Lectures 34-35: Pharmacology of Glucocorticoids and Mineralocorticoids | Quizlet
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are the 2 types of corticosteroilds?
Glucocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids
What secretes aldosterone?
zona glomerulosa of adrenal cortex
What secretes cortisol?
Zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex
What secretes DHEA?
zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex
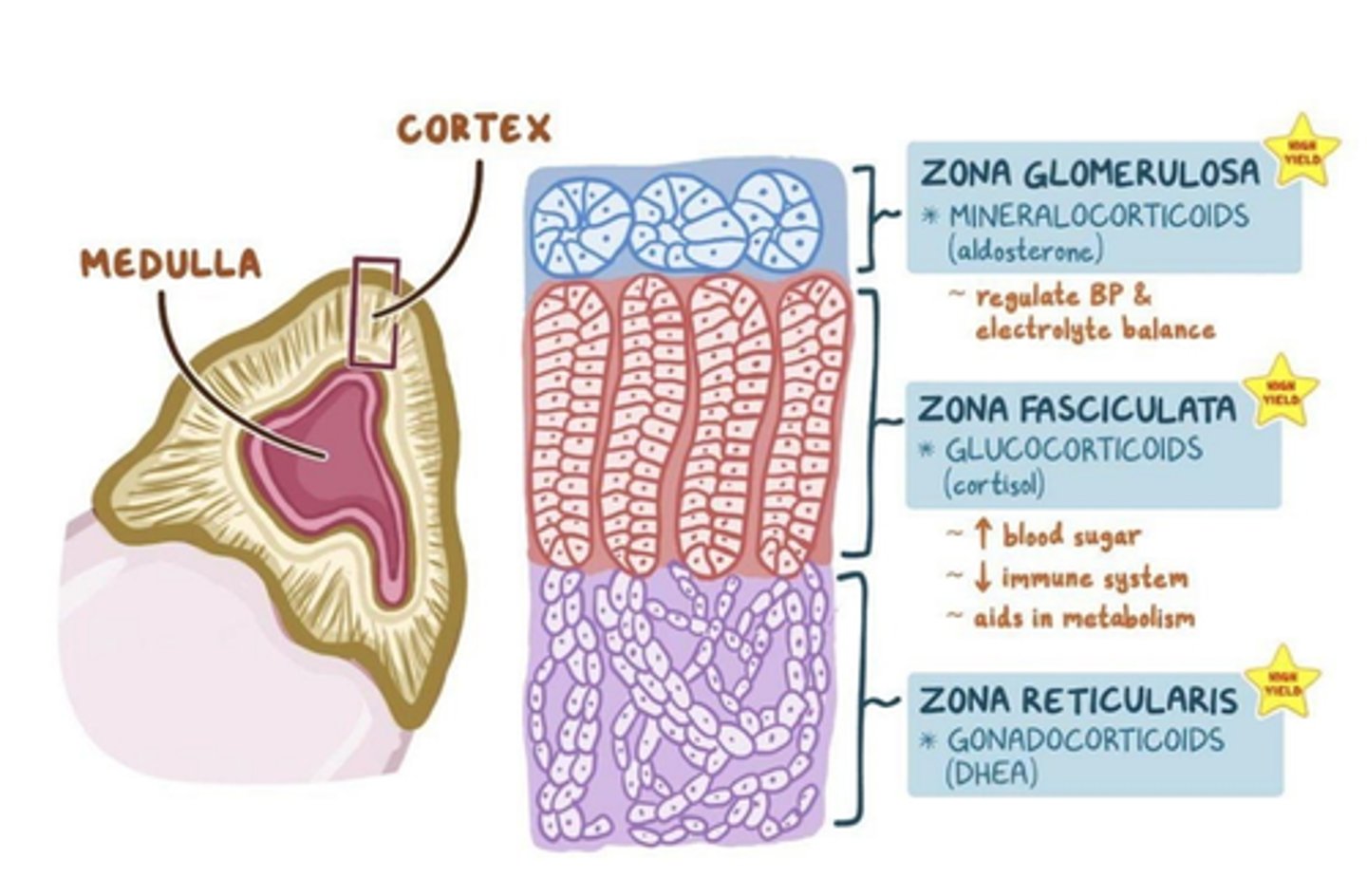
List the layers of the adrenal cortex from outermost to innermost
Glomerulosa
Fasciculata
Reticularis
Describe the mechanism of the HPA axis
Hypothalamus releases corticotropic releasing hormone which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release ACTH
ACTH then acts on the adrenal cortex to produce glucocorticoids
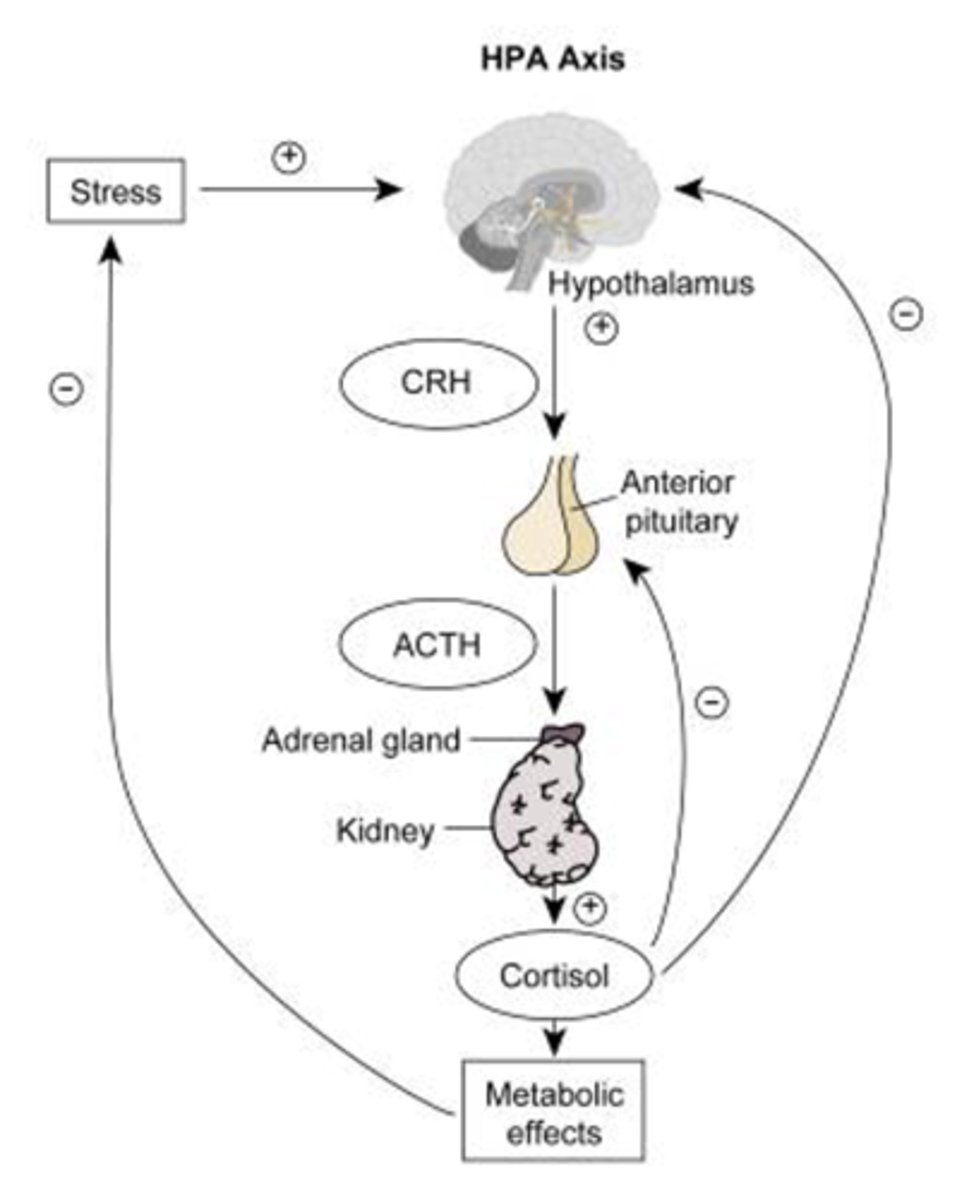
What are the characteristic modes of regulation of the HPA axis?
Basal steroidogenesis (diurnal rhythm)
Negative feedback regulation by adrenal corticosteroids
Stress
Glucocorticoid levels peak at what time of day?
about 8 am
The HPA axis is a ____________ feedback loop.
negative
How does stress increase corticosteroid production?
it overcomes the negative feedback regulation
What 2 steroids are released by the adrenal cortex?
Androgens
Corticosteroids
What is the purpose of corticosteroids in the body?
Allow capacity to resist stressful circumstances
Glucorticosteroids
class of steroid hormones that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor and regulates glucose metabolism, its synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and steroid structure
What are the general uses for glucocorticoids?
used to treat diseases caused by an overactive immune system
EXAMPLES:
Allergies
Asthma
Autoimmune diseases
Sepsis
Cancer (in high doses)
What is the most important human glucocorticoid?
cortisol (hydrocortisone)
