Chapter 18: The Heart
5.0(1)Studied by 8 people
Card Sorting
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:06 PM on 2/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
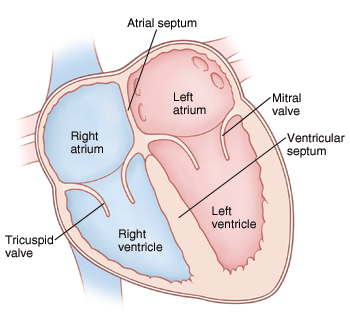
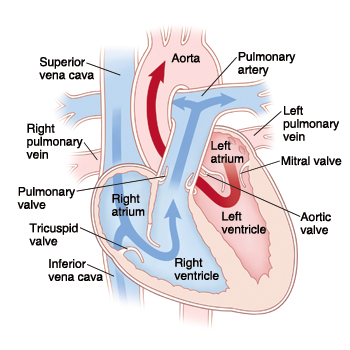
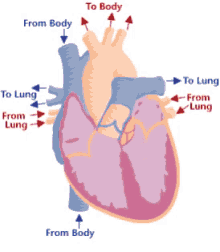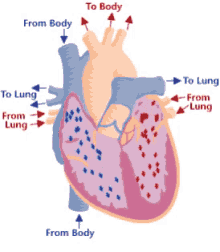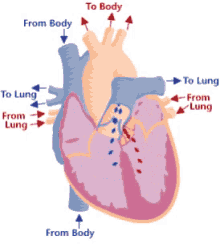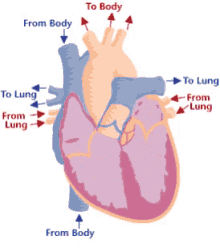
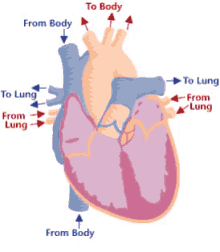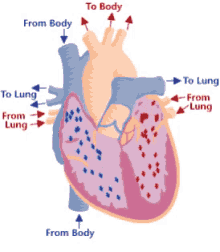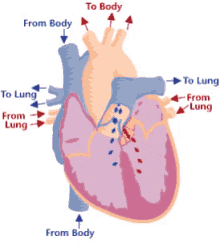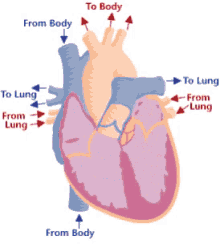
Chambers of the heart
right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle
2
New cards
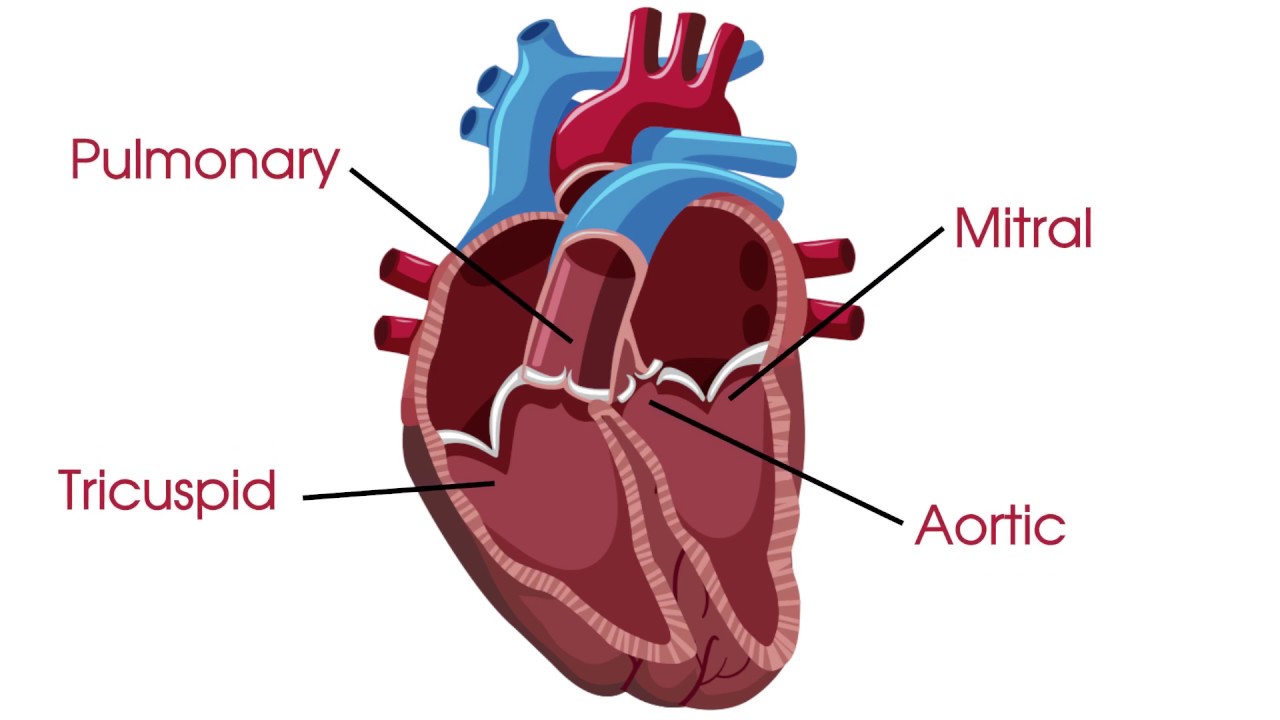
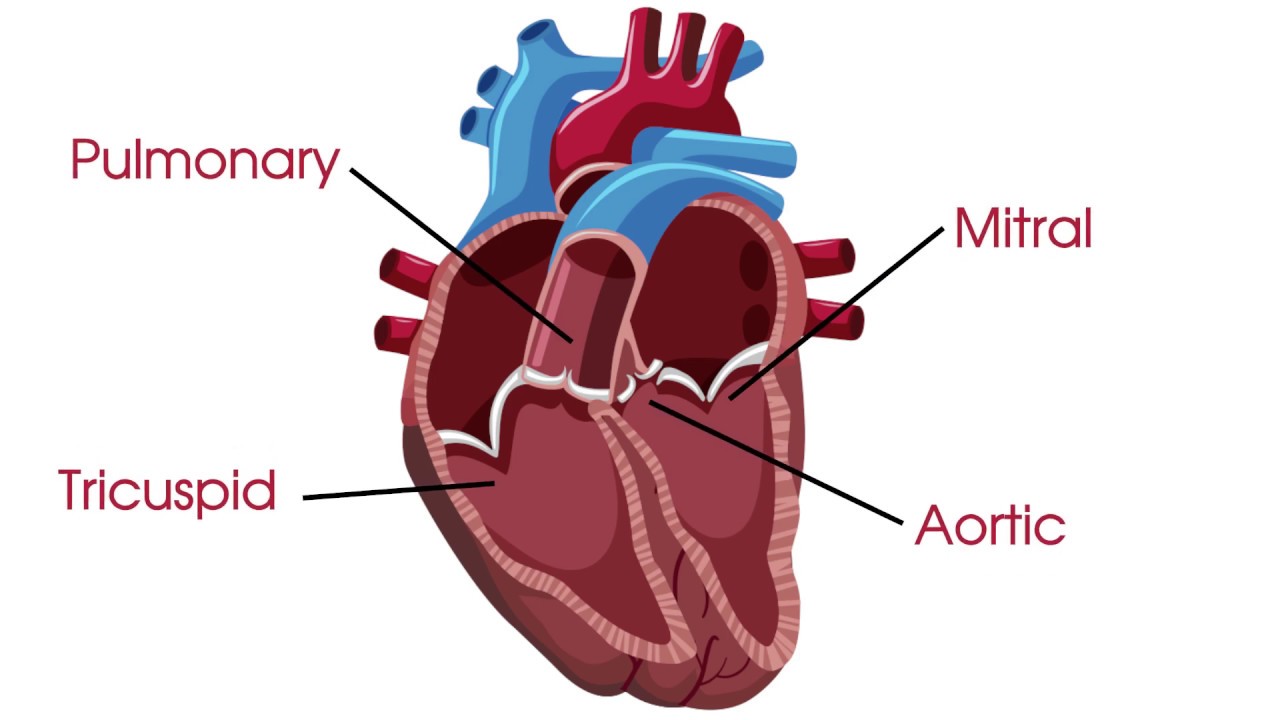
Valves of the heart
tricuspid valve, bicuspid valve, pulmonary valve, aortic valve
3
New cards
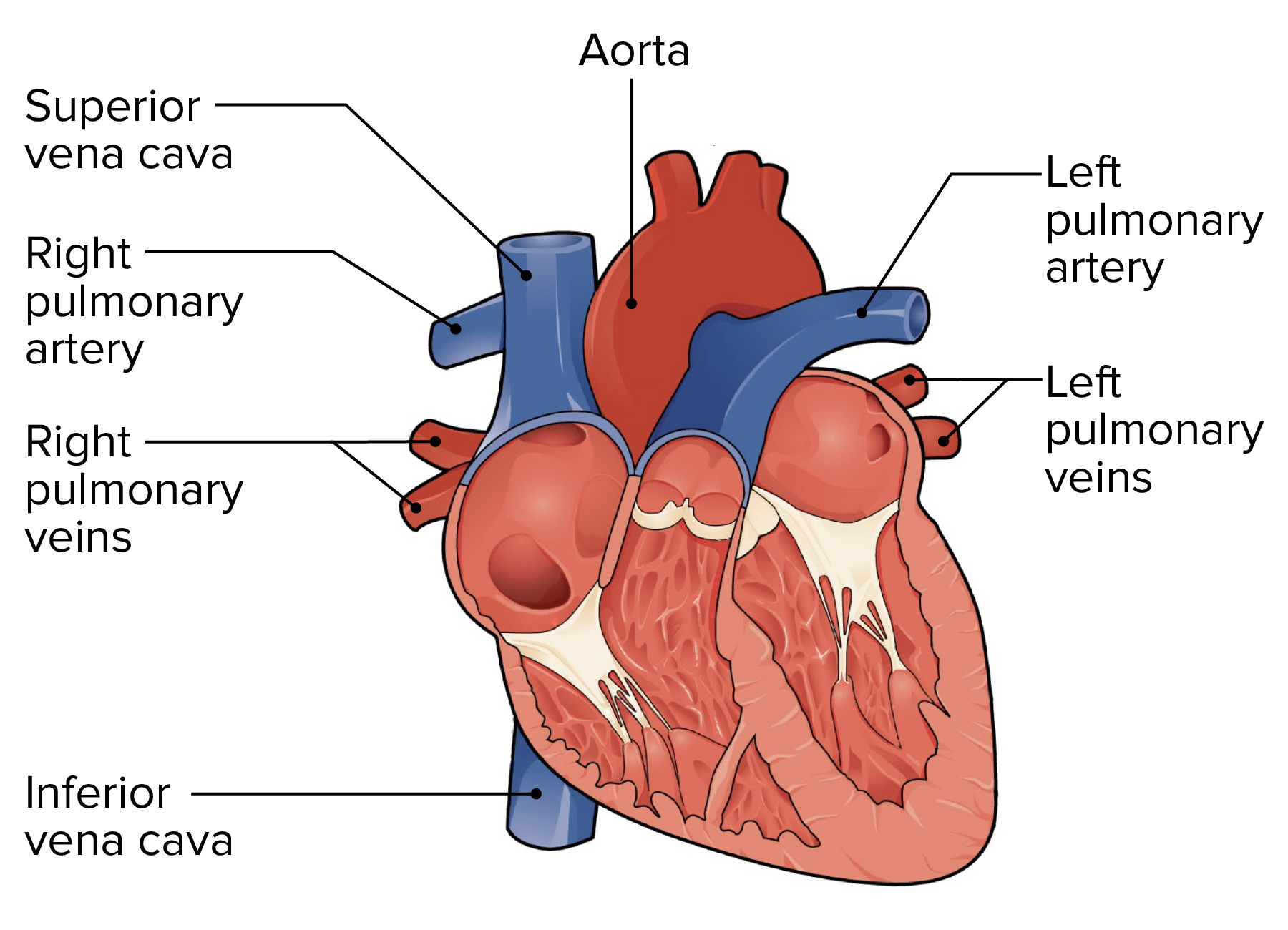
Great vessels of heart
pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries, aorta, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava
4
New cards
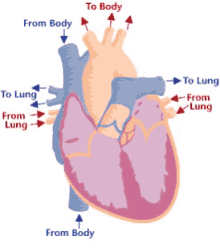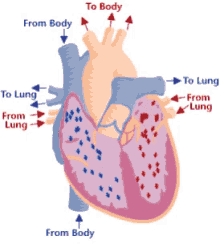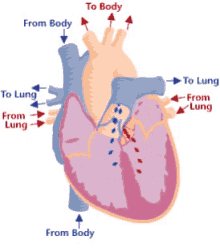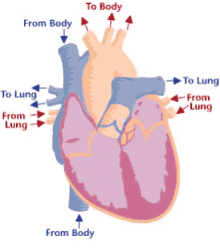
Deoxygenated structures
right atrium, right ventricle, tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, pulmonary veins, pulmonary veins
5
New cards
Oxygenated structures
left atrium, left ventricle, bicuspid valve, aortic valve, pulmonary arteries, aorta
6
New cards
Systemic
left side, oxygenated, from heart -> body
7
New cards
Pulmonary
right side, deoxygenated, from heart -> lungs
