Anatomy and Physiology - Chapter 3: Skeletal System
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Skeletal system functions
Support, storage, protection, blood cell formation, movement
Blood Shape categories
Long, short, flat, irregular
Long bone example
Humerus
Short bone example
Carpals
Flat bone example
Sternum
Irregular bone example
Vertebrae
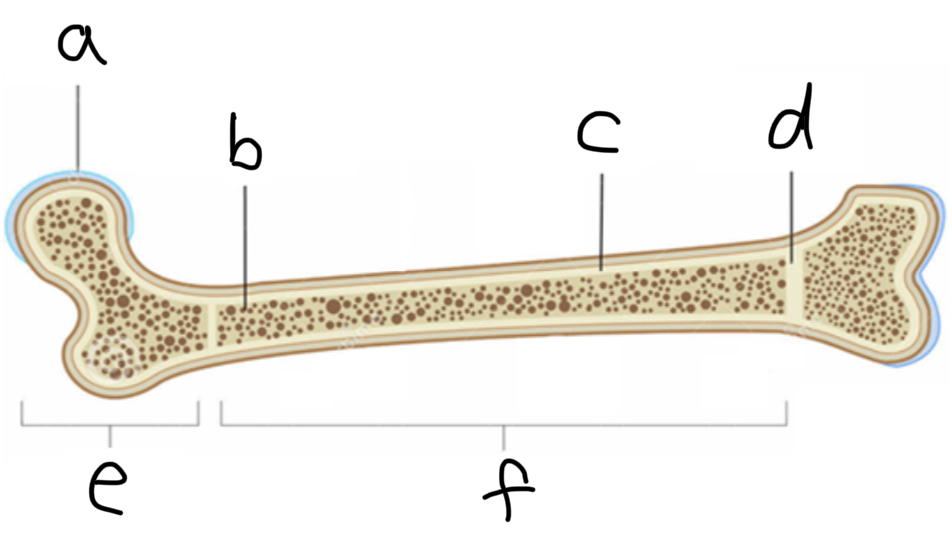
What is A
Articulate hyaline cartilage
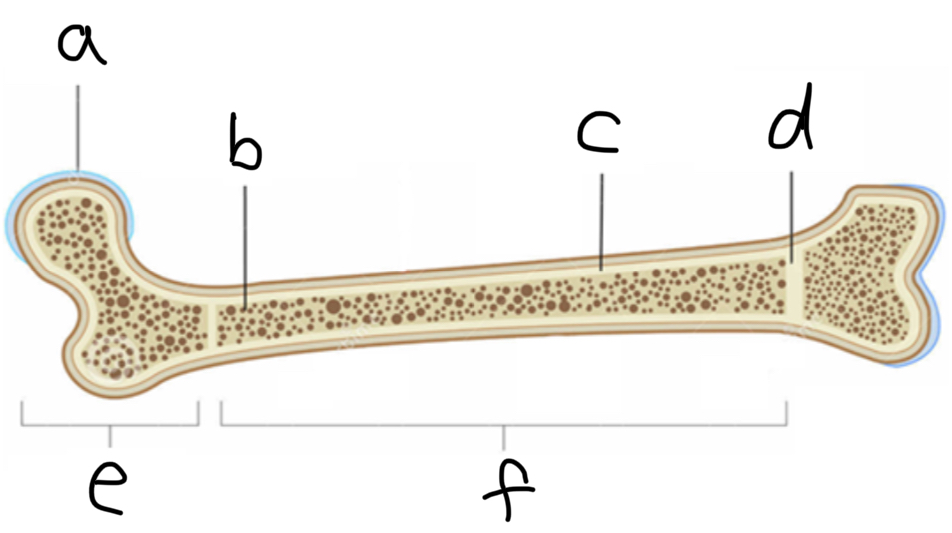
What is B
Spongy Bone
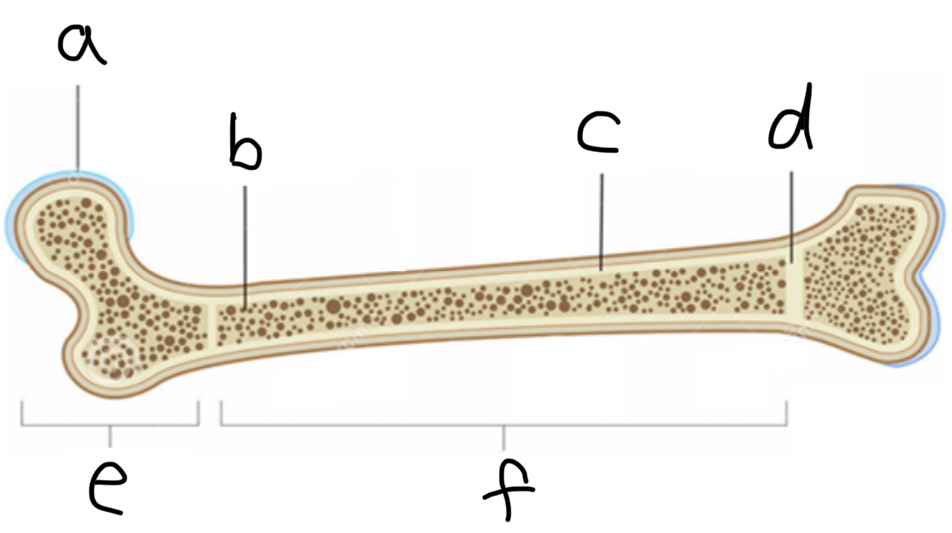
What is C
Compact bone
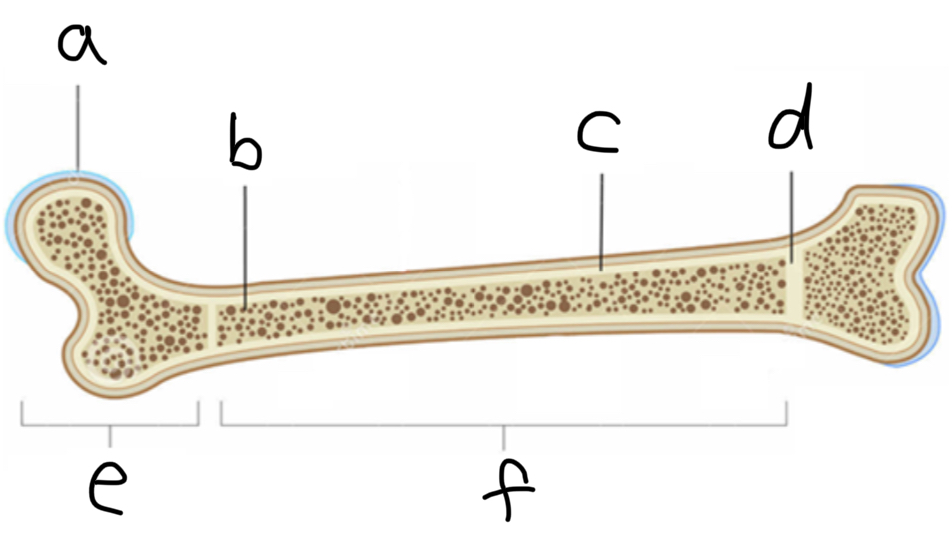
What is D
Epiphyseal plate
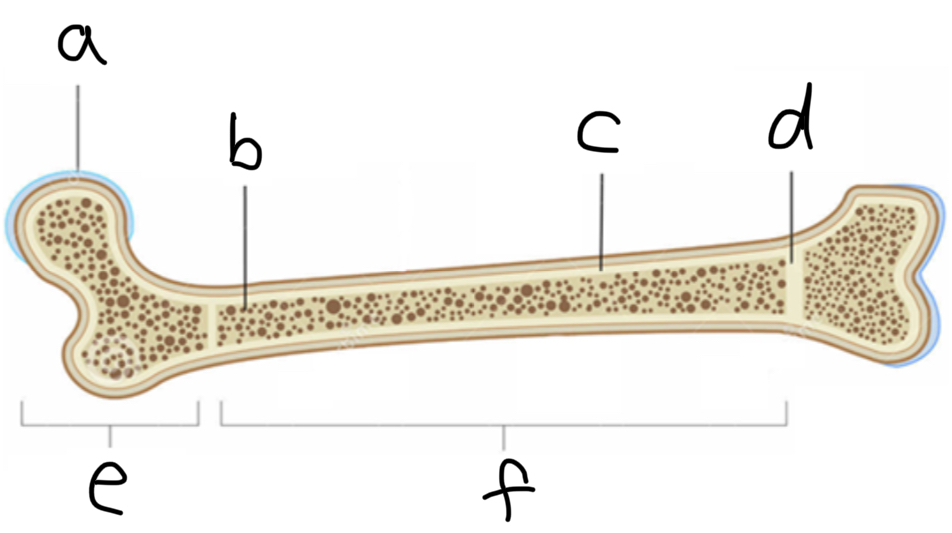
What is E
Epiphysis
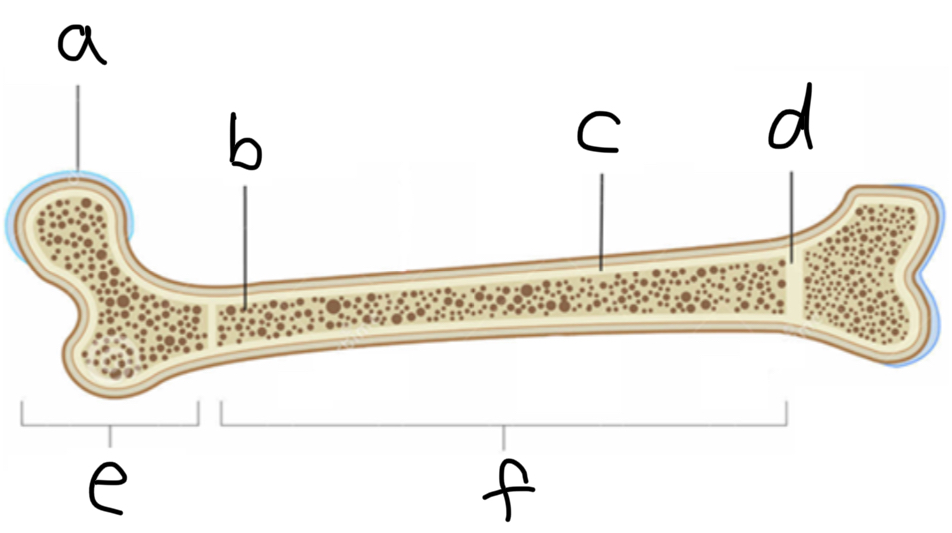
What is F
Diaphysis
Osteoblasts
Build bone tissue
Osteoclast
Break down bone tissue
Hypertrophy
Stronger bones
Atrophy
Weaker bones
Axial skeleton
Skull
Vertebrae column
Thoracic cage
Ribs
Sternum
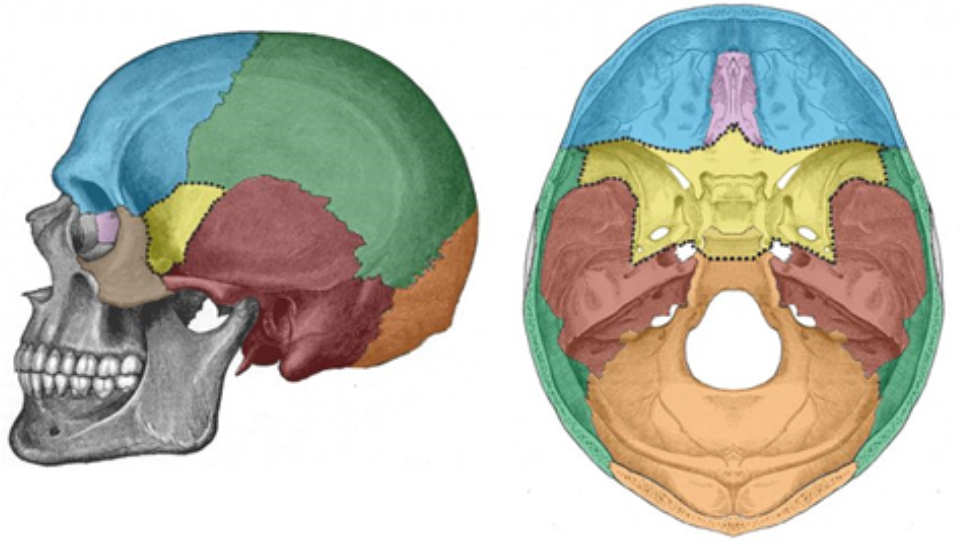
What bone is blue
