VETS 401 Exam 3 Female Reproductive Anatomy
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Components of female reproductive system
Paired gonads (ovaries); Paired uterine tubes; Uterus; Vagina; Vestibule; Vulva
Location of ovaries in adult animal
In dorsal abdomen, close to uterine horns
Location of ovaries in newborn
Lateral aspect of the pelvis, close to the anterior superior iliac spines, just below the iliac crests and umbilicus, and above the pubic symphysis
Location of ovaries in fetus
Initially located in the false pelvis, migrating towards their final position between the internal and external iliac arteries by the end of the 40th week
Ovaries have both _____ and _____ functions.
Endocrine; exocrine
What tissue surrounds the ovaries in females?
Broad ligament (mesovarium)
What tissue surrounds the uterine tubes in females?
Broad ligament (mesosalpinx)
What tissue surrounds the reproductive tract in females?
Broad ligament (mesometrium)
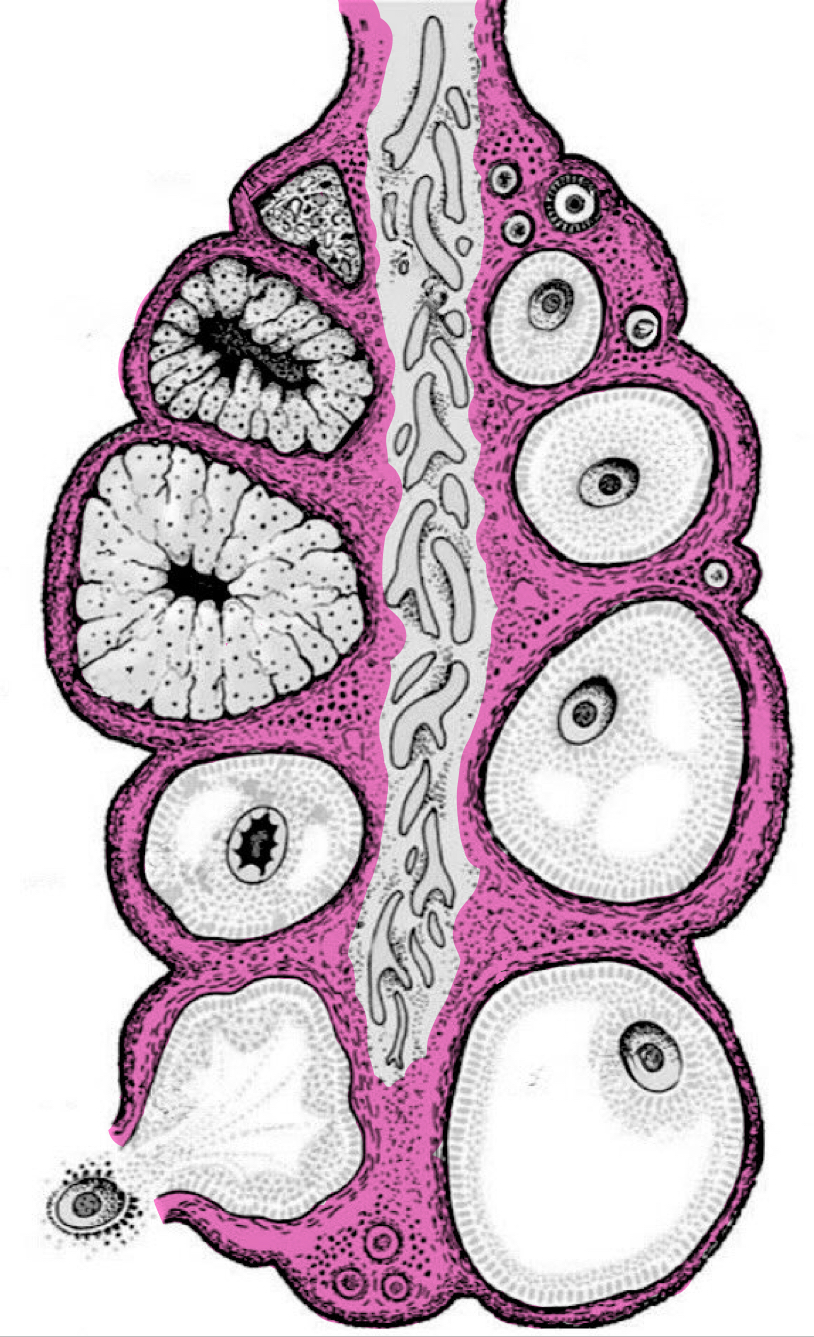
Components of ovarian structure
Visceral peritoneal lining; cortex; medulla
Visceral peritoneal lining in ovaries
Superficial epithelium
Outer zone of ovarian structure
Cortex
Contents of cortex in ovaries
Follicles in various stages of development; corpora lutea; connective tissue
Contents of medulla in ovaries
Blood vessels; nerves; lymphatics; smooth muscle; connective tissue
Inner zone of ovarian structure
Medulla
Ovarian structure in mares, dogs, and cats
Caudal to kidneys (sublumbar region)
Ovarian structure in cows, ewes, and sows
Pelvic inlet due to caudal migration
