Midterm Geometry Review
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
flashcards for geo midterm!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Rigid Transformations
Transformations that do not change the shape or size of a geometric figure.
Congruent Triangles
Triangles that are identical in shape and size.
SAS
Side-Angle-Side; a method for proving triangle congruence.
ASA
Angle-Side-Angle; a method for proving triangle congruence.
SSS
Side-Side-Side; a method for proving triangle congruence.
Proofs
Logical arguments that use deductive reasoning to show that a statement is true.
Parallelograms
A quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length.
Dilations
Transformations that alter the size of a figure but maintain its shape.
Similarity
Two figures that have the same shape but may differ in size.
Pythagorean Theorem
c²=a²+b²
Transversal Lines
Lines that cross at least two others at distinct points.
Vertical Angles
Angles opposite each other when two lines intersect.
Supplementary Angles
Two angles whose sum is 180 degrees.
Complementary Angles
Two angles whose sum is 90 degrees.
Segment Bisector
A line, ray, or segment that divides another segment into two equal parts.
Angle Bisector
A ray that divides an angle into two equal angles.
Axis of Symmetry
A line that divides a figure into two mirror-image halves.
Exterior Angle Theorem
The theorem that states that the measure of an exterior angle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
Dilation Scale Factor
The ratio that describes how much a figure is enlarged or reduced.
Perpendicular Bisectors
Lines that cut another line segment into two equal parts at a 90-degree angle.
Parallel Lines
Lines in a plane that never meet and are always the same distance apart.
Supplementary Angles
Angles that add up to 180 degrees.
Constructing Perpendicular Lines
Creating lines that intersect at a right angle.
Symmetry
A property where one half of an object is a mirror image of the other half.
90 Degree Rotation
Turning a shape to face a different direction, 90 degrees clockwise or counterclockwise.
180 Degree Rotation
Turning a shape halfway around, resulting in an upside-down position.
Line Segment
Part of a line that has two endpoints.
Transformations
Operations that alter the position, size, or shape of a figure.
Congruent Parts
Parts of figures that are equal in measure.
Proportional Relationships
Relationships between quantities where one quantity is a constant multiple of the other.
Scale Factor
The ratio that compares the size of a model to the size of the original figure.
Triangle Congruence
A condition where two triangles are identical in size and shape.
Constructing Angle Bisectors
Dividing an angle into two equal angles.
Quadrilateral
A four-sided polygon.
Similar Right Triangles
Right triangles that have the same shape but differ in size.
Dilations in Geometry
Transformations that enlarge or reduce figures while preserving their proportions.
Congruent Parts in Triangles
Corresponding sides and angles in congruent triangles that are equal in measure.
Constructing Parallel Lines
Creating lines that are equidistant and never intersect.
Triangle Properties
Characteristics and rules applicable to triangles, such as angle sum and congruence.
Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Theorem
A method for proving the congruence of two right triangles if the lengths of the hypotenuse and one leg are equal.
Hypotenuse
The longest side of a right triangle, opposite the right angle.
Leg of a Right Triangle
Either of the two shorter sides that form the right angle.
Right Triangle
A triangle that has one angle measuring 90 degrees.
Congruence Criteria for Triangles
Rules that determine when two triangles are congruent, including HL, SAS, SSS, and ASA.
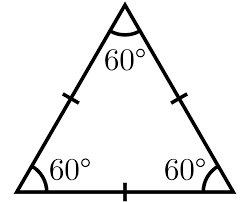
Equilateral Triangle
A triangle with all three sides of equal length.
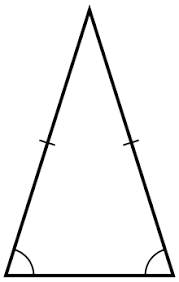
Isosceles Triangle
A triangle with at least two sides of equal length.
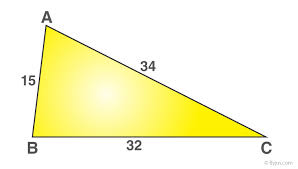
Scalene Triangle
A triangle with all sides of different lengths.
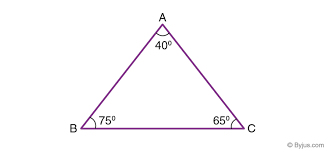
Acute Triangle
A triangle with all angles measuring less than 90 degrees.
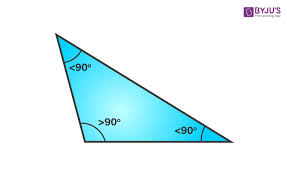
Obtuse Triangle
A triangle that has one angle measuring more than 90 degrees.
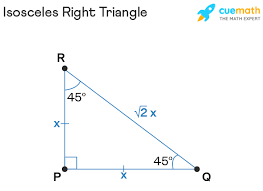
Right Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle with a right angle.
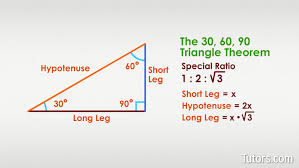
30-60-90 Triangle
A special right triangle with angles measuring 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees.
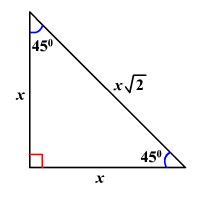
45-45-90 Triangle
A special right triangle where the angles are both 45 degrees and the legs are equal.
Area of Triangle
Calculated as 1/2 times the base times the height.
Translation
A rigid transformation that slides a figure from one position to another without rotating or flipping it.
Rotation
A rigid transformation that turns a figure about a fixed point.
Reflection
A rigid transformation that flips a figure over a line, creating a mirror image.
Rigid Motion
Another term for a rigid transformation, emphasizing that the figures retain their size and shape.
Composition of Rigid Transformations
Applying multiple rigid transformations in sequence to a figure.