Fundamentals of Human Physiology Exam 1 UIOWA
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Physiology
Study of human function
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment to support optimal function under given circumstances
regulated variables of homeostasis
Blood pressure, pH, body temperature, blood sugar
Set point
value where we keep regulation in homeostasis
sensors (homeostasis)
detect changes in variables and relays to integrator
Integrator (homeostasis)
Makes decision what to do to regulate variables
effectors (homeostasis)
any organ or tissue that receives information from the integrating center and acts to bring about the changes needed to maintain homeostasis
Negative feedback system
a process that results in a response that reverses the original stimulus
Positive feedback system
strengthens or reinforces a change in one of the body's controlled conditions (not as common)
feedforward control
The anticipation of stimuli, activates effectors in advance (think sprinter before race, body starts to make changes to prepare for event)
levels of organization in the body
atomic
cell
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
Atomic/Molecular Level
all higher level functions are based upon the principles of physics and chemistry
cellular level of organization
basic unit of structure and function of living things
tissue level of organization
groups of similar cells that have a common function
organ level of organization
contains two or more types of tissues that form a structure with a specific function
organ system level of organization
Consist of different organs that work together closely to perform related functions
Organism level of organization
organ systems make up an organism
Four types of tissue
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
Muscle tissue
A body tissue that contracts or shortens, making body parts move.
types of muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac (heart), smooth (organs)
Nervous tissue
Cells designed to receive and transmit information through neurons
Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Neuroglia
cells that support and protect neurons
epithelial tissue
A body tissue that covers the surfaces of the body, inside and out
- Functions: Regulates movement of materials, barrier, protection, form exocrine glands
Connective tissue
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts
Stem cells
unspecialized cells that retain the ability to become a wide variety of specialized cells
totipotent stem cells
Stem cells that can differentiate into ANY type of specialised cells found in organisms of that species.
pluripotent stem cells
Stem cells that can become almost all types of tissues and cells in the body but CAN'T form another organism
multipotent stem cells
stem cells that can become only one type of tissue and cell in the body
Body Fluid Compartments
intracellular and extracellular
intracellular fluid
fluid within cells
Extracellular fluid (interstital)
Fluid between cells
Extracellular fluid (Plasma)
plasma fluid
Chemical bond
the force that holds two atoms together by interaction of valence electrons
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Cation
Atom that loses an electron, becomes POSITIVE
Anion
atom that gains electrons, becomes NEGATIVE
Hydrogen bonds
Weak intermolecular attraction between polar molecules, the (-) of one polar molecule is attracted to the (+) end of another polar molecule
Acid
Release H+ when mixed with water
Bases
Gains H+ when mixed with water
Organic Macromolecules
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
major source of energy in body
categories of carbohydrates
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
- One carbon ring
- Basic unit
- Ex: glucose, fructose, galactose
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
- Ex: glycogen, starch, fiber
Lipids
compounds that cannot mix with water
- Subclasses: triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids
Triglycerides
Stored form of energy in plants and animals
- Two types: saturated and unsaturated
Phospholipids
a lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule instead of third fatty acid
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes
- Amphipathic
- Hydrophilic head
- Hydrophobic tail
Steroids
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
- Ex: cholesterol, corticosteroids, sex steroids
Proteins
Chains of amino acids
amino acid structure
a carboxyl group, amine group, and R group
R group (side chain)
What group differentiates amino acids?
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure of protein
protein structure is formed by folding and twisting of amino acid chain
- due to hydrogen bonds forming between peptide bonds
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide
- due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain
quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits
Glycoproteins
A protein with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates
Lipoproteins
protein + lipid
- Carrier molecules in blood
nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
Nucleic acid composition
five-carbon sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
DNA
two strands linked together by hydrogen bonds
- Form double helix
- strands are complementary
- Recipe for proteins
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Microvilli
Fingerlike extensions of plasma membrane, increase surface area
Lysosomes
contains digestive enzymes
- Destroy: bacteria, old organelles, food molecules
Golgi apparatus
sorts and packages proteins made by ribosomes on rough ER
Gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Genome
All the genetic information in an organism; all of an organism's chromosomes.