Cortex and medulla in mare
Reversed; cortex is central, surrounded by medulla
Cortex (ovary)
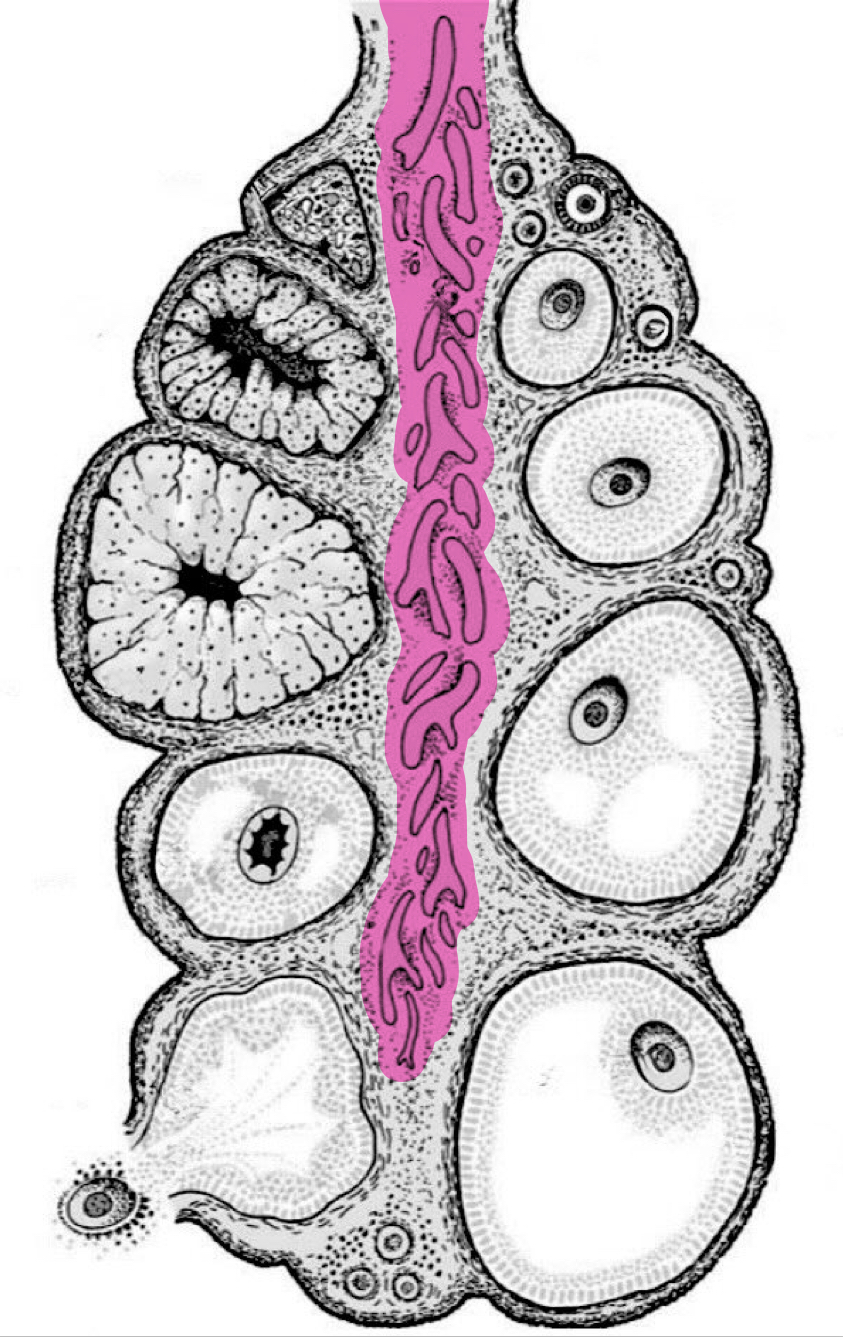
Medulla (ovary)
Broad ligament (mesometrium)
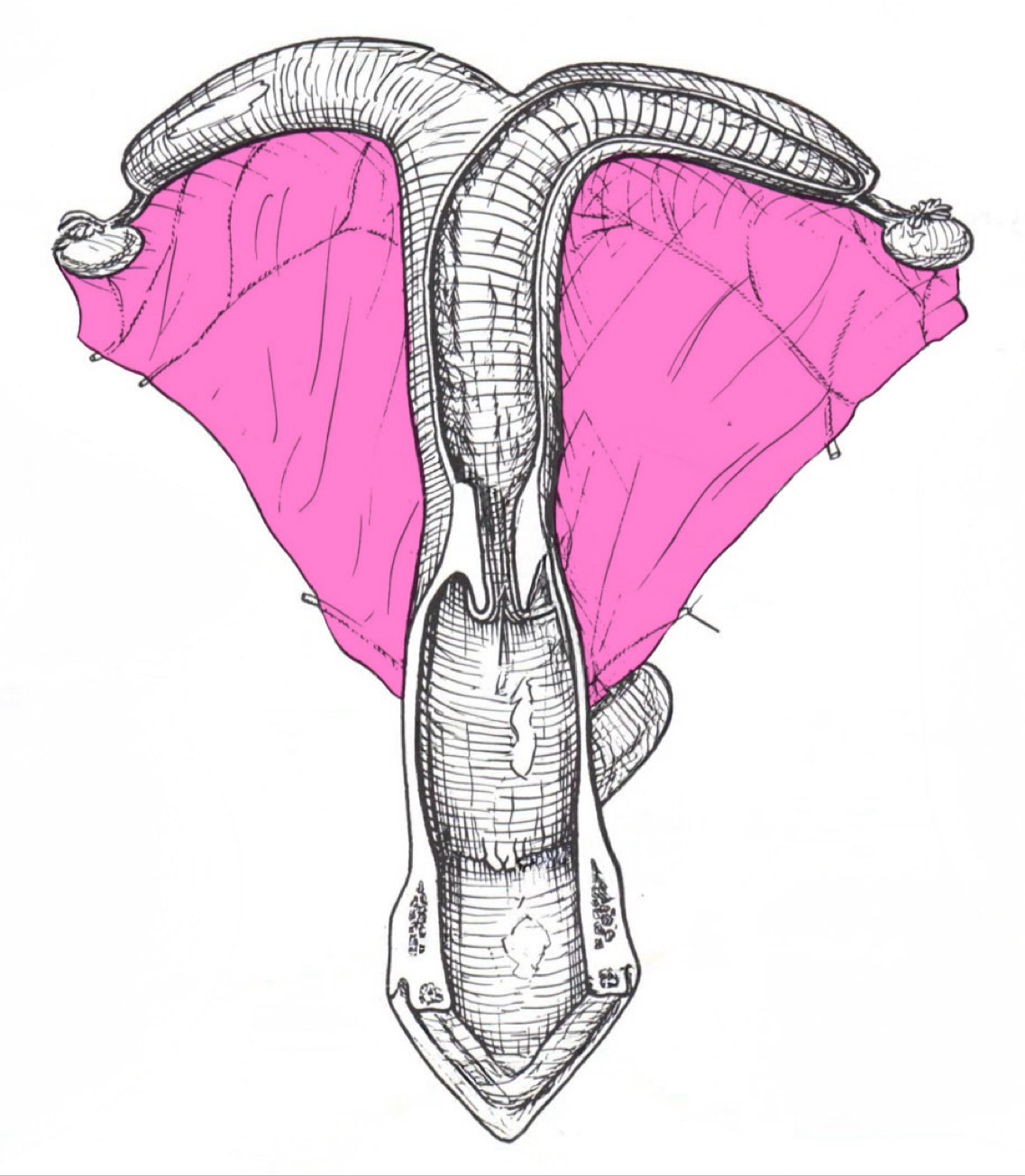
Proper ligament of the ovary
Attaches ovaries to the uterus
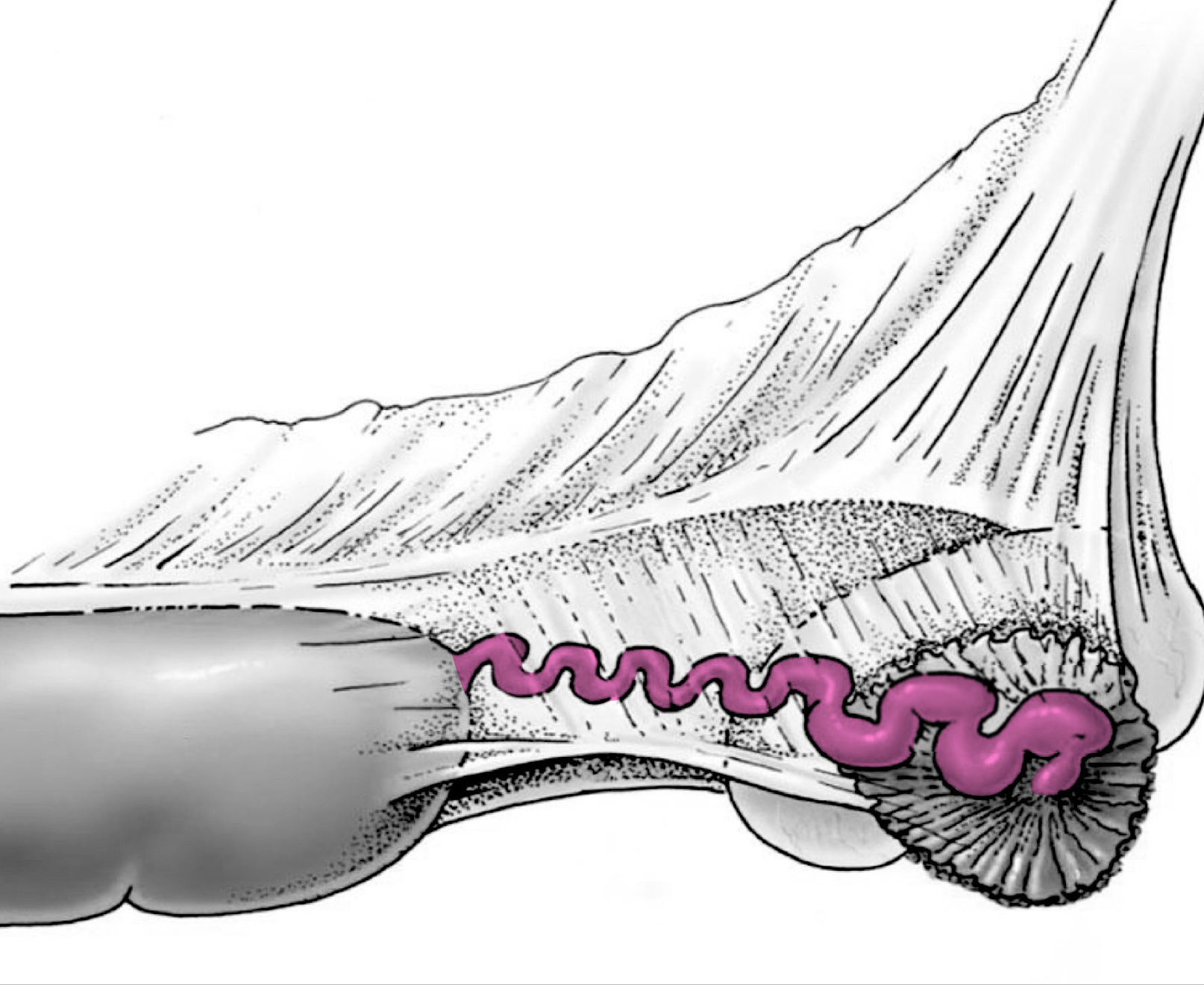
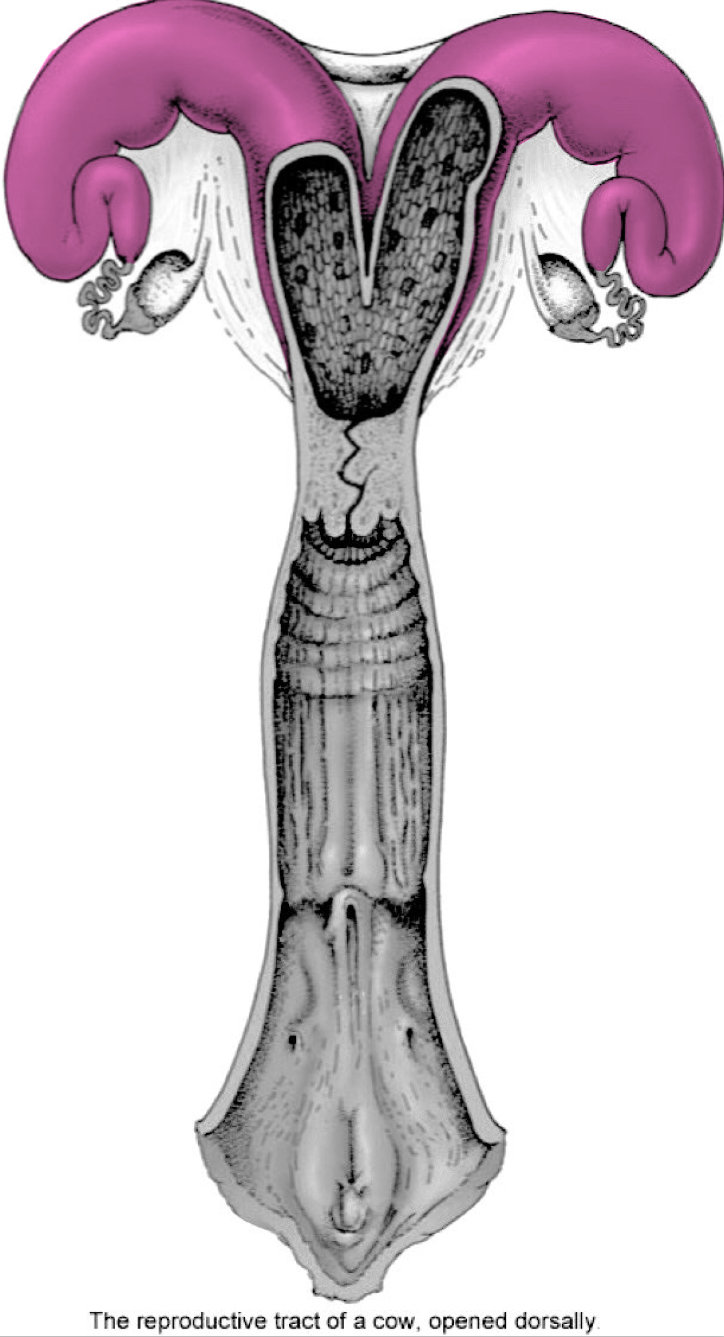
Uterine tubes / salpinx / Fallopian tubes
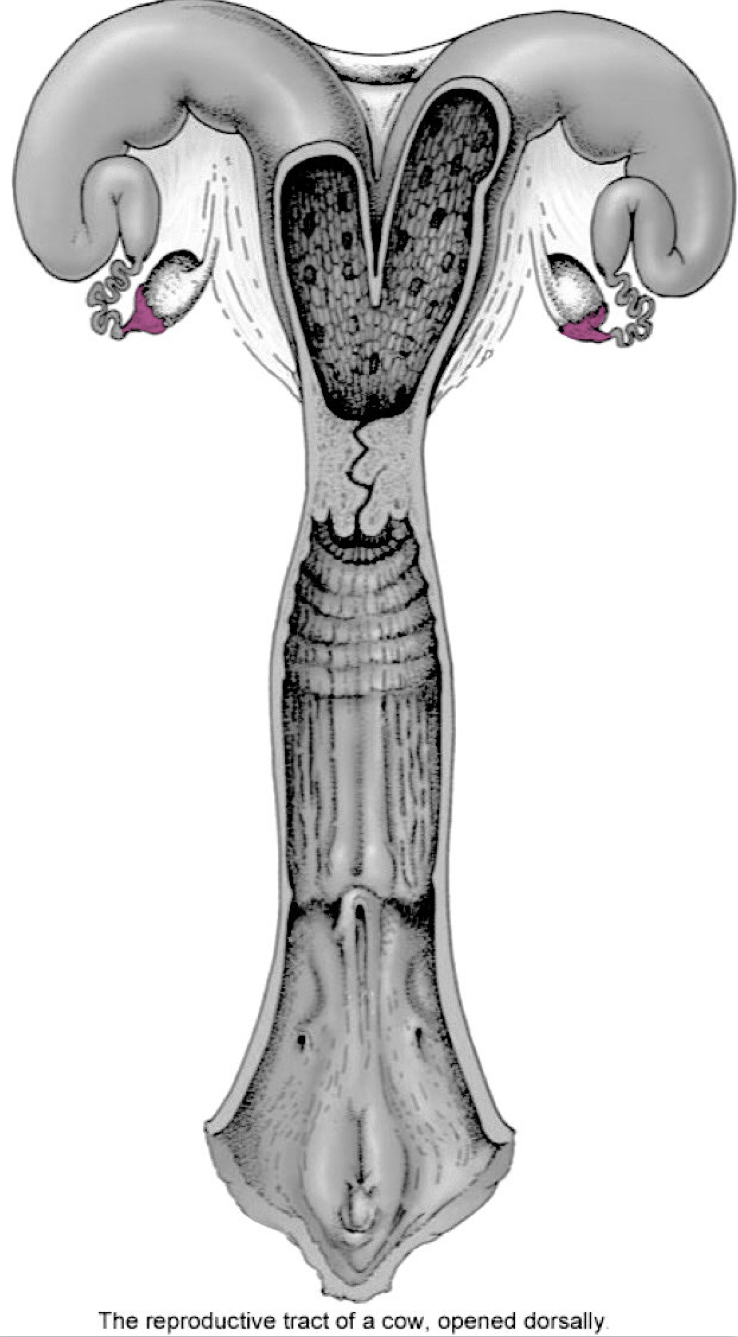
Infundibulum
Fimbriae
Finger-like projections on the ends of your fallopian tubes closest to your ovaries
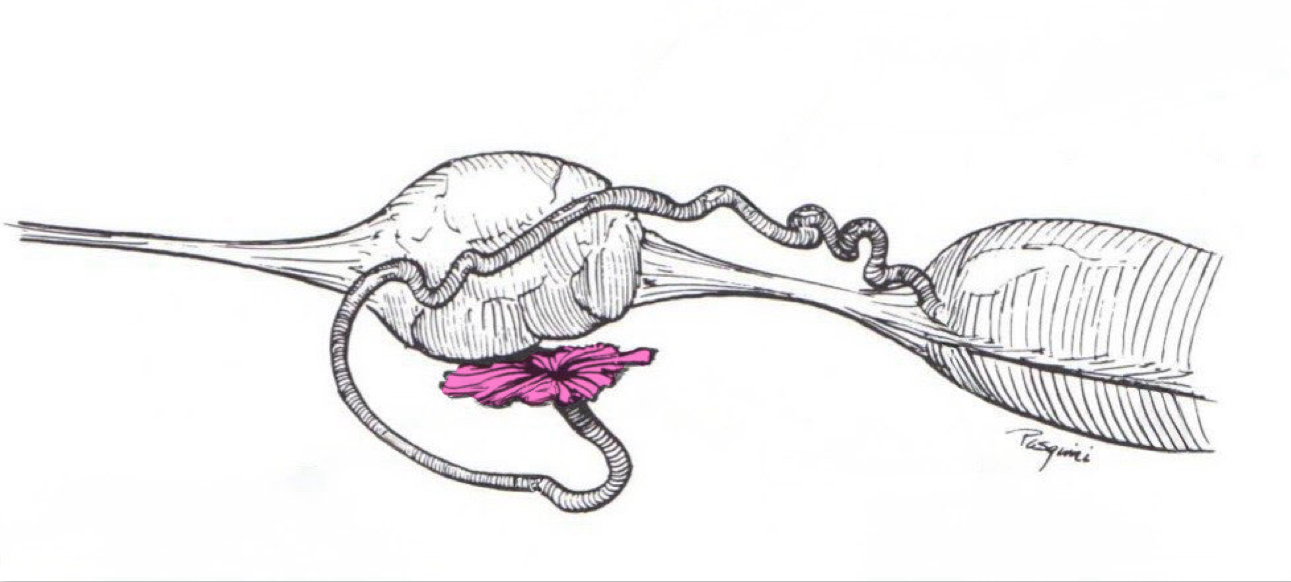
Fimbriae
Uterine ampulla and isthmus
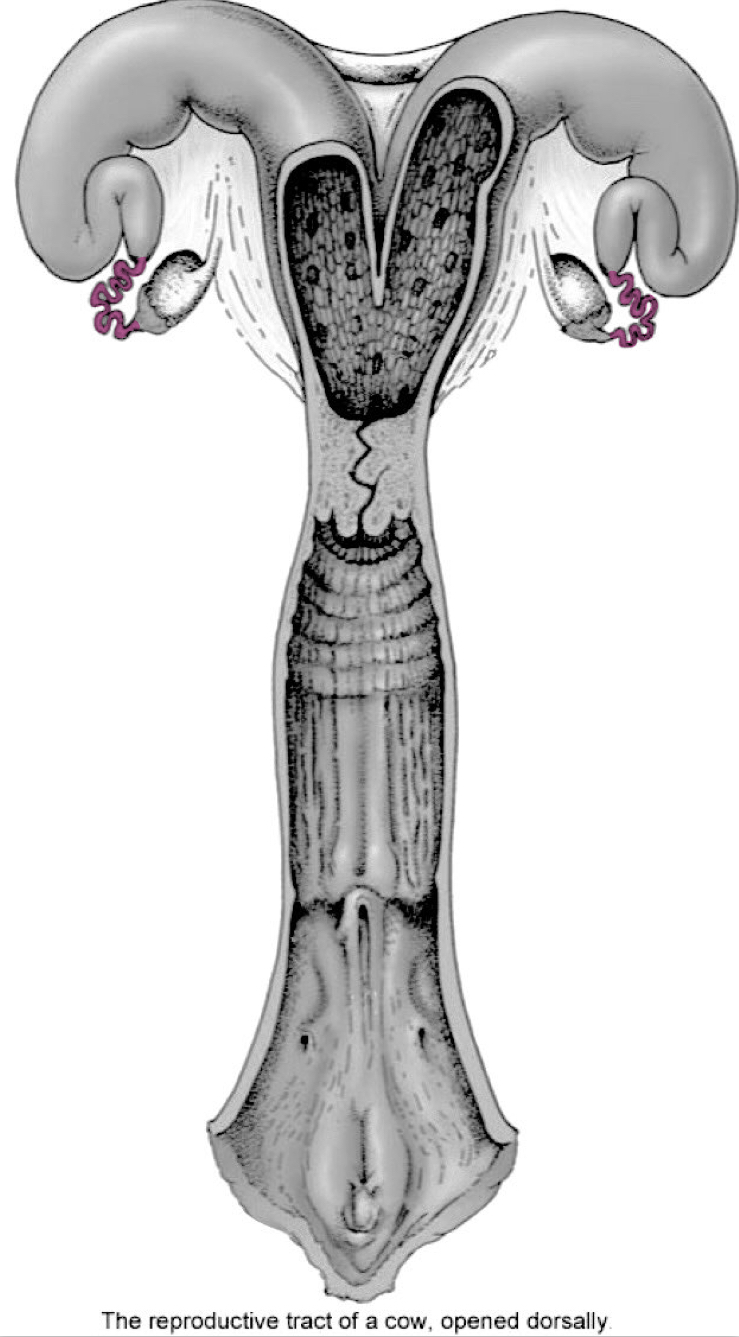
Uterus/Uterine horns
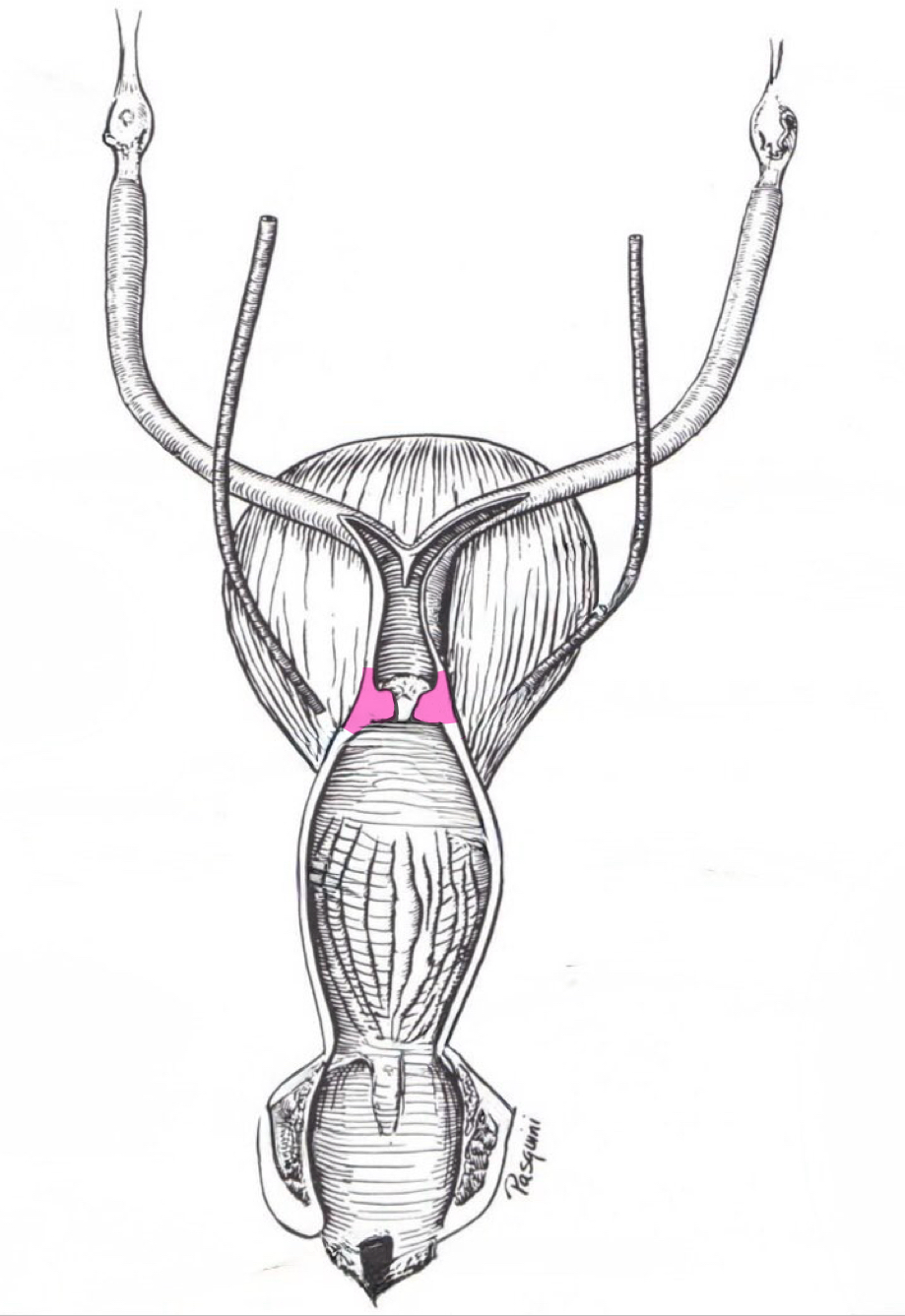
Cervix
External uterine ostium (external urethral orfice)
Opening into uterine body