8
New cards
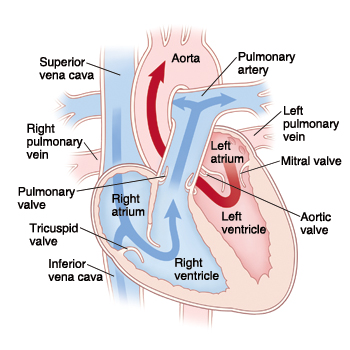
Step 1 of blood circulation
Deoxygenated blood pools in right atrium
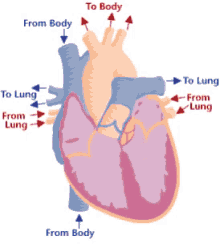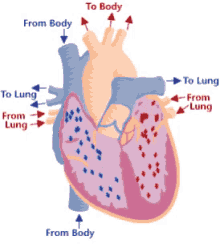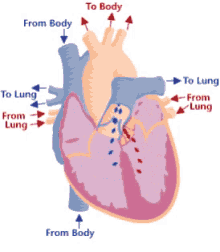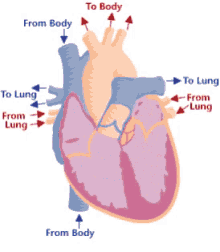
9
New cards
Step 2 of blood circulation
Right atrium fills and tricuspid valve opens
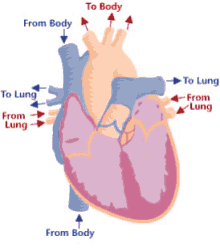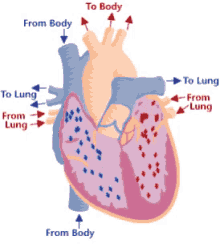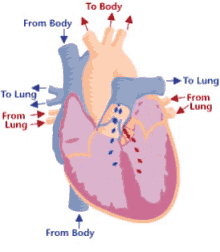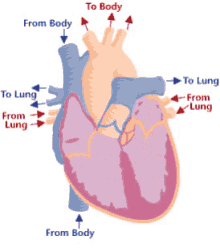
10
New cards
Step 3 of blood circulation
Blood is squeezed through pulmonary valve into pulmonary trunk
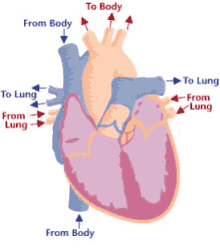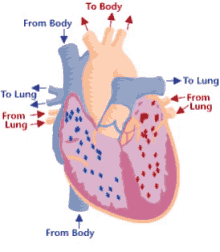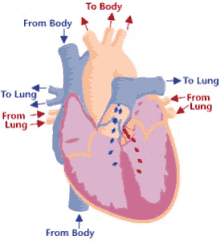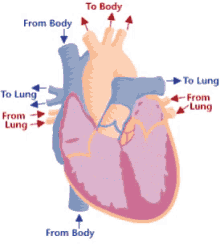
11
New cards
Step 4 of blood circulation
Deoxygenated blood continues through the left and right pulmonary arteries to the lungs
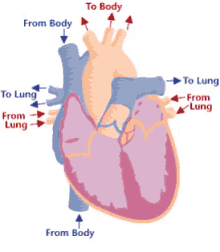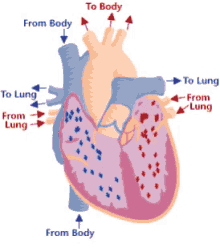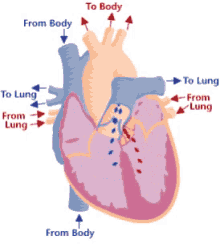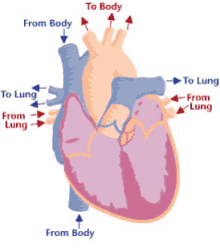
12
New cards
Step 5 of blood circulation
Lungs exchange CO2 for O2
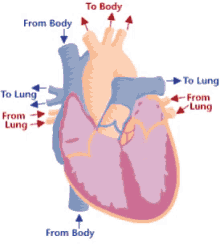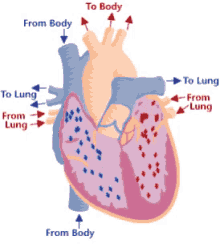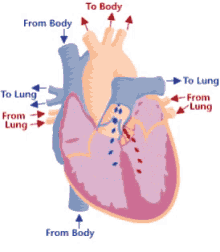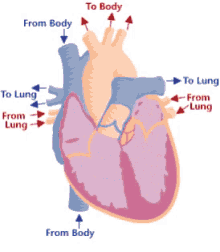
13
New cards
Step 6 of blood circulation
Now oxygenated blood collects in left atrium
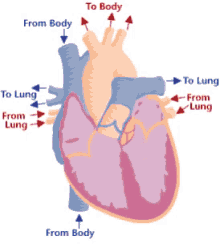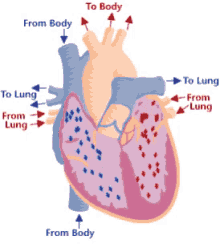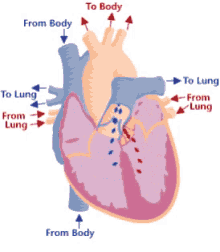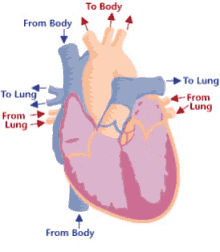
14
