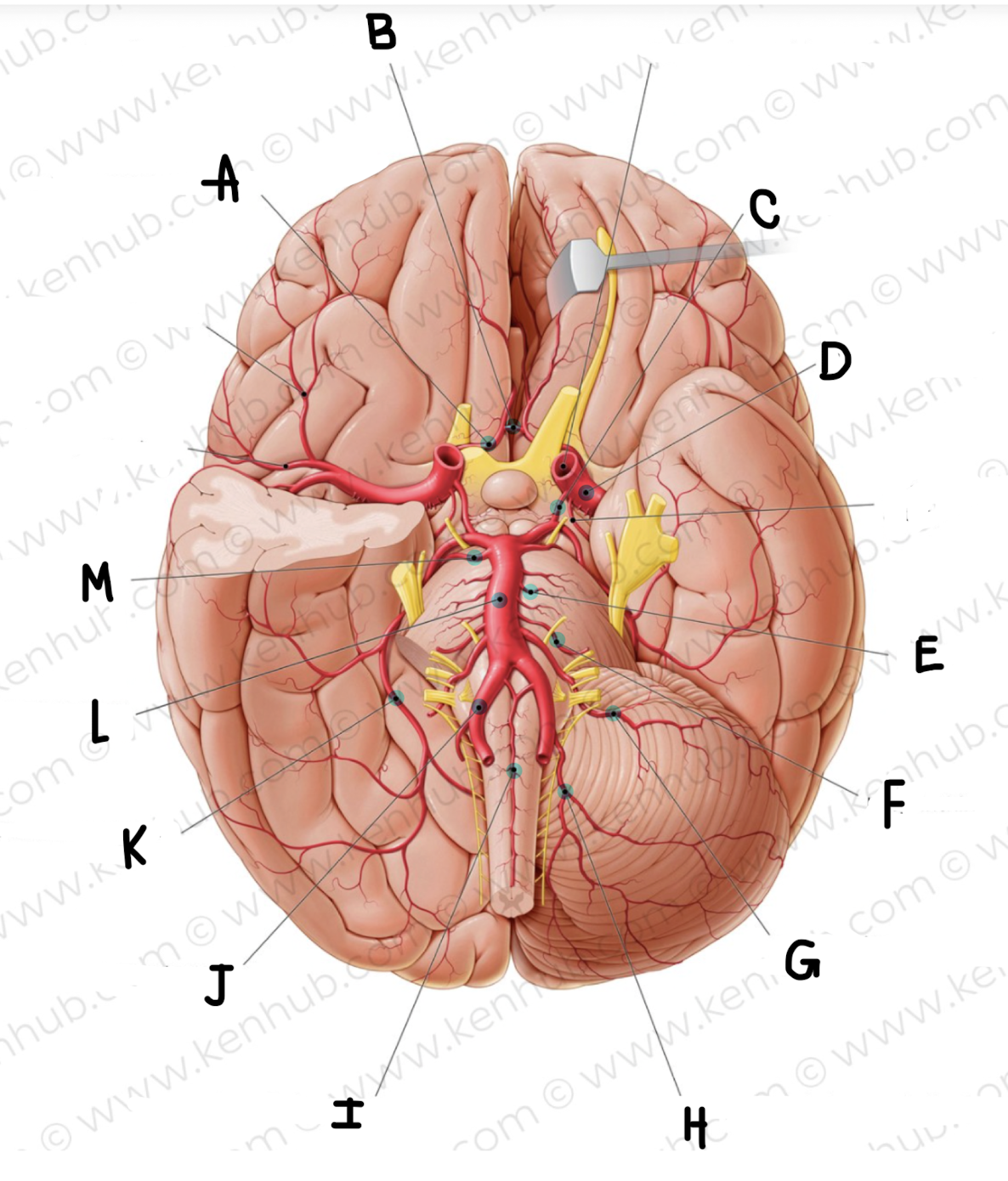
What is the name of the artery labeled A?
Anterior cerebral artery
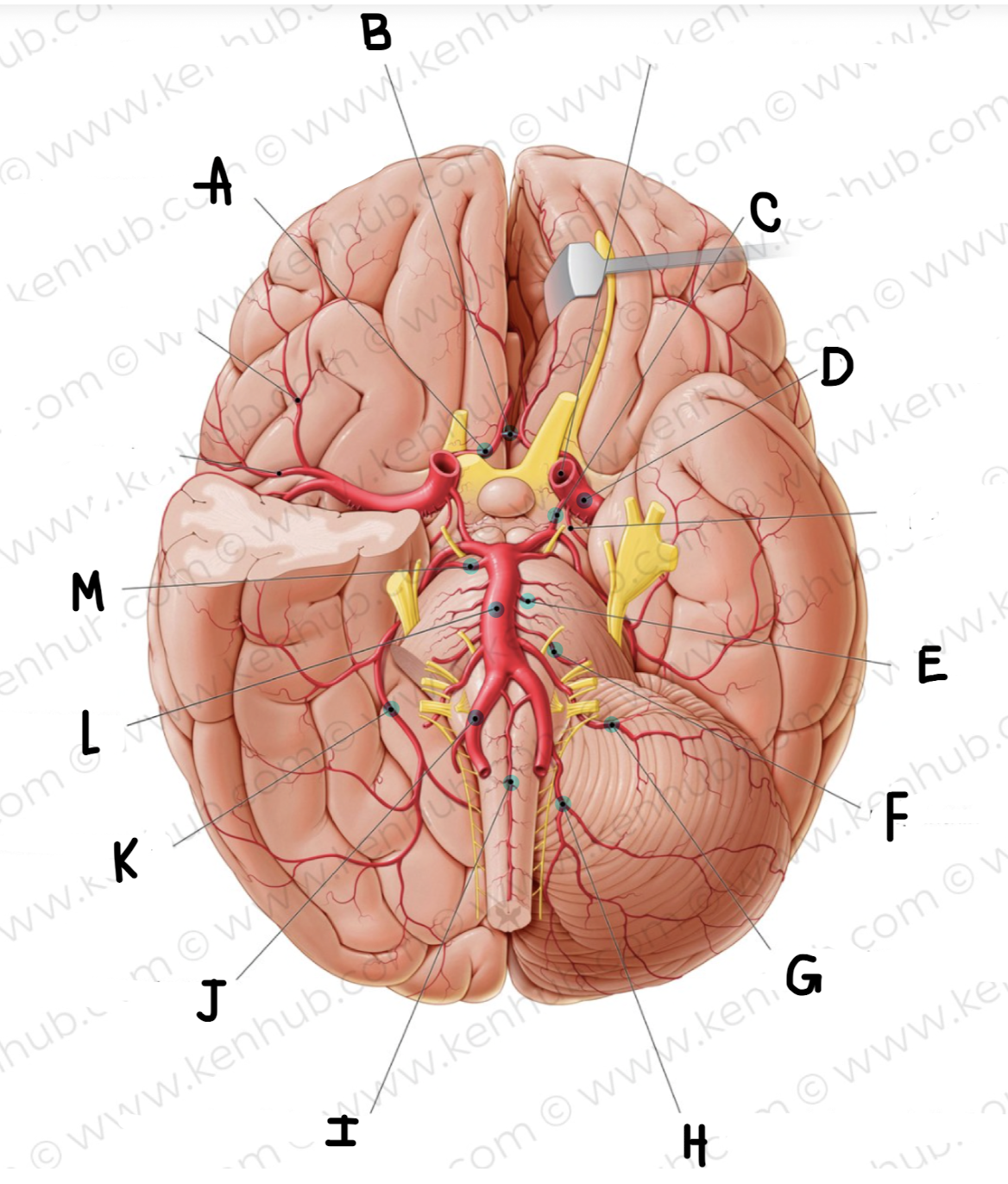
What is the name of the artery labeled B? (click on picture and scroll to see which is labeled B)