Internal uterine ostium (internal urethral orfice)
Opening into vagina
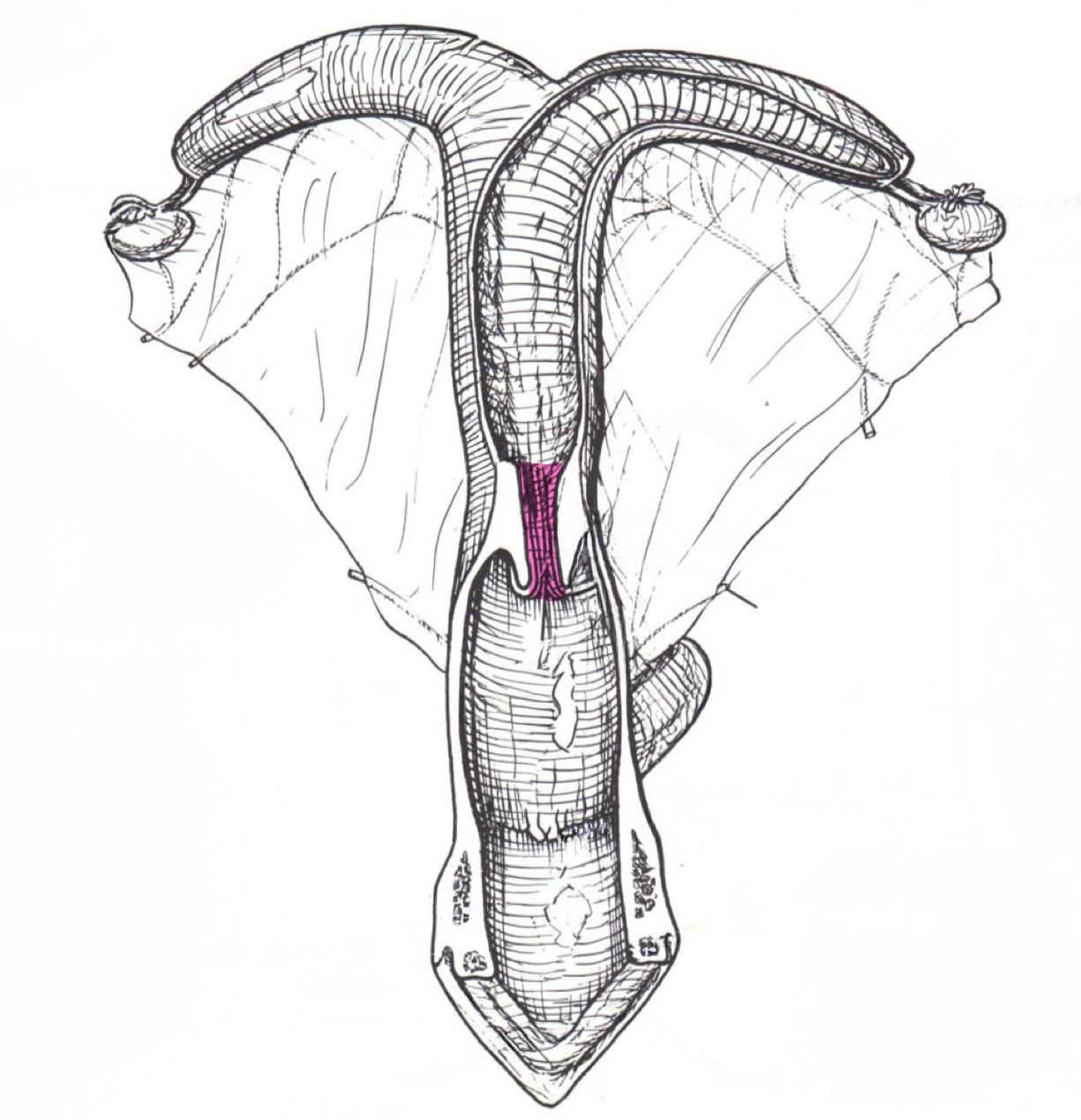
Internal uterine ostium
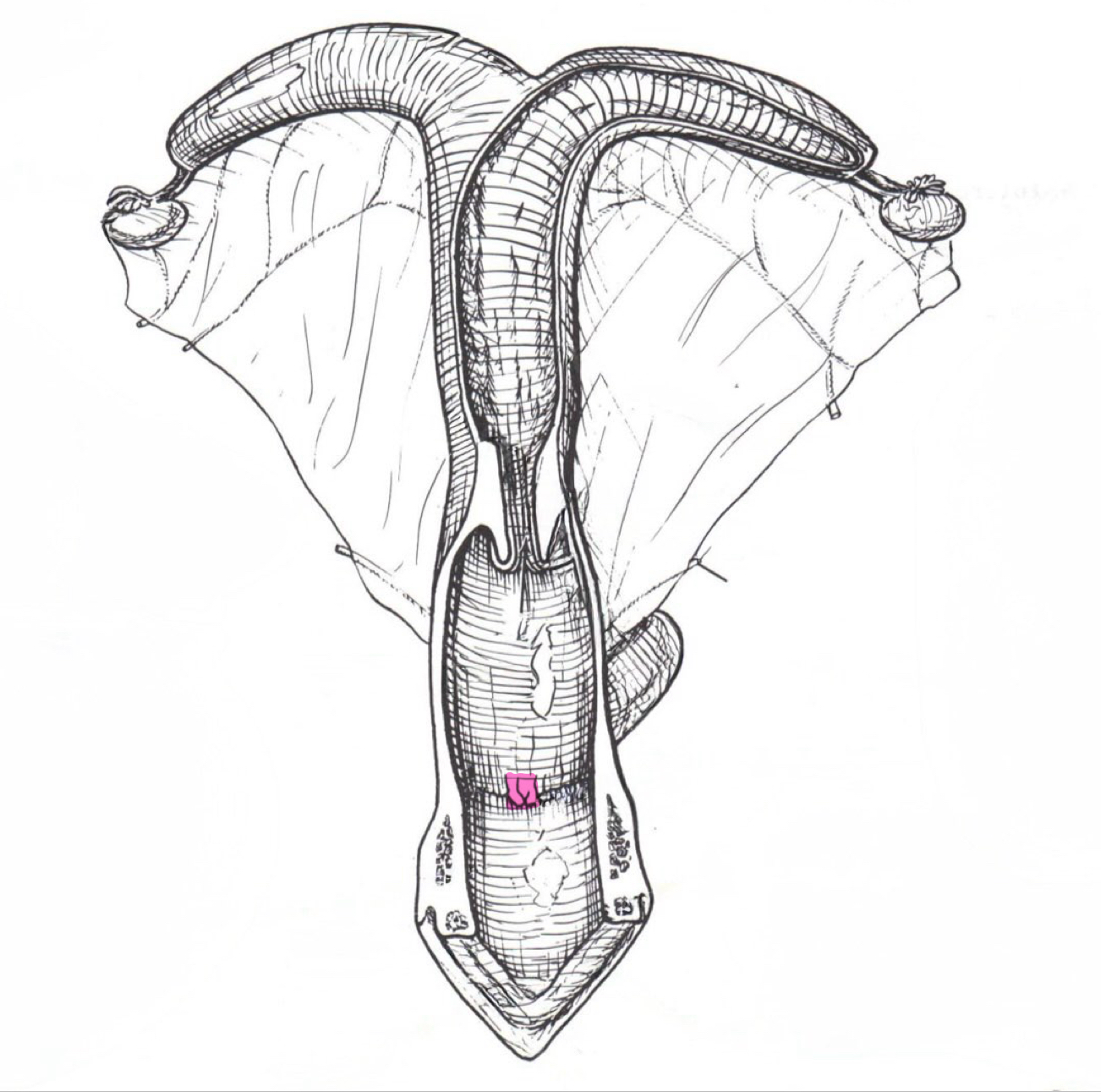
External uterine ostium
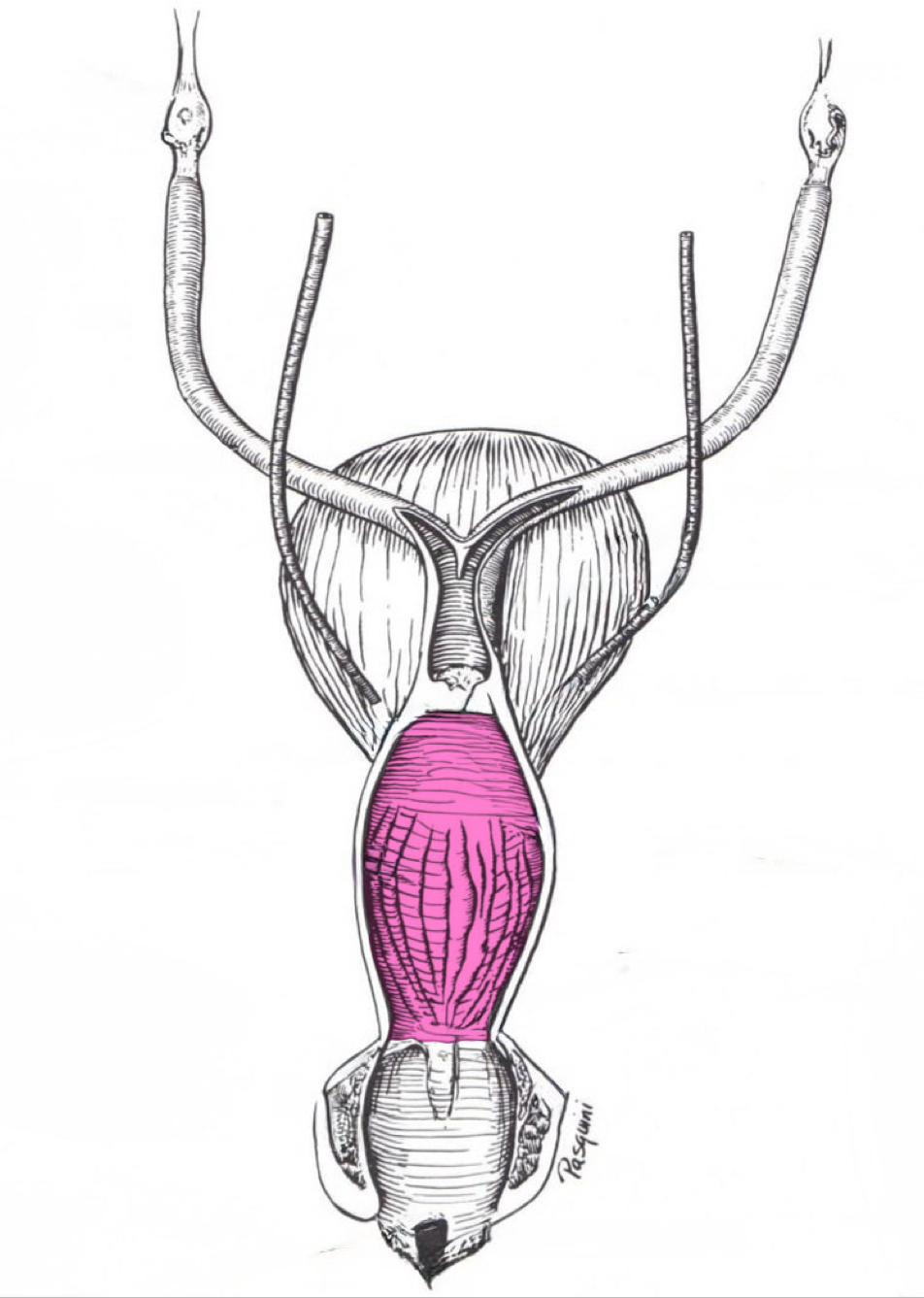
Vagina
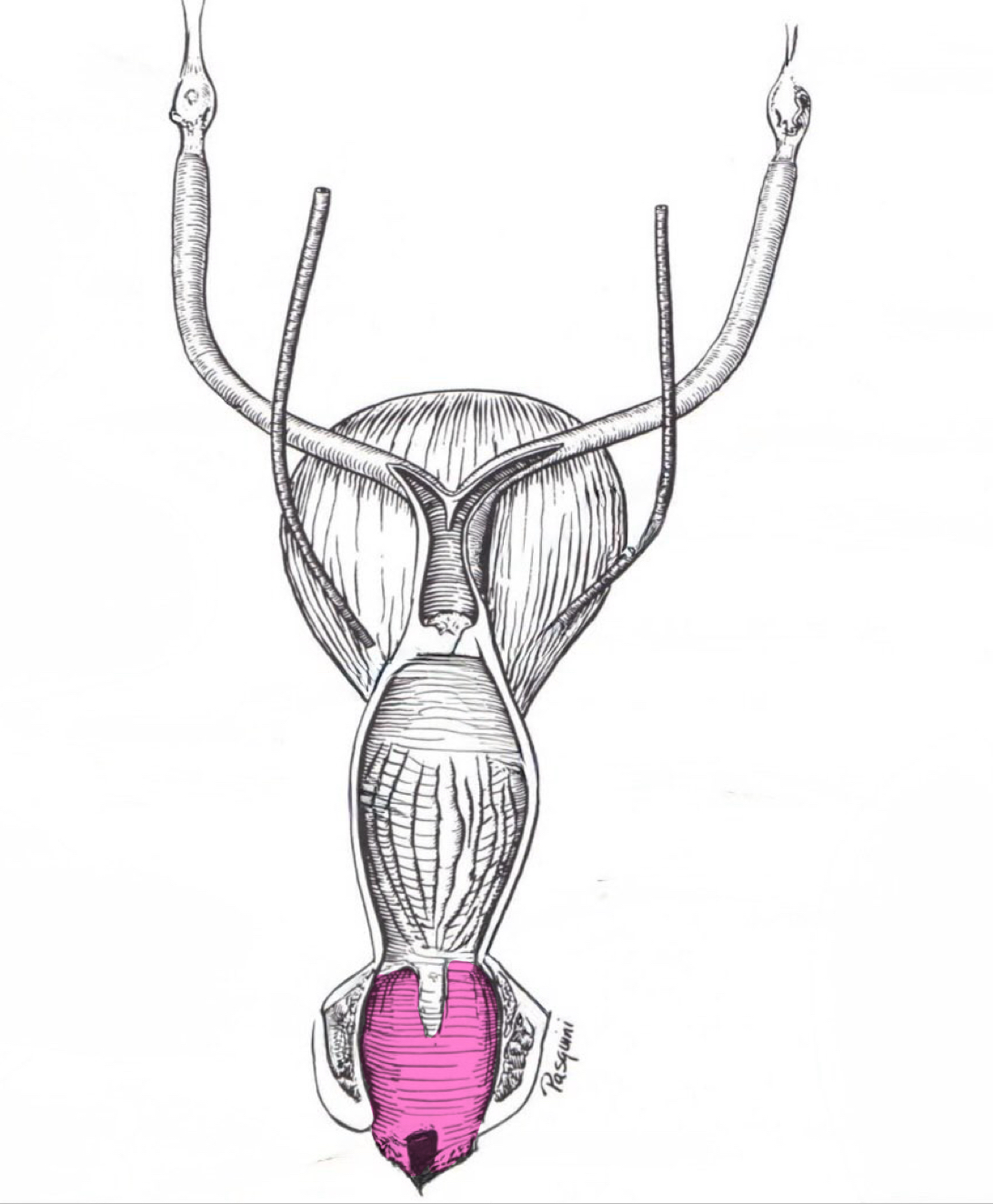
Vestibule
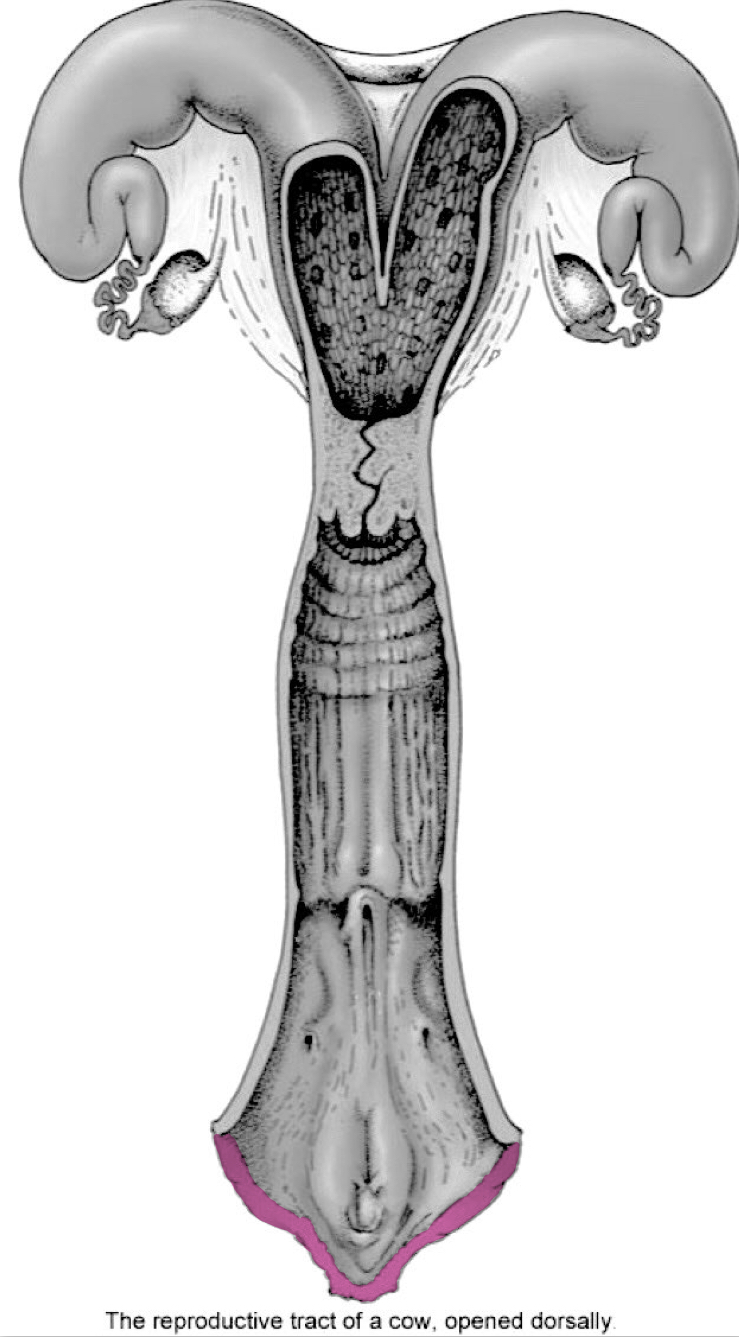
Vulva
Explain this statement: “The abdominal opening in the center of the infundibulum is the only opening of the peritoneal cavity to the outside in the female animal.” (Pasquini, Ch VIII, p 340, 11th ed)
Abdominal opening in infundibulum to uterine tube, into uterine horn, then uterine body and cervix, is only opening from peritoneal cavity to external body in females; Males have no such opening
Structure of the ovary in cows ewes, and sows