New cards
Step 7 of blood circulation
Left atrium fills and bicuspid valve opens, releasing into left ventricle
15
New cards
Step 8 of blood circulation
Pumped through aorta and into left and right pulmonary veins
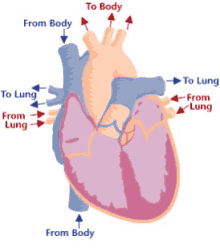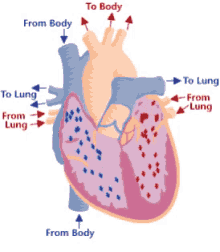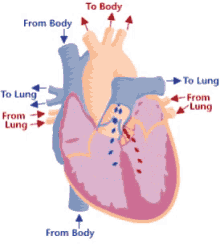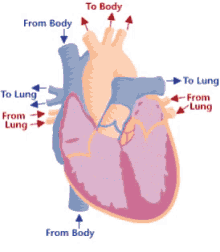
16
New cards
Step 9 of blood circulation
Travels through systemic circuit
17
New cards
Step 10 of blood circulation
Returns via the superior vena cava and right atrium
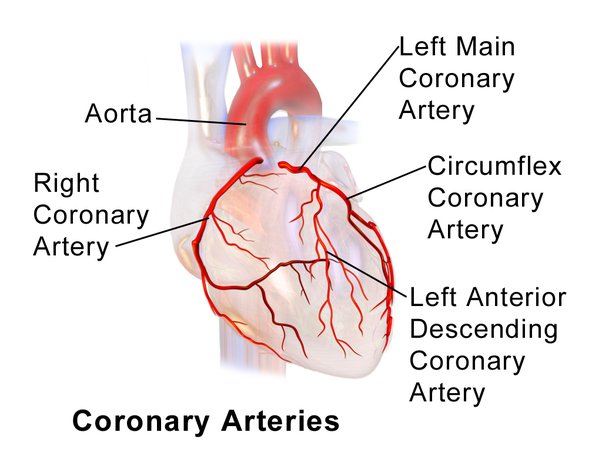
18
New cards
Coronary circuit
Supplies the heart with blood, coronary arteries bring blood to myocardium of the heart, form anastomoses
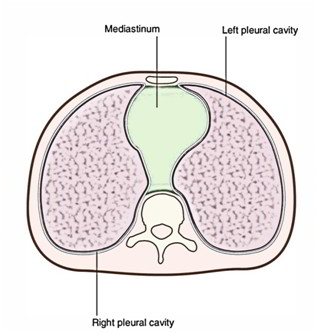
19
New cards
Mediastinum
cavity in center of chest between lungs (where the heart is located)
20
New cards
Anastomoses
connections between arteries
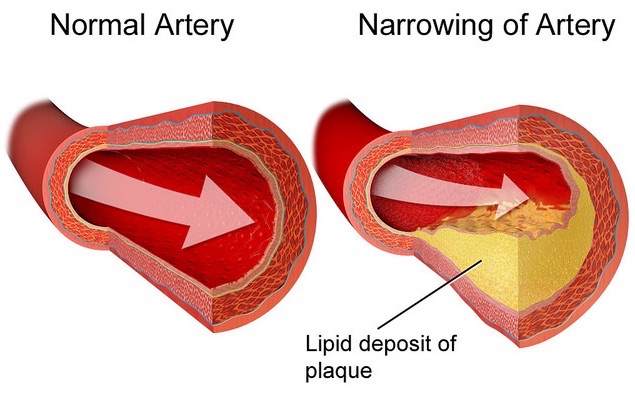
21
New cards
Atherosclerosis
narrowing of arteries due to fatty plaque
22
New cards
Foam Cell
localized to fatty deposits on blood vessel walls, where they ingest LDLs and become laden with lipids
23
New cards
Angiogram
test injecting dye into vessels to see blockage
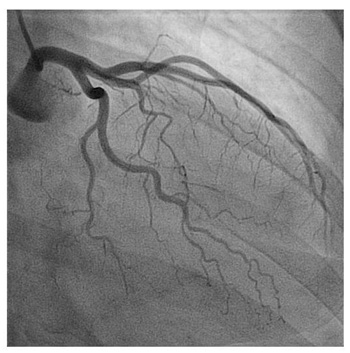
24
New cards
Angioplasty
inserting a balloon into artery to smash plaque against wall to open up vessel
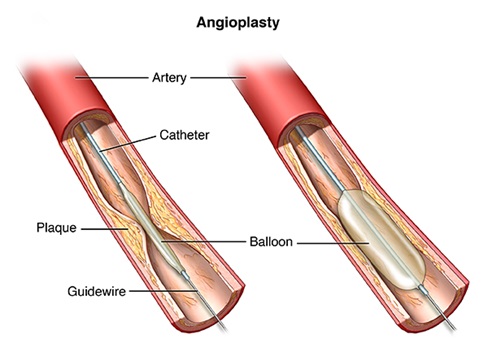
25
New cards
Myocardial Infarction
heart attack, blockage of an artery to the heart due to atherosclerosis and blood clot
26
New cards
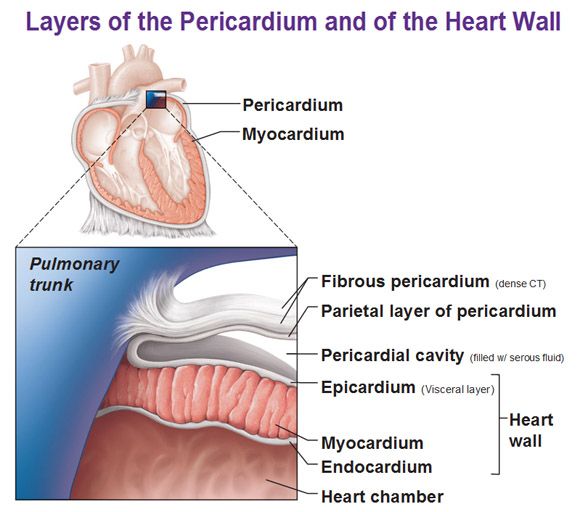
