Reproduction
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
State the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction.
Sexual
2 parents
genetic exchange
genetically unique offspring
better suited to changes in the environemnt
takes 2, more energy intense
Asexual
1 parent
no exchange of genetic info
genetically identical offspring, variation only occurs if there is a mutation
in a stable non changing environment, they produce offspring already suits that environment
if envienrment changes, all will be negatively affected due to lack of variation
State the differences between the female and male gametes physically.
Male
flagella to move
long cells, small volume
small, only enough nutrients to get them to the female gamete
a lot
Female
cannot move alone
large and spherical
large, many nutrients for development
few, sometimes only one
Define sex chromosomes, gonads, gametes and genitals, with examples.
Sex chromosomes - determines the development of into female or male characteristics (XX or XY)
Gonads - organs that produce hormones or gametes for reproduction (ovaries or testes)
gametes - specialized haploid cells from meiosis (sperm/egg)
genitals - external reproductive structures (penis/vulva)
Draw and label the female reproductive system.
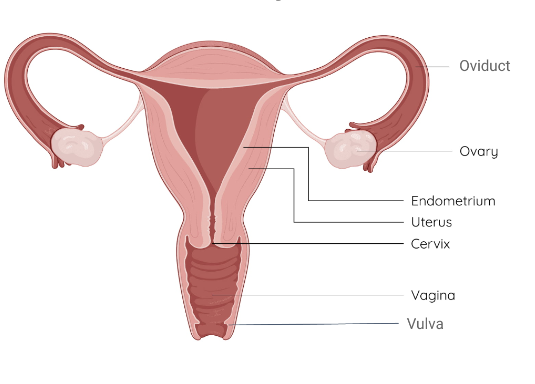
What is the function of the ovaries?
Produce and store eggs as well as make hormones which control the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
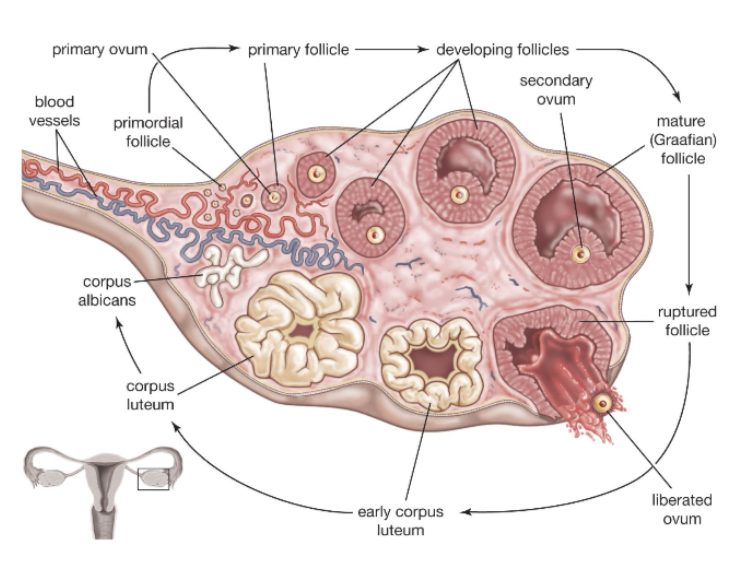
Explain the cycle of the egg within the ovary and draw/label.
What is the function of the oviducts/fallopian tubes?
Passage for eggs between the ovaries and uterus. If fertilized, egg will travel through oviduct to uterus.
State the function of uterus and endometrium.
To develop fetus prior to birth, the endometrium is a blood vessel rish layer from which the fetus is nourished. It is shed during the menstrual cycle if not pregnant.
Function of cervix
Allows fro sperm to enter the uterus. It is a chemical and physical defense against infection and pathogens, produces mucus to as a primary defense.
Function of vagina and vulva
Muscular tube full of mucus membranes, connects cervix and vulva, vulva - sensory tissues and external protection of internal structures from infection.
