Neonatology and Pediatrics
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and concepts from the neonatology/pediatrics lecture notes to aid quick memorization and exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Neonate
Birth - 10 days/2 weeks
Perinatal period < 1 day
Infant
2-5/6 weeks
preweaning
Juvenile
Postweaning to about 6 months
physiologic processes mature by 8–12 weeks
adult tooth eruption around 16 weeks.
Perinatal period
Time around birth, defined as less than 1 day
Altricial
Born in an underdeveloped state requiring parental care; dogs and cats are more altricial than humans.
Hand-rearing
Raising neonates by humans when the dam cannot or will not nurse; includes warmth, feeding, and environment management.
How often do puppies need to nurse?
2-3 hours
Fading puppy syndrome
A neonatal condition where a healthy-looking neonate stops nursing and dies with no clear cause; sepsis is commonly suspected.
hypothermia
hypovolemia
hypoglycemia
hypoxemia
Neonatal isoerythrolysis
Kittens of type A or AB born to a type B queen; colostral anti-A antibodies cause red blood cell destruction; at-risk kittens may need separation.
Omphalitis
Infection of the umbilical stump; cord remnants typically present for 2–3 days.
Umbilical stump
Cord remnant left after birth, typically present for a short period before falling off.
Meconium
The first stool of a newborn; normally pasty, brown; changes can indicate dehydration or illness if abnormal.
Cleft palate
Congenital defect where the palate fails to close, causing feeding and breathing difficulties.
Righting reflex
The neonate’s ability to reorient itself to an upright position when placed off-balance.
Rooting reflex
The infant turns toward and searches for a nipple when the cheek or mouth is stroked; aids feeding.
Suckling reflex
The automatic ability to suckle when the mouth is touched; essential for feeding newborns.
Gavage
Tube feeding directly into the stomach using a stomach tube; used when bottle feeding is not possible.
Proctoclysis
Rectal infusion of fluids as an alternate method to gavage for hydration.
Bottle feeding
Feeding neonates with a nursing bottle and nipples; proper placement and nipple maintenance are important.
Hypothermia
Abnormally low body temperature; in neonates it can be physiologic or pathologic and requires warming measures.
Hypovolemia
Low circulating blood volume; treated with fluids via various routes including gavage, IV, subcutaneous, or intraosseous.
Hypoglycemia
Low blood glucose; in fading neonates, treated with dextrose administration.
Hypoxemia
Low blood oxygen level; managed with supplemental oxygen.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
A heart defect where the ductus arteriosus remains open after birth, causing abnormal blood flow.
Cyanosis
Bluish discoloration of mucous membranes due to hypoxemia.
Weaning
Transition from milk to semisolid/solid foods; typically begins around 3–4 weeks and advances to solid meals by 5–6 weeks.
What is the normal growth rate for neonates?
Neonates should roughly double their birth weight within the first 7–10 days
Daily weight monitoring
Weigh neonates 2x daily (at least through the first 3 weeks)
Warmth and environmental needs
Neonates require warm, stable environments (e.g., around 32°C (89 F) in the first week and appropriate humidity) to prevent hypothermia and support growth.
Umbilical care
Clean, monitor, and disinfect umbilical remnants; manage umbilical infections with proper antisepsis.
Portosystemic shunt
A congenital liver vascular anomaly where blood bypasses the liver; detectable by ultrasound and associated with systemic signs.
5 signs of a sick neonate
weak (limp, poor refluxes)
restlessness, persistent vocalization
being ignored
isolation
poor weight gain
What are neonates prone to?
dehydration and volume overload due to immature renal function and high metabolic rates.
tongue should be light pink and moist
Poikilothermic
puppies cannot regulate its body temperature and relies on external sources
shiver reflex at 6 days
Normal HR for a neonate
>200 bpm
When do neonates open their eyes and ear?
5-14 days
manace, PLR, hearing mature by 4 weeks
What causes focal alopecia?
prematurity, grooming
What causes erythemia?
redness of the skin caused by increased blood flow to the superficial capillaries → heat stress, sepsis
What causes ulcers?
septic emboli
What pathogen can cause petechiation?
canine alphaherpesvirus
What can cause ecchymoses?
hypoprothrombinemia → is almost always due to vitamin K deficiency, compounded by poor placental transfer, sterile gut, immature liver function, and species-specific low milk vitamin K, leading to impaired synthesis of prothrombin and other vitamin K–dependent clotting factors → hemorrhagic risk.
What can cause gas distension in the abdomen?
canine alphaherpesvirus
Erythematous
caused by diarrhea
Imperforate
anus is a congenital condition where the anal opening is absent or blocked, preventing normal bowel movements → leads to constipation
Bright yellow stool can indicate what?
canine alphaherpesvirus
What would blood tinged stool indicate?
sepsis
What does Bocavirus CPV-1 cause in puppies?
It causes respiratory illness and severe gastrointestinal disease, leading to vomiting and diarrhea in affected puppies.
Open fontanelle
is a soft spot on the skull where the bones have not yet fused. It allows for brain growth and passage through the birth canal.
How long will the puppy need to be on milk replacer for hand rearing?
first 3-4 weeks
after that can move onto soft gruel and supplement with milk replacer
Hand rearing feeding schedule
1st week every 2-3 hrs
2nd week every 4 hrs
3rd - 4th week every 6 hrs
What are puppy and kittens energy requirements in the first week of life?
puppies → fat
kittens → protein
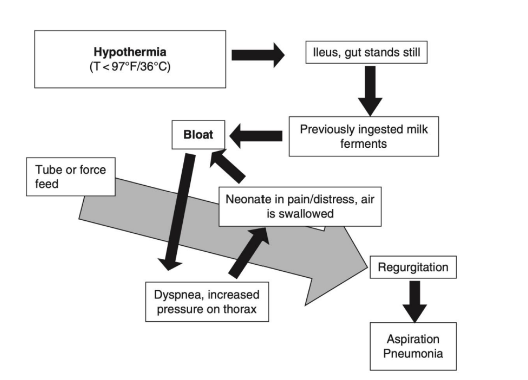
At what temperature should neonates NOT be fed at?
below 36 C (96.8 F)
Head posture for bottle feeding vs tube feeding?
For bottle feeding, the head should be elevated, while for tube feeding, the head should be kept down
When tube feeding what do we always check?
negative pressure
puppy is vocal
pinch tube and remove quickly
What can we do if a newborn is not breathing but the heart is beating?
keep warm and stimulate
oxygen mask
Jen Chung acupunture point
doxapram only if oxygenated → umbilical vein
Risk factors for fading puppy syndrome?
dystocia and low birth weight
Treatment for fading puppy syndrome
isolate from mother
treat hypothermia
treat hypovolemia by giving fluids
treat hypoglycemia by giving dextrose
treat hypoxemia by giving oxygen
treat sepsis
relieve abdominal distension