Frontal bone
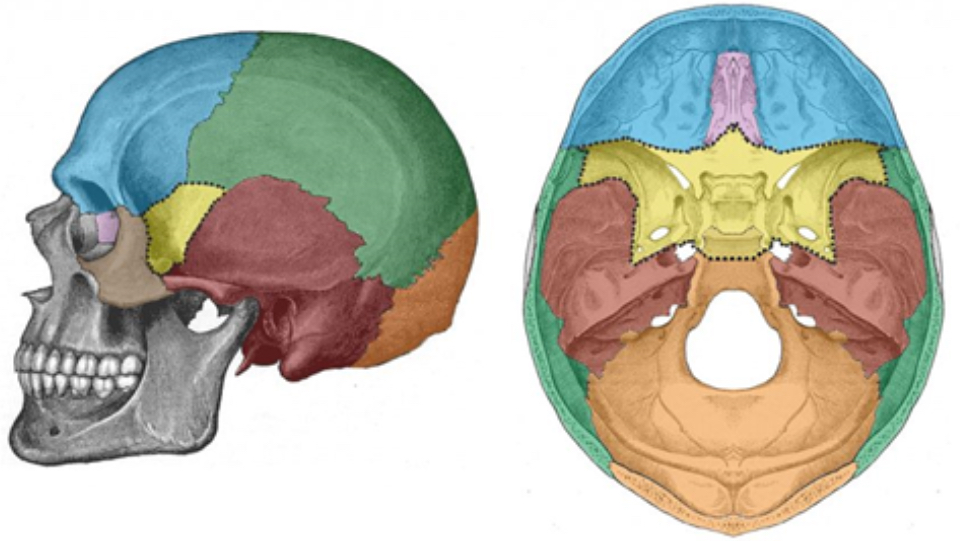
What bone is green
Parietal bone
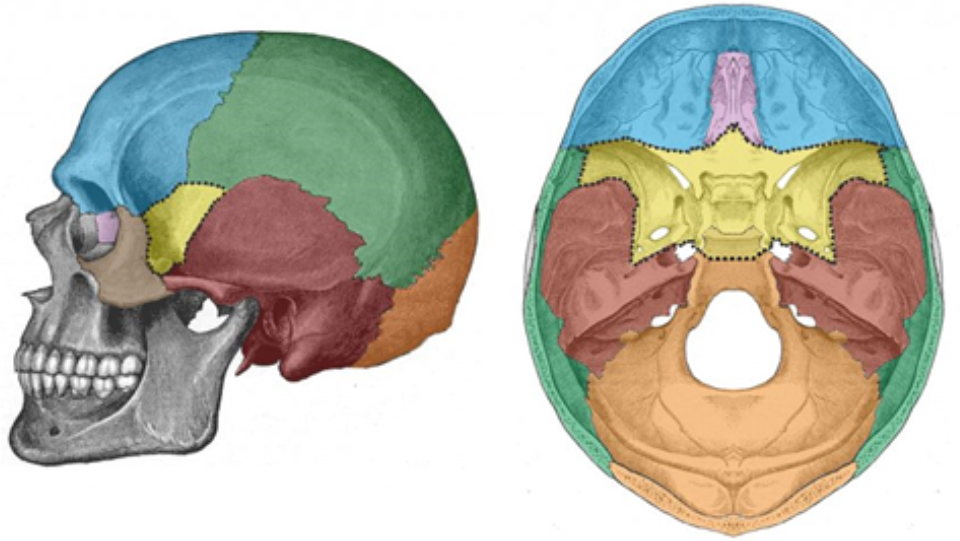
What bone is purple
Ethmoid bone
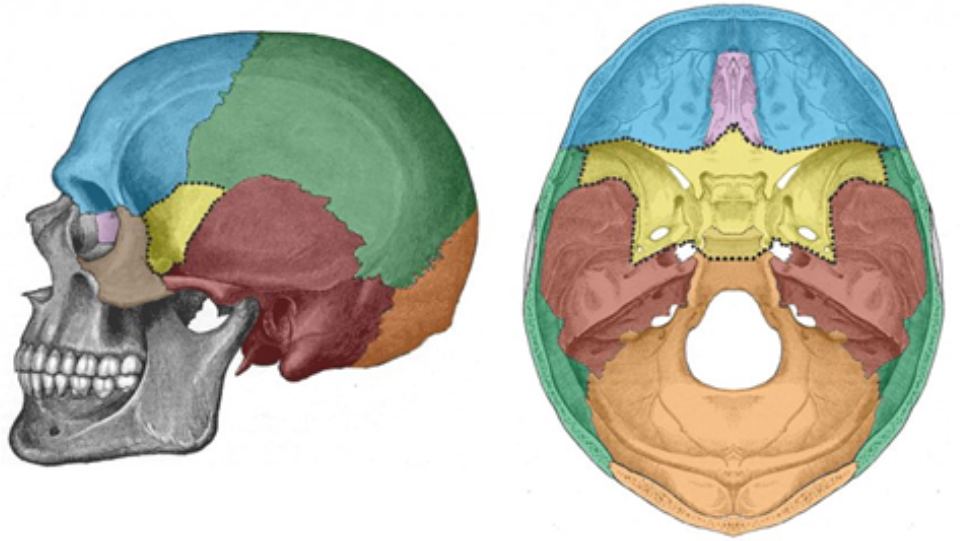
What bone is yellow
Sphenoid bone
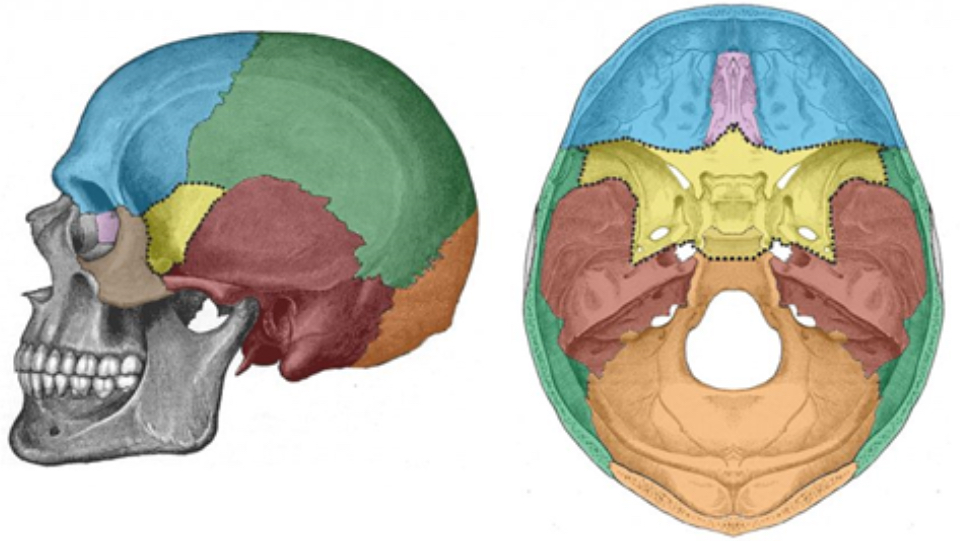
What bone is red
Temporal bone
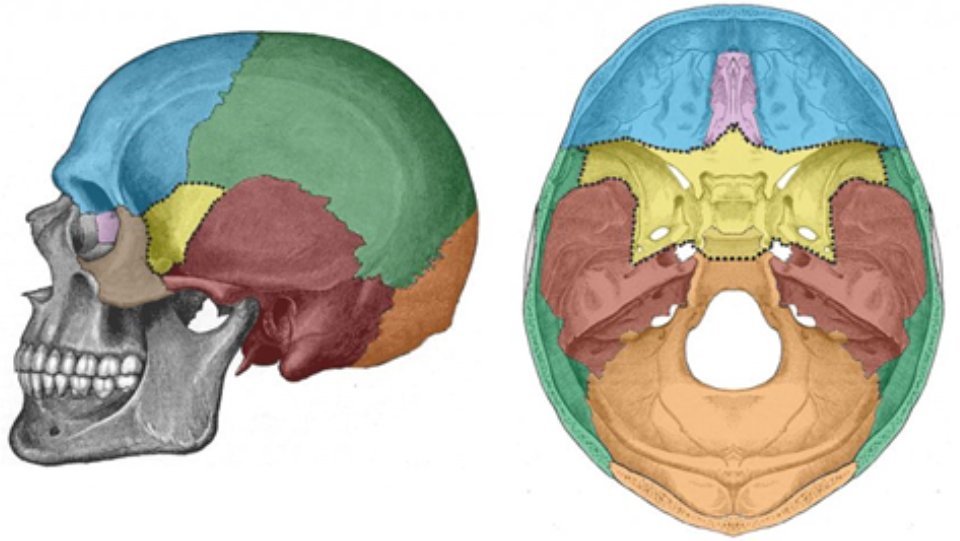
What bone is orange
Occipital
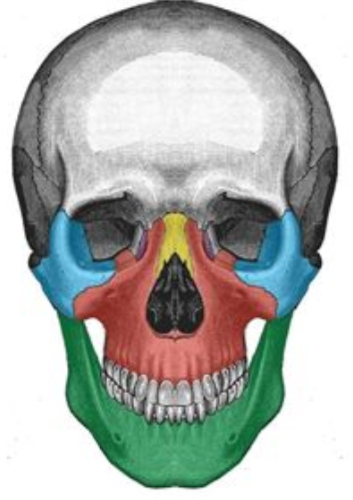
What facial bone is blue
Zygomatic bone
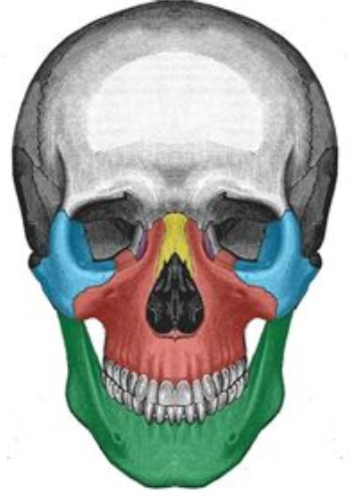
What facial bone is yellow
Nasal
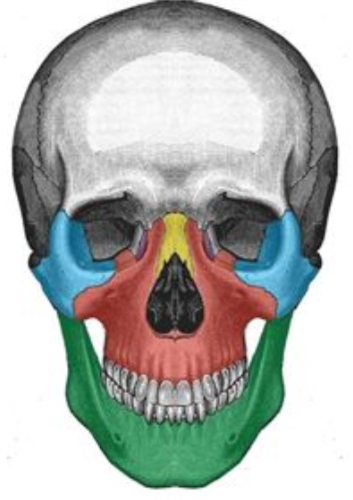
What facial bone is red
Maxilla
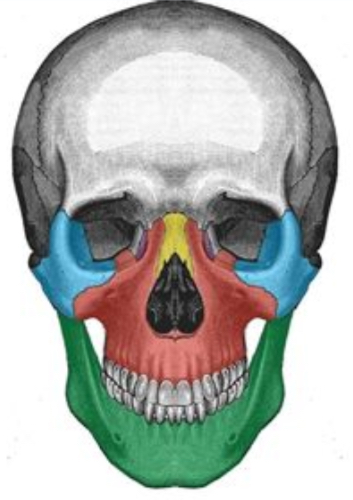
What facial bone is green
Mandible
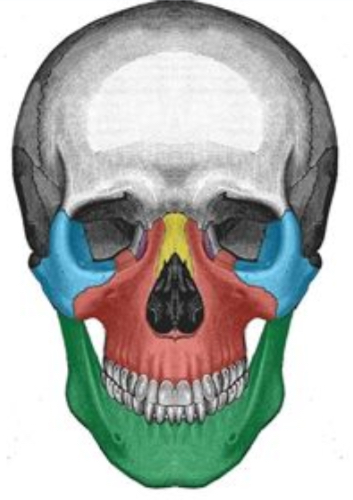
What facial bone is purple
Lacrimal
Vertebrae column
Cervical
7
Thoracic
12
Lumbar
5
Sacrum
Coccyx
Abnormal spine curvatures
Lordosis
Kyphosis
Scoliosis
Lordosis
Excessive curvature of lumbar spine
kyphosis
Excessive curvature of thoracic spine (hatchback)
scoliosis
