NURS 321: Lecture 6 - Reality and Choice Therapy and Decision-Making, Conflict, Group Dynamics and De-Escalation (still refining it)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Whose behaviour is the only one we can control according to Choice Theory?
Our own behavior.
What is the only thing that we can give another person according to Choice Theory?
Information.
What type of problems are long-lasting psychological problems according to Choice Theory?
Relationship problems.
How is the problem relationship relevant to our present life according to Choice Theory?
It is always a part of our present life.
According to Choice Theory, how does the past relate to our present?
What happened in the past influences who we are today, but we can only satisfy our needs in the present.
How can we satisfy our needs according to Choice Theory?
By satisfying the pictures in our Quality World.
What is the only thing that we do according to Choice Theory?
Behave.
What are the four components of Total Behaviour according to Choice Theory?
Acting, thinking, feeling, and physiology.
Which components of Total Behaviour do we have direct control over?
Acting and thinking.
How can we control our feelings and physiology according to Choice Theory?
Indirectly, through our choices in acting and thinking.
What is Total Behaviour designated and named by?
Verbs and the most recognizable part.
What is reality therapy?
A therapy that helps individuals take more control of their lives.
Who developed reality therapy?
William Glasser.
What does Glasser believe is the root cause of unhappiness?
The way people choose to behave, particularly in unsatisfying relationships.
What is William Glasser's foundational belief?
People making better choices will lead to better relationships and overall happiness.
What are the 5 basic needs identified in Choice Theory?
Survival, love and belonging, power, freedom, and fun.
Our 5 basic needs are equal in strength according to Choice Theory. (True/False)
False
1 multiple choice option
Out of our 5 basic needs, what is our primary need as social beings?
The need for belonging.
What does it mean when we feel bad according to Choice Theory?
One of our 5 basic needs is not being met.
We do not satisfy needs directly according to Choice Theory. (True/False)
True
1 multiple choice option
What is the quality world?
Images in our minds of anything we want.
What is the most important component of our quality world?
People we are closest to and enjoy being with.
According to Choice Therapy, where does everything we choose to do come from?
