Economy Exam 1 Practice
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Production Possibilities Frontier
Given two goods, which combination of the goods are feasible, efficient, and/or unreasonable.
Opportunity Cost
What must be given up to pursue a particular chosen activity.
The Opportunity Cost of one additional unit of Good X
( # of units of Good Y lost )/( # units of Good X gained)
Opportunity Costs of a Linear PPF
OCs are constant along a linear PPF, because all resources are equally suited to producing both goods.
Opportunity Costs of a Bowed Out PPF
OCs are increasing along a Bowed Out PPF, because not all resources are equally suited to producing both goods.
Absolute Advantage
A firm has an Absolute Advantage in producing a particular good or service if it can produce more units of that good or service than other firms.
Comparative Advantage
A country has a Comparative Advantage in producing a particular good or service if it can do so at a lower opportunity cost than other countries.
Demand
The relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded of that same good or service, all else held equal.
What counts in “Quantity Demanded”?
Consumers want this quantity at the price.
Consumers can afford this quantity at the price.
Consumers would purchase this quantity if offered at the price.
Allocating Limited Income Elsewhere
Sometimes people “cant afford” something, not because they don’t have the monetary funds required, but because that cannot afford other important things if they had bought it.
Normal Good
A good with demand determined by consumers income in a positive relationship, that is, if a consumer’s income increases, they will spend more on this good.
Inferior Good
A good with demand determined by consumers income in a negative relationship, that is, if a consumer’s income decreases, they will spend more on this good.
Substitutes
A good with demand determined by the prices of related good in a positive relationship, that is, if a good’s price increases, then the demand for a substitute good increases.
Ex: price of cookies go up, demand for brownies go up
Compliment
A good with demand determined by the prices of related goods in a negative relationship, that is if the price of a good decreases, the demand for a complimentary good decreases.
Ex: price salsa goes down, demand for chips goes up.
Demand Shifters
Consumer’s incomes
Normal Good (+)
Inferior Good (-)
Prices of related goods
Substitutes (+)
Compliments (-)
Preferences and Advertising
The availability of credit
Expected Future Price
Supply
The relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied by firms of that same good or service, all else held equal.
Law of Demand
The demand curve is downward sloping. As the price of a good or services rises (falls), the quantity demanded decreases (increases).
Law of Supply
The supply curve is upward sloping. As the price of a good or service falls (rises) the quantity supplied decreases (increases).
Why does the supply curve have a positive slope?
As the quantity supplied increases, the per-unit costs of production may rise. Firms would then require higher prices to increase their output quantity.
As the price of a good rises, more firms change to enter the market, which increases the total quantity supplied.
Supply Shifters
cost of production/price on essential inputs (-)
technological advancements (+)
prices of related goods in production
substitutes in production
compliments in production
state of nature
changes to the expected future price
Market Equilibrium
the price of a good or service at which the quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
When the price is below the equilibrium…?
The quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
There is a shortage of a good or service.
The price will rise towards the equilibrium price.
When the price is above the equilibrium price..?
The quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
There is a surplus of the good or service.
The price will fall toward the equilibrium price.
Consumer Surplus
Measures the additional well-being that consumers enjoy when they purchase a specific good or service.
Calculated as the difference between the consumers maximum willingness to pay for a good or service and the price that they actually pay.
Producer Surplus
Measures the additional well-being enjoyed by firms when they sell a good or service.
Can be measured as the difference between the firms minimum willingness to accept the price they actually receive.
The total amount of Consumer Surplus is:
Below the demand curve
Above the price
Out to the quantity consumers purchased
The total amount of Producer Surplus is:
Below the price
Above the supply curve
Out to the quantity that sellers actually sell
Price Ceiling
A maximum allowable price for a specific good or service that is set by the governments. It only has an affect if set below the equilibrium price.
Deadweight loss
Reduction in total surplus.
Excise Tax
specified tax per unit. Ex: fueling your car/federal gas tax
Ad valorem tax
Percentage based tax. Ex: sales tax, personal income tax.