Lateral curvature of the vertebral column
Ribs
True ribs
14
False ribs
6
Floating ribs
4
True ribs
7 ribs on each side attached to sternum
false ribs
3 ribs on each side that don’t attach to the sternum but only connect to the cartilage
Floating ribs
2 ribs on each side that is connected to the vertebral column not the cartilage or sternum
Sternum: superior portion
Manubrium
Sternum: middle portion
Body
Sternum: inferior portion
Xiphoid process
Shoulder girdle/complex
Clavicle (collarbone)
Scapula
Arm bones
Humerus
Radius (connects to thumb)
Ulna
metacarpals
In between phalanges and carpals
Phalanges
Distal, middle, proximal (touching metacarpals)
Thumb only has distal and proximal
Carpal bones
“Sally left the party to take Cathy home”
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetrum
Pisiform
Trapezium
Trapezoid
Capitate
Hamate
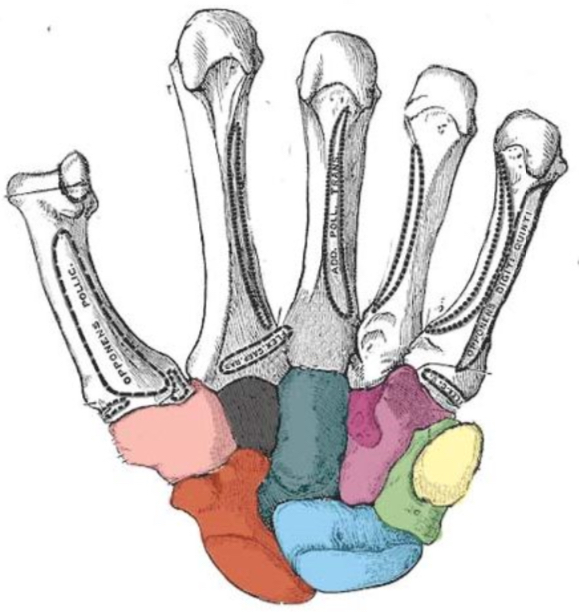
What carpal bone is red
scaphoid
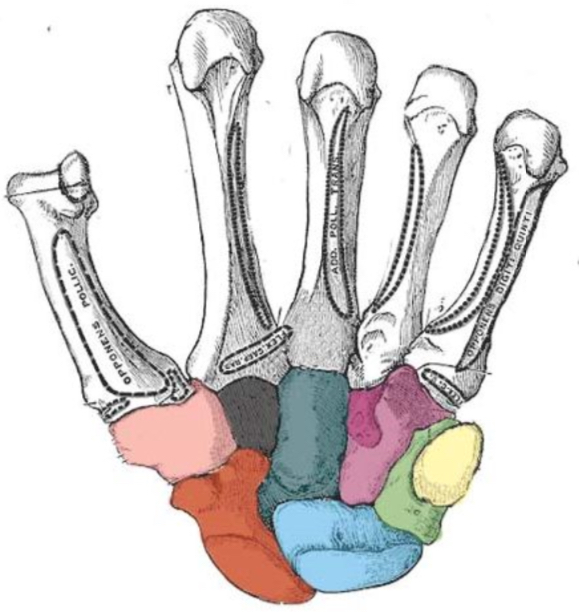
What carpal bone is blue