Draw and label the male reproductive system.
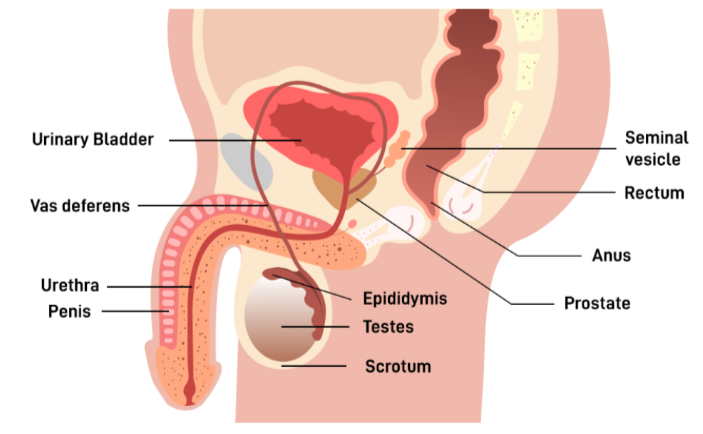
Function of scrotum/testes
Scrotum - sac that protects testes, keeps them outside of body and cold
testes - produces sperm and testosteone- which deepens voice, grows hair and develops muscle in fellas.
Function of epididymis and vas deferens
Epididymus - where sperm matures
vas dereferns - transports sperm to urethra in prep for intercourse, this is what’s cut in a vasectomy
Function of seminal vesicle and prostate
seminal vesicle - produces a fluid hish in fructose to nourish sperm (major component of semen)
Prostate adds and alkaline base to semen to neutralize the slightly acidic vagina
Fucntion of urethra and penis
Urethra moves sperm and urine to outside of body, penis is used during intercourse to position sperm closer to cervix
State function of testosterone and estrogen and effect on developing fetus.
Steroid hormones which give male/female characteristics in puberty
Test - deepens voice, grows hair, muscle development, behavioral masculinization
oestragen - female fat deposits position, menstrual cycle, everything
State the phases and hormones in the ovarian cycle.
Follicular phase - triggered by GNRH from hypothalamus FSH is released from the pituitary gland and travels through blood to the ovaries FSH causes development of the follicle and production of estrogen oestradion
ovulation - rupture of developed follicle triggered by rapid rise in luteinizing hormoneIs (also triggered by GNRH from hypothalamus) at ovaries it causes partial digestion of the follicle wall allowing to burst and release the egg
lutel phase - After luteinizing hormone (LH) is released and egg drops the luteam corpus develops. the cells of the corpus luteum secrete ostragine and progesterone which cause the thickening of the uterus endometrium. The corpus luteum will break down if fertilizing doesn't occur
State the phases and hormones of the uterine cycle
menses low estrogen and progesterone trigger. (short)
Proliferation rising levels of Australia and progesterone from ovary follicle benin corpuscum cause growth of endometrium in anticipation of pregnancy (Looong)
secretory dropping levels of hormones cause endometrium to begin to weaken and degrade (shortish)
State a positive feedback loop with LH and OES
hypothalamus produces GNRH which comes from it which causes the pituitary to create luteinizing hormone which causes the rupture follicle which causes the secretion of estrogen.
State a negative feedback loop with FSH and OES
hypothalamus secretes GNRH which promotes the pituitary gland to produce LH which causes the growth of follicle which causes the secretion of estrogen
What is FSH? Where is it produced? Target cells?
Follicle Stimulating hormone - triggered by gnrh from hypothalamus, FSH is released from pituitary and travels through blood to ovary to cause the development of the follicle +production of estrogen. I
Define zygote, blastocyst and fetus
Zygote= fertilized egg from male and female gamete, diploid. Blastocyst, hollow ball of 250ish cells, embryo is considered a fetus at end of 8 weeks
Outline embryonic development from zygote to blastocyst
Embryo development(morula 5d), blastocyst(250ish hollow cells) hatches out of zona pellucida, fetus(from inner cells of blastocyst, formation of internal organs heart around 16d done by 10w except spinal cord and brain.
