Spine Kinesiology Part 1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Spine Functions
Shock absorption
Rigid column
Attachment for muscles & ligaments
Protect spinal cord
Supports the thorax
Spinal Vertebrae
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral (fused)
4 coccygeal (fused)
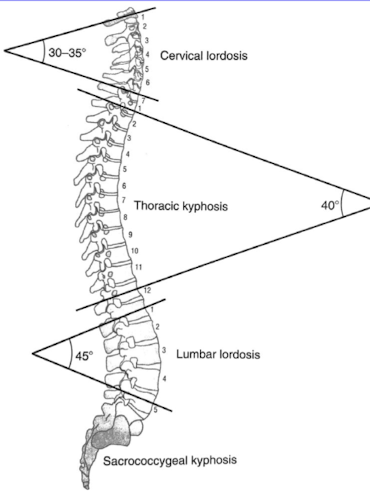
Spinal Curves
Lordotic, kyphotic, and compensatory curves that provide flexibility, balance, and support to the spine.
Cervical lordosis
Thoracic kyphosis
Lumbar lordosis
Sacrococcygeal kyphosis
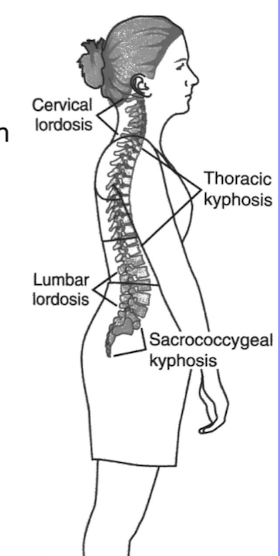
Lordosis
Projecting anterior, inward facing curve, anterior direction for convexity in the lumbar and cervical regions of the spine.
Kyphosis
Projecting posterior, outward facing curve, posterior direction for convexity. This curve is prominent in the thoracic and sacral regions of the spine.
Scoliosis
A lateral curvature of the spine that can occur in the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions, often presenting as a C or S shape.
Normal spinal curves develop as ____ posture is assumed.
Upright
Cervical Spine Development
By age 3 months
Lumbar Spine Development
Complete by age 10
True or False: Spinal curves are static.
FALSE; a change in one curve is compensated by a change in another curve.
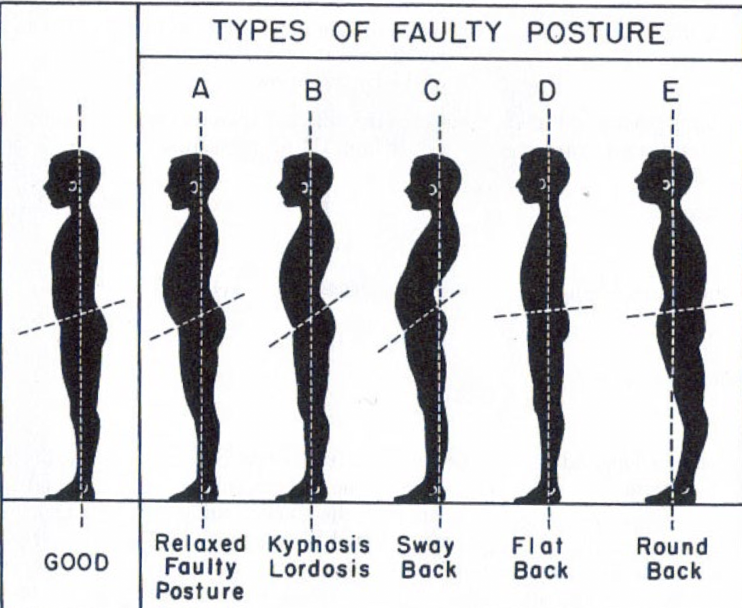
Types of Faulty Posture

Angle of Pelvic Inclination (Pelvic Tilt)
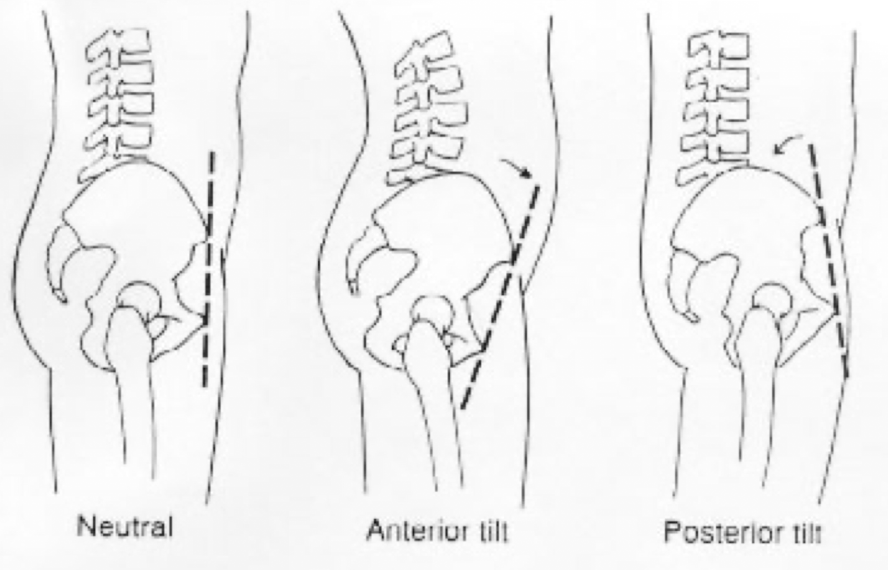
What effect does an anterior pelvic tilt have on the lumbar spine curvature?