Lunate
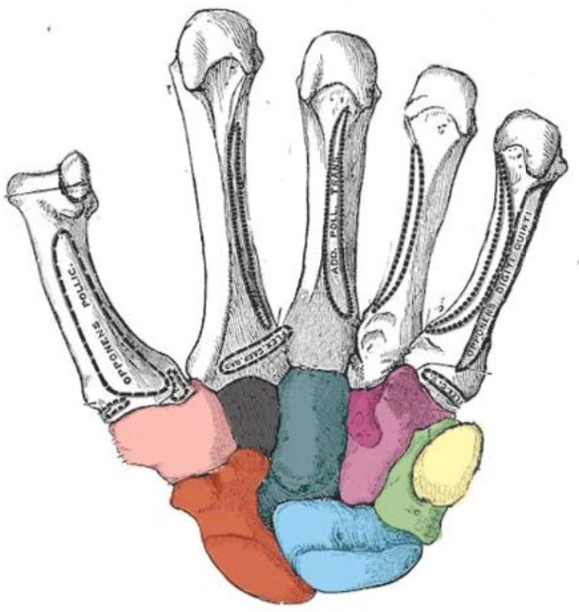
What carpal bone is green
Triquetrum
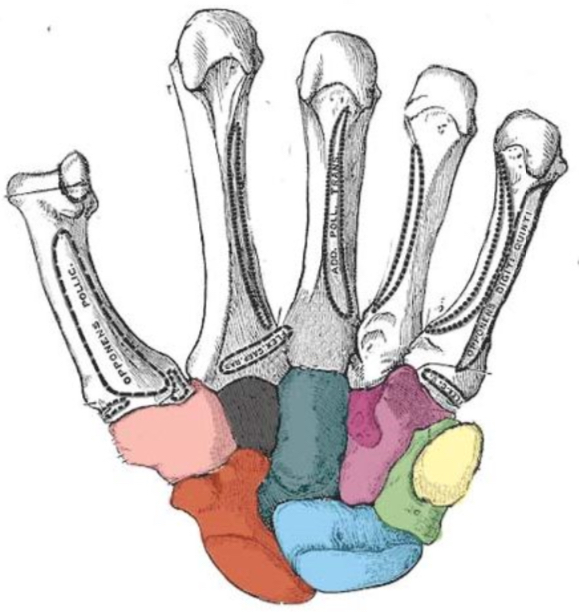
What carpal bone is yellow
Pisiform
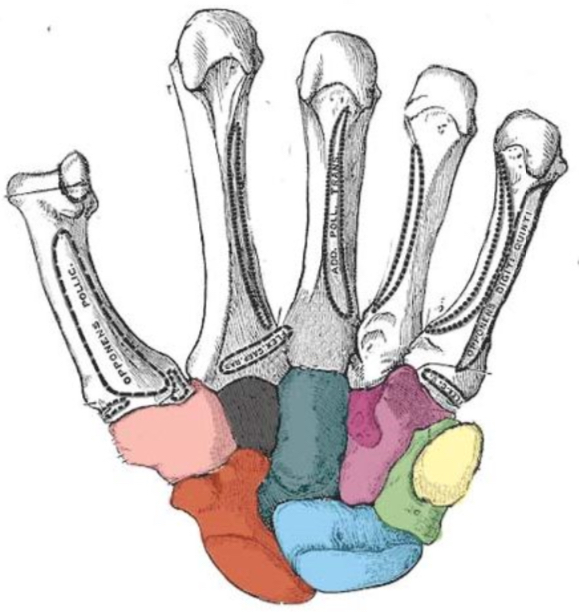
What carpal bone is pink
Trapezium
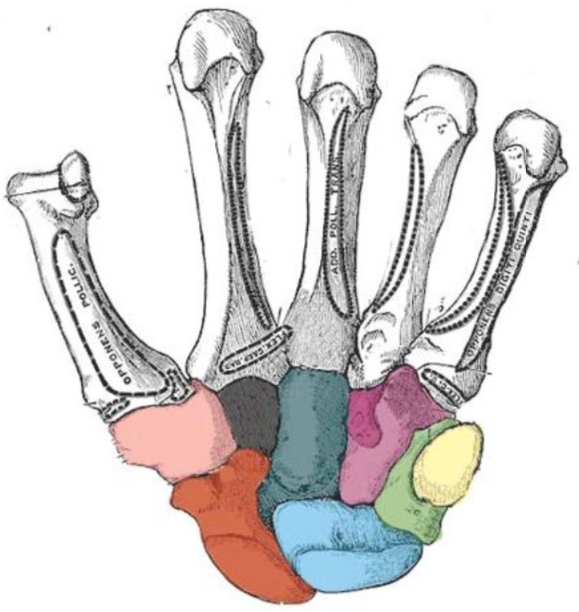
What carpal bone is black
Trapezoid
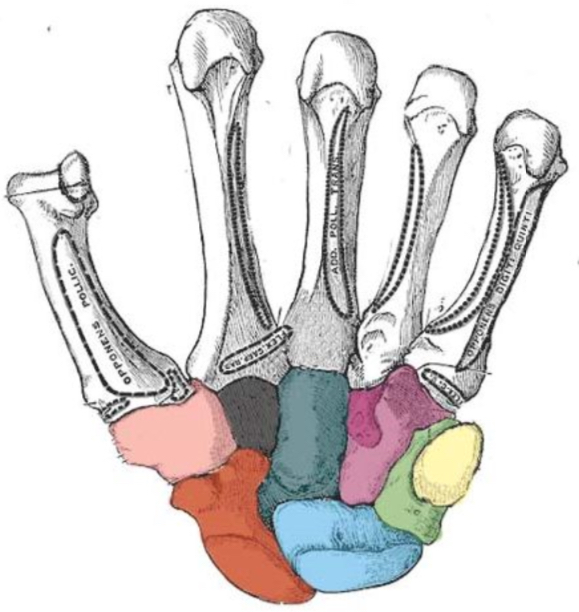
What carpal bone is dark blue
Capitate
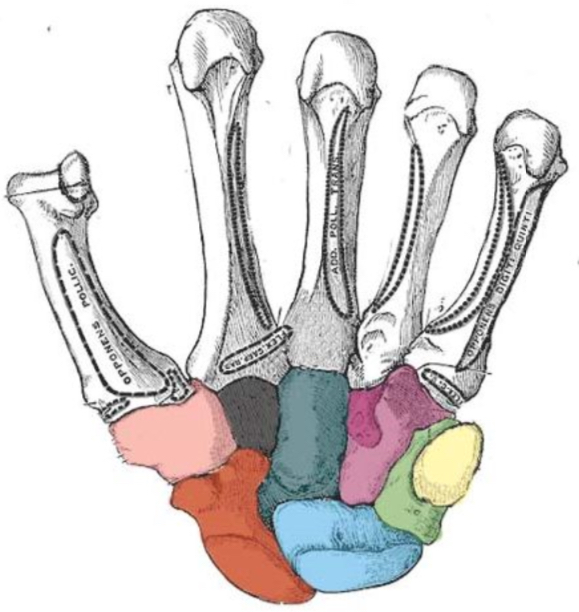
What carpal bone is purple
Hamate
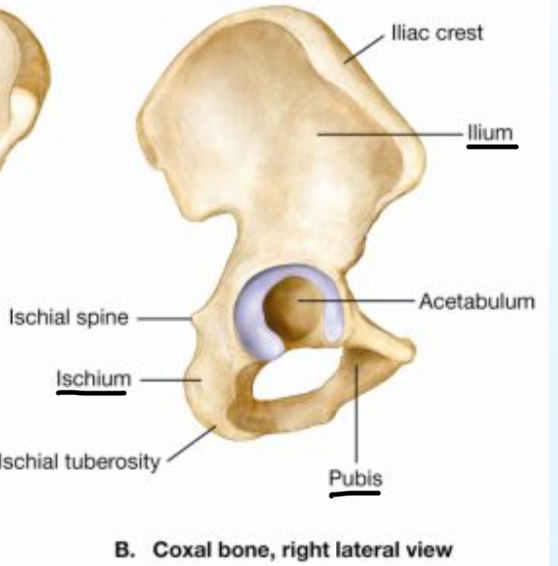
Pelvic girdle
Illium
Ishcium
Pubis
Metatarsals
in between phalanges and tarsals
Tarsals
Calcaneus
Talus
Navicular
Cuboid
Medial cuneiform
Intermediate cuneiform
Lateral cuneiform
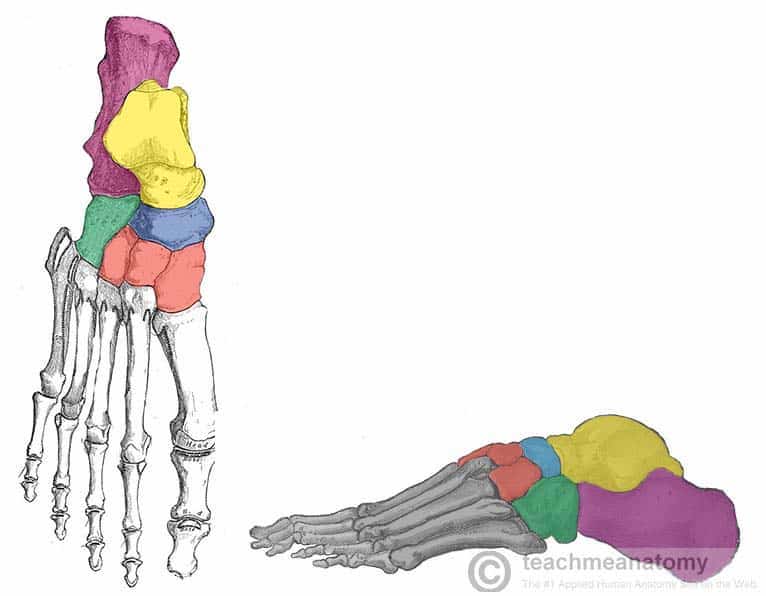
What tarsal bone is purple
Calcaneus
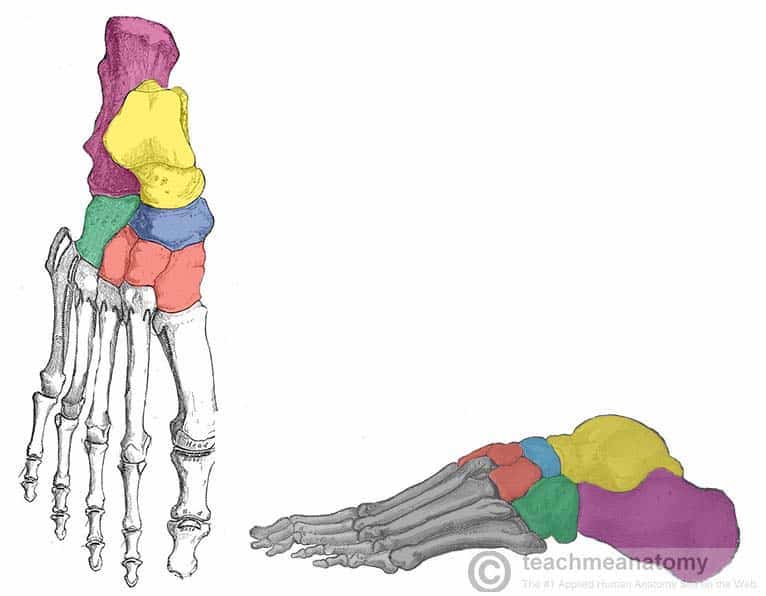
What tarsal bone is yellow
Talus
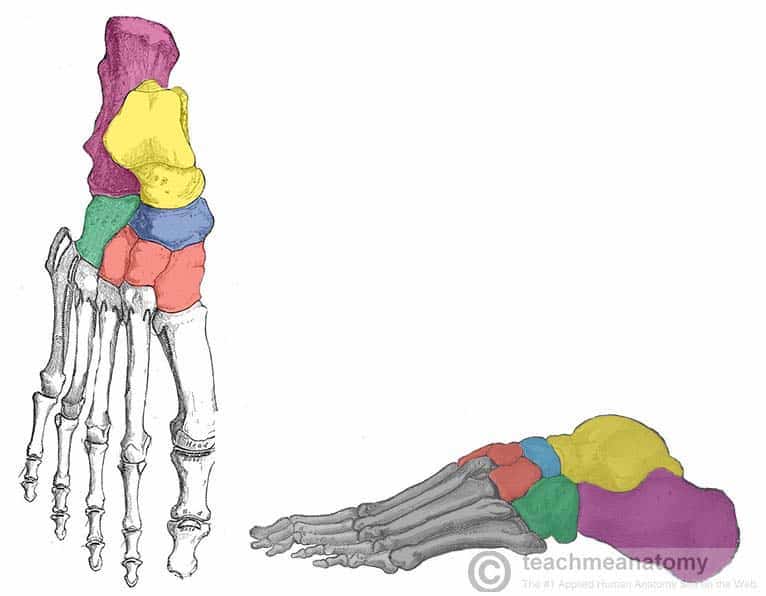
What tarsal bone is blue
Navicular
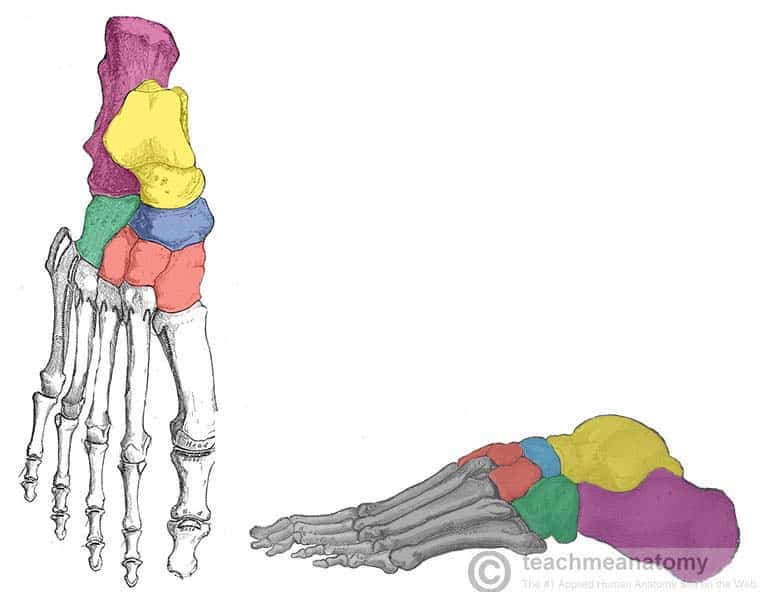
What tarsal bone is green
