05.M BIO Fermentation (PART M)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Fermentation (Description)
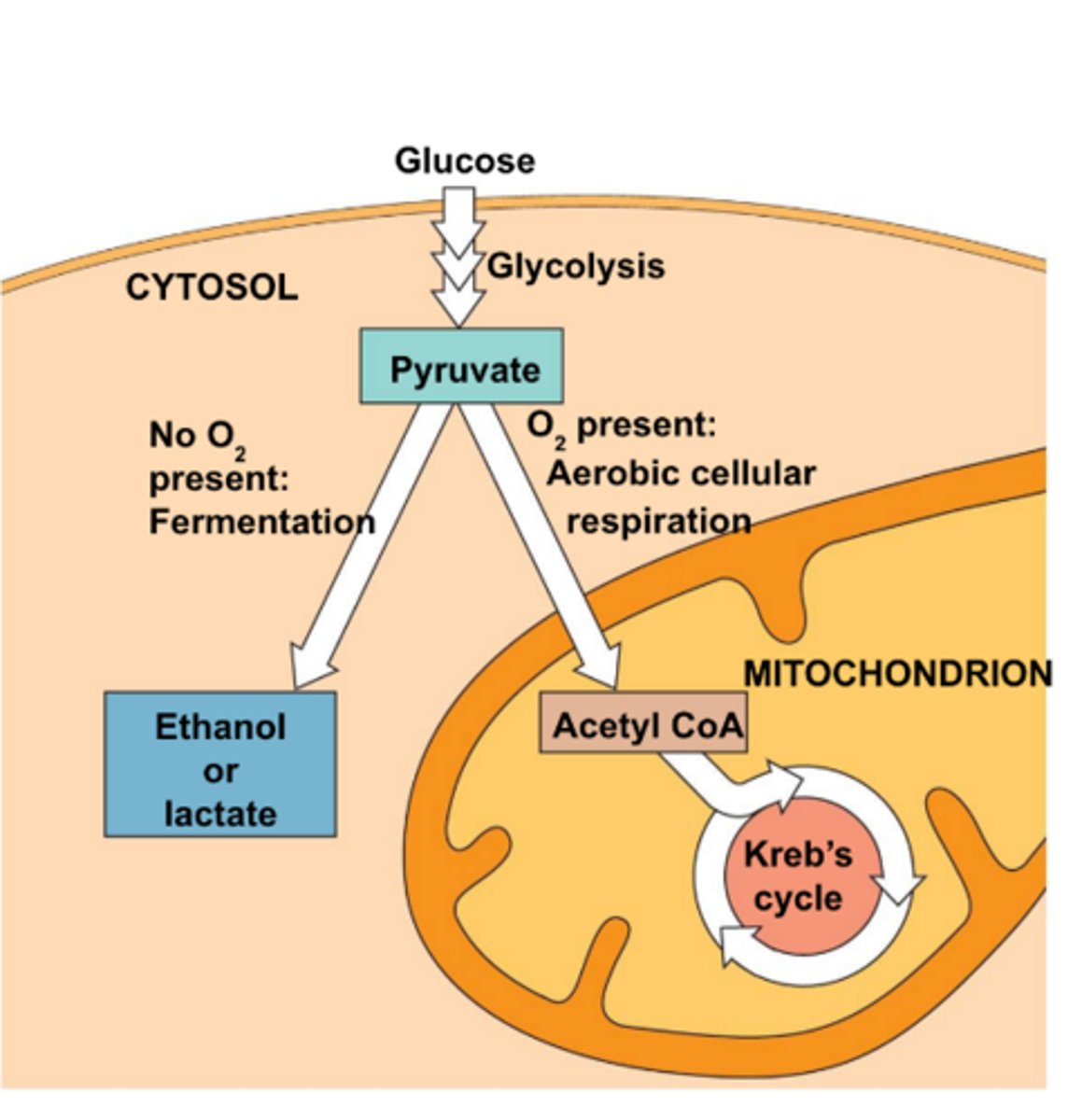
A process by which energy can be released from food molecules in the absence of oxygen
Follows glycolysis and converts NADH produced in glycolysis back into the electron carrier NAD+, which allows glycolysis to continue producing ATP
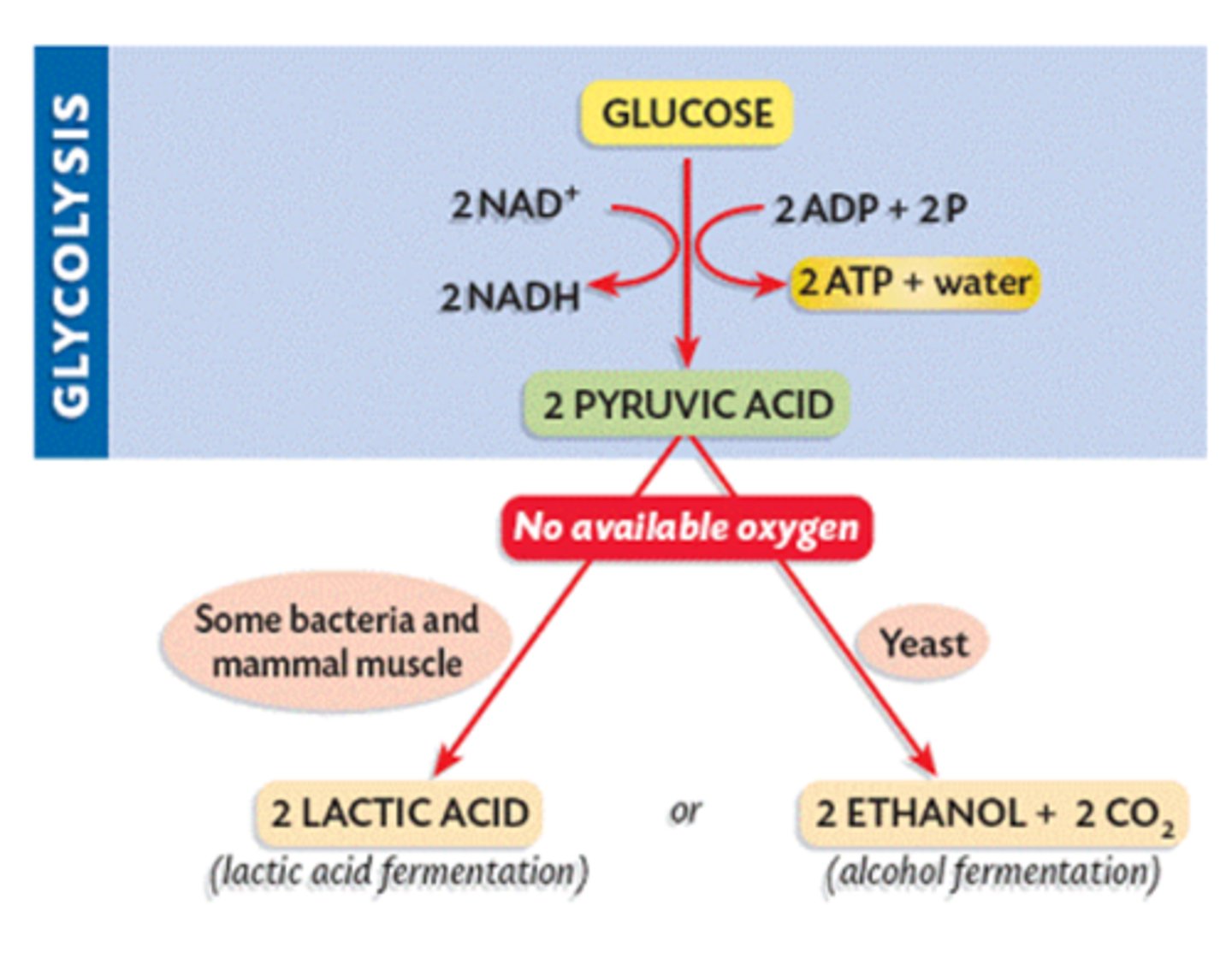
Fermentation (Location)