Glucocorticoid effects can be classified into what two categories?
Immunologic
Metabolic
What are the immunologic effects of glucocorticoids?
increase anti-inflammatory proteins
decrease pro-inflammatory proteins
What are the metabolic effects of glucocorticoids?
Increases blood sugar levels (gluconeogensis)
Inhibits uptake of glucose into cells
Stimulates fat breakdown
What is the action of mineralcorticoids?
Active sodium reabsorption
Passive water reabsorption
Active secretion of potassium and protons
- all to increase blood pressure and volume
What is the primary endogenous mineralcorticoid?
Aldosterone
What are the minerals that mineralcorticoids regulate?
Sodium and potassium
Where is the major target of aldosterone? What does it do
acts on the distal tubule of kidney to stimulate exchange of sodium and potassium
What are the two categories of toxic effects of adrenocortical steroids?
Withdrawal (HPA axis suppression)
Supraphysiological doses
When does withdrawal occur?
rapid withdrawal of corticosteroids after prolonged therapy
What are the S/Sx of corticosteroid withdrawal?
Fever
Myalgia
Arthalgia
Malaise
Pseudotumor cerebri
What occurs when glucocorticoids are continued at supraphysiological doses?
Fluid and electrolyte abnormalities
HTN
Hyperglycemia
Increased risk of infection
Osteoporosis/ osteonecrosis
Myopathy
Behavioral disturbances
Cataracts
Peptic ulcers
When are glucocorticoids used therapeutically?
replacement therapy in deficiency
Allergic disease
Bronchial asthma
GI diseases
Why should intermediate acting steroids be given in the morning?
to diminish HPA axis suppression by following the normal diurnal rhythm
Which steroid can be used in GI diseases? Why?
Budesonide - quickly inactivated by hepatic metabolism
Glucocorticoids
Cortisol (Hydrocortisone)
Prednisone
Prednisolone
Triamcinolone
Methylprednisolone
Dexamethasone
Mineralcorticoids
Fludrocortisone
Aldosterone