Cuboid
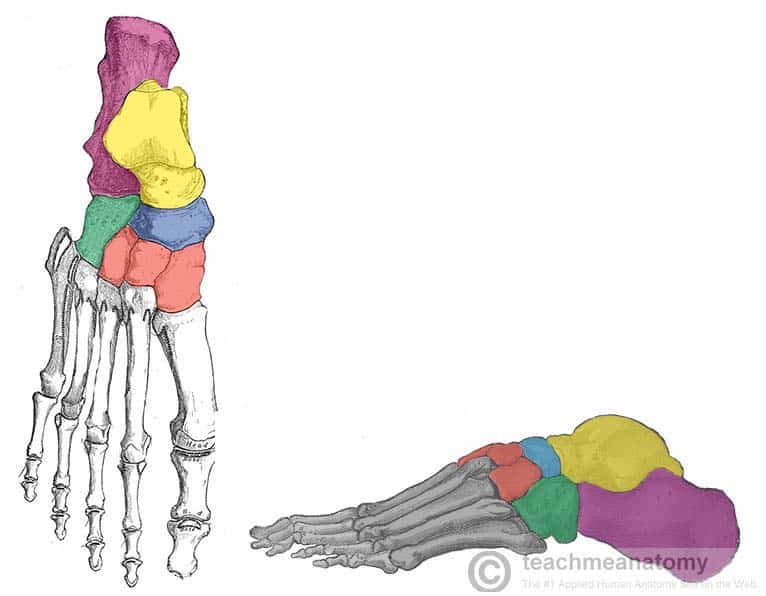
What tarsals are red
Cuneiforms
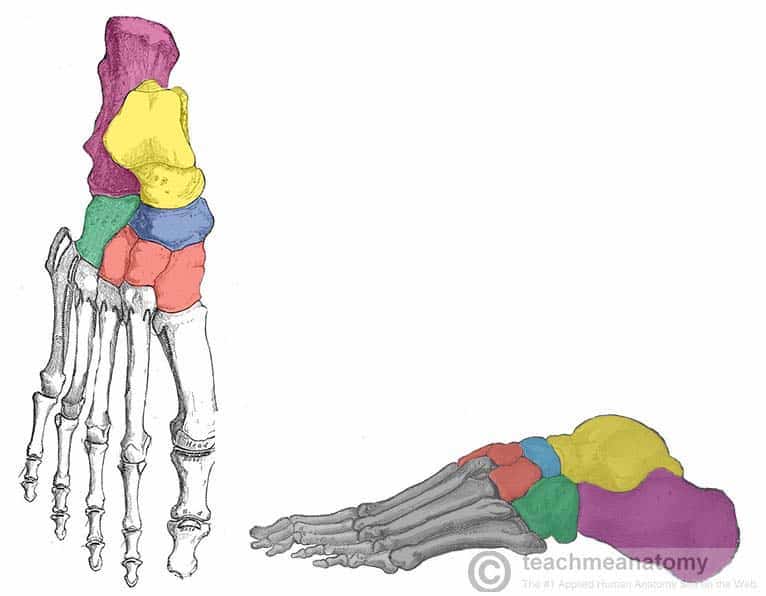
What cuneiform is to the left
Medial cuneiform
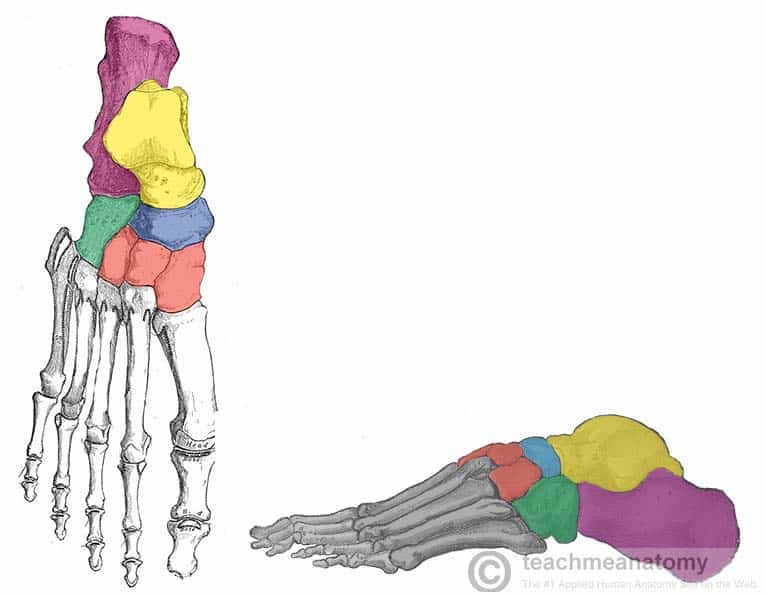
What cuneiform is in the middle
Intermediate cuneiform
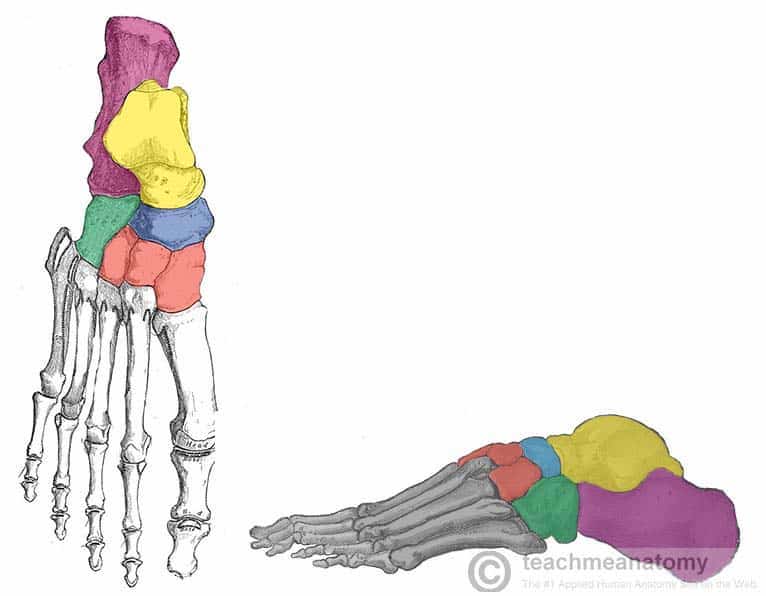
What cuneiform is to the left
Lateral cuneiform
Projections (aka processe)
markings that grow out from the bone (condole, epicondyle, head, facet, crest (line), tubercle, tuberosity, trochanter, spine)
Depressions (cavities)
Markings that indent the bone (sinus, foramen, sulcus/groove, fossa)
synarthrosis
Immovable joints (skull, coracoacromial joint, distal tibiofibular joint)
amphiarthrosis
Slightly moveable (sternocostal joint, vertebral joints, pubic symphysis)
Synovial (Diarthroses) joints
Freely movable
Synovial joint types
Hinge
Humerus and ulna (humeroulnar)
Condylar
Phalanx and metacarpal bone (metacarpophalangeal)
Pivot
Radius and ulna (radioulnar)
Ball and socket