Increased lordotic curve
What effect does a posterior pelvic tilt have on the lumbar spine curvature?
Decreased lordotic curve (flattens the back- “flat back”)
Spinal Weight-Bearing
Vertebral body/disc and facet joints
Vertebral Body/Disc
Want evenly distributed load on disc
Most important in lumbar spine; bear approximately 80% of weight
Facet Joints
Bear approximately 20% of weight
Relative load on facet vs. disc depends on spinal curvature and habitual motions
Extreme extension and increased lordotic curve= an increased load on what type of joint?
Facet jointand increased stress on the lumbar spine.
Extreme flexion= an increased load on what?
Vertebral Body/Disc (Loading Rate= 90/10)
Neural/Vertebral Arch
Transverse processes (2)
Spinous process
Pedicles (2) (connect arch to vertebral body)
Lamina (2) (spinous to transverse process)
Articular facets (4)
2 superior, 2 inferior
Facet joints or Zygapophyseal or Apophyseal joints
C-Spine Spinous Processes
C2 first prominent, then C6 & C7 (typically bifid in C-spine)
T-Spine Spinous Processes
Shingle effect
L-Spine Spinous Processes
Thick, flat SP
Spinal Flexion and SP
Increase space between SP
Spinal Extension and SP
Decrease space between SP
Transverse Processes
Serve as “outriggers” for attachments of muscles
C1 prominent (only 1 in C-spine)
Transverse foramen for Vertebral Artery
T1-T12 TP’s prominent– articulate with the ribs
Mid-thoracic TP: at Sp level of superior segment
L1-L5: TP very prominent (1” from SP)
Vertebral Bodies
Primary weight-bearing site spine
Increased thickness from C-spine to L-spine
C3-C7 Uncinate Processes: on superior aspect of vertebral body
Spinal Segment
Consists of two adjacent spinal vertebrae and the articulations that joint them together (L4-L5, T5-T6, C6-C7, etc…)
All spine motion: top segment moves on the bottom
Segments between 2 regions of the spine are called “transitional” segments (T12-L1, L5-S1)
If patients perform extension, how does Intervertebral Foramen (IVF) size change?
Decrease
If patients perform flexion, how does Intervertebral Foramen (IVF) size change?
Increase
“Mixed” Nerve Root Exits at IVF
Mixed nerve root has both sensory & motor fibers
Dorsal (afferent) carries sensory info
Ventral (efferent) carries motor info & both combine to form mixed nerve root which exits at IVF
Intervertebral Disc
One between each 2 adjacent vertebrae, C2-S1
(Zyg)Apophyseal (Facet) Joints
2 between each 2 adjacent vertebrae (R&L)
“Special”/Atypical Joints
Occiput-C1 (Atlantooccipital or AO joint)
C1-C2 (Atlantoaxial or AA joint)
Uncovertebral: Typically C3-C7
Rib articulations
Pelvis: sacrum articulates with the ilium bone (SI joint)
Zygapophyseal (Facet) Joints
Synovial joint
Planar joint surfaces that slide rather than roll
Guide intervertebral motion based on orientation direction
Facet Joint Orientation: C2-S1
Facets are planar joints that glide rather than roll/slide. Primary direction of glide depends on facet joint orientation.
C2-C7: 45º from post-inf to ant-sup
T-spine: frontal plane, provides 1º side bending
L-spine: sagittal plane, provides 1º flex/ext
Transitional spine segments: C7-T1, T12-L1, L5-S1
Facet Joint Orientation: Upper Cervical Spine is Unique
C0-C1: occiput convex, C1 concave
C1-C2: horizontal, thus rotation most prominent motion here!
