NUR 355 Exam 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What is cutaneous pain?
derived from skin surface and subcutaneous tissues; injury is superficial, with a sharp, burning sensation
What is referred pain?
pain felt in a part of the body other than its actual source
What is neuropathic pain?
- pain that arises from abnormal or damaged pain nerves [e.g., phantom limb pain, pain below the level of a spinal cord injury, diabetic neuropathy];
- usually intense, shooting, burning, or "pins and needles"
What is visceral pain?
Originating from interior organs
Aching, Poorly localized, Often accompanied by autonomic responses (vomiting, nausea, pallor, diaphoresis)
What does a low neutrophil count indicate?
usually indicates an autoimmune disease, chemotherapy, or a bone marrow disorder; HIGH RISK FOR INFECTION BY OPPORTUNISTIC PATHOGENS
What is the normal neutrophil level?
Why are pain specialists used?
If the cause of the pain is known (or unknown), serious disease excluded, no curative treatment is readily available, current treatment is not helping, or the pain interferes with daily function
What labs would be positive in urosepsis?
positive urine culture, positive blood culture, low WBC's, high serum lactate, high C-reactive protein
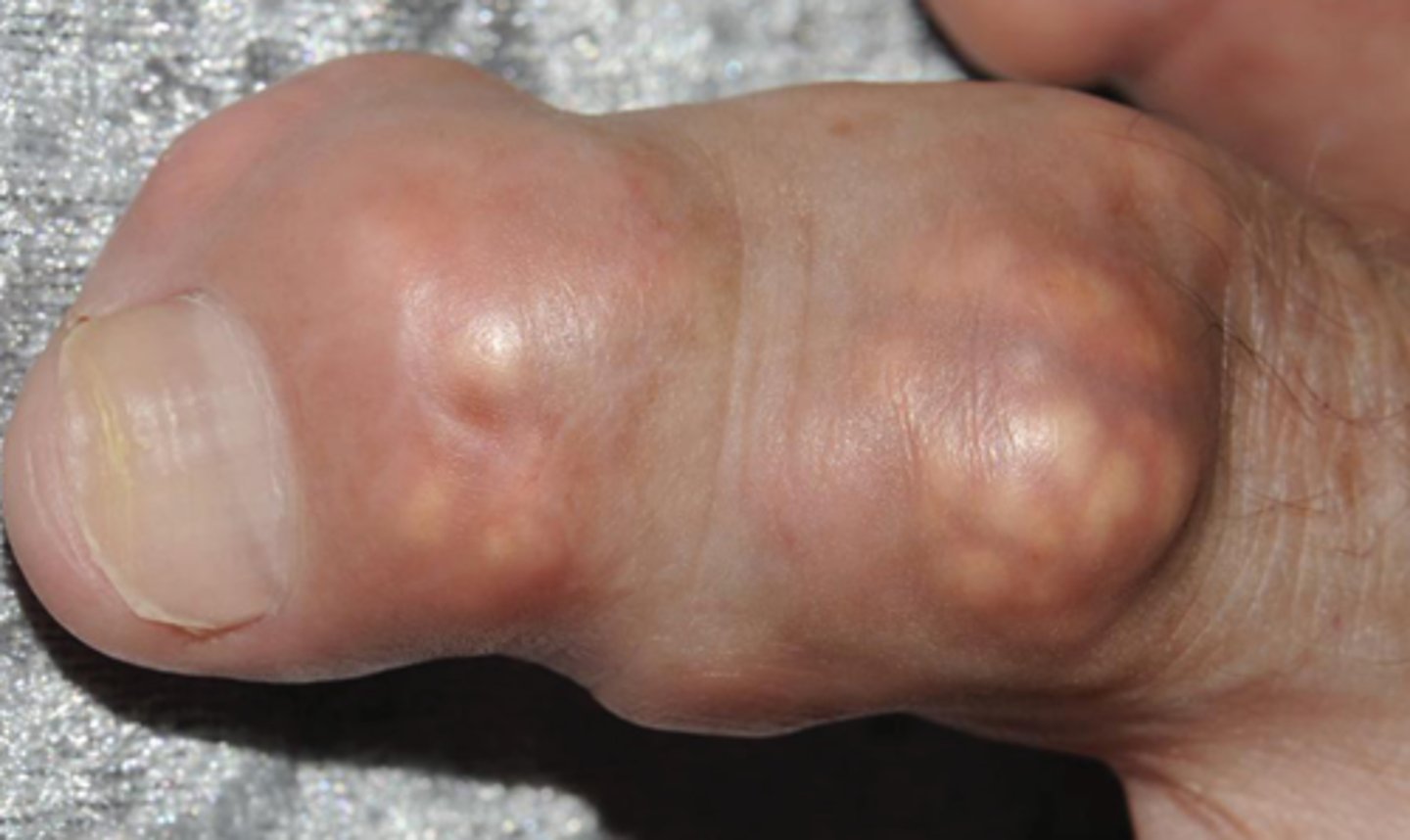
What are tophi?
