circulatory system
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
shock
•A state of acute circulatory collapse
•Inability to transport sufficient oxygen around the body
•Organ failure
•Death
nurse would look for - MM colour, IVFT, temperature, CRT, digital pulse and quality
4 types of shock
hypovolaemic
distributive
cardiogenic
obstructive
hypovolaemic shock
•Most common
•Secondary to significant loss of circulating fluid volume
RTA, haemorrhage, burns
signs of hypovolaemic shock
•Tachycardia
•> CPR
•Pale MMs
•Poor pulse quality - bpdy is contricting vessles to organs
•Low blood pressure
treatment of hypovolaemic shock
•Fluid Replacement (Electrolytes)
•Arrest of haemorrhage
•O2 Supplementation
•Warmth
•Urine output
•Lactate - gives incite to oxygen levels and how much oxygen organs are receiving.
Demeanour may be quiet, lethargic, dull, agitated, stressed, little urine output, brown in colour, (very concentrated),
-Might need to manage stress to prevent further complications.
distributive shock
allergic reaction or toxic shock
•The body has suffered an insult (usually severe infection or inflammation).
•Generalised release of inflammatory mediators that promote vasodilation
•Body unable to control where blood volume is distributed
-Body releases inflammatory mediators against the allergen – promotes vasodilation – sending blood everywhere, not normal regulation, body isn’t preserving blood flow to the organs and important parts. -
seems like low BP
signs of distributive shock
same as hypo
red MMs
treatment of distributive shock
same as hypo
antivenom/ antibiotic
endotoxic shock
– bacterial infection and the bacteria cells have broken down and released a toxin.
ectotoxic shock
bacteria cells within the body
neurogenic shock
damage to nervous system - could cause distributive shock
e.g. poisoning, meningitis, trauma, signals not telling circulatory system the right thing
cardiogenic shock
•A condition where the heart can no longer pump effectively
•Commonly seen in degenerative conditions of the heart muscle
not enough O2 to organs
signs of cardiogenic shock
heart murmur
irregular pulses
treatment of cardiogenic
•Underlying cause - manage
•Provide intravenous access/IVFT
•O2 Supplementation
•Warmth/monitor body temp
•Urine output
•Lactate
•Close monitoring
obstructive shock
blockage near the heart, blood cannot get to where it needs to be
a blockage of the aorta
a reduction in venous return
pathophysiology of shock
•A state of organ hypoperfusion which causes cellular dysfunction and damage.
•Once perfusion declines, the oxygen delivery to cells is inadequate for aerobic metabolism.
•Cells shift to anaerobic metabolism with increased production of carbon dioxide and elevated blood lactate levels.
•Cellular function declines and if not corrected cell damage and death occurs.
•Decreased circulating volume (hypovolaemic shock)
•Decreased cardiac output (carcinogenic and obstructive shock)
•Vasodilation (distributive shock)
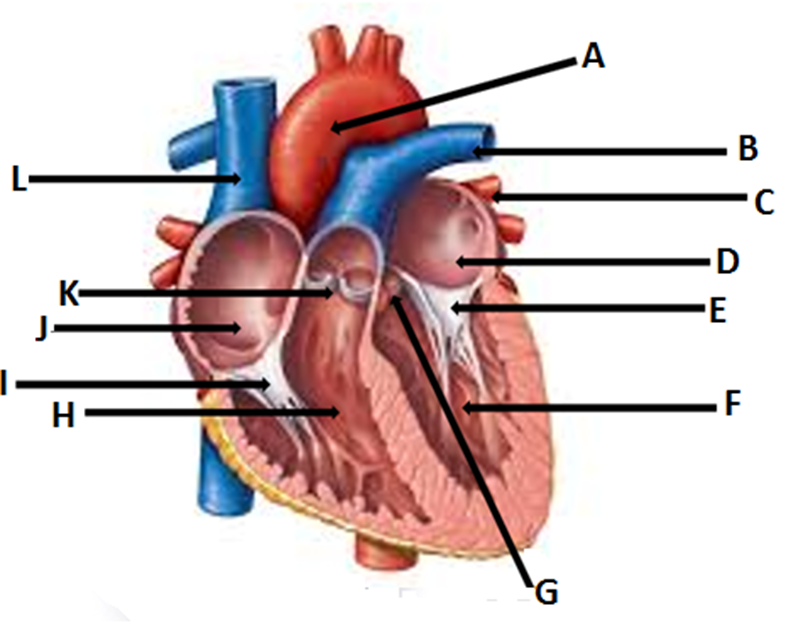
A- Aorta
B- pulmonary vein
C- pulmonary artery
D- left atrium
E-bicuspid valve
F- left ventricle
G- aortic valve
H- right ventricle
I- tricuspid valve
J- right atrium
K- pulmonary valve
L- vena cava
4 heart sounds and function
1st lub - closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves
2nd dub - closure of the aortic and pulmonary valves
3rd sound - passive diastolic filling CAN’T HEAR
4th sound - ventricular filling and atrial contraction - CAN’T HEAR
grade 1 heart murmur
very soft and barely noticeable
grade 2 murmur
very soft but easily diagnosed w stethoscope
grade 3 murmur
moderate murmur easily heard but lacks any vibration when hand is on the animals chest.