Anterior communicating artery
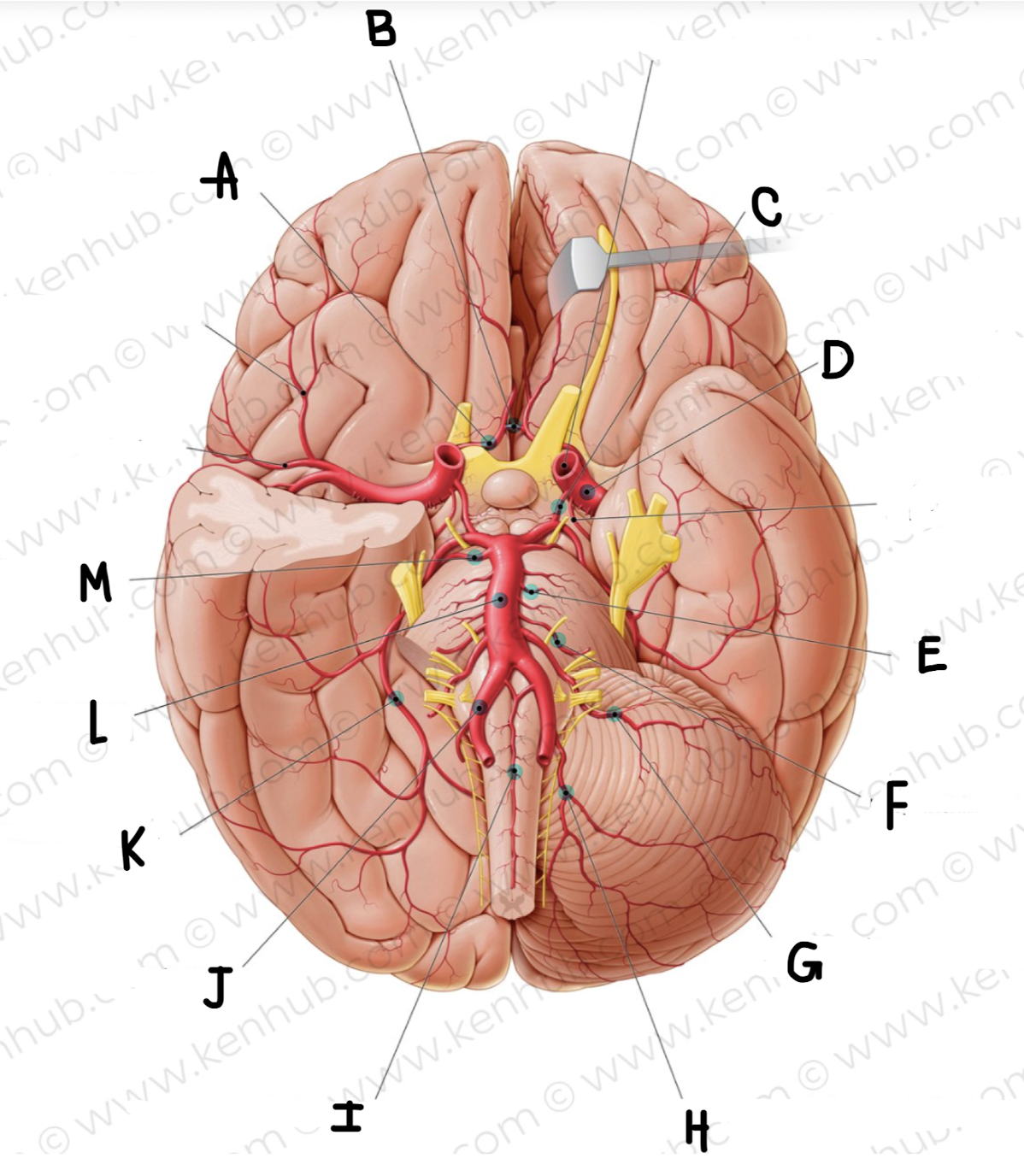
What is the name of the artery labeled C?
posterior communicating artery
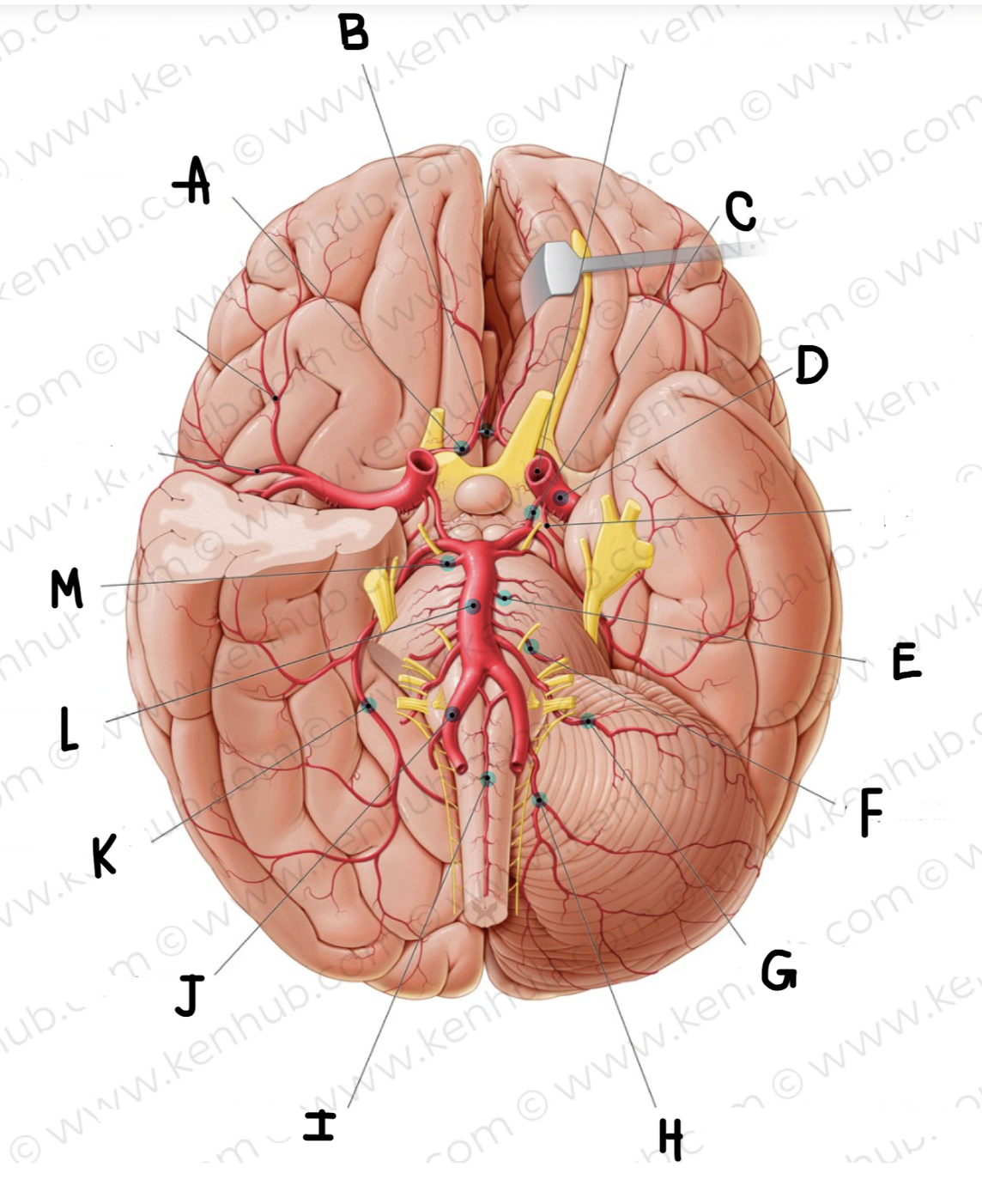
What is the name of the artery labeled D?