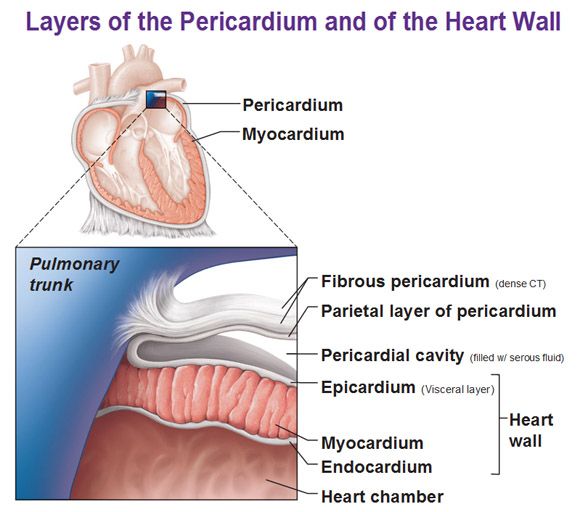
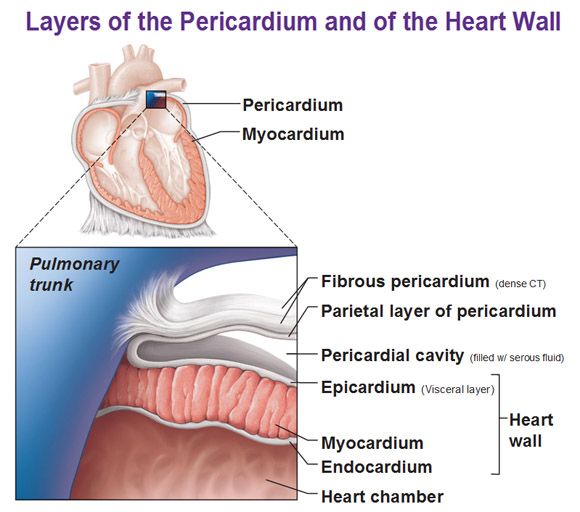
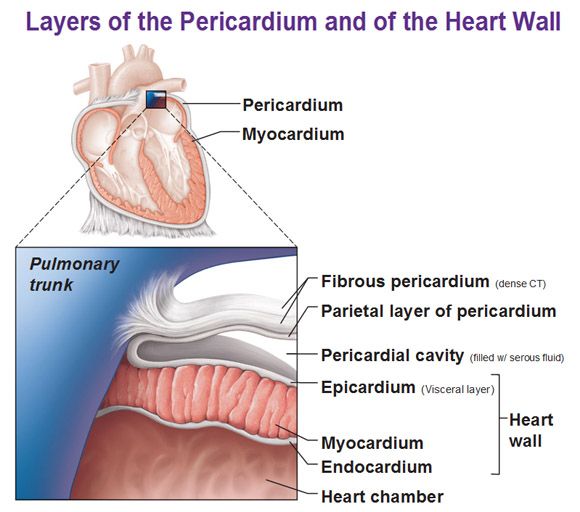
1st layer of the heart
Epicardium
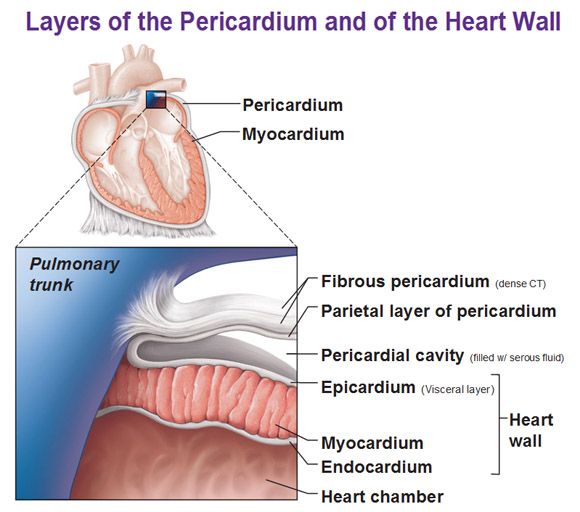
27
New cards
Epicardium
same as visceral pericardium, outermost layer composed of serous membrane
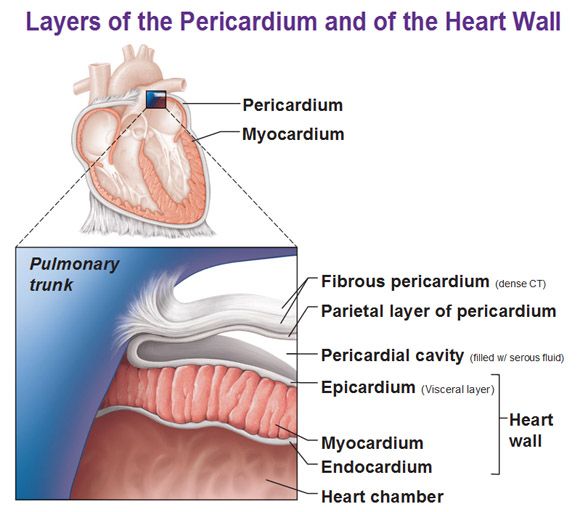
28
New cards
2nd layer of the heart
Myocardium
29
New cards
Myocardium
middle layer (thickest), cardiac muscle, contracts the heart
30
New cards
3rd layer of the heart
Endocardium
31
New cards
Endocardium
innermost layer, simple squamous epithelium, provides smooth lining for blood
32
New cards
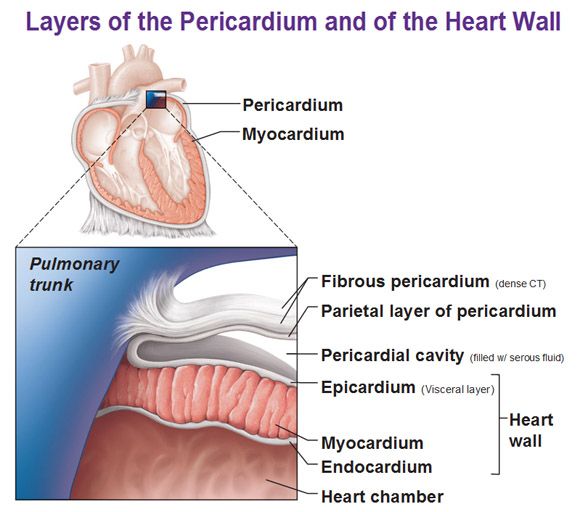
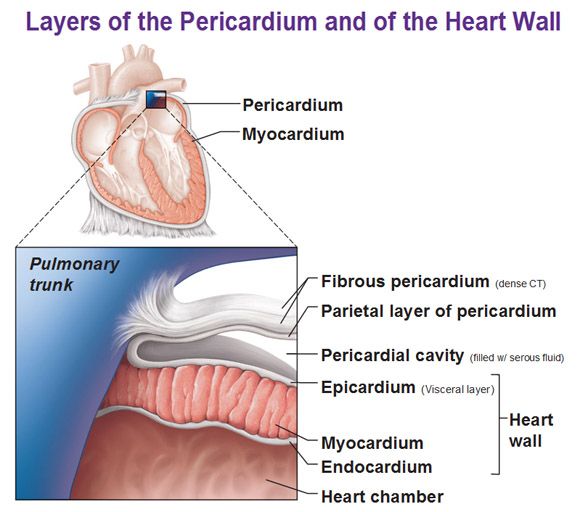
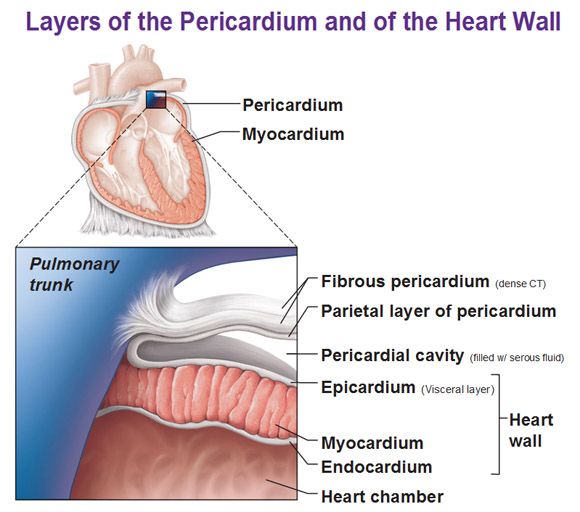
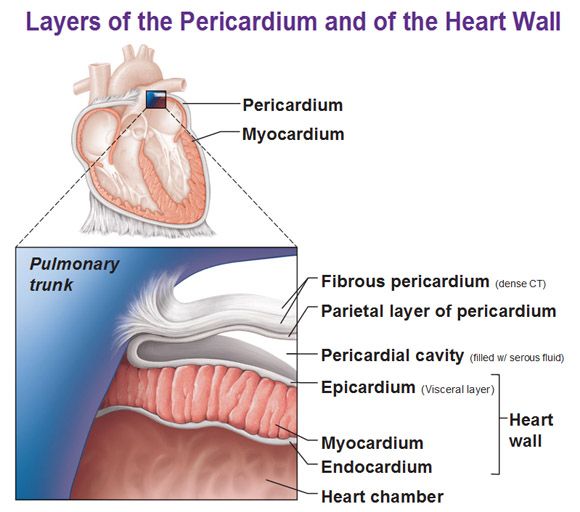
1st layer of the pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium
33
New cards
Fibrous Pericardium
outermost layer composed of dense connective tissue for protection
34
New cards
2nd layer of the pericardium
Parietal Pericardium
35
New cards
Parietal Pericardium
composed of serous membrane producing serous fluid to reduce friction
36
New cards
3rd layer of the pericardium
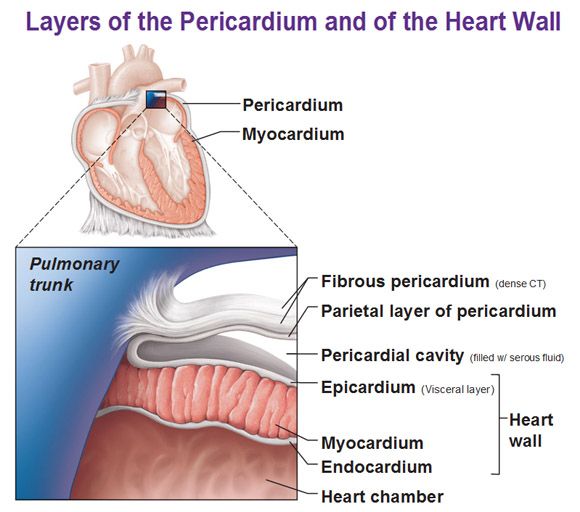
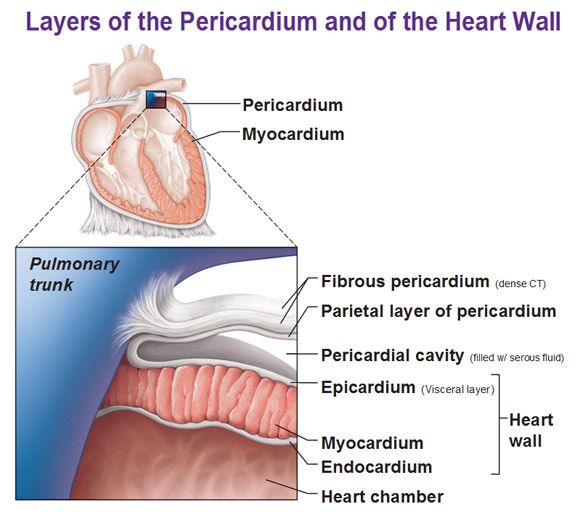
Visceral Pericardium (epicardium)
37
New cards
Visceral Pericardium (epicardium)
folded part of parietal pericardium, between parietal pericardium and visceral pericardium space called pericardial cavity for the serous fluid
38
New cards
Function of heart valves
one way flaps that close to prevent back-flow of blood
39
New cards
10
?