Pelvic inlet - due to caudal migration
Location of the ovary in mares, dogs, and cats
Caudal to kidneys - sublumbar region
Location of ovulation in mare
Ovulation fossa; central depression on the ovary
Where does fertilization occur in domestic animals?
Uterine tubes
Uterine tubes
Narrow, flexible tubes that capture released ova; carry fertilized ova to tip of uterine horn; convey sperm to ovary from the uterus; site of fertilization
Implantation (what is implanted?)?
Sperm
What’s in the uterine tubes
Infundibulum; Ampulla – proximal portion, abdominal orifice; Isthmus; Suspended in the broad ligament - mesosalpinx
Infundibulum
Expanded, funnel-shaped free cranial end of tube; irregular, finger-like projections (tags) arise from free edge of infundibulum; may actually come in contact with the ovary – adhesions
Ampulla
Proximal portion of uterine tubes, abdominal orifice
Isthmus
Distal portion of uterine tube, joins uterine horn
Mesosalpinx
Suspended in the broad ligament
Layers of uterine wall
Serosa; muscle; mucosa; caruncles (ruminants); broad ligament
Serosa layer of uterine wall
Contains perimetrium
Muscle layer of uterine wall
Contains myometrium
Mucosa layer in uterine wall
Contains endometrium
Caruncles layer in uterine wall
Found in ruminants
Myometrium
Located in muscle layer of uterine wall; Weak longitudinal and stronger circular layers; Very vascular
Perimetrium
Located in serosa layer of uterine wall
Endometrium
Located in mucosa layer of uterine wall; Thick layer with numerous tubular glands
Broad ligament (Mesometrium)
Supportive tissue; Suspends uterus in peritoneal cavity