middle cerebral artery
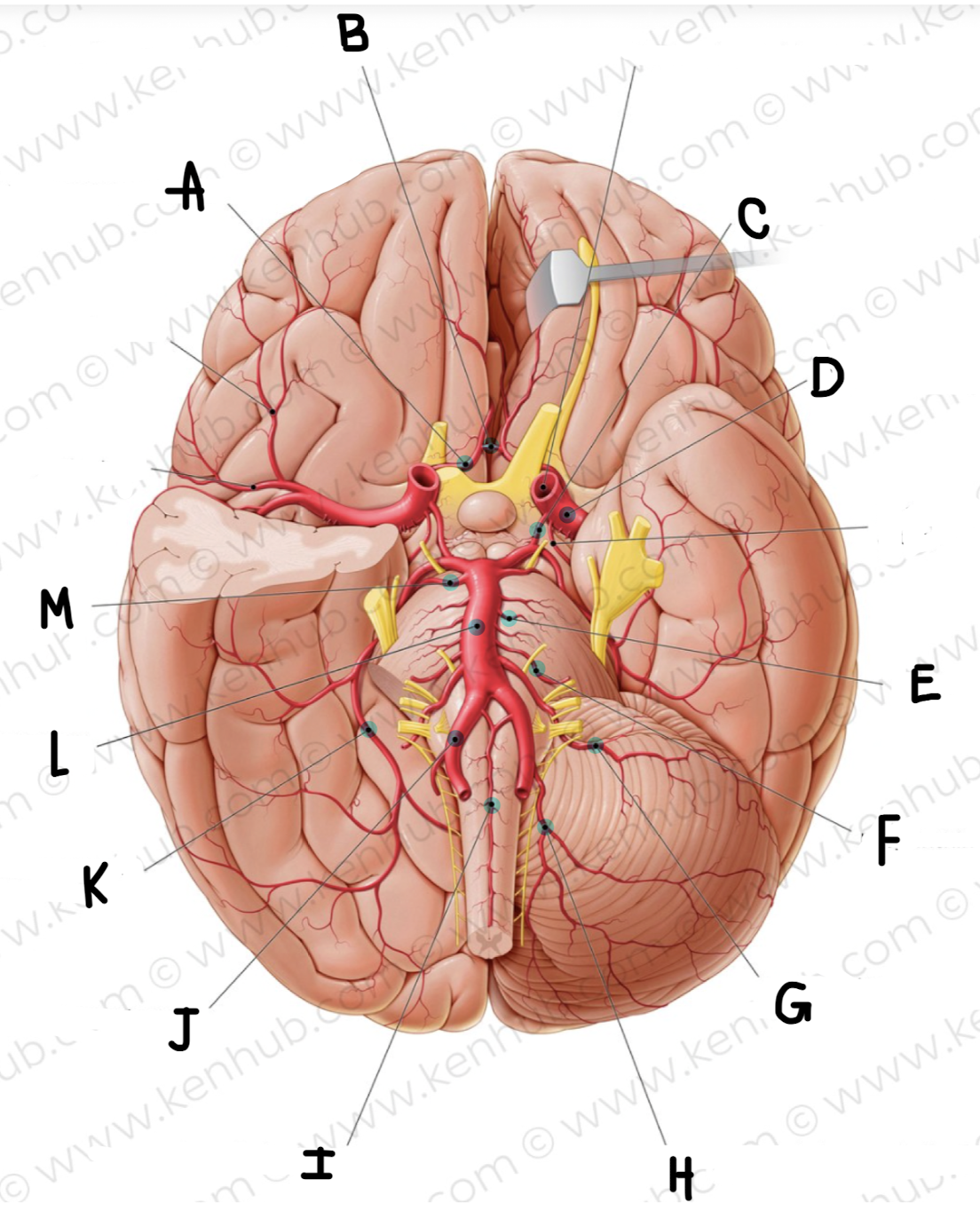
What is the name of the artery labeled E?
pontine arteries
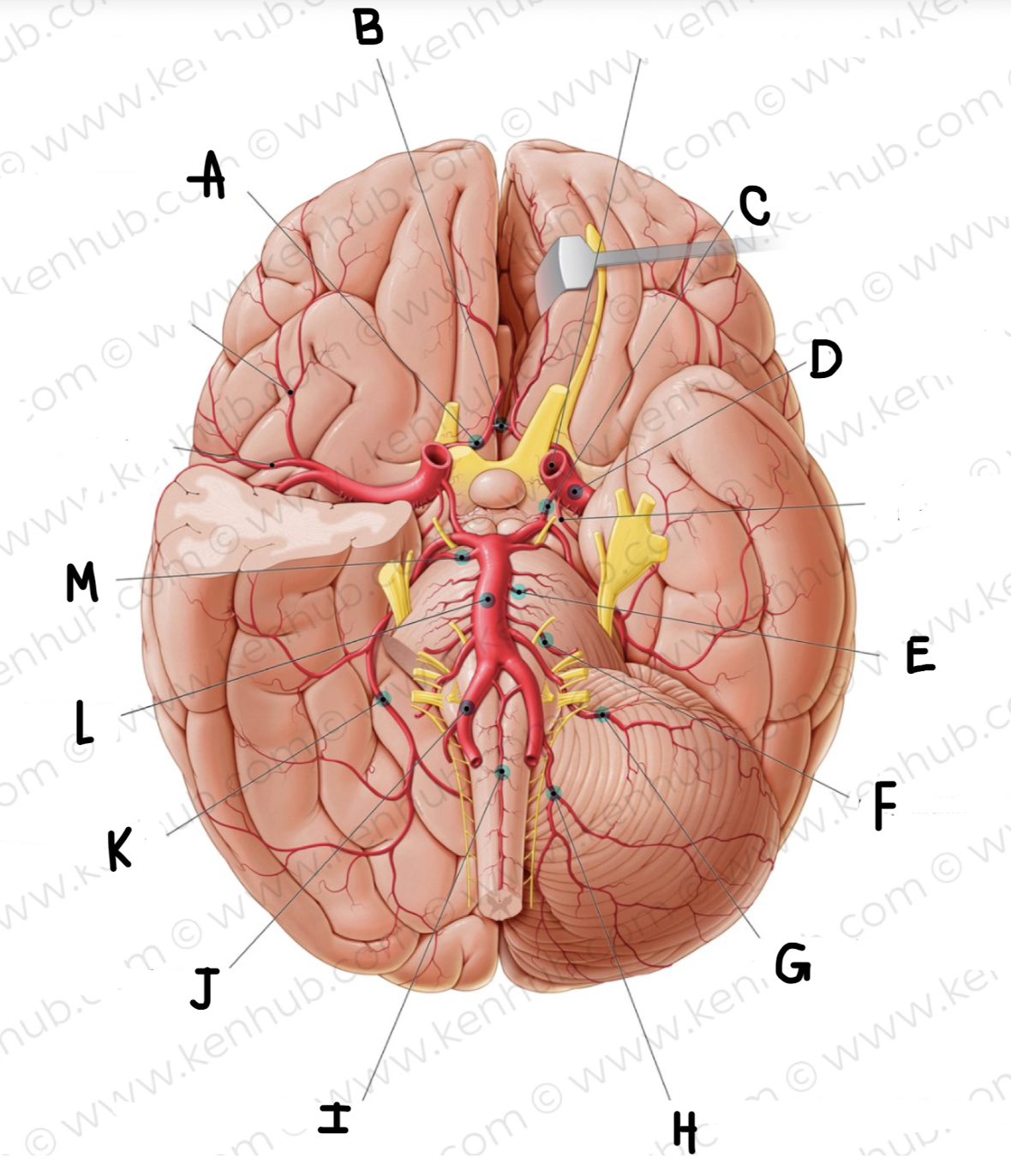
What is the name of the artery labeled F?