Occurs in the cytoplasm of cells
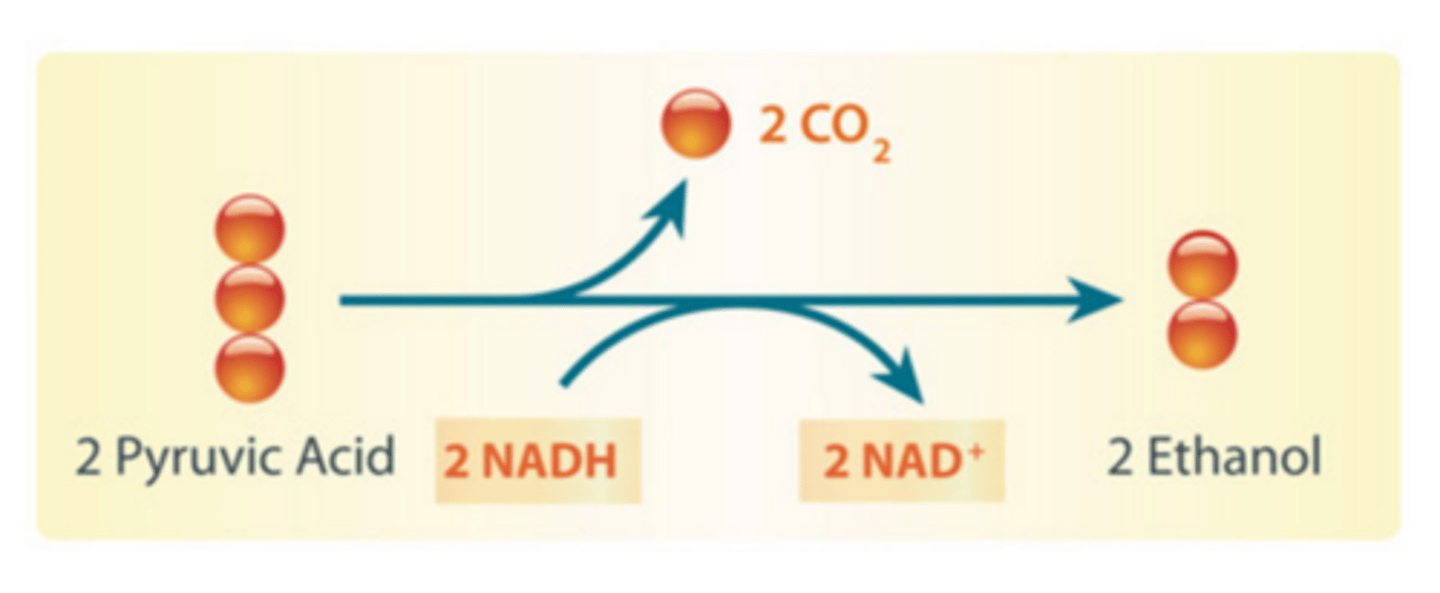
Ethyl alcohol
2-carbon molecule produced as a result of alcoholic fermentation
Also known as ethanol
Alcoholic fermentation (Description)
An anaerobic process that produces ethanol.
Alcoholic fermentation (Organisms)
Yeast and a few other microorganisms (some bacteria)
Alcoholic fermentation (Human uses)
Humans use to produce alcoholic beverages and causes bread dough to rise
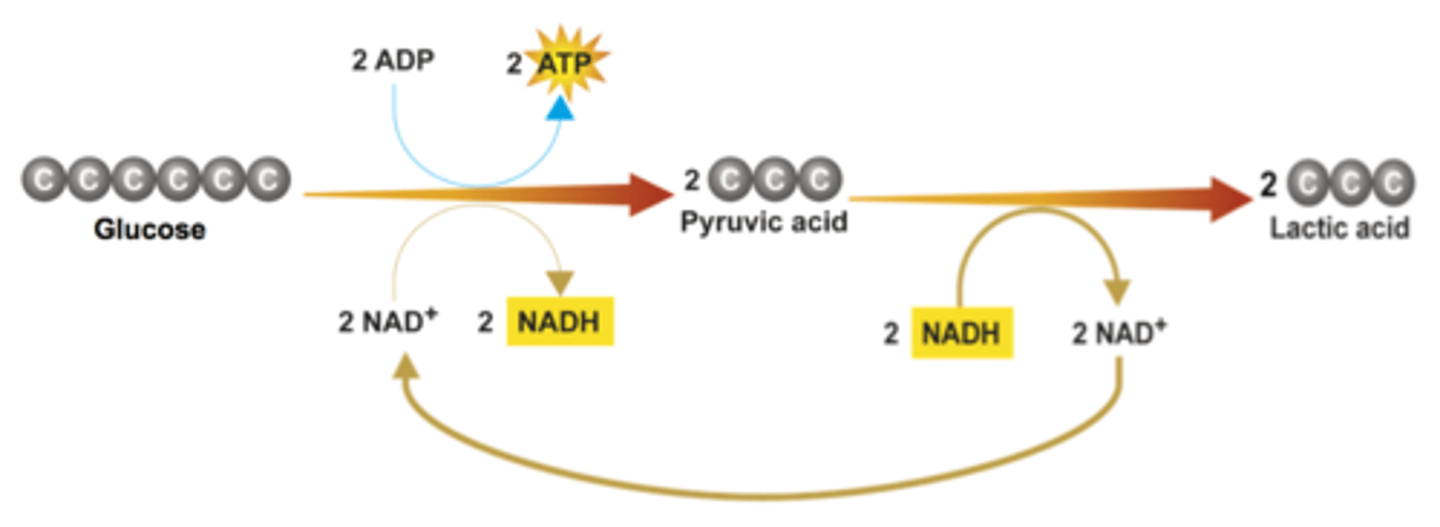