State the process of IVF treatment
1 - down regulation (meds for 3 w which stop FSH and LH secretion/stop periods)
2 - superovulation - dose of FSH (across 7-12d) to have multiple follicles develop
3 - egg retrieval - oocyte retrieval occurs with a needle
4 - fertilization - each egg inseminated
5 - endometrial prep - given estrogen and progesterone
6 - embryo transfer - embryo placed in uterus, grows naturally
Compare the processes of spermatogenesis and oogenesis, including the number of gametes, size of gametes, the timing of formation and release of gamete
Similarities
-Both result in the formation of haploid gametes
-Both undergo the process of mitosis, meiosis and growth
Spermatogenesis:
-Produced in testes
-Life long production
-Four haploid cells produced
-Starts at puberty
-Released any time
Oogenesis:
-Produced in ovary
-Fixed production
-One cell produced
-Starts at fetal development
-Released once a month
Outline the processes involved in spermatogenesis within the testes, including mitosis, cell growth, the two divisions of meiosis and cell differentiation
- The germline epithelium is divided via mitosis
- spermatogonia then undergo a period of growth
- 2 meiotic divisions that result in four haploid cells
- haploid cells are then differentiated into sperm cells
(nourished by Sertoli cells)
Explain the process of oogenesis using the terms ovary, primary follicle, meiosis, FSH, mature follicle, secondary oocyte and corpus luteum
within the ovary the primary site is formed via meiosis, then promoted by FSH it develops into a mature follicle containing a secondary usite which eventually becomes a corpus luteum and then a corpus albicans.
describe the process of spermatogenesis Use the terms testes, seminiferous tubules, interstitial cells, germinal epithelium, spermatozoa, Sertoli cells, spermatids
During spermatogenesis sertoli cells which are found within the seminiferous tubules provide physical support and nourishment to developing sperm cells, coupled with interstitial cells which produced testosterone, they help the spermatozoa develop within the seminiferous tubules on top of the testicles. germinal epithelium contains the spermatogonia which contain undifferentiated diploid cells which will become spermatozoa
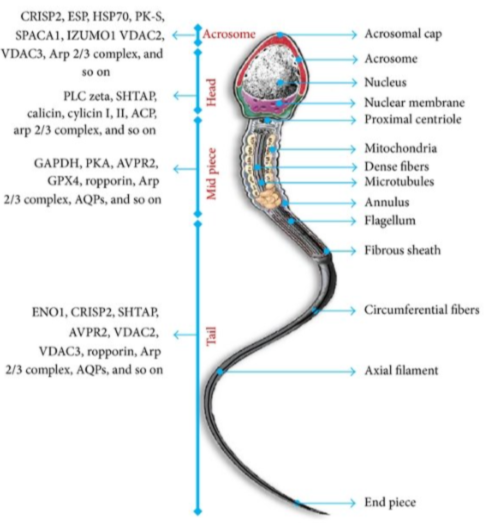
Draw and label a diagram of a sperm cell
Draw and label a diagram of an egg cell
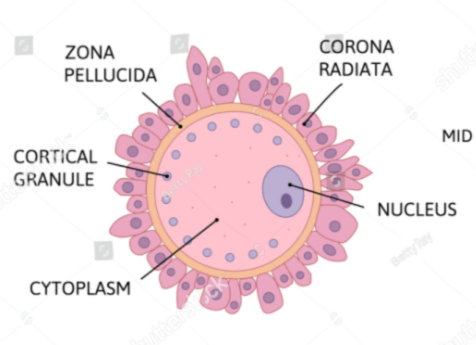
explain the difference in the number of viable eggs in spermatogenesis and ogenesis.