labyrinthine artery
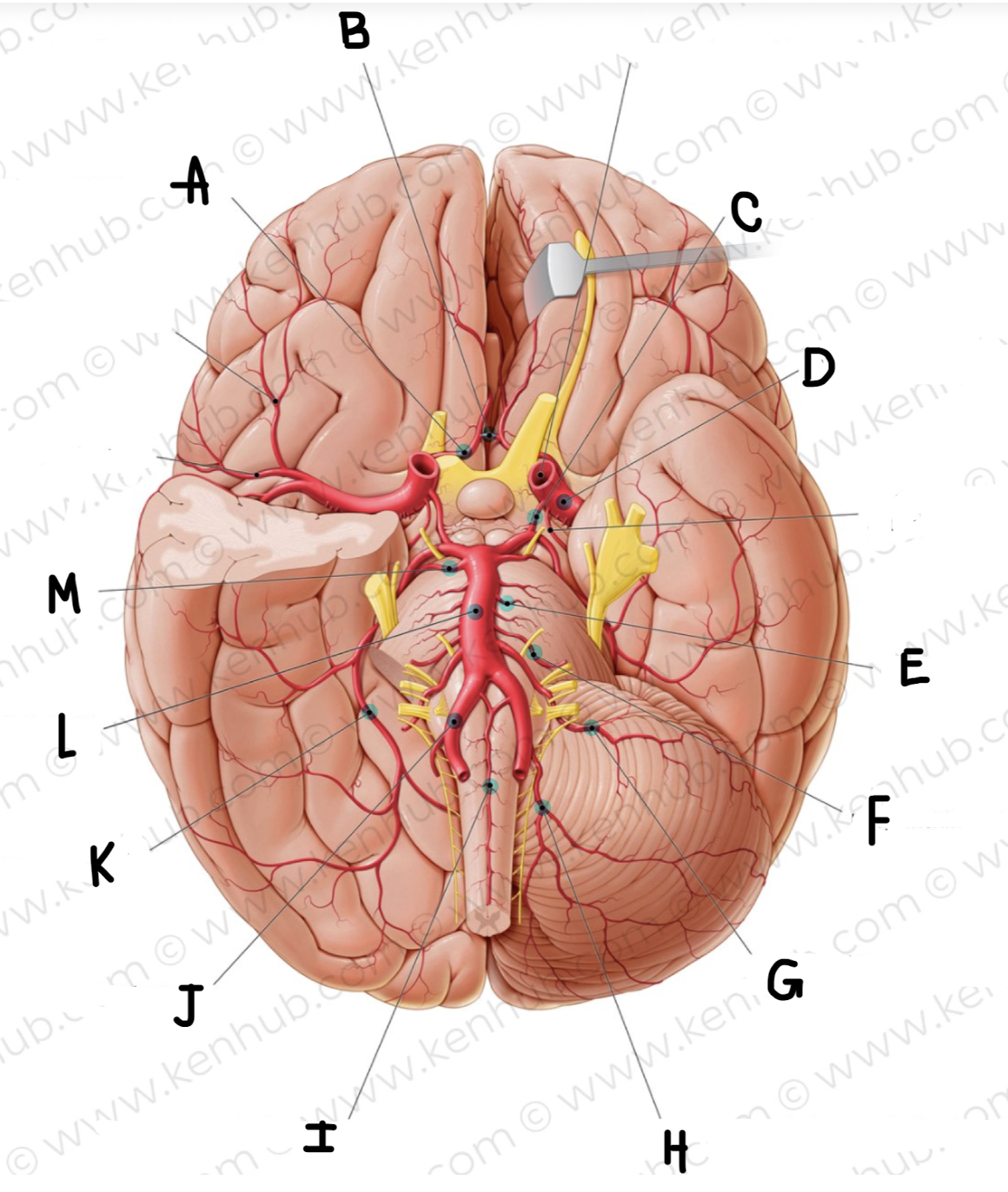
What is the name of the artery labeled G?
Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
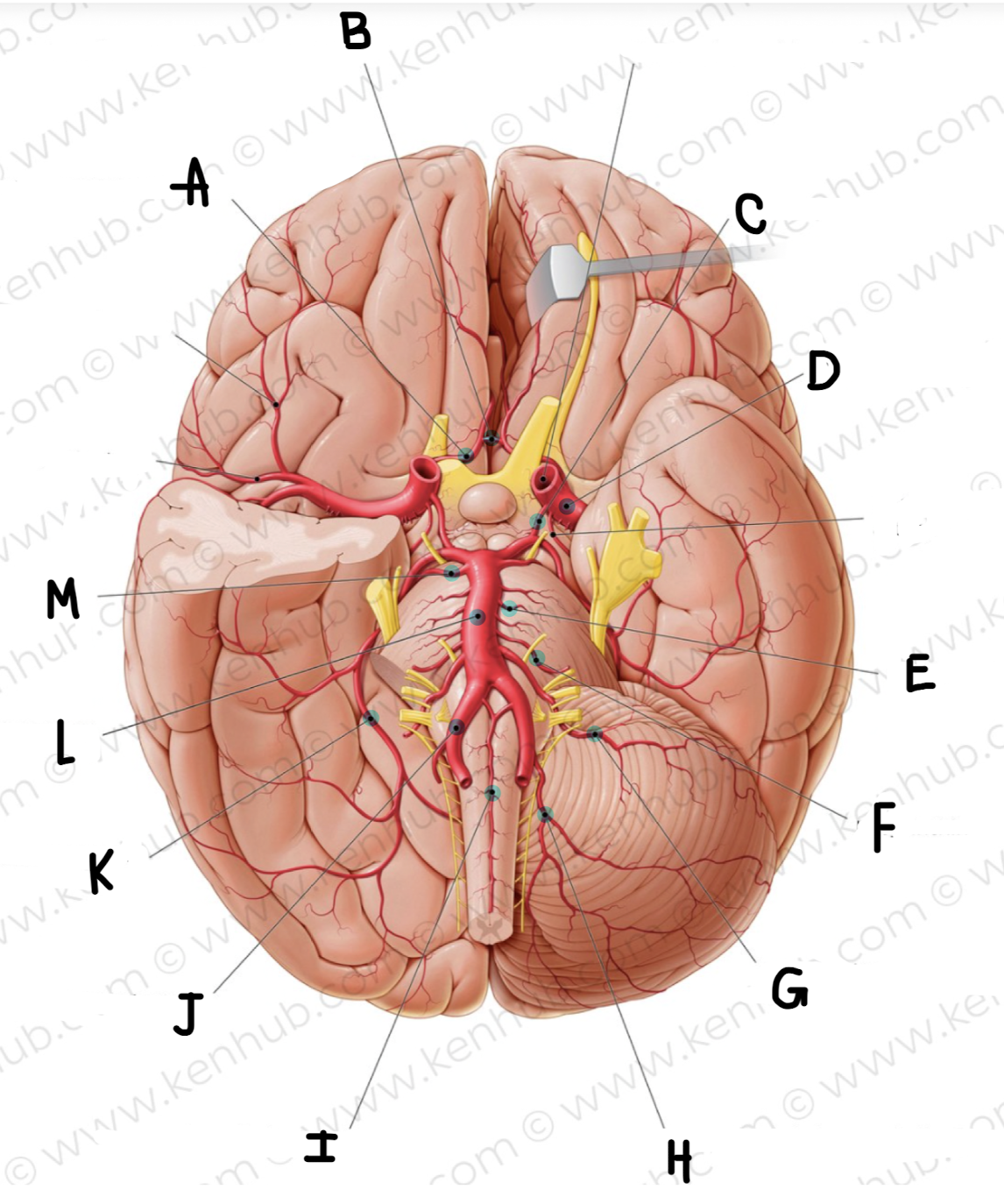
What is the name of the artery labeled H?
posterior inferior cerebellar artery
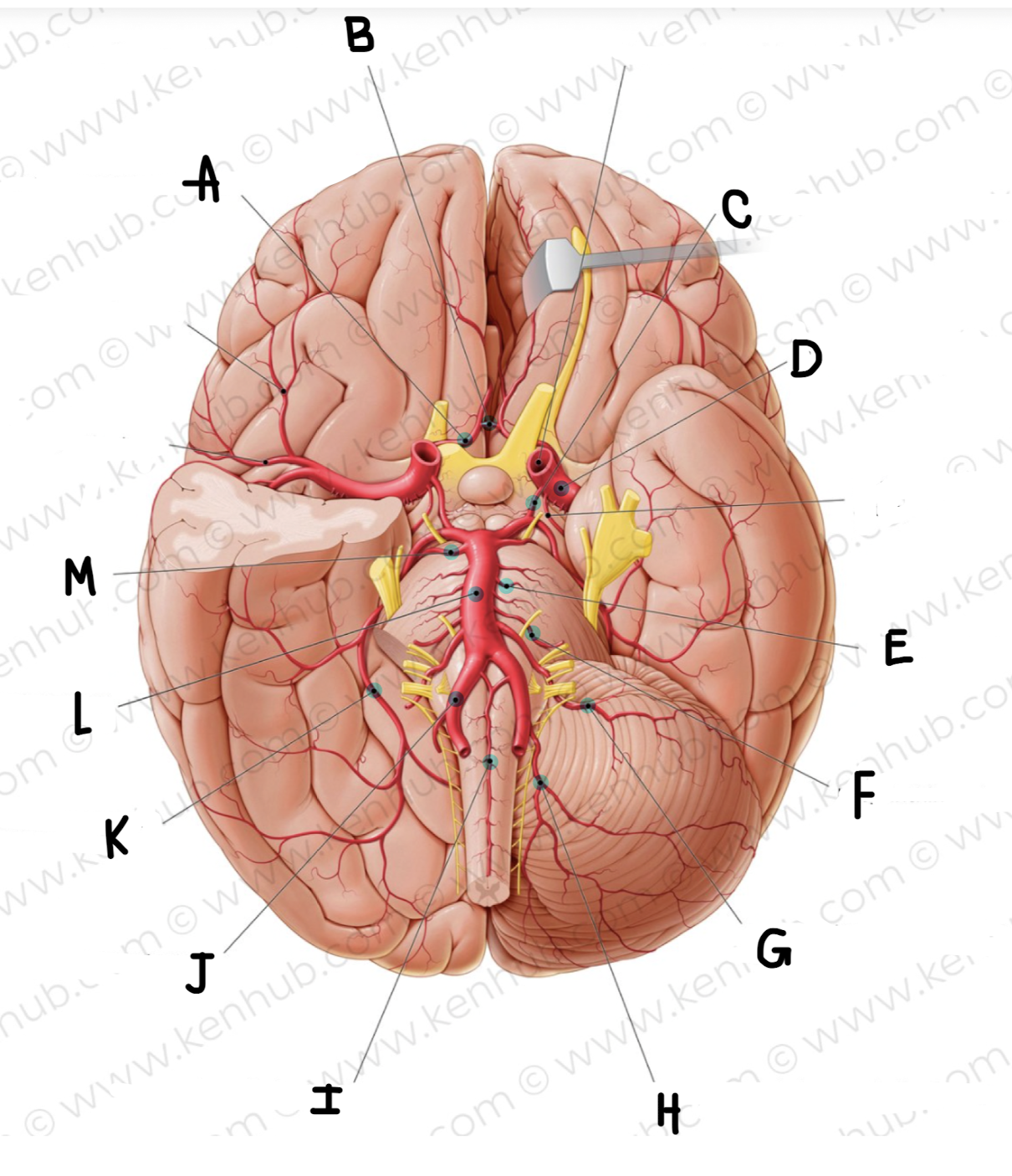
What is the name of the artery labeled I?