Exports
Domestically produced goods and services that are produced by foreign consumers.
Imports
Goods and services that are produced abroad but consumed by domestic consumers.
When we import a good or service, the domestic production of that good or service decreases. Domestic employment in that sector is reduced, but not employment generally.
Tariffs
A tax on imported goods.
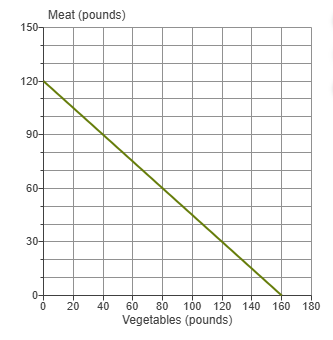
Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the production possibilities frontier for Mendonca, an agrarian nation that produces two goods, meat and vegetables. What is the opportunity cost of one pound of meat?
1\frac13 pounds of vegetables
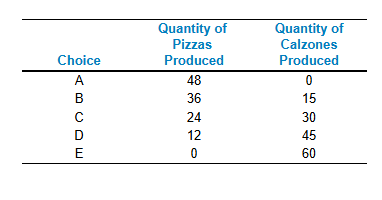
Refer to the table. Assume that Tomaso's Trattoria only produces pizzas and calzones. A combination of 24 pizzas and 15 calzones would appear
Inside Tomaso’s production possibilities frontier
Harry produces 7 balloon rides and 10 boat rides an hour. Harry could produce more balloon rides without producing fewer boat rides.
Is Harry producing on his production possibilities frontier?
Harry is producing inside the production possibilities frontier.
The production possibilities frontier model shows that:
If all resources are fully and efficiently utilized, more of one good can be produced only by producing less of another good.

Huey and Steve can grow potatoes or tomatoes. The table above shows the pounds of potatoes and tomatoes Huey and Steve can grow in a week. Based on the table, Steve has a comparative advantage in:
Potatoes.
The attainable production points on a production possibility frontier are:
the points along and inside the production possibility frontier.
If the production possibilities frontier is ________, then opportunity costs are constant as more of one good is produced.
linear
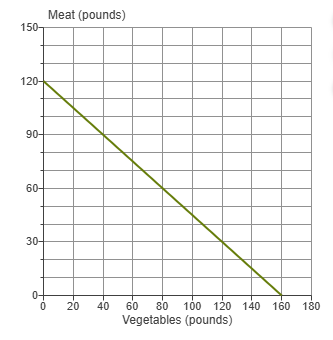
Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the production possibilities frontier for Mendonca, an agrarian nation that produces two goods, meat and vegetables. What is the opportunity cost of one pound of vegetables?
\frac34 pounds of meat.

Huey and Steve can grow potatoes or tomatoes. The table above shows the pounds of potatoes and tomatoes Huey and Steve can grow in a week. Based on the table, Huey's opportunity cost of producing one pound of tomatoes is:
1.5 pounds of potatoes
Increasing opportunity cost is represented by a ________ production possibilities frontier.
bowed out
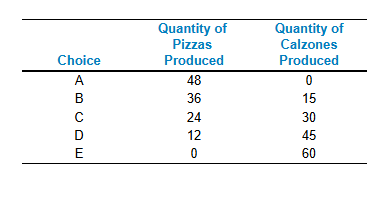
Refer to the table. Assume that Tomaso's Trattoria only produces pizzas and calzones. Tomaso faces ________ opportunity costs in the production of pizzas and calzones.
constant
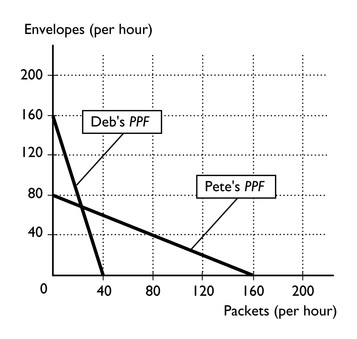
Deb and Pete have volunteered to help their favorite charity mail out fundraiser information. The figure shows their production possibilities frontiers for assembling packets and stuffing envelopes. Which of the following statements is correct?
