Vertebrate Zoology Flashcards
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key topics in vertebrate zoology, including reproduction, feeding, locomotion, respiration, skin, evolution, skeletal systems, and classification.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the female reproductive organs in sharks and rays, and their reproductive modes?
Paired ovaries, oviducts with shell glands, and uteri. Modes include oviparity (egg-laying), ovoviviparity (eggs hatch internally), and viviparity (live birth with placental or yolk sac support).
Describe the reproductive anatomy of birds from copulation to egg laying.

Males transfer sperm via cloacal contact. Fertilization occurs in the infundibulum; eggs pass through the magnum (albumen), isthmus (shell membranes), and uterus (calcareous shell) before oviposition via cloaca.
What are key differences between prototherians and therian mammals?
Prototherians are oviparous, possess cloacae, and lack nipples. Therians (marsupials like Macropus, eutherians like Homo sapiens) are viviparous with varying placental complexity.
Why do mammals have differentiated (heterodont) dentition?
To perform specific roles: incisors (cutting), canines (piercing), premolars/molars (grinding). Reflect dietary adaptation, allowing mechanical breakdown, slicing, or food grinding for efficient digestion and niche specialisation.
Name the organs of the mammalian digestive system and note any specialisations.
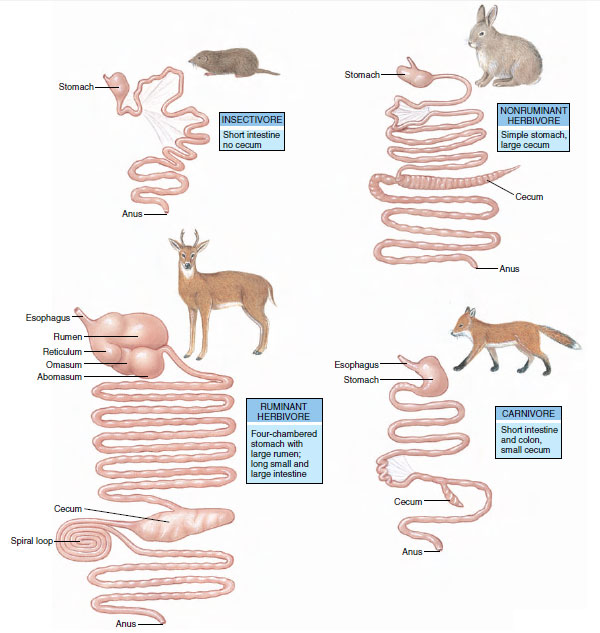
Mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, liver, pancreas. Herbivores (e.g., ruminants) have multi-chambered stomachs for microbial fermentation (e.g., rumen); carnivores have enlarged stomachs with low pH for proteolysis and shorter intestines to digest proteins.
Describe 5 specialist mammalian feeding adaptations.
Baleen in whales, long tongues in anteaters, hypsodont teeth in grazers, venom delivery in monotremes, tool use in primates.
Describe feeding adaptations in birds from capture to excretion.

Beak shape reflects diet; crop stores food; gizzard grinds it; cloaca excretes uric acid with minimal water loss.
What is the anatomy of a bird wing and how do muscles enable flight?
Forelimb modified into wing with humerus, radius, ulna, carpometacarpus. Pectoralis muscle powers downstroke, supracoracoideus powers upstroke via triosseal canal.
What are key anatomical adaptations for bird flight?
Keel on sternum, air sacs, lightweight skeleton, fused vertebrae, and feathers.
Compare locomotory adaptations across mammals.

Cursorial for speed, fossorial for digging, volant for flight, aquatic for swimming, arboreal for climbing.
Describe the structure and function of shark gills.
Water passes over gill filaments containing capillaries for gas exchange via countercurrent flow. Some use buccal pumping or ram ventilation.
What limitation does the turtle shell place on ventilation?
Fused ribs prevent thoracic expansion, so turtles rely on muscle contractions around the viscera and limb movement.
Did lungs first evolve in tetrapods?
No. Primitive lungs appeared in sarcopterygian fish (e.g., lungfish).
How do frogs change skin colour?
Using chromatophores: melanophores (dark), xanthophores (yellow), and iridophores (reflective). Controlled by hormones and neural signals.
What are functional features of amphibian skin?
Permeable for cutaneous respiration, contains mucus glands to retain moisture and poison glands for defence.
Compare the skin of sharks and frogs.

Sharks: dermal denticles reduce drag. Frogs: thin, moist, glandular skin facilitates gas exchange and water balance.
What do anatomical differences between sharks and dolphins indicate?

Convergent evolution: both have streamlined bodies and fins, but sharks are fish; dolphins are mammals.
What adaptations are needed for aquatic vertebrates to live on land?
Lungs, limb-based locomotion, impermeable skin, internal fertilisation, and sensory changes.
Compare vertebrate adaptations for air vs water.
Air: lungs, strong limbs, keratinised skin. Water: gills, fins, lateral line, reduced gravity effects.
Give examples of herbivorous dinosaurs and their skeletal specialisations.
Triceratops, Stegosaurus, Iguanodon, all for defence or display.These dinosaurs had specialized jaws and teeth for processing plant material, with features such as strong, column-like legs for support and a stable posture.
What theropod features are similar to modern birds?
Hollow bones, feathers, furcula (wishbone), three-toed limbs, and potential for brooding behaviour.
What are the parts of the turtle shell and how do they vary?

Carapace (dorsal), plastron (ventral), both made of dermal bone. Variants include reduced ossification and hinged plastrons.
What are the main characteristics of prototherian and therian mammals?
Prototherians are egg-laying, lack nipples, and retain cloaca. Therians give live birth, have nipples, and possess distinct urogenital openings.
What does comparative anatomy across vertebrates reveal?
Homologous structures show common ancestry, while analogous structures reveal functional convergence.