White chalky aggregates of uric acid crystals with fibrosis and giant cell reaction in soft tissues and joints; seen in gout
Why are mental changes in HIV+ patients concerning?
HIV can trigger inflammation that can damage the brain and spinal chord, higher risk for sepsis, higher risk for CNS infection and malignancies; CHANGES CAN INCLUDE CONFUSION AND DELERIUM
What does pain look like in dementia patients?
Constant pacing, moving or unwillingness to sit down. Moaning, crying, sighing and even heavy breathing. Frowning, grimacing or a furrowed brow. Sleeping all day or not being able to sleep.
What is leukocytosis?
high WBC count (above 10,000)
what is the normal leukocyte range?
5,000-10,000
Who cannot receive live vaccines? why?
pregnant women, PT's with a high fever, and immunocompromised; they are susceptible to actually being infected by the live attenuated pathogens
- people allergic to eggs cannot get the flu shot
What is the pathology of gout?
high uric acid levels within the blood begin to deposit within the synovial fluid filled joints, frequently beginning with the big toe; known as an inflammatory arthritis
What is the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis?
-chronic, systemic, inflammatory autoimmune disease
-exaggerated immune response
-neutrophils degrade surface layer of cartilage -inflammatory cytokines breaking down cartilage and bone then T-cells
-fibroblasts to turn into a thick abnormal layer of tissue
-inflammation is constant and spreads to ALL synovial joints
What is the pathology of osteoarthritis?
Caused by wear and tear of hyaline cartilage to the point where it is worn away.
What is the pathology of lupus?
autoimmune disorder characterized by multisystem inflammation with the generation of autoantibodies; development is frequently associated with retroviruses, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and HIV type 1 virus
What are some type 1 hypersensitivity reactions?
- immediate reaction
- anaphylaxis, allergic rhino-conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma, allergic dermatitis
What are some type 2 hypersensitivity reactions?
- antibody mediated immune reaction in which antibodies and directed against cellular or extracellular matrix antigens; results in CELL LYSIS or damage to cells or tissues
- forms of anemia, blood transfusion reactions myasthenia gravis, Rh+/Rh-, certain platelet disorders, and some types of tissue transplant rejection.
What are some type 3 hypersensitivity reactions?
- abnormal immune response
- vasculitis (skin), serum sickness (systemic), RA, and Lupus; immune complexes deposit in various tissues
What are some type 4 hypersensitivity reactions?
- Delayed Hyper-sensensitivity
- contact dermatitis, latex allergy or in response to some diagnostic procedures as in the tuberculin skin test
What is the pathology of fibromyalgia?
stress-related disorder that involves abnormal functioning in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Similarly to other psychiatric disorders, fibromyalgia has been associated with the inability to suppress cortisol; widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues
What is the first thing you should do if a patient is having an allergic reaction to an IV infusion?
stop the infusion, remove the tubing, protect the airway, call for rapid response, apply O2 and pulse ox; do not need to remove IV as its important to maintain access if they go into shock
What are the s/s of anaphylaxis?
Tachycardia, hypotension, wheezing, swallowing difficulties, angioedema that starts at the face and moves down the airway. (No peripheral edema)
What position is used for SOB?
high fowler's position or orthopenic position
What are eosinophils?
disease fighting WBCs; often related to severe allergic reactions
What are neutrophils?
WBC's that ingest and destroy microbes in a process called phagocytosis; usually first one to injury site
What are basophils?
make up less than 1% of all circulating WBCs, have the ability to detect and destroy some early cancer cells
What are lymphocytes?
b cells (which produce antibodies that are used to attack invading pathogens) and t cells (focus on specific foreign particles)
What are monocytes?
long life span, and break down bacteria
What is the role of neutrophils that we should know?
first to respond to viruses and bacteria
what is the role of eosinophils that we should know?
known for their role in allergy symptoms
what is the role of basophils that we should know?
known for their role in ashtma
what is the role of monocytes that we should know?
clean up dead cells
What is the role of lymphocytes that we should know?
fight infection by producing antibodies
What are the tests for lupus?
positive ANA
What does lupus affect?
everything; tons of pain
what is the treatment for lupus?
Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, steroids and other immunosuppressants for acute flare-ups; needs to be seen by a rheumatologist; fluoroquinolones
What lab values can be affected by lupus?
all organ function, but specifically kidney function (the complexes formed in the blood can be deposited into the kidneys and lower kidney function; look at creatine)
symptoms of lupus
butterfly shaped rash on chin & cheeks, pericarditis, pleuritis, extreme fatigue, painful or swollen joints, and kidney problems.