Caruncles
In ruminants; regularly spaced, circular to ovoid, specialized thickenings
Uterus/uterine horns in carnivores
Very long compared to uterine body
Uterus/uterine horns in sows
Very long, almost intestine-like loops
Uterus/uterine horns in mares
Relatively short horns, equal length to body
Uterus/uterine horns in cows/ewes
Horns longer than body, coiled at ends (bound by intercornual ligaments)
What is the blood supply to/from the ovaries?
Ovarian arteries and uterine arteries
What is the blood supply to/from the uterus?
Uterine arteries and branches from the ovarian arteries
What does the term “gravid” mean? Non-gravid?
"gravid" (Latin: gravidus "burdened, heavy") is used to describe the condition of an animal (most commonly fish or reptiles) when carrying eggs internally
What is the fornix? What is the significance of this structure?
Craniodorsal recess in cow/ewe
What is the urethral diverticulum? What is its significance?
Part of vulva found in cows/ewes
What is the female homologue to the penis?
Clitoris
Homologue
Structures or traits that share a common evolutionary origin, meaning they are similar in structure or position, even if they have different functions in different organisms
Os penis
The bone found in the penis of carnivores
Os clitoridis
The bone found in the clitoris of carnivores
Vestibular bulbs
Organized erectile venous tissue; Allow the “tie” to occur when bulbs press against penis caudal to the enlarged bulb of the glans penis
Location of vestibular bulbs
In vestibule walls
What species do we find vestibular bulbs?
Mare and bitch