Deb has a comparative advantage in stuffing envelopes.
A substitute is a good that is _____ another good, and a complement is a good that is _____ another good.
consumed in place of; consumed together with
During the Covid-19 lockdown, yeast's popularity increased as millennials and home chefs were willing and able to spend more time cooking.
Did yeast's increased popularity increase demand or the quantity of yeast demanded?
Yeast’s popularity increased by ______.
the demand for yeast and the demand curve for yeast shifted rightward
Donuts and chocolate chip cookies are substitutes.
If the price of a donut increases, how does the demand for chocolate chip cookies change?
If the price of a donut increases, the demand for chocolate chip cookies will _______.
increase, and the demand curve for chocolate chip cookies will shift rightward
As the price of a gym membership decreases, the quantity of bottled water that people buy increases.
How do we categorize gym memberships and bottled water?
We categorize gym memberships and bottled water as ______.
compliments
As Gustavo’s income increases, his demand for T-shirts decreases.
What type of good are T-shirts for Gustavo?
For Gustavo, T-shirts are _____.
inferior goods
Demand is _____, when all other influences on buying plans remain the same.
the relationship between the quantity demanded of a good and the price of the good
Why does demand not change when the price of a good changes with no change in the other influences on buying plans?
Consider the demand for pasta.
The demand for pasta does not change when a change in _______ occurs.
the price of pasta
Why does demand not change when the price of a good changes with no change in the other influences on buying plans?
Consider the demand for pasta.
An increase in the price of pasta _______.
decreases the quantity of pasta demanded and results in a movement up along the demand curve for pasta
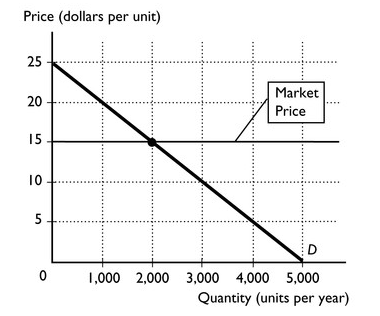
In the figure above, at the market price of $15, the consumer surplus equals
$10,000
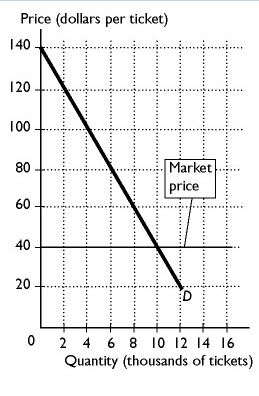
The figure on the right shows that for the 8,000th ticket, the marginal benefit is ____ and the consumer surplus is _____.
$60, $20.
Does an increase in the demand for hot dogs bring a surplus or a shortage of hot dogs at the original price? How does the market price change as the market moves to its new equilibrium?
An increase in the demand for hot dogs brings a_______ of hot dogs at the original price and the market price will_______.
shortage; rise
Does an increase in the supply of ramen noodles bring a surplus or a shortage of ramen noodles at the original price? How does the price change as the market moves to its new equilibrium?
An increase in the supply of ramen noodles brings a_______ of ramen noodles at the original price and a_______ in their price.
surplus; fall
An increase in the demand for tank tops together with a decrease in the supply of tank tops occurs.
Is there a surplus or a shortage of tank tops at the original price? How does the price change?
An increase in the demand for tank tops together with a decrease in the supply of tank tops brings a _______ of tank tops at the original price and a _______ in their price.
shortage; rise
The price of fish fillets, a substitute in production of fish cakes, rises. What is the effect on the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of fish cakes?
An increase in the price of fish fillets, a substitute in production of fish cakes, will _______ the equilibrium price of fish cakes and _______ the equilibrium quantity of fish cakes.
increase; decrease
Assume that potatoes are an inferior good. Which of the following would cause both the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of potatoes to decrease?
an increase in consumer income
Which of the following would cause the equilibrium price to decrease and the equilibrium quantity of white bread to increase?
