anabolic reactions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
steps which are different in gluconeogenesis compared to glycolysis
pyruvate carboxylase converts pyruvate into oxaloactetae
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase converts oxaloacetate into phosphoenolpyruvate
fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase is used instead and requires ATP
glucose 6 phosphatase instead - removes phosphate group
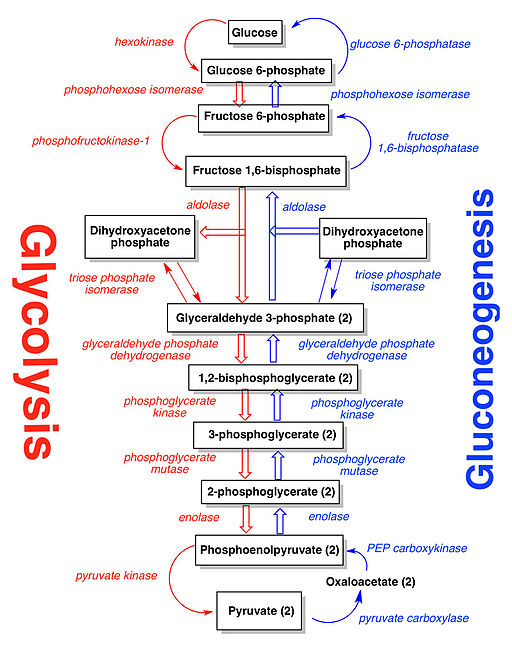
does glycolysis generate more energy than is required for gluconeogenesis
yes
pyruvate carboxylase
converts pyruvate into oxaloacetate using CO2 and ATP
requires biotin
allosterically activated by actetylcoa
tetramer w 4 subunits each
biotin
covalently attached to pyruvate carboxylase
through lys side chain
carrier of actviated carbon dioxide - carboxybiotin
where is glycogen stored
cytosolic granules in the liver
muscle cells in vertebrates
glycogenin
protein at centre of glycogen
acts as a primer for glycogen synthesis
glycogenolysis
cleavage of α-1,4 glycosidic bonds
catalysed by glycogen phosphorylase
glycose 1 phosphate → glucose 6 phosphate
catalysed by phosphoglucomutase
when does glycogen phosphorylase stop?
glycogen phosphorylase stops at 4 residues from branch point
function of transferase
shifts three glucoses from one branch to another
function of glycogen-debranching enzyme a -1,6-glucosidase
removes branched glucose and leaves elongated unbranched chain
udp glucose
generated from glucose 1 phosphate and UTP
for glycogen synthesis
catalysed by UDP glucose phosphorylase
polymerisation of glucose
glycogen synthase needs at least 4 glucoses
glycogenin initiates polymerisation
linear growth
major regulatory step in glycogen synthesis
transfer of glucose to growing chain
branching in glycogen formation
one 1,4 bond is broken and transferred to form 1,6 linkage
different enzyme introduced branching
inc glycogen solubility, rate of synthesis and rate of degradation
glucokinase
liver enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6- phosphate
affinity of glucokinase compared to hexokinase
much lower
Km is 50 fold higher
GLUT2
pancreatic beta cells and liver
transports glucose when blood conc is high
GLUT4
found in muscle and fat cells
stimulated by insulin binding to insulin receptor
recruits vesicles of GLUT4
GLUT1
in nearly all mammalian cells
12 membrane alpha helices
six form channel
n and c termini are on cytoplasmic side of membrane
which glutamate receptors are maintained at a constant rate
GLUT1,3
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6P)
Potent allosteric activator of phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1), the key regulatory enzyme of glycolysis.
Potent allosteric inhibitor of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, a key regulatory enzyme of gluconeogenesis.
how is F2,6P synthesised
phosphorylation of single serine residue of fructose 6 phosphate
catalysed by phosphofructokinase 2
what happens to PFK2 levels and F2,6BP with low blood glucose
glucagon rises
inc phosphorylation of PFK2
inc of FBPase2
levels of F2,6BP decrease
what happens to PFK2 levels and F2,6BP with high blood glucose
glucagon falls
insulin rises
inc PFK2
FBPase2 dephosphorylated
levels of F2,6BP inc
co-ordinated control of PFK2 and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate
found on the same protein