Lactic acid
3-carbon molecule produced as a result of lactic acid fermentation
Also known as lactate
Lactic acid fermentation (Description)
An anaerobic process that converts pyruvic acid to lactic acid in the absence of oxygen
Lactic acid fermentation (Organisms)
Occurs in bacteria, fungi and humans
Lactic acid fermentation (Human uses)
Humans use to make cheese and yogurt
Energy Use in Humans
For short, quick bursts of energy, the body uses ATP already in muscles as well as ATP made by lactic acid fermentation. For exercise longer than about 90 seconds, cellular respiration is the only way to continue generating a supply of ATP.
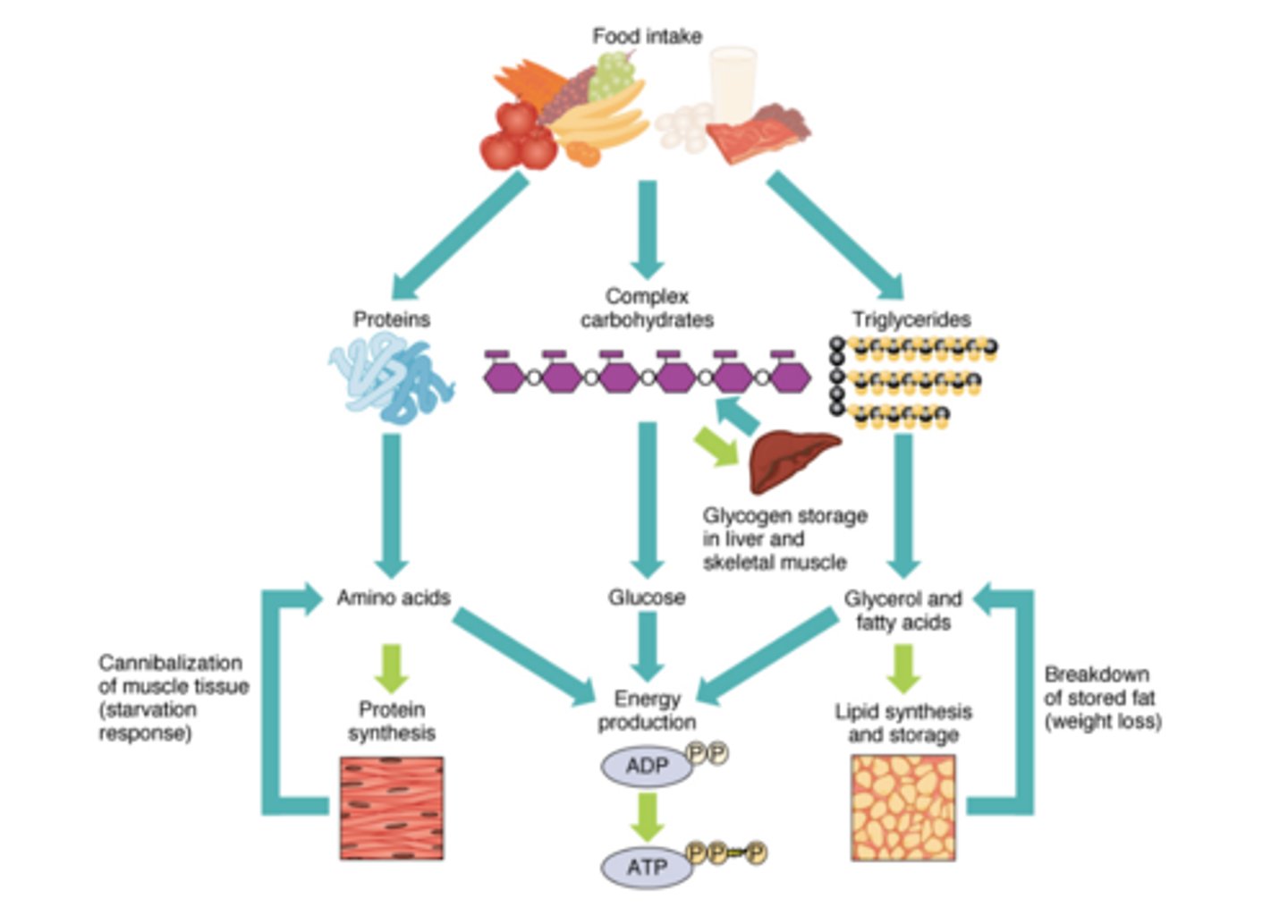
Short-term Energy Use in Humans
Cells normally contain small amounts of ATP produced during cellular respiration, enough for a few seconds of intense activity. Lactic acid fermentation can supply enough ATP to last about 90 seconds.