A decrease in the price of flour
An increase in the demand for lobster due to changes in consumer tastes, accompanied by a decrease in the supply of lobster as a result bad weather reducing the number of fishermen trapping lobster, will result in:
an increase in the equilibrium price of lobster; the equilibrium quantity may increase or decrease.
A decrease in the demand for soft drinks due to changes in consumer tastes, accompanied by an increase in the supply of soft drinks as a result of reductions in input prices, will result in
a decrease in the equilibrium price of soft drinks; the equilibrium quantity may increase or decrease.
Lucinda buys a new motorcycle helmet for $250. She receives consumer surplus of $75 from the purchase. What value does Lucinda place on her motorcycle helmet?
$325
Each point on a ________ curve shows the willingness of consumers to purchase a product at different prices.
demand
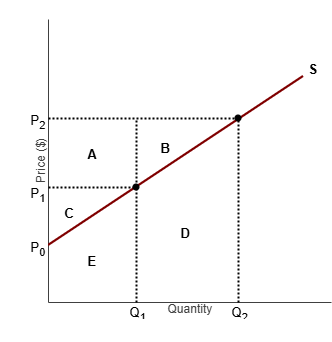
Refer to the diagram to the right. What area represents the increase in producer surplus when the market price rises from P1 to P2?
A + B
When a timber mill makes logs from trees it also produces sawdust, which is used to make plywood.
Explain how a rise in the price of sawdust influences the supply of logs.
A rise in the price of sawdust _______.
Explain how a rise in the price of sawdust influences the supply of plywood.
A rise in the price of sawdust _______.
increases the supply of logs; decreases the supply of plywood
As the price of a sports car increases, the quantity of sedans that firms plan to sell decreases, so sports cars and sedans are _______.
substitutes in production
The supply of chocolate bars will decrease if _______.
the number of chocolate manufactures decrease.
The price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied is the equilibrium price because _______.
the plans of producers and consumers are coordinated and there is no influence on the price to change
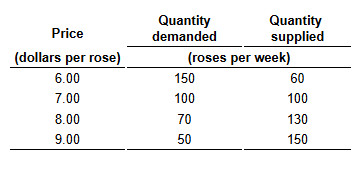
Rose sellers know that it's Mother's Day next weekend and they expect the price to be higher, so they withhold 60 roses from the market this weekend.
What is the price of a rose this weekend?
The price of a rose this weekend is____.
$8.
An increase in the price of bread, a complement in production of wheat bran, will _______ the equilibrium price of wheat bran and _______ the equilibrium quantity of wheat bran.
decrease; increase
A minimum wage set below the equilibrium wage _______.
has no effect on the equilibrium wage rate or the quantity of labor employed
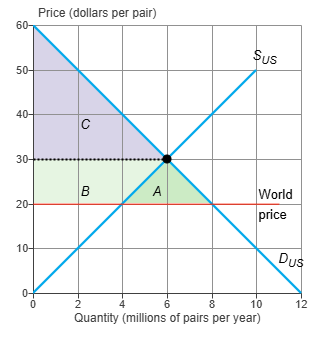
The graph shows the U.S. demand for and U.S. supply of shoes. The world price of a pair of shoes is $20. With free international trade, U.S. consumer surplus _______ and U.S. producer surplus _______.
increases by the area A + B; decreases by area B
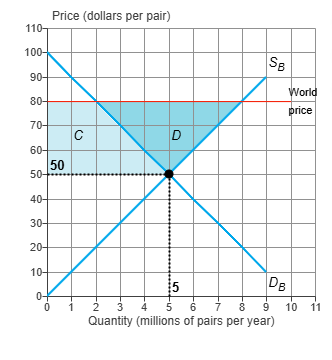
If the world price of a pair of shoes is $80 and Brazil opens up and trades internationally, producer surplus in Brazil _______ and consumer surplus in Brazil _______.
increases by area C + D; decreases by area C