Who is at high risk for lupus?
women and african americans
PT teaching for lupus
eat small frequent meals
What is something that should be assessed regularly when a lupus patient is taking a fluoroquinolone?
eye function (fluoroquinolones are known to cause blurred vision and can impair thinking and ractions)
What are s/s of inflammation?
redness, heat, swelling, pain, loss of function
What s/s are seen with RA?
pain, boutonnières, swan neck deformation, ulnar deviation, affects body bilaterally
What s/s are seen with OA?
pain, herberten's nodes, boucharde's nodes, usually is unilateral unless there is equal use of joints of both sides
RA treatments
use heat therapy to loosen up joint, inflammatory modifying agents such as corticosteroids, NSAIDs for pain and inflammation
OA treatments
little bit of GENTLE movement such as walking or swimming, NSAIDs for pain
what are the s/s of gout?
sudden severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in one or more joints; often wakes patient in the middle of the night with a burning sensation which is the most severe for the first 4-12 hours, discomfort will linger for days to weeks; with progression, joint ROM can become limited
What cannot be used to relieve gout pain?
aspirin
What are some risk factors for gout?
- diet: eating lots of red meat and shellfish, drinking beverages sweetened with fructose, consuming alcohol but especially beer
- weight: being overweight
- medical conditions: untreated hypertension, diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and kidney disease
- meds: low dose aspirin, some hypertension meds (ACE inhibitors and beta blockers), anti-rejection drugs
- family Hx of gout
- being male (usually develop between 30-50) or being a woman after menopause
- recent surgery or trauma
Diagnostic lab for gout
uric acid above 6.5; should also check creatinine levels to check for uric acid deposits in the kidney's than can result in kidney stones or failure
What diseases require contact precautions?
MRSA, VRE, scabies, RSV, C. Diff., herpes
What diseases require droplet precautions?
influenza, mumps, strep, pneumonia
What diseases require airborne precautions?
measles, varicella, TB
What PPE is included in contact precautions?
gown and gloves for contact with person and environment, remove PPE before leaving room
What PPE is included in droplet precautions?
surgical mask when within 3-6 ft of PT plus standard precautions; remove PPE inside of room
What PPE is included in airborne precautions?
respirator and face shield plus standard precautions; remove PPE outside of the room
What is SIRS?
systemic inflammatory response syndrome; category of sepsis with very subtle changes
What are the signs a patient has developed SIRS?
have two of the following
- fever >38.0°C or hypothermia <36.0°C
- tachycardia >90 beats/minute
- tachypnea >20 breaths/minute,
- leukocytosis >12*109/l or
- leucopoenia <4*109/l
What is sepsis?
met SIRS criteria AND have a confirmed infection
S/s of sepsis?
•Rapid breathing and heart rate.
•Shortness of breath.
•Confusion or disorientation.
•Extreme pain or discomfort.
•Fever, shivering, or feeling very cold.
•Clammy or sweaty skin.
What is important to do before treating sepsis?
obtain a serum lactate and 2 cultures before antibiotic treatment
what does a serum lactate level tell you?
measures the amount of lactic acid in the blood and is a fairly sensitive and reliable indicator of tissue hypo-perfusion and hypoxia
What is septic shock?
sepsis and hypotension; fluid challenge of 30 mL IV fluids given and if their BP does not rise, this indicates septic shock
What should we remember about epi-pens?
- check fluid to ensure no changes in the color or opacity of the liquid
- monitor PT's for HR, cardiac rhythm, and BP
- NO ABSOLUTE CONTRAINDICATIONS because not using it can result in death
- some relative contraindications include hypersensitivity to sympathomimetic drugs (agents that mimic responses of sympathetic nerves), closed angle glaucoma, and anesthesia w/ halothane (can result in ventricular dysrhythmias)
How to administer an epipen?
- pull off blue safety release
- hold leg still and place orange end against outer mid thigh
- push down HARD until click is felt, hold in place for 3 seconds then remove
What is HIV?
HIV is a virus that affects the immune system and eventually causes AIDS
How do people die with HIV/AIDS?
they get an infection that they cannot fight off
What is the number one nursing intervention for HIV/AIDS?
patient education! encourage adequate nutrition w/ high protein, encourage taking prescribed antivirals to prevent viral replication, educate on the importance of using a barrier style protection when engaging in intercourse
What is the diagnostic level for AIDS?
CD4 level below 200
What is natural immunity?
acquired as part of normal life experiences such as infection or breastfeeding
what is artificial immunity?
acquired through a medical procedure such as a vaccine or blood transfusion
What is active immunity?
the immunity that results from the production of antibodies by the immune system in response to the presence of an antigen. examples: infection OR vaccination
What is passive immunity?
short term immunity using antibodies produced outside the body; example: mother gives baby antibodies through breast milk but these antibodies don't last much longer than the baby is breastfeeding OR monoclonal antibodies being passed through a blood transfusion
what is the treatment for fibromyalgia?
gabapentin or other nerve pain meds, self-care, antidepressants (which boost neurotransmitters such as serotonin, noradrenaline, and dopamine that reduce sensation of pain and relieve depression associated with chronic pain. PT's w/ fibromyalgia have been found to have low levels of these neurotransmitters)
What is the most common spot for MRSA infections?
small cuts in the hand or on the face
How is Acinetobactor baumannii spread?
because it can live for a long time on wet and dry surfaces, it is frequently spread in hospitals via contamination
what are some risk factors for C. diff?
- Use of antimicrobials
- Age > 64 years
- Immunosuppression