Long-term Energy Use in Humans
Humans store energy in an intermediate form called glycogen and a long-term storage as lipids
Glycogen
Intermediate storage form of energy in humans that consists of long chains of glucose that can last for 15 to 20 minutes of activity
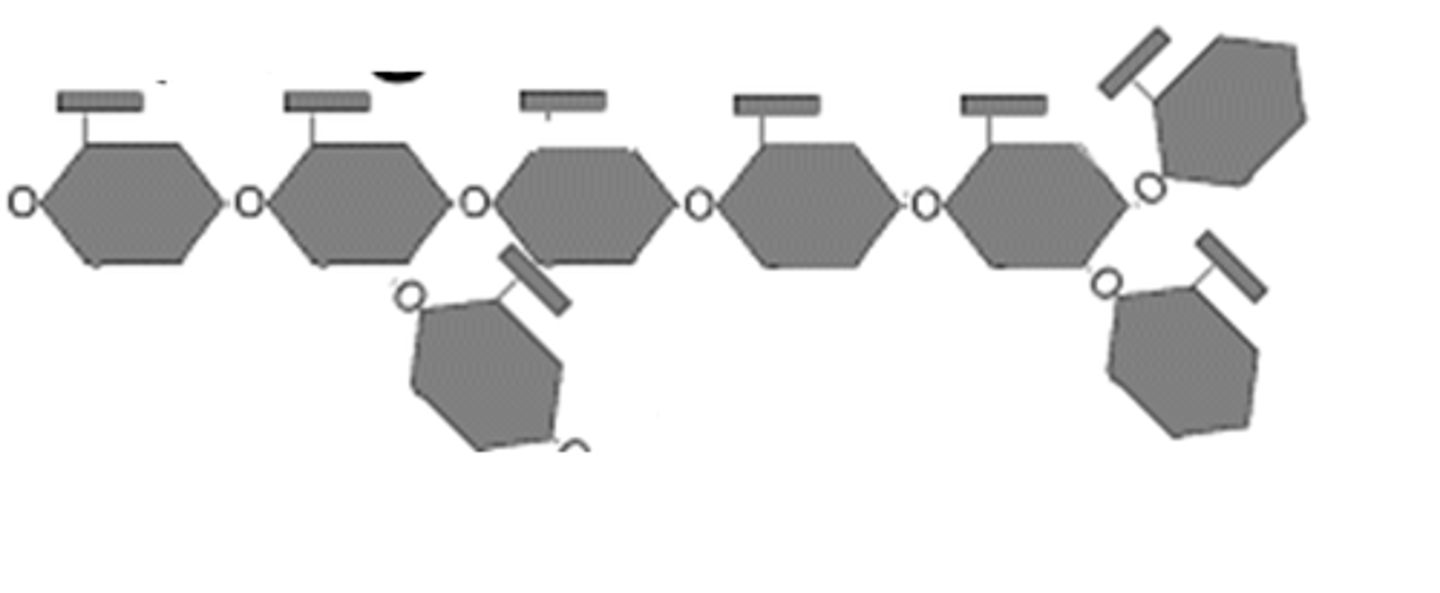
Lipids
Long-term energy storage in humans that are used when other forms of energy, including glucose and glycogen are used up