40
New cards
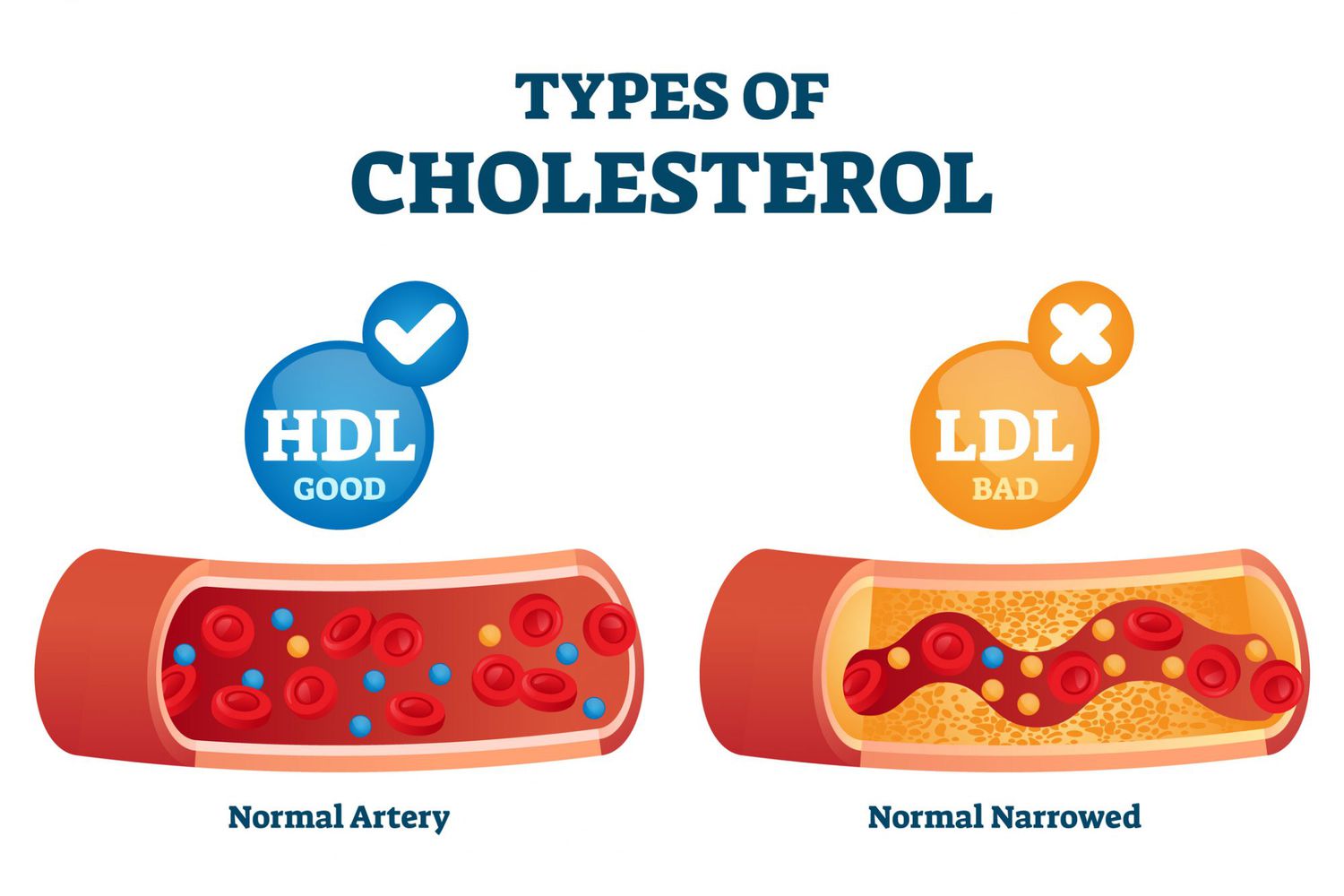
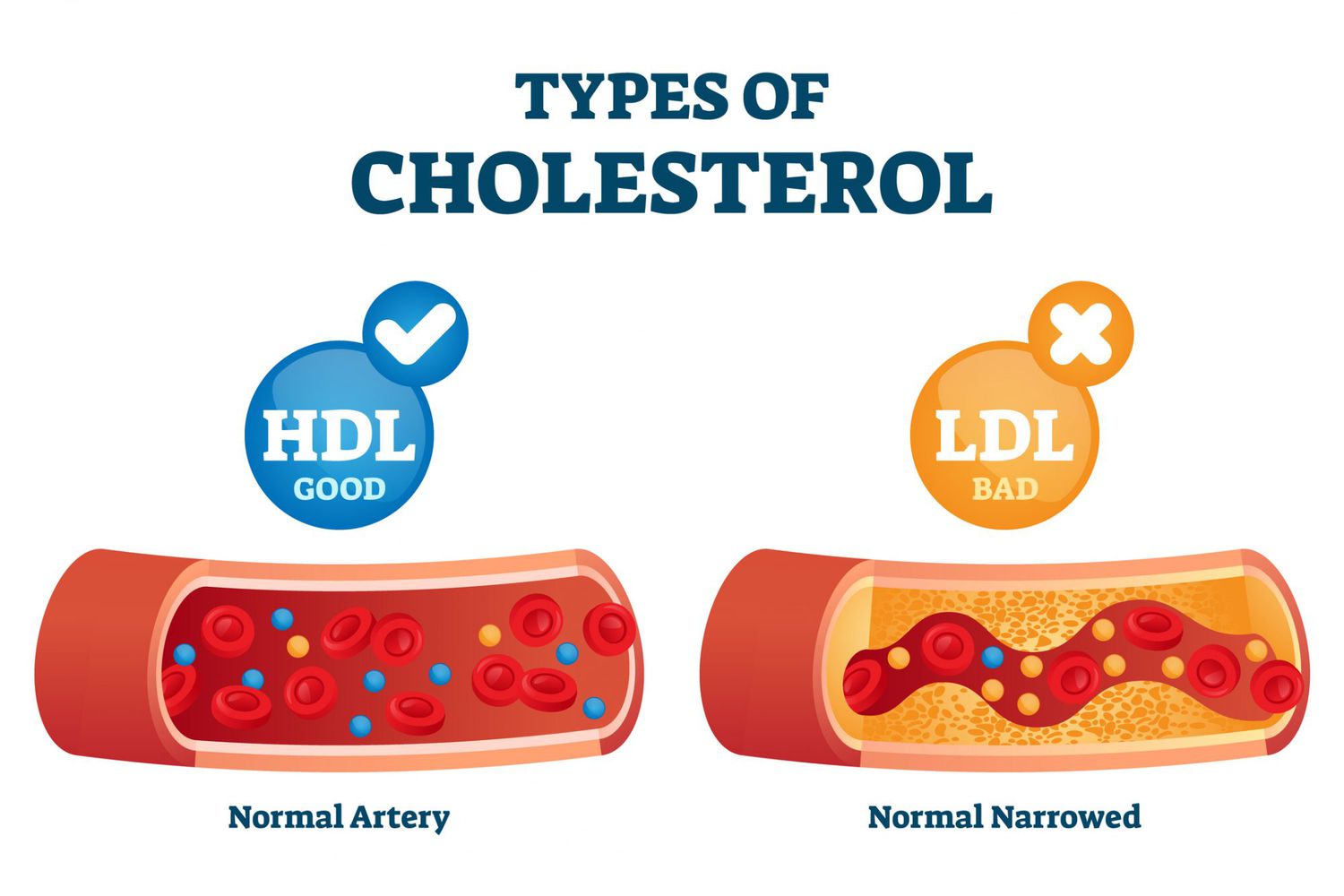
LDL
bad cholesterol
41
New cards
HDL
good cholesterol, scavenges LDL and brings it back to liver
42
New cards
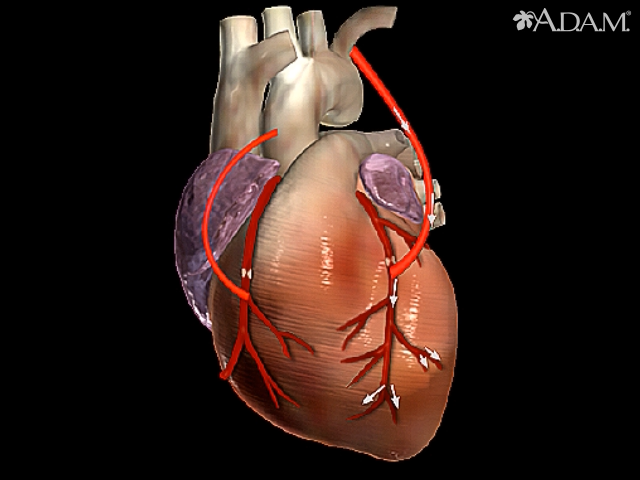
Coronary bypass surgery
\-A vein from the leg is reattached around clotted coronary artery to maintain blood flow
\-Used when arteries are too clogged for angioplasty to work
\-Used when arteries are too clogged for angioplasty to work
43
New cards
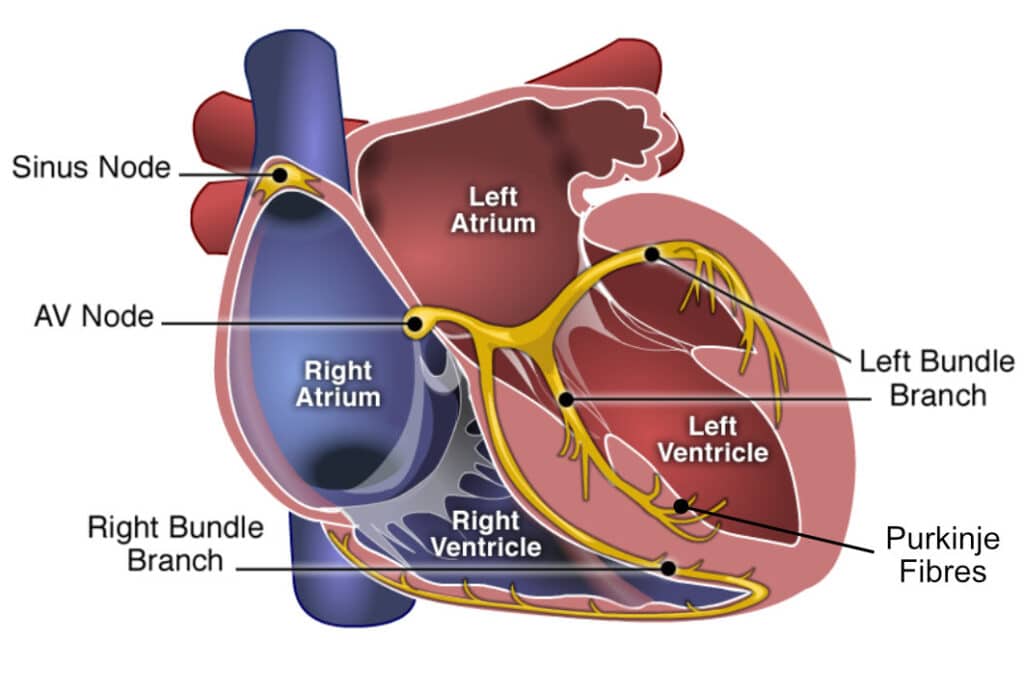
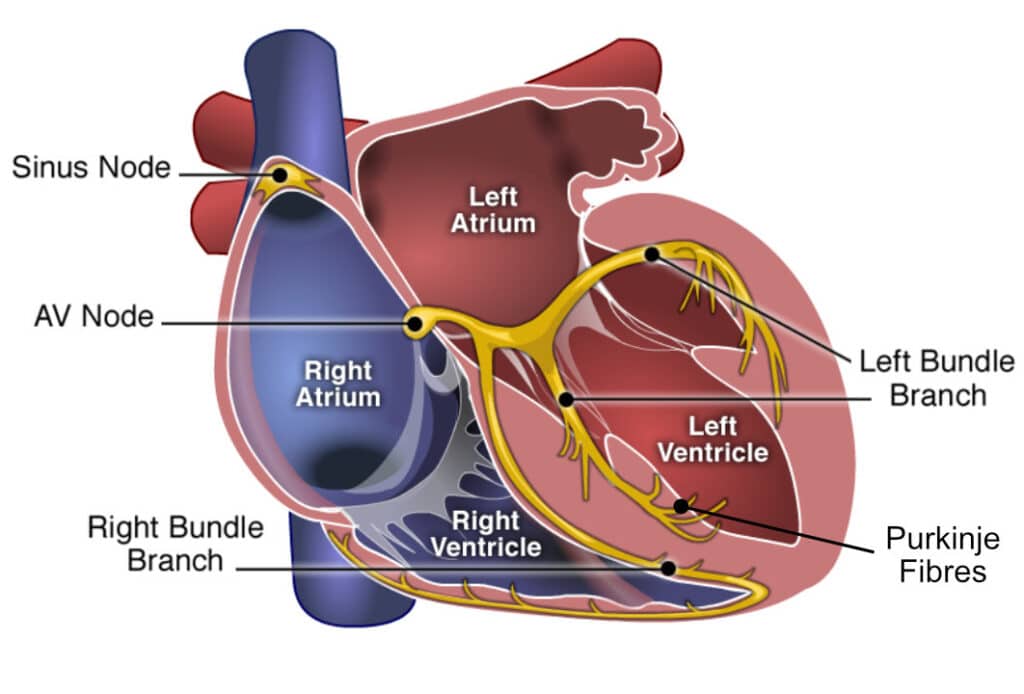
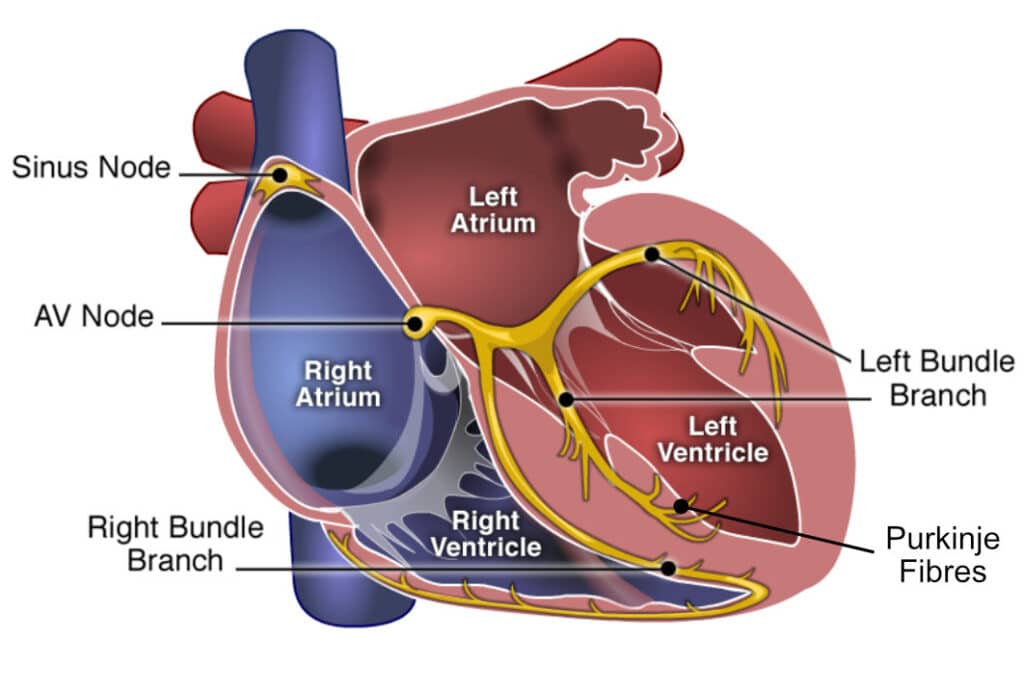
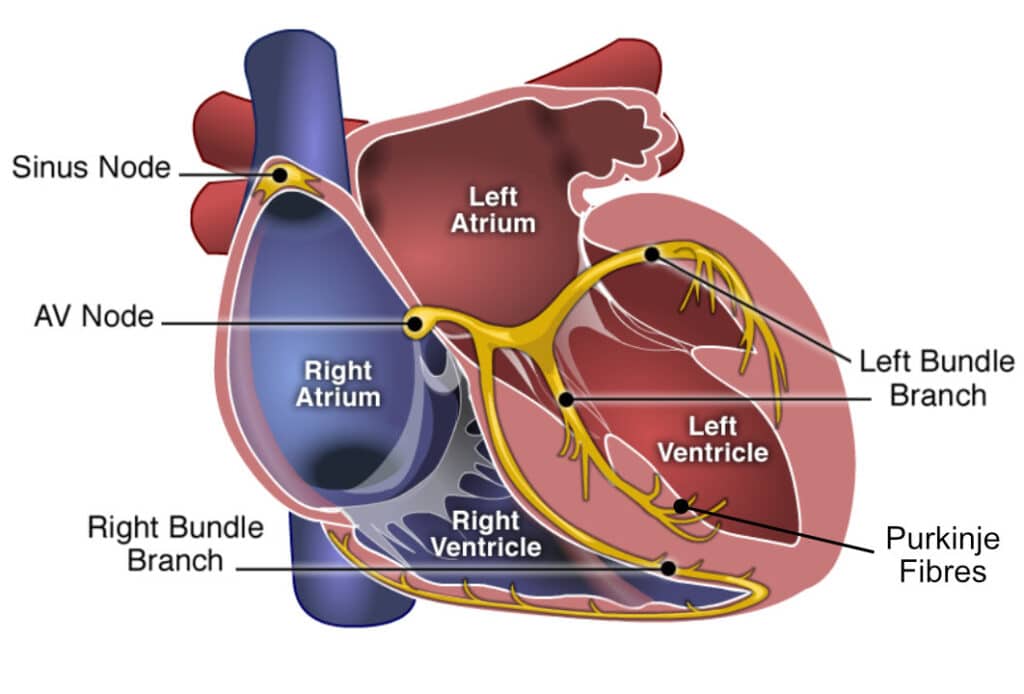
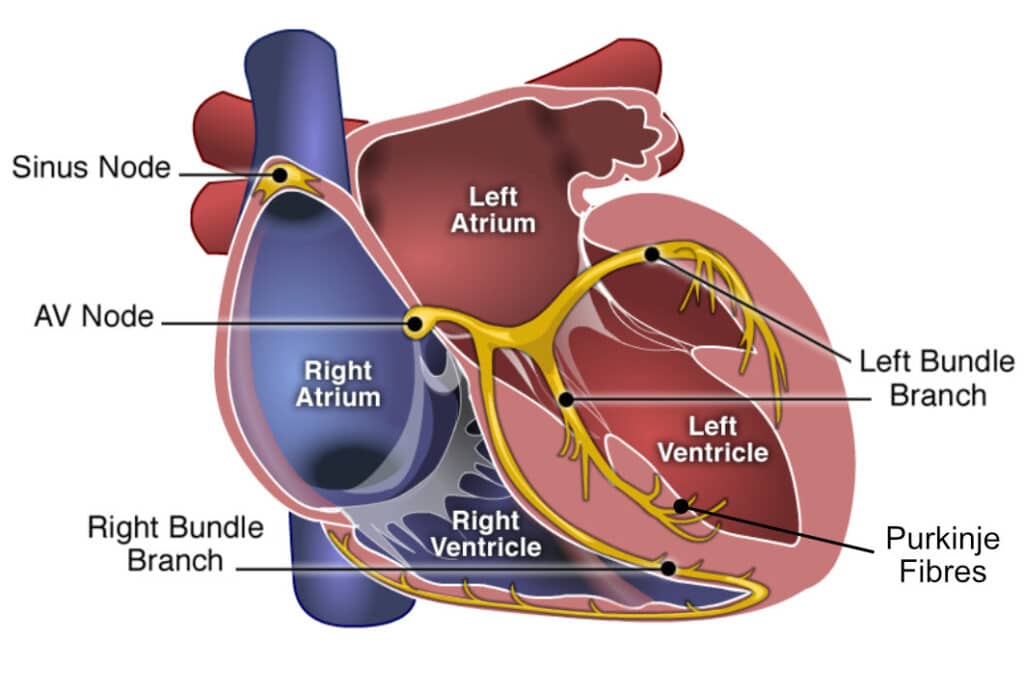