grade 4 murmur
loud with no noticeable vibration
grade 5 murmur
loud with some virbation but cannot hear withouth stethoscope
grade 6 murmur
loud, severe vibration and can be felt and heard without stethoscope
congenital heart disease
•A disease that is present at birth
•Breed specific(?)
•Usually detected in the health check at first vaccination
•Clinical signs:
•Poor growth
•Exercise intolerance
•Lethargy
•Dyspnoea
•Coughing
•Diagnosis
•History
•Clinical examination
•Thoracic radiographs
•ECG
patent ductus arteriosis PDA
•Most common congenital defect in dogs
•In the fetus a vessel (ductus arteriosus) connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta
•If this fails to close at birth the lungs become overloaded
deoxygenated blood goes back into the lungs
if large enough- risk of pneumonia
mitral/ tricuspid valve dysplasia
•Malformation of the mitral or tricuspid valves
•Blood regurgitates into the atria
•Workload increases and they enlarge leading to congestion
•
•Clinical signs
•Heart murmur
•Heart failure
•
•Treatment
•As for heart failure
increases heart muscle as has to work harder to pump blood
ventricular/ atrial septal defects
•‘Holes in the heart’ connecting with either the atria or ventricles
•Blood flows through the heart abnormally
• heart cannot control where the blood is going within the heart.
•Clinical signs
•Heart murmur (loud on R-side)
•Asymptomatic or congestive heart failure
•pale MM, lethargic, exercise intolerant, arrythmia, tachycardia as working harder
•Treatment
•As for heart failure
tetralogy of fallot

patient isn’t well oxygenated as has many defects
several issues
don’t usually make a year old
seizures
persistent right aortic arch (vascular ring anomaly)
•Malformation of the major arteries of the heart
•Traps the oesophagus
•blood vessel doesn’t disappear as animal grows and restricts the oesophagus
•Clinical signs:
•Regurgitation of food
•Poor doer
•Aspirational pneumonia
•Treatment:
•Surgery to ligate and cut the remnant
•Feeding from a height - aspiration
endocardial disease: endocardiosis (aquired)
•A progressive condition
•The mitral valve is most commonly affected (also tricuspid valve)
•Commonly due to fibrosis which affects function of valves
•Blood regurgitates into the atria increasing workload
•Causes congestion and heart failure
valves degenerate and deform, age related
•Clinical signs:
•Heart murmur
•Left sided heart failure or
•Right sided heart failure
•Diagnostics:
•History
•Thoracic radiographs
•ECC & ECG
•Blood culture
ultrasound - see blood flow
dye in blood - highlight vessels and valves
•Treatment:
•Treat as for heart failure
•(Endocarditis – broad spectrum AB’s following blood culture results) rule out infection
myocardial disease
•Cardiomyopathies are diseases associated with cardiac dysfunction
affects the muscle, altering ability to contract or expand
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
•Thickening of the heart muscle interferes with relaxation of the heart
•Normal filling of the heart is prevented
•Poor diastolic function
•Decreased cardiac output
•Heart failure
•
•Clinical signs:
•Silent
•Dyspnoea, tachypnoea, tachycardia
•Heart murmur
cannot hear a murmur, symptoms not noticeable until developed.