anterior spinal artery
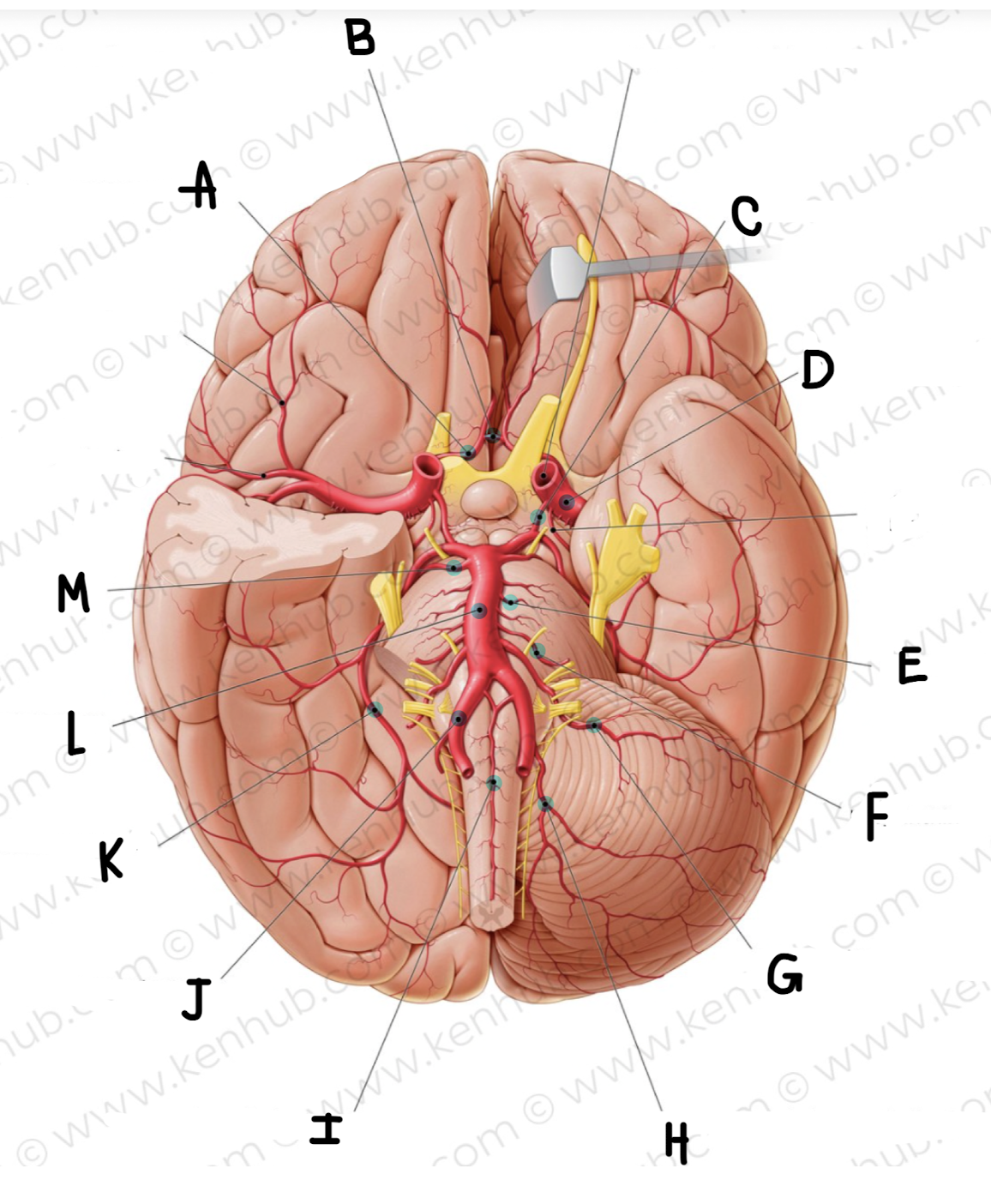
What is the name of the artery labeled J?
vertebral artery
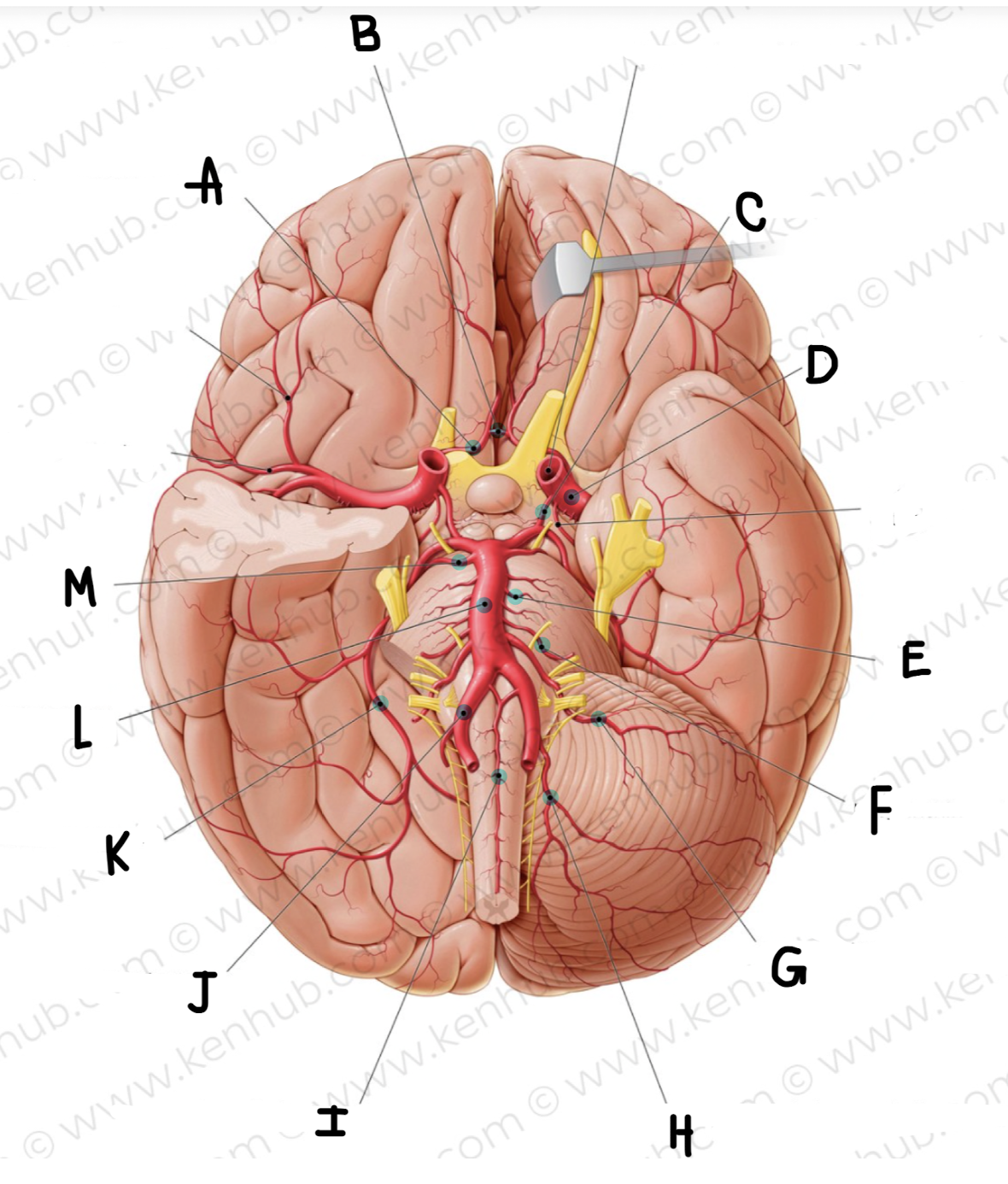
What is the name of the artery labeled K?