From within ourselves.
Which parts of Total Behaviour does Choice Theory emphasize?
Thinking and acting.
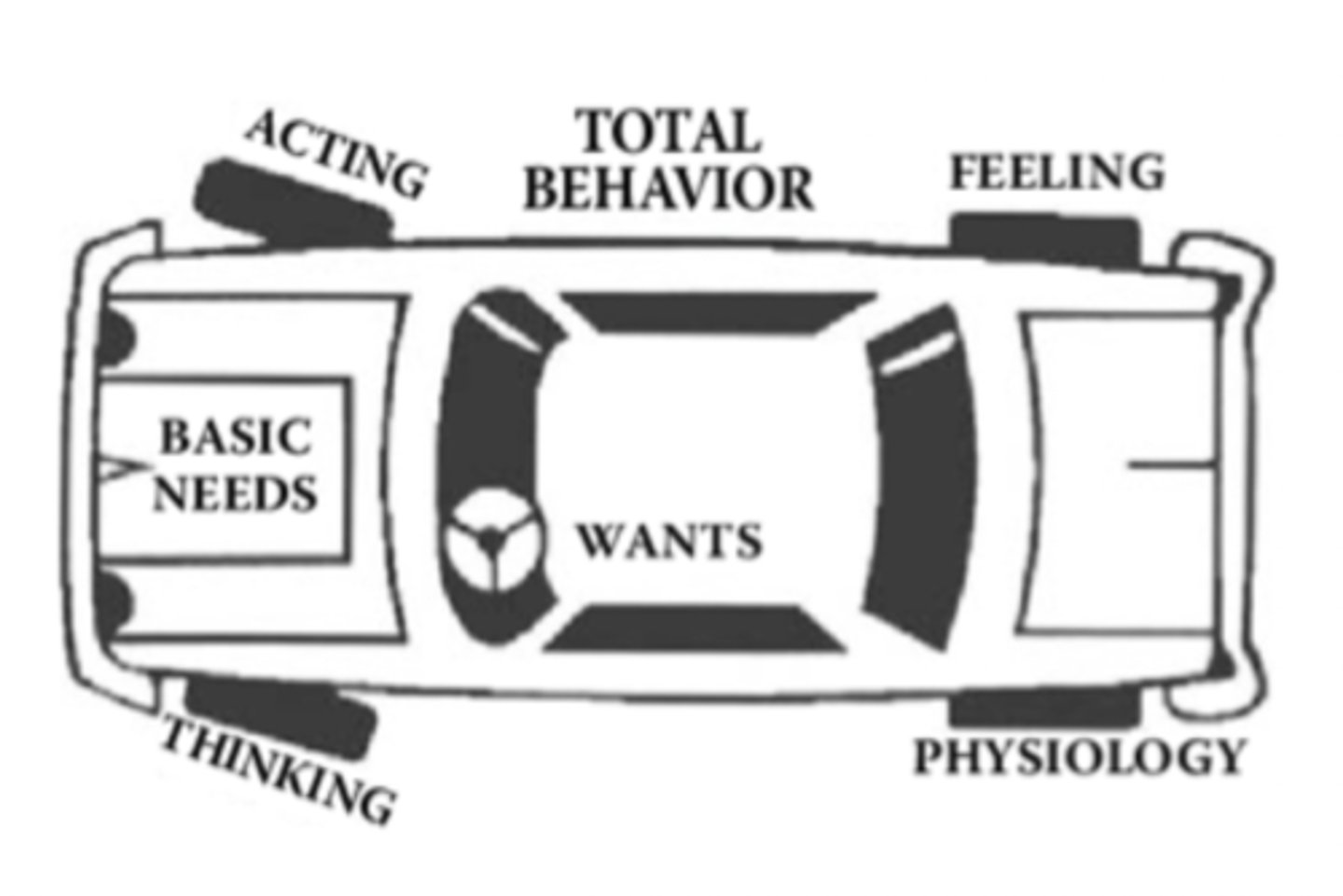
Choice Theory focuses on the past instead of the present. (True/False)
False
Choice Theory encourages you to discuss with your client their symptoms and complaints so that the main problem can be addressed. (True/False)
False
1 multiple choice option
What is the goal of reality therapy?
To help clients be connected with people who satisfy them and to consistently live in a quality world.
What is the role of the therapist in Reality Therapy?
To build a therapeutic alliance, challenge clients, and teach them the 7 deadly and 7 caring habits.
What are the 7 deadly habits?
Criticizing, blaming, complaining, nagging, threatening, punishing, and bribing.
What are the 7 caring habits?
Supporting, encouraging, listening, accepting, trusting, respecting, and negotiating differences.
What is the WDEP system in Choice Therapy?
Wants, Doing, Evaluation, and Plan.
What does SAMIC stand for in goal-making for reality therapy?
Simple, attainable, measurable, immediate, and controllable.
What is the primary factor that determines group effectiveness?
A group's ability to make sound decisions on various issues.
What is a simple majority vote?
A voting method requiring more than half of the group to agree.
What is a two-thirds or three-fourths majority vote?
A voting method requiring either 2/3 or 3/4 of the votes to agree.
What are delegated decisions?
Decisions made by an individual or individuals given autonomy, but with limitations.
What is multiple voting?
A process involving several rounds of voting, progressively narrowing down alternatives.
What is the purpose of polling in decision-making?
To gather feedback, opinions, preferences, and insights from individuals.
What is consensus in decision-making?
A process that results in a group agreement where everyone is comfortable with the outcome.
A consensus leads to an outcome that everyone agrees with. (True/False)
False
What is groupthink?
A problem-solving process where ideas are accepted without critical appraisal, often due to social pressure.
What are some antecedent conditions that can lead to groupthink?
Time pressures, high cohesiveness, isolation from information, and directive leadership.
What are some symptoms of groupthink?
Illusions of invulnerability, illusions of unanimity, in-group favouritism, little search for new information, belief in the morality of the group, and pressure on the dissenters.