•Diagnostics
•ECC & ECG
•Thoracic radiographs
•Blood tests and pressure measurement, Clotting profile
•Abdominal ultrasonography
•Treatment
•Cardiac relaxation and slowing heart rate
•Pain relief, antithrombotics and vasodilators
signs of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with aortic thromboembolism
•Acute onset of uni/bilateral paresis/paralysis of the hindlimbs
•Lack of arterial pulse in the affected leg(s)
•Pain
•Hindlimb(s) cool to the touch
•Dyspnoea, tachypnoea
treat with antithrombotic and vasodilator
dilated cardiomyopathy
•Dilation of the heart chambers
•Enlargement of the heart
•Poor systolic function
•Congestions and heart failure
•Clinical signs
•Anorexia, weight loss
•Reduced exercise intolerance/lethargy
•Ascites
•Heart murmur, arrhythmias
•Usually left sided heart failure, sometimes right
•Sudden death
can be disease, age, infection, etc.
muscle weakened as not used•Diagnostics
•ECC & ECG
•Thoracic radiographs
•
•Treatment
•Individual assessment
•As per Heart failure
arryhtmias

may be no other signs that listening
sinus arrythmia
speed up when breathe in and slow down when breathe out, not a problem just there. Often correlated with respiration
atrial fibrillation
underlying issue, rapid. Can be corrected through GA and electrical stimulation, oral medication Quinidine. Affects HR careful handling. Can cause animal to drop dead as a risk.
heart block
missed beat, more common in dogs, but rare, at rest hear every 4-6 beats – normal when exercise
pericardial disease
•An effusion accumulates in the pericardial sacs
•Restricts filling of the right side of the heart
•Right-sided heart failure
•
•Clinical signs
•Pale MMs, muffled heart sounds, tachycardia, variable pulse quality
•Distended abdomen
•Exercise intolerance, collapse
•
•Diagnostics
•ECC & ECG and thoracic radiographs
•
•Treatment
•Relieving pressure around the heart
•Fluid removal and analysis
heart failure
•Circulatory failure
•Unable to meet the needs of the body - not enough oxygen to organs
•Congestion
•Clinical signs dependent on the type of failure
•Acute heart failure
•Left-sided heart failure
•Right-sided heart failure
•Diagnostics
•Thoracic radiographs
•ECC & ECG
•Blood tests
signs, treatment and nursing of acute heart failure
•Reluctance to exercise, collapse
•Pale MMs, cyanosis, slow CRT, weak pulse and quality, heart murmur
•Cough, dyspnoea, tachypnoea,
•Treatment
•Medical therapy – thoracocentesis, diuretic, other under veterinary direction
•
•Nursing Care
•Do not stress, cage rest, provide O2, keep warm, monitor RR and vital signs
signs of left-sided heart failure
•Reluctance to exercise, fatigue, lethargy
•Pale MMs, cyanosis, heart murmur, tachycardia, dysrhythmias
•Cough, dyspnoea, tachypnoea,
signs of right sided HF
•Ascites, abdominal distention
•Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly
•Reluctance to exercise, fatigue, lethargy
•Pale MMs, cyanosis, heart murmur, tachycardia, dysrhythmias
•Dyspnoea, tachypnoea,
to lungs
Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly- Liver and spleen enlarged because not receiving right amount of circulation and lack of oxygen.
•Reduce exercise, reduce obesity (if applicable), low salt diet, O2, keep warm, monitor RR and vital signs
nursing chronic heart failure
•Nursing Care
•Reduce exercise, reduce obesity (if applicable), low salt diet, O2, keep warm, monitor RR and vital signs
•Chronic cases
•Decrease stress and exercise
•Weight loss management
•Monitor vital signs
•Blood tests – dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
•Nutrition
•Palatable diets
•Additional nutrients
•Electrolyte balance