Humerus and scapula (humeroscapular)
Gliding
Carpal bones (intercarpal)
Saddle
Metacarpal bone and carpal bone (trapeziometacarpal)
Tendons
Muscle to bone
Ligaments
Bone to bone
How to name joints
Proximal bone or labrum name(minus ending)
Add “O”
Add distal bone name (change ending to ar/al)
types of motion
Abduction
Adduction
Depression
Elevation
Eversion
Inverison
Flexion
Extension
Hyperextension
Medial(internal) rotation
Lateral(external) rotation
Plantar flexion
Dorsiflexion
Pronation
Supination
Protraction
Retraction
Radial deviation
Ulnar deviation
Circumduction
Opposition
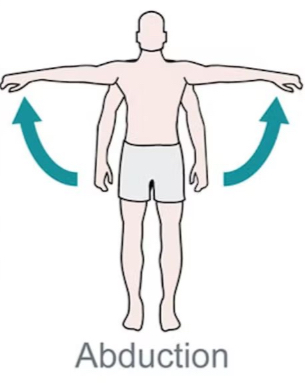
Abduction
moving a part away from midline
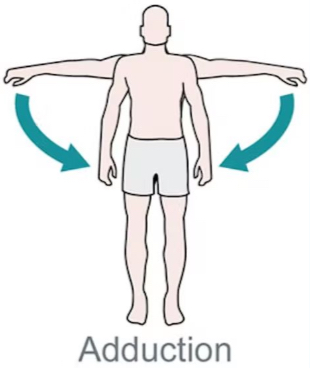
Adduction
Moving a part toward midline
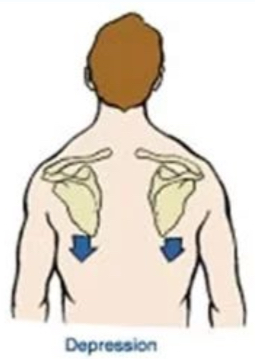
Depression
lowering a part (scapula only)
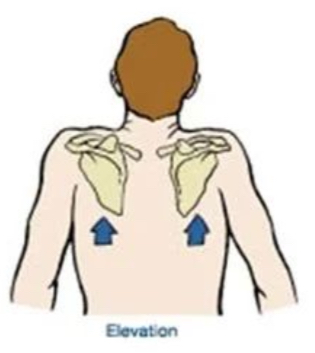
Elevation
Raising a part (scapula only)
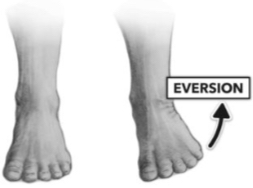
Eversion