How can groupthink be prevented?
By using smaller groups, keeping leaders' opinions private, seeking outside opinions, and employing a 'devil's advocate.'
What is conflict in group dynamics?
Disagreement and discord among group members or different groups, often involving divergent ideas.
What is a win-lose approach to conflict resolution?
An ineffective method that increases distrust and decreases cohesion by refusing to listen to the other side.
What is a no-lose approach to conflict resolution?
Finding mutually acceptable outcomes where all parties' needs are met.
What are 'I' messages in conflict resolution?
Statements that reduce defensiveness and facilitate open communication, structured as 'When you _____, I feel ______.'
What is disarming in conflict resolution?
Finding some truth in the other person's viewpoint and sharing agreement, even if you disagree.
What is stroking in conflict resolution?
Stating something positive about the person you are in conflict with.
What is role reversal in conflict resolution?
Each individual expresses their opinions after restating the ideas and feelings of the opposing individual.
What does empathizing involve in conflict resolution?
Putting yourself in the other person's shoes and expressing understanding of their perspective.
What is inquiry in conflict resolution?
Using gentle, probing questions to learn more about what the other person is thinking.
What is mediation in conflict resolution?
An intervention involving a neutral third party to resolve conflict between disputing groups.
What is the RAP framework in addressing racial dynamics?
Recognize, Anticipate, and Problem-Solve.
What are some tips for challenging group members?
Be self-aware, focus on behaviour, do not dismiss members, educate about group processes, encourage exploration of defensiveness, face conflict, find balance between support and challenge, and invite sharing of feelings.
What is conflict transformation?
A process of constructively changing attitudes, behaviors, and relationships to promote collaboration.
What is escalation?
An increase in intensity or seriousness of something.
What are the 3 phases of the escalation cycle?
Trigger phase, escalation phase, and crisis phase.
What is the trigger phase in the escalation cycle?
The first phase involving the event that causes stress.
What is the escalation phase in the escalation cycle?
The second phase in which the anxiety builds up, resulting in an emotional response.
What is the crisis phase in the escalation cycle?
The third phase in which the client experiences a loss of self-control and reason.
Violence occurs in the escalation phase of the escalation cycle. (True/False)
False
1 multiple choice option
What are the 5 emotions involved in escalation?
Calm, anxious, agitated, aggressive, and violent.
What are the associated behaviours with anxiety?
Tense posture, fidgeting, pacing, hand-wringing, foot-tapping, irritability, and nail-biting.
What are some de-escalation interventions for someone with anxiety?
Encourage verbalization, ask open-ended questions, offer a book or magazine, move the patient to a quiet environment, offer a snack, encourage relaxation exercises, put on some pleasant music, and decrease stressors.
What are the associated behaviours with agitation?
Teeth-clenching, clenched fists, cursing, shouting, red face, and abrupt movements.
What are some de-escalation interventions for someone with agitation?
Encourage verbalization, ask open-ended questions, offer to help, resolve the issue, help with pain, offer help, offer a puzzle or game, encourage journaling, and encourage relaxation.
What are the associated behaviours with aggression?
Issuing insults or threats, intimidating others, slamming doors, invading rights, destroying property, and grabbing.
What are some de-escalation interventions for someone with aggression?
Redirect patient, set limits, engage in therapeutic communication, encourage verbalization, ask open-ended questions, and offer choices.
What are the associated behaviours with violence?
Striking, punching, slapping, biting, hair-pulling, throwing, and kicking.
What are some de-escalation interventions for someone who is violent?
Say stop, open lines of communication, encourage cooperation, administer PRN, and call for assistance.
What are the signs of increasing agitation in a client?
Changes in words, tone, facial expression, demeanor, and hand movements.
What is the importance of early intervention in conflict situations?
It is easier to de-escalate an anxious person than a violent one, making early recognition crucial.
What are some common triggers of escalated behavior in healthcare?
Inadequate security, stressful environments, lack of de-escalation training, and poor working conditions.