posterior cerebral artery
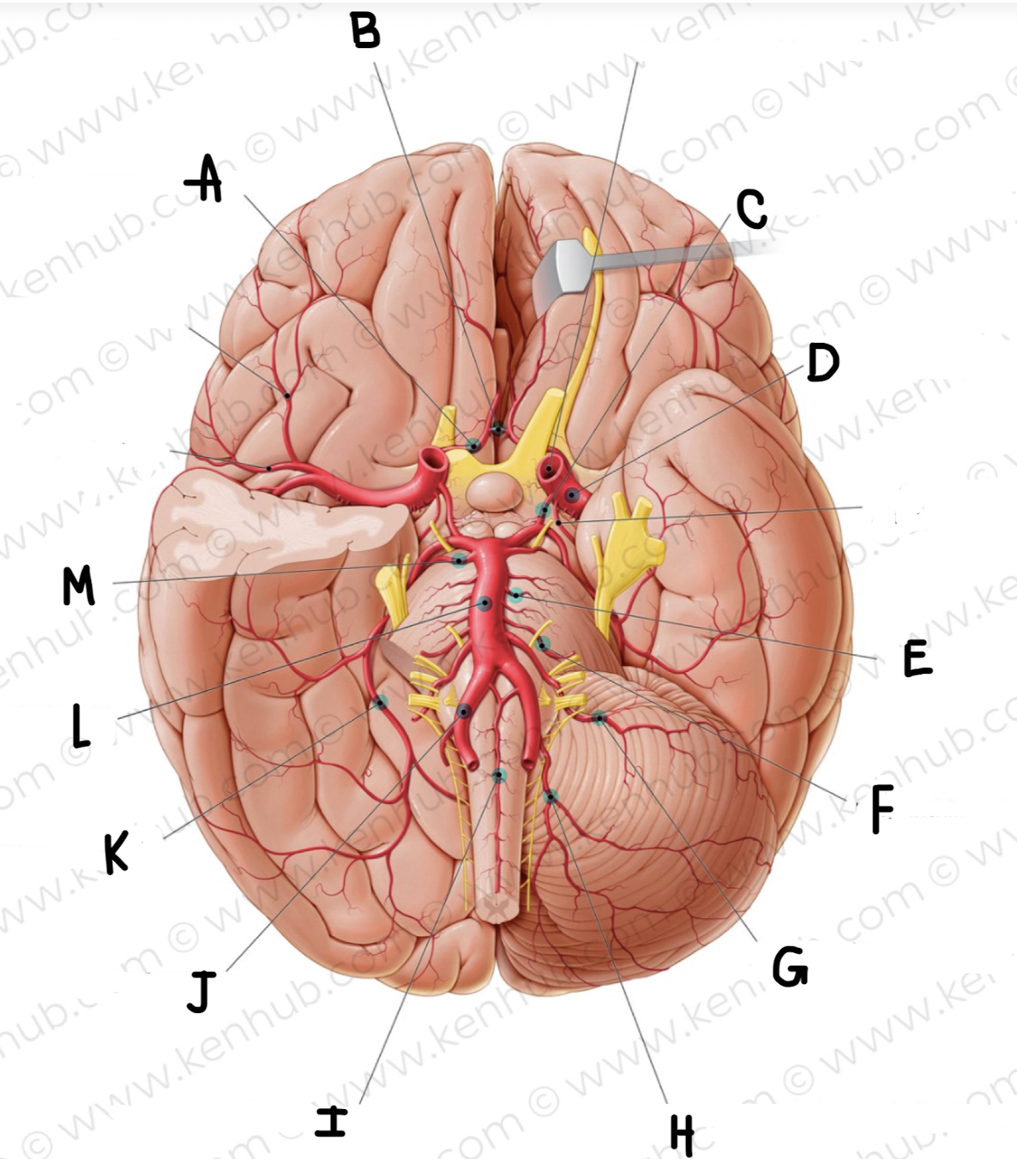
What is the name of the artery labeled L?
basilar artery
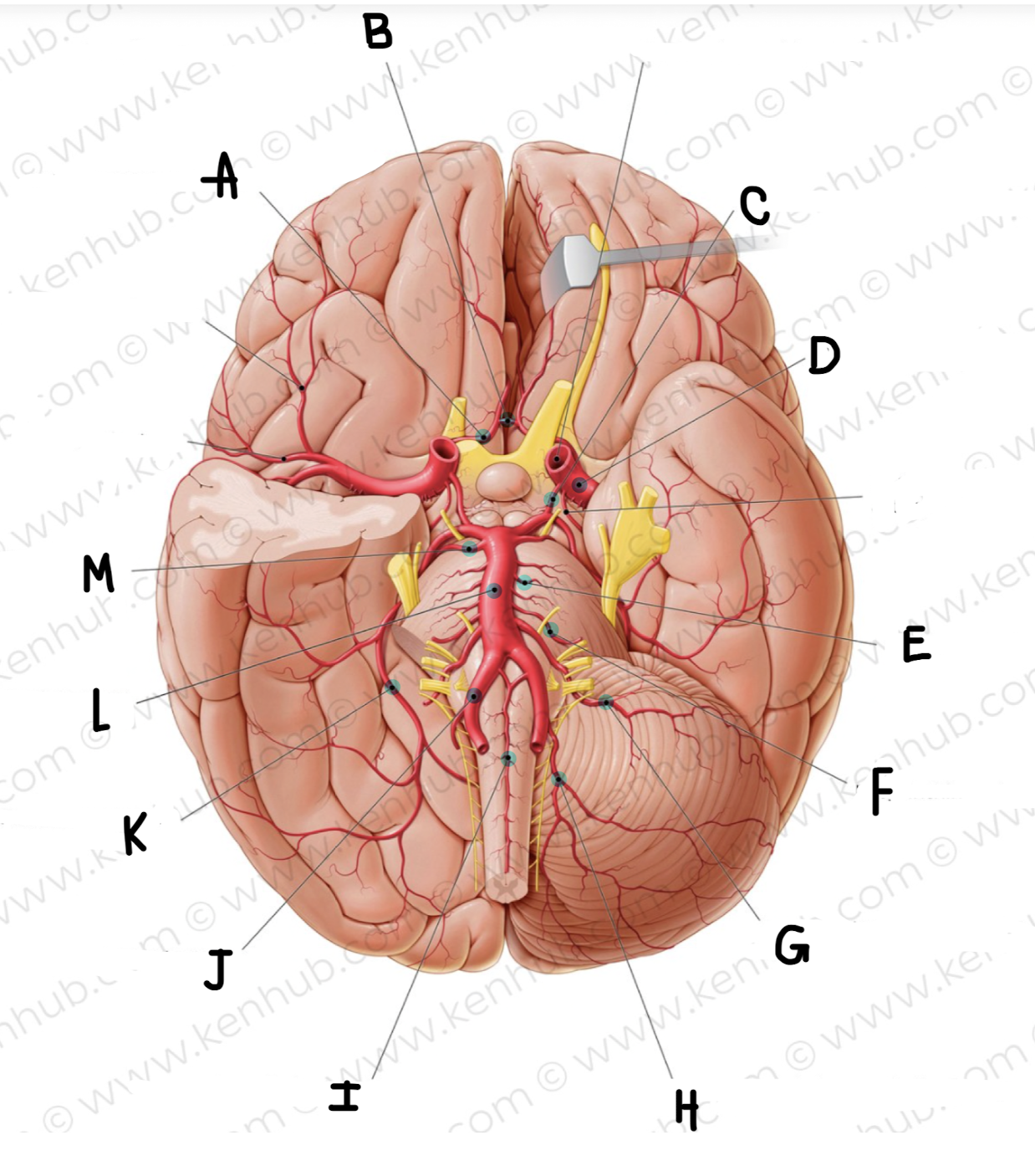
What is the name of the artery labeled M?
superior cerebellar artery
Where does the internal carotid artery travel through to get into the subarachnoid space of the brain?
first it travels through the carotid canal and then through the foramen lacerum to get into the subarachnoid space
Once in the middle cranial fossa, the internal carotid artery become what two terminal branches?
Anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
Why is the ophthalmic artery important?
this has blood supply for the eyes
if there is plac or something that forms within cardiac system it can travel through the system and the 1st place it will go is the this artery and cause occlusion which leads to loss of vision in one or both eyes
What is the circle of willis?
The circle of Willis (cerebral arterial circle or circulus arteriosus) is an anastomotic ring of arteries located at the base of the brain. This arterial anastomotic circle connects the two major arterial systems to the brain, the internal carotid arteries and the vertebrobasilar (vertebral and basilar arteries) systems. It is formed by four paired vessels and a single unpaired vessel with numerous branches that supply the brain.
The main function of the circle of Willis is to provide a collateral blood flow between the anterior and posterior arterial systems of the brain. Additionally, it offers the alternate blood flow pathways between the right and left cerebral hemispheres. This way the circle protects the brain from ischemia and stroke in cases of vascular obstruction or damage.
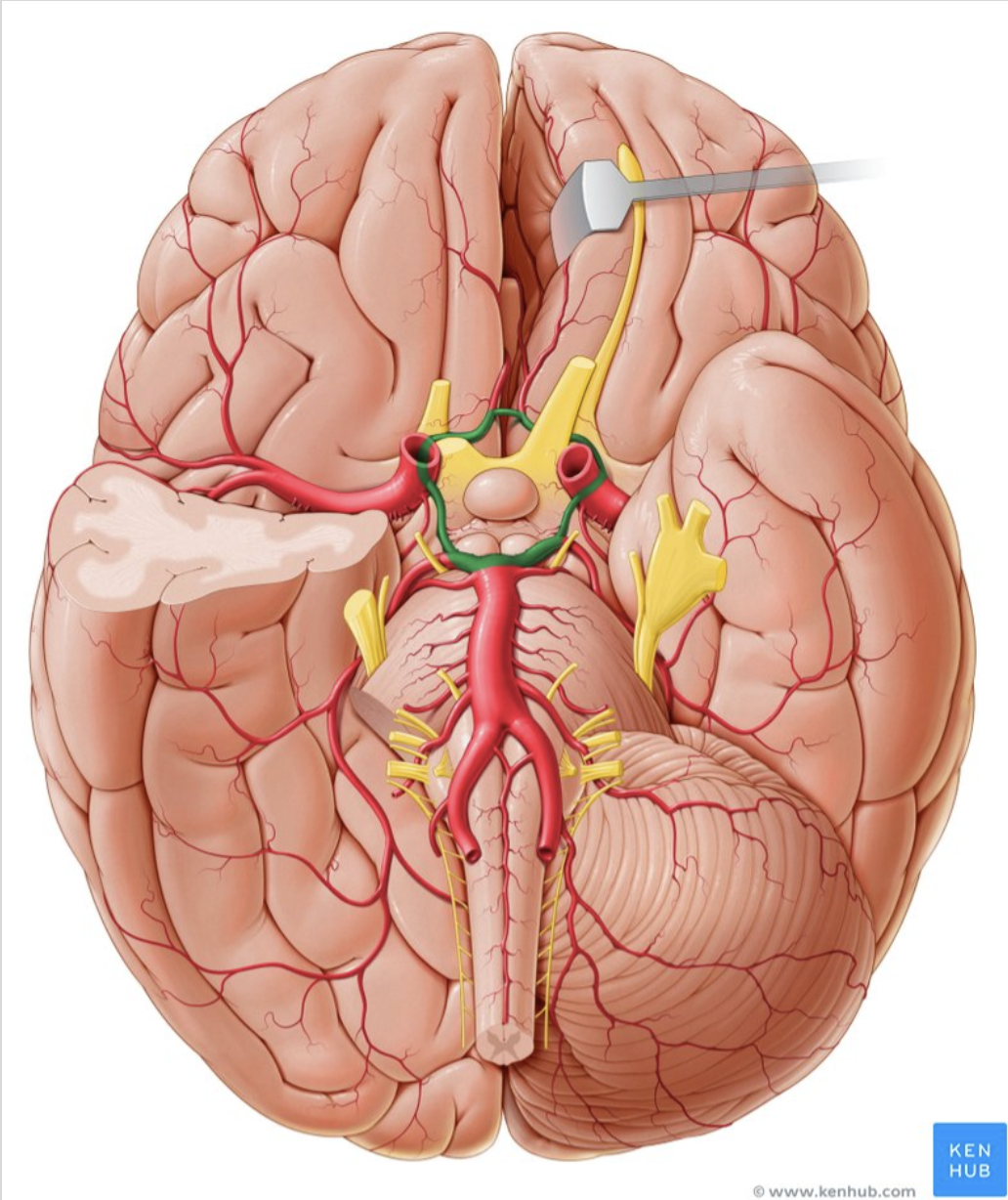
What structure is in green?
circle of willis
incredible protective system —> it compensates for itself when there is an infarct
what is an ischemic stroke?
An ischemic stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die in minutes. A stroke is a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial. Early action can reduce brain damage and other complications.
get to the hospital within 4.5 hrs you are able to be administered TPA which is a clot buster and will allow you to get better quicker
what is a hemorrhagic stroke?
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures and bleeds either inside or on the surface of the brain.
mosy likely to not survive this one but if you do the rehab is faster than that of a ischemic stroke
what is a transient ischemic attack?
lasts ~30 minutes
when a clot moves and stops
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary period of symptoms similar to those of a stroke. A TIA usually lasts only a few minutes and doesn't cause permanent damage.
Often called a ministroke, a TIA may be a warning. About 1 in 3 people who has a TIA will eventually have a stroke, with about half occurring within a year after the TIA.
Describe the Anterior Spinal Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
Anterior 2/3 of spinal cord
anterior spinal syndrome
paralysis down from point of occulsion
likely to occur between T4-L1
Describe the Posterior Spinal Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
posterior 1/3 of spinal cord
paralysis down from point of occlusion
T1,2,3
Describe the Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery — PICA (coverage, CVA symptoms)
lateral medulla, posterior inferior cerebellum
ataxia, vertigo, balance difficulty
vertebral system
Describe the Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
Lateral Pons, Anterior Inferior Cerebellum
ataxia, vertigo, balance difficulty
vertebral system
Describe the Labyrinthine Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
inner ear
tinnitus, vertigo
vertebral system
Describe the Superior Cerebellar Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
superior cerebellum
ataxia, vertigo, balance issues
vertebral system
Describe the Posterior Cerebral Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
midbrain + occipital lobe
swallowing, vision problems
Vertebral system
Describe the ophthalmic Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
Visual Centers
Blindness
carotid system
Describe the Middle Cerebral Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
frontal, temporal loves
broca’s aphasia, wernickes aphasia, loss of sound localization
carotid system
Describe the Anterior Cerebral Artery (coverage, CVA symptoms)
Parietal Lobes
Proprioception
Carotid System