Intervertebral Discs
Increased thickness from cervical to lumbar spine
Increased disc thickness allows more motion per segment
Nerve roots exit adjacent to disc via intervertebral foramen
C-spine roots exit above vertebrae
L-spine roots exit below vertebrae
Intervertebral Discs and Water
Approximately 80% water in lumbar spine disc vs. less water % in C-spine discs
Disc herniation more common in L-spine– more fibrous in C-spine, so less disc herniations
Discs make up 25% of spine length
Why do we get shorter as we age or during the course of a day?
OUr discs dry out and we lose height ever so slightly. Overnight, our discs can rehydrate. Reduced load at night. Compression of our spine is greatly reduced.
Intervertebral Disc Functions
Absorb shock
Disperse stress
Bind vertebra together
Contribute to the spinal curves
Allow movement (along with facet joint)
Stress Dispersion and Spinal Movement: Pascal’s Law
Pressure applied to a liquid is dispersed equally in all directions
Vertical load is distributed outward against disc annulus
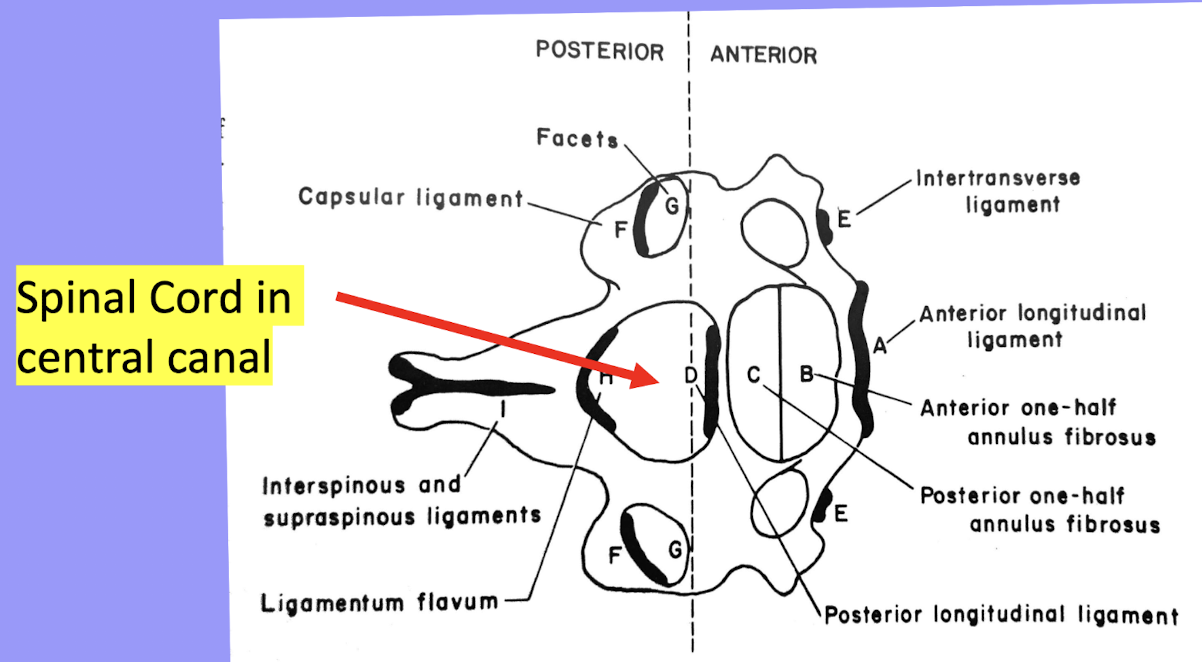
Spine Ligaments: Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)
ALL runs along anterior vertebral body from C2-sacrum
Limits extension
Thicker and stronger than PLL (2x), thus minimizes anterior disc herniations
Narrow in C-spine & wider in L-spine
Spine Ligaments: Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)
PLL runs along posterior vertebral bodies from C2-sacrum
Limits flexion of spine
Thick/wide in C-spine– less posterior disc herniations in C-spine
Narrow in L-spine– allows more posterior disc herniations in L-spine
Ligamentum Flavum
Connect lamina to lamina from C2-sacrum, limits flexion
Supraspinous & Interspinous Ligament
Run between spinous processes; limit flexion
Spine Ligaments Relative to Spinal Cord
Spinal Cord in Central Canal
Thoracolumbar Fascia
Non-contractile connective tissue
Plays role in stabilizing lumbar spine (and SI joint) due to connections to spine, erector spinae, QL, gluteus max, latissimus, and abdominals