Proteome
the entire set of proteins expressed by a given cell or group of cells
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
RNA polymerase
Separates the double-helix and creates a copy of one of the strands
Codons
A three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code
Splicing
the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons in a pre-mRNA
alternative splicing
regulated process during gene expression that results in a single gene coding for multiple proteins
Translation
the synthesis of a protein molecule from an mRNA strand
steps of translation
1. mRNA binds to a ribosome
2. Ribosome moves down mRNA looking for start codon
3. tRNA brings the appropriate amino acid into place
4. mRNA strand advances to next codon, where a new amino acid is brought in an peptide bond is formed
5. Continues as chain grows until a stop codon is reached
Hyperplasia
growth through cell multiplication
hypertrophy
growth through increase in cell size
Mitosis
Formation of two identical daughter cells from cell division following DNA synthesis
Meosis
Process by which two cell divisions produce haploid gametes
Necrosis
tissue death
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
lock and key model
The model of the enzyme that shows the substrate fitting perfectly into the active site
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism to maintain homeostasis
Anabolism
Requires the input of energy to synthesize molecules
Catabolism
Releases energy by breaking down molecules into smaller molecules
Macronutrients
______________________ are catabolized to release chemical energy
Glucose Catabolism
1. Glycolysis (always)
2. Citric Acid (krebs) cycle (IF O2 is present)
3. Electron transport chain (IF O2 IS PRESENT)
glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid
- 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
Lactic Acid Pathway
- anaerobic conditions
- Pyruvic acid converted into lactic acid
- the process that occurs in absence of O2, cell must have an alternative pathway for pyruvate
The Krebs Cycle
second stage of aerobic cellular respiration, occurs in mitochondrial matrix
- pyruvate combines with coenzyme A to form Acetyl CoA
- then Acetyl CoA reacts to form 6 NADH, 2 ATP, 4 CO2
electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP
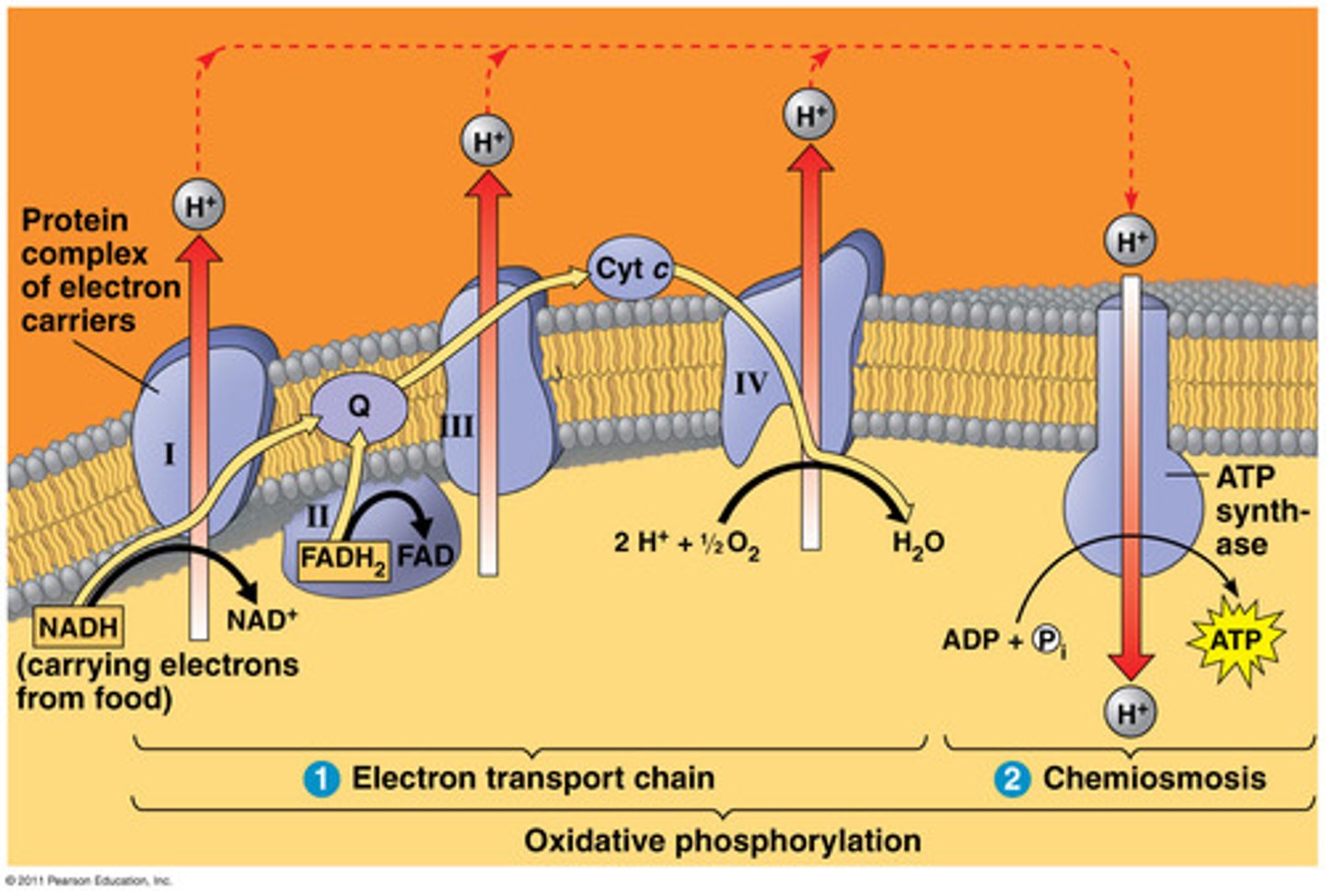
NAD+
In the electron transport chain, NADH produced from the krebs cycle is converted into _____________________