Turning the foot so the sole faces laterally
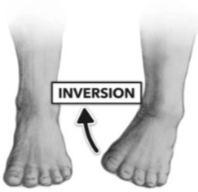
Inversion
Turning the foot so the sole faces medially
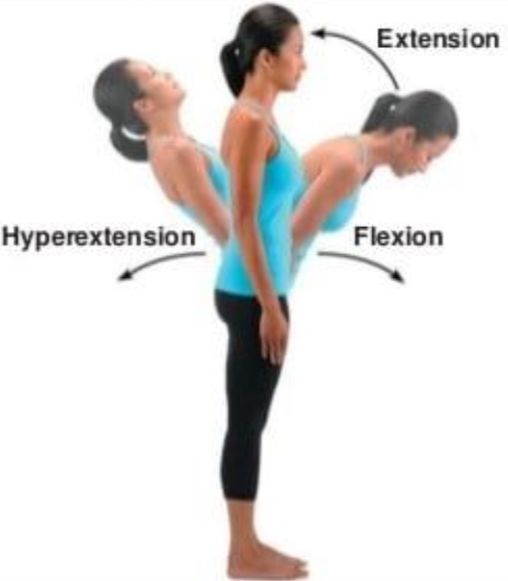
Flexion
Bending so joint angle decreases, parts come closer together
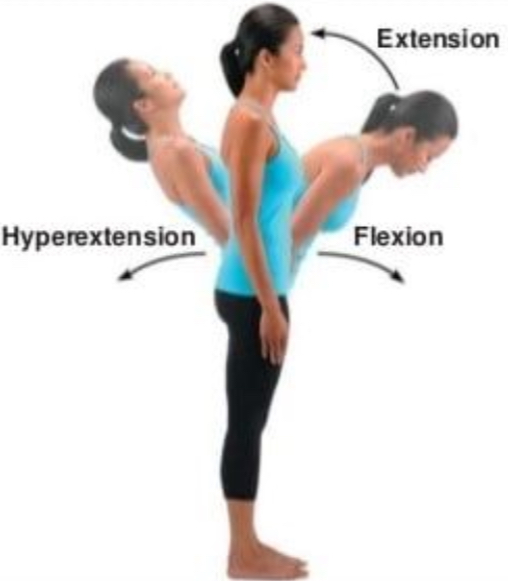
Extension
Straightening of joint so angle increases, parts farther apart
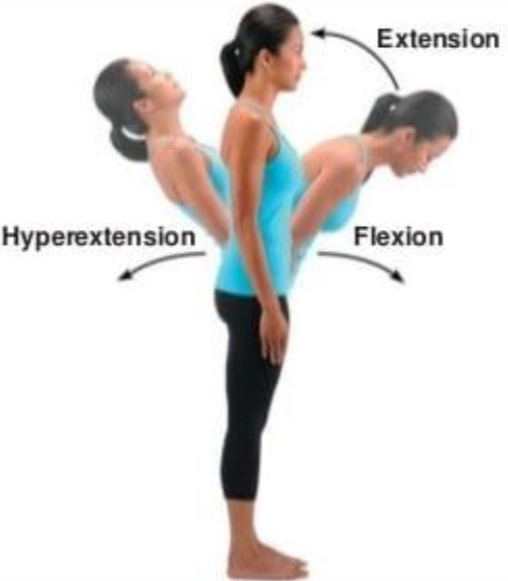
Hyperextension
Excessive extension beyond anatomical position
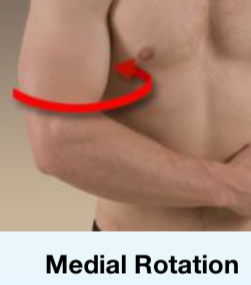
Medial rotation
Rotation towards the center of the body
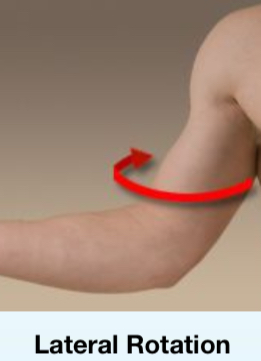
Lateral rotation
Rotation away from the center of the body
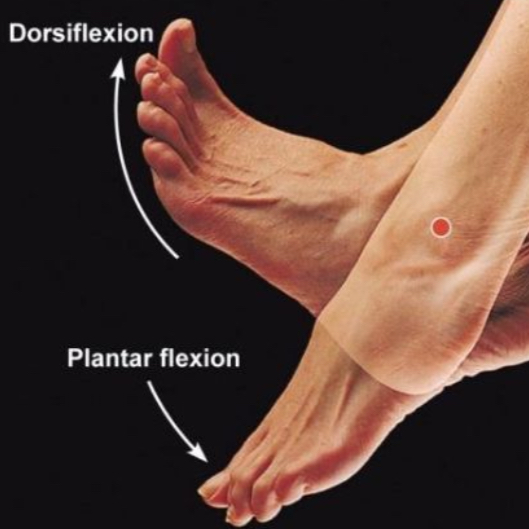
Plantar flexion
Bending of foot at ankle to “point the toes”
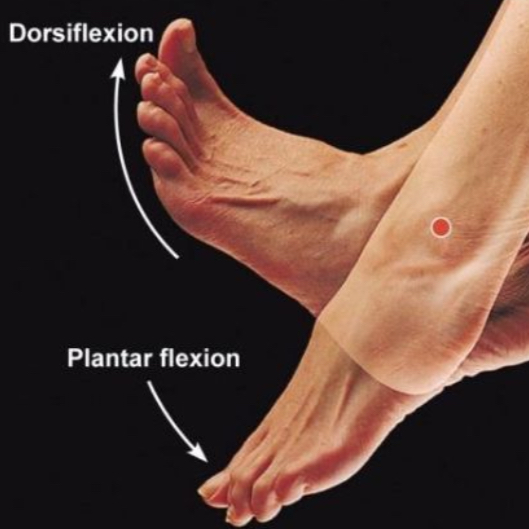
Dorsiflexion
Bending of foot at ankle toward tibia
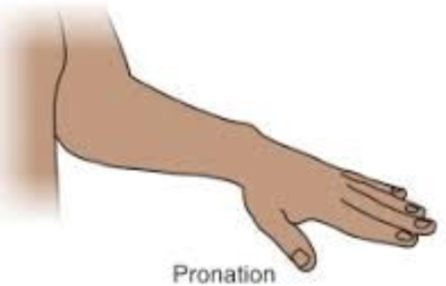
Pronation
Turning the hand so the palm to downward
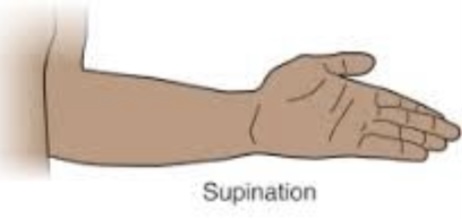
Supination