In spermatogenesis millions of eggs are created and used whereas in Ogenesis only one egg is viable at a time. spermatogenesis produces four viable offspring whereas oogenisis as produces only one viable ovum
how is polyspermy prevented in the fertilization of an egg?
Membrane depolarization leading to the inability of other sperm cells to attach to it or the hardening of zona pellucida caused by the cortical granules when they release their contents and modify it.
explain the difference between internal and external fertilization and give an example for both.
Antenna fertilization is within the animal whereas external fertilization is within the environment but outside of the animal. An example of internal fertilization would be chickens, an example of external fertilization would be salmon egg spawning.
what is a blastocyst? When does it become implanted in the lining of the uterus? What strategy does it used to ensure attachment?
Adhesion proteins extend from the cells of the endometrium and the surface of the blastocyst. The cell adhesion molecules help the cells stick together during implantation.
- if it doesn’t implant there'll be no pregnancy, known as a chemical pregnancy, may result in a positive test or missed period
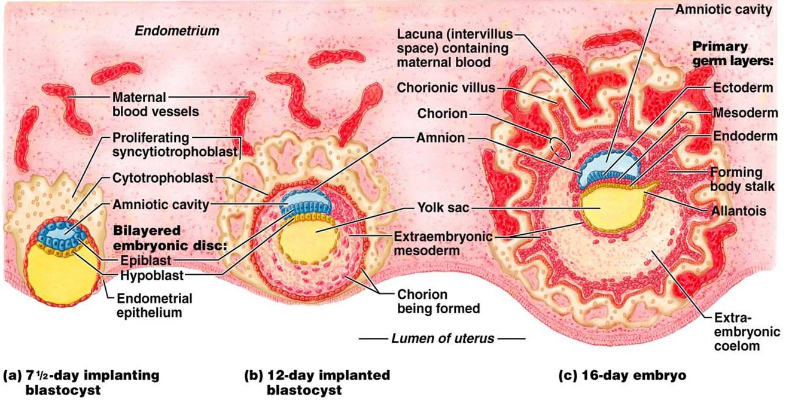
why is it important that the embryos secretes HCG?
HCG is only produced in pregnancy by the outer cells of the embryo and also by the placenta after placenta has been developed. Its function is to maintain/thicken endometrium during pregnancy. If endometrium is not maintained, menstruation will begin, it will shed, and cause a miscarraige.
Why is HCG the ideal hormone to use in pregnancy testing?
Because it is only produced in pregnancy.
when the corpus luteum disintegrates around the 9th week of pregnancy what structure takes over the production of estrogen and progesterone?
Placenta
how is the process of giving birth an example of positive feedback?
Drink childbirth contractions will start which will stimulate the production of oxytocin from the pituitary which will cause more contractions which will stimulate more oxytocin to be produced.
how does the placental barrier of placenta allow for the exchange of material between the fetus and the mother's blood? What types of material needs to be exchanged?
Around the terminal villi in the intervilus space.
Oxygen and CO2(simple diffusion/high to low conc.), glucose(facilitated diffusion), hormones and antibodies(bulk transport, chorionic villi, endocytosis, vesicles, exocytosis to fetal blood supply) to the fetus. urea, waste, hormones to mother
Water moves by osmosis, high to low concentration.
Describe the difference between precocial and altricial strategy of gestation Give an example of an animal that uses each strategy.
An example of a precocial species would be ducks after hatching their offspring are able to move around by themselves after birth. An example of an altricial offspring would be humans as we are not able to fend for ourselves after birth.
what is HRT?
HRT is hormone replacement therapy and is/was commonly used in older woman going through menopause and also in transgender persons. It was thought to have alleviated the symptoms of menopause by process of administering estrogen to menopausal women to alleviate their symptoms of a lack of estrogen during menopause. However it was found that it was actually a carcinogen and contributed to heart higher rates of cardiac disease. The only reason it was thought to have helped with the symptoms of menopause was because the studies were only done on higher economic class woman.