Heart (intrinsic) conduction system #1
SA (sinatrial) node
44
New cards
Heart (intrinsic) conduction system #2
AV (atrioventricular) node
45
New cards
Heart (intrinsic) conduction system #3
AV bundle
46
New cards
Heart (intrinsic) conduction system #4
Right and left bundle branches
47
New cards
Heart (intrinsic) conduction system #5
Purkinje fibers
48
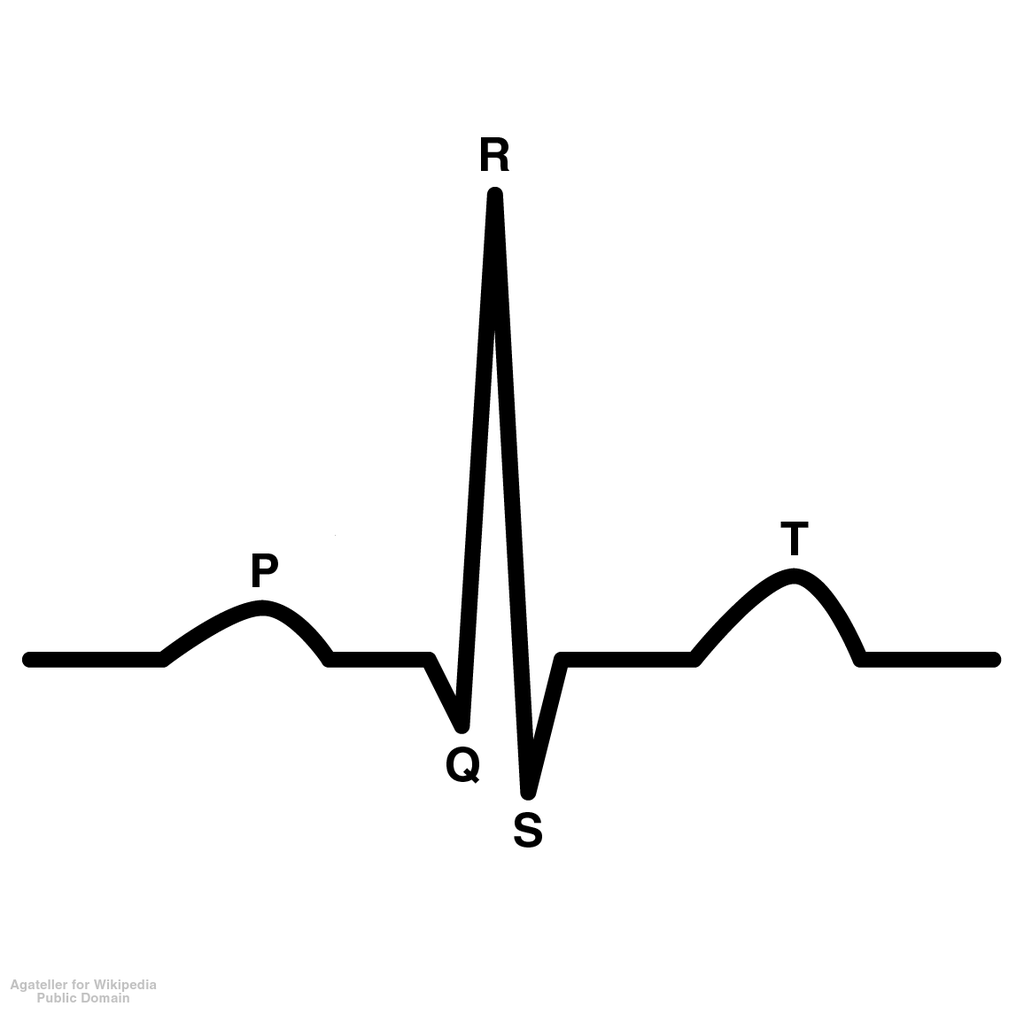
New cards
P wave
depolarization of atria which causes contraction of atria
49
New cards
QRS wave
depolarization of ventricles; atrial repolarization is blocked
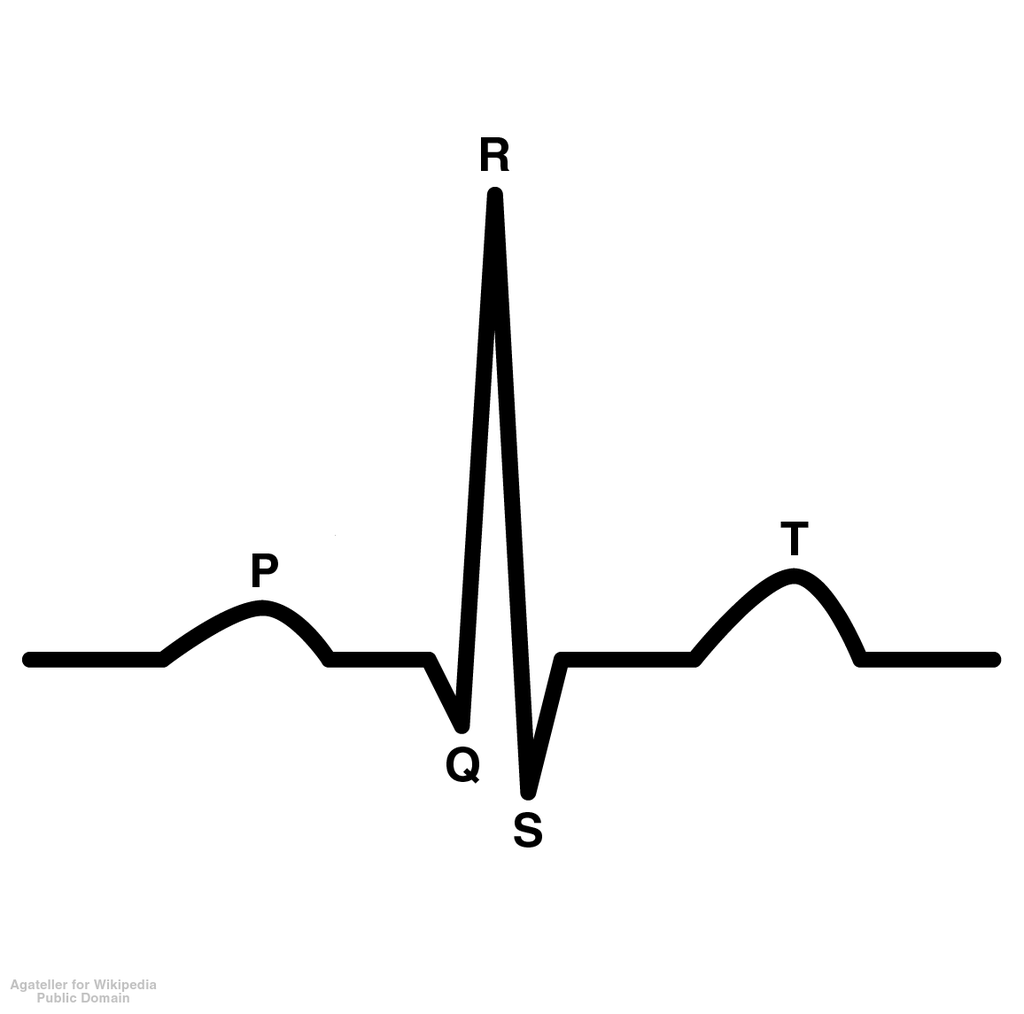
50
New cards
T wave
repolarization of ventricles
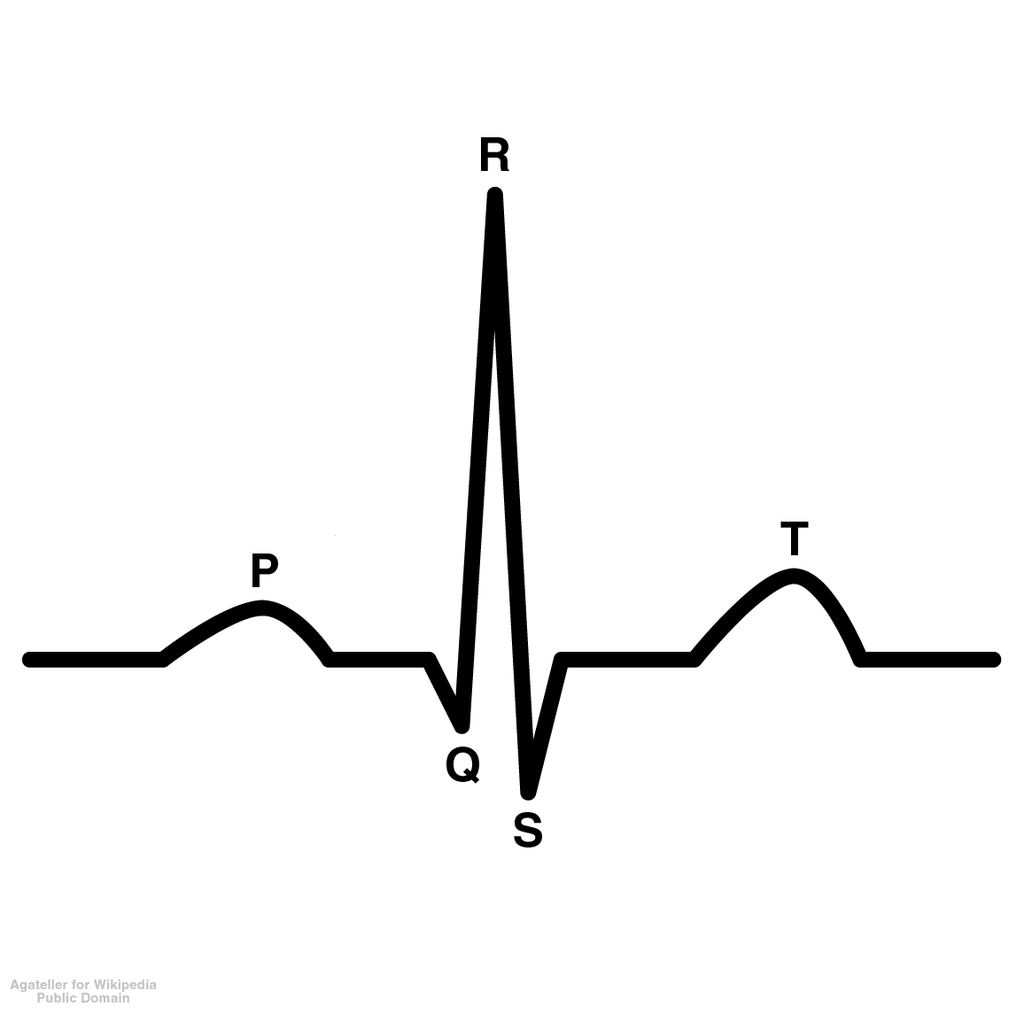
51