Turning the hand so the palm is upward
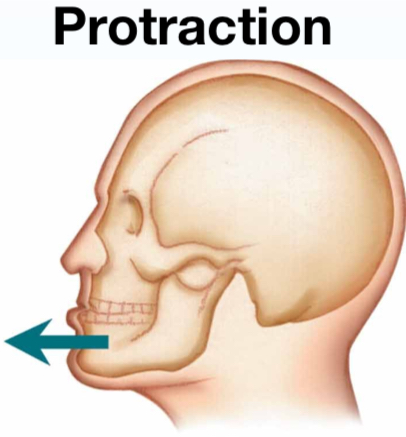
Protraction
Moving a part forward (mandible and scapula only)
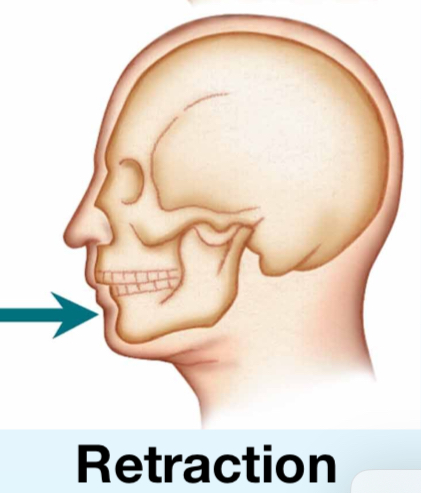
Retraction
Moving a part backward (mandible and scapula only)
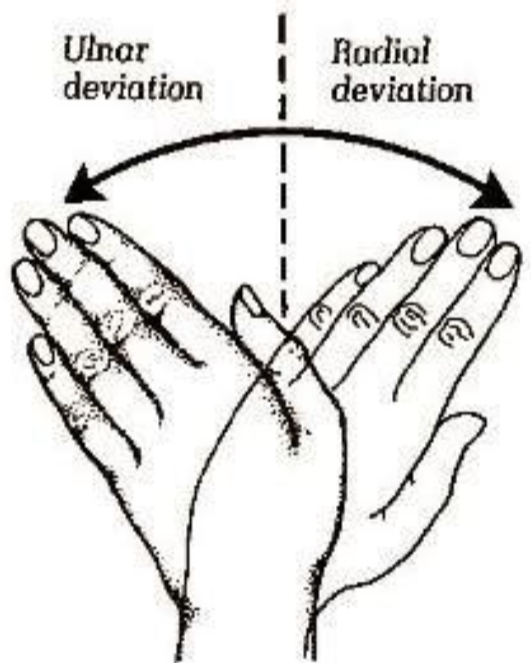
Radial deviation
Rotation of the wrist laterally
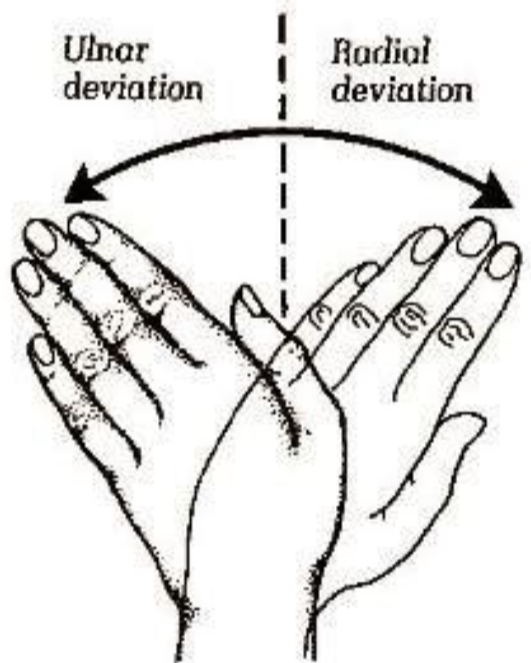
Ulnar deviation
Rotation of the wrist medially
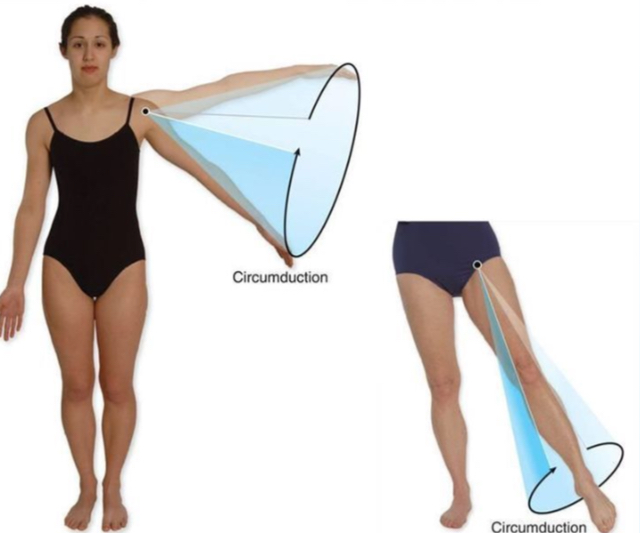
Circumduction
Moving a part so that its end follows a circular path

Opposition
Touching any finger to the thumb
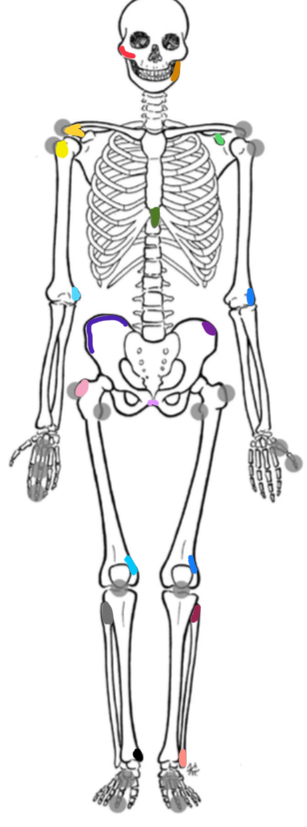
What marking is red
Zygomatic pirch
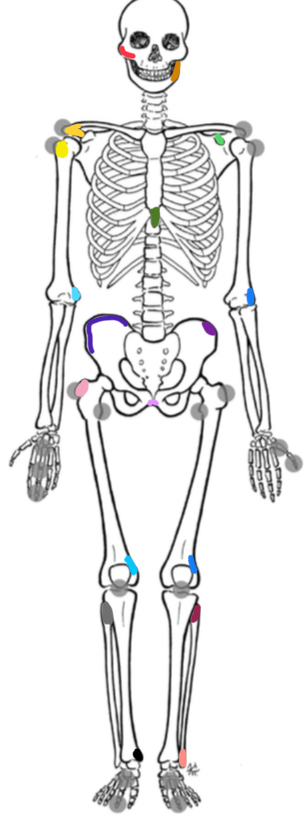
What marking is orange
Ramus of the mandible
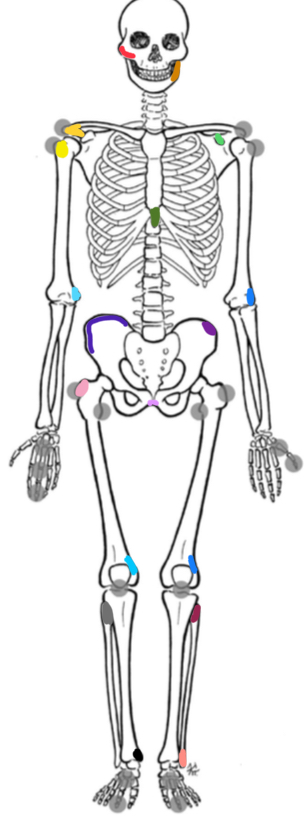
What marking is yellow-orange
Acromion process
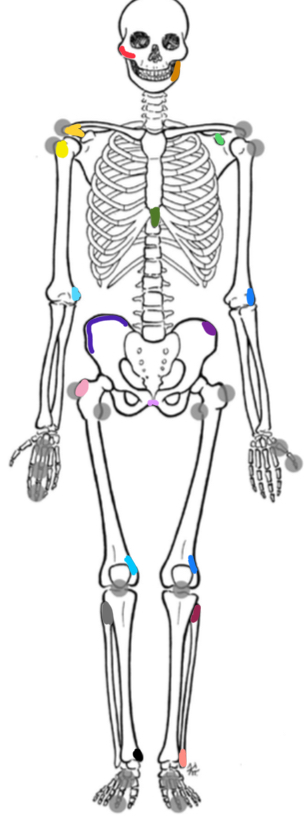
What marking is yellow
Bicipital groove
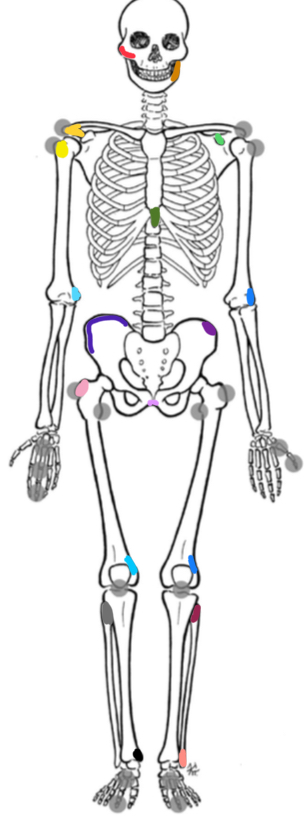
What marking is light green
Coracoid process