New cards
Arrhythmias
no p wave-> atria/SA node not working, irregular heart rate
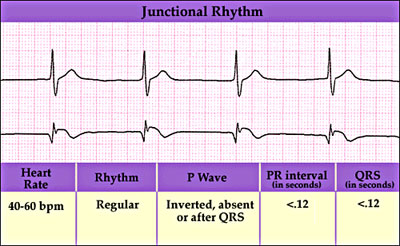
52
New cards
Autorhythmic
heart produces its own pulses through electrochemical stimuli originating from a small group of cells in the wall of the right atrium, known as the sinoatrial node (or SA node)
53
New cards
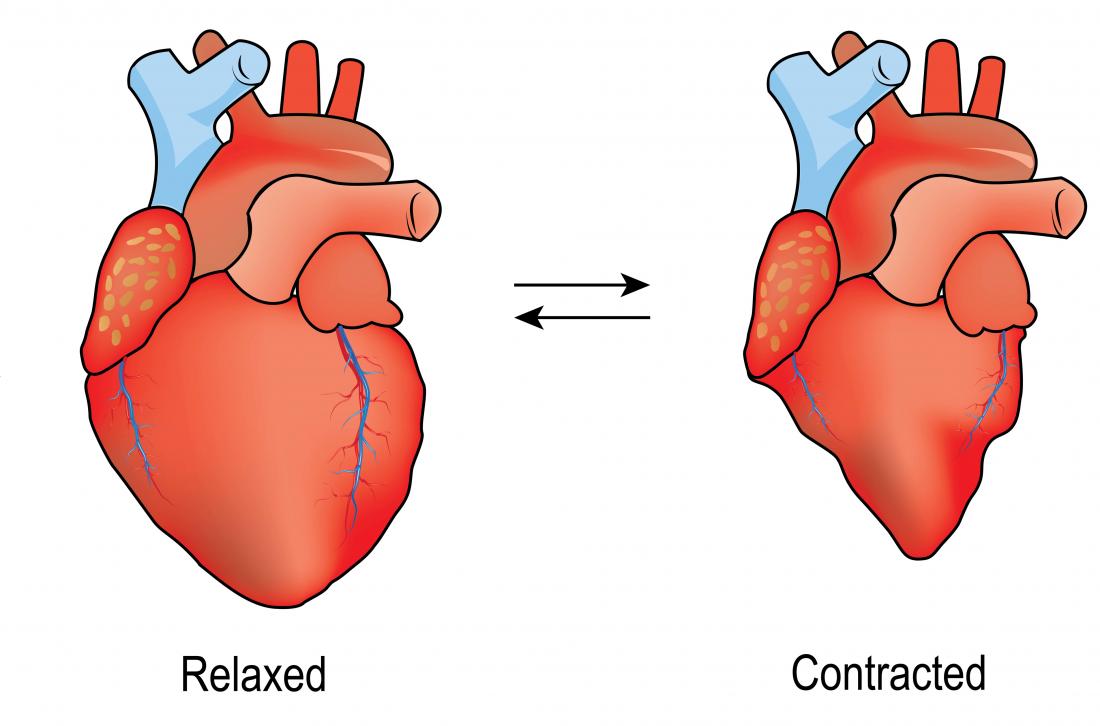
Systole
rate of contraction (depolarization), pressure when heart is squeezed
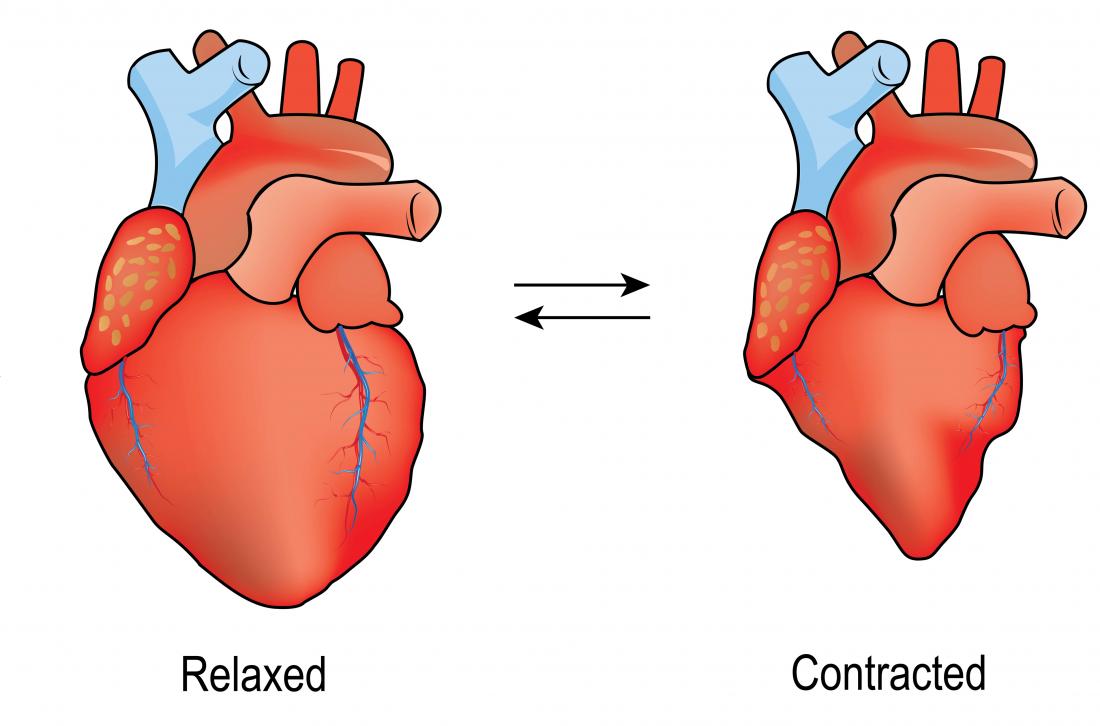
54
New cards
Diastole
rate of relaxation, heart relaxes
55
New cards
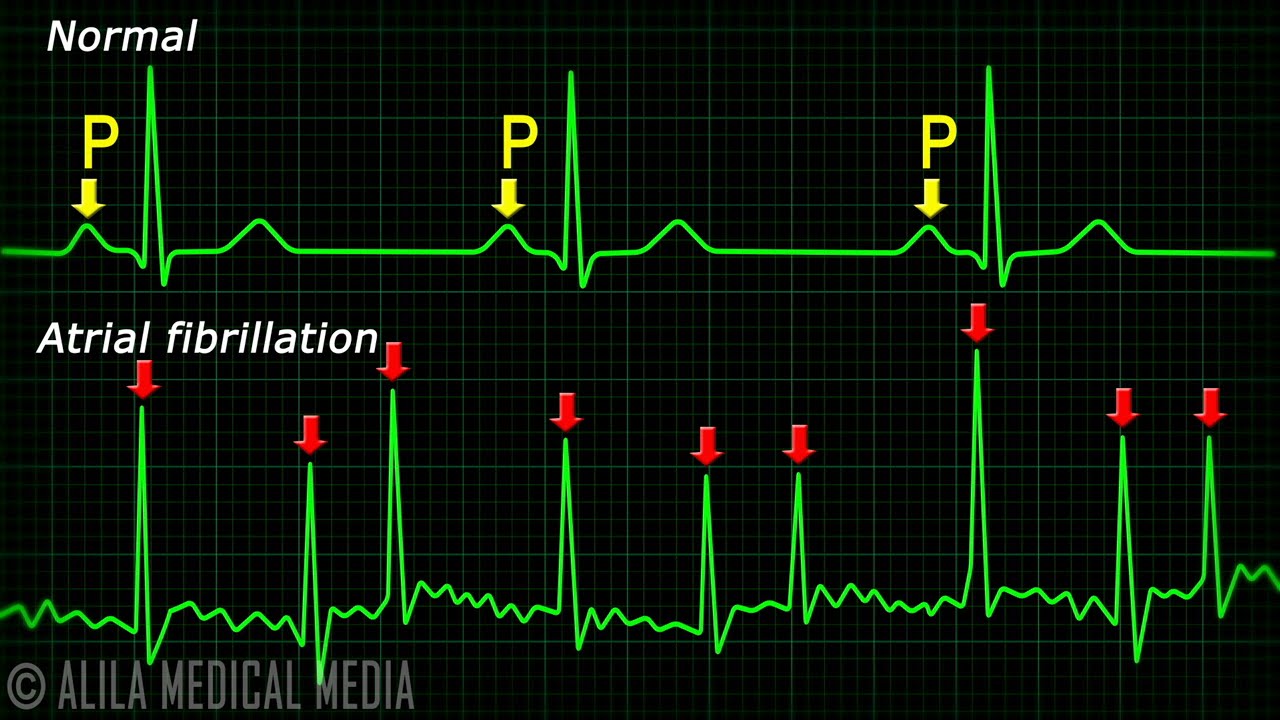
Fibrillation
waves undisguisable, chaotic rhythm, all cells have different electrical impulses and beat out of sync
56
New cards
Tachycardia
heart beats too fast, bpm >100

57
New cards
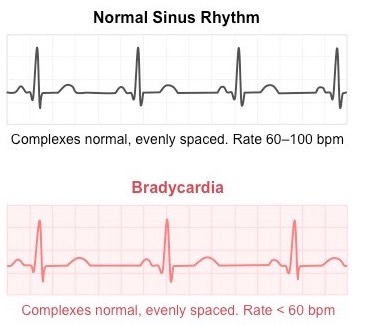
Bradycardia
heart beats too slow, bpm
58
New cards
Hypertension
high blood pressure > 140/90
59
New cards
16
?
60
New cards
Normal heart rate
60-100 bpm
61
New cards
Normal blood pressure
120/80
62
New cards
Systolic pressure
1st # in blood pressure, contraction of heart
63
New cards
Diastolic pressure
2nd # in blood pressure, relaxation of heart
64
New cards
Cardiac output
amount of blood pumped out by each ventricle in 1 minute, blood/min
65
New cards
? \* ?=blood/min
Heart rate \* stroke volume
66
New cards
70\*75=?
5250mL or 5.25L per minute