CPCU 500
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/98
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
1
New cards
Sets of data that are too large to be gathered and analyzed by traditional methods
big data
2
New cards
An innovative item that uses sensors; wireless sensor networks; and data collection, transmission, and analysis to further enable the item to be faster, more useful, or otherwise improved.
smart product
3
New cards
A network of objects that transmit data to and from each other without human interaction.
Internet of Things (IoT)
4
New cards
Information, technology, and storage services contractually provided from remote locations, through the internet or another network, without a direct server connection.
cloud computing
5
New cards
A distributed digital ledger that facilitates secure transactions without the need for a third party.
blockchain
6
New cards
The use of technological devices in vehicles with wireless communication and GPS tracking that transmit data to businesses or government agencies; some return information for the driver.
telematics
7
New cards
Obtaining information through language recognition.
text mining
8
New cards
The use of emerging technologies in the insurance industry.
insurtech
9
New cards
A device that detects and measures stimuli in its environment.
sensor
10
New cards
Statistical and analytical techniques used to influence or prevent future events or behaviors.
preventive analytics
11
New cards
A device that converts one form of energy into another.
transducer
12
New cards
A mechanical device that turns energy into motion or otherwise effectuates a change in position or rotation using a signal and an energy source.
actuator
13
New cards
A device that measures acceleration, motion, and tilt.
accelerometer
14
New cards
A foundation for applying the risk management process throughout the organization.
risk management framework
15
New cards
Information used as a basis for measuring the significance of a risk.
risk criteria
16
New cards
The most experienced risk professionals understand how to exploit pure risk for upside.
false (Although risk professionals ultimately try to manage threats and opportunities holistically, not all individual risks have upsides. In fact, the defining feature of pure risk, which constitutes a significant portion of the risks that organizations confront, is that there is no associated chance of gain—only loss or no loss.)
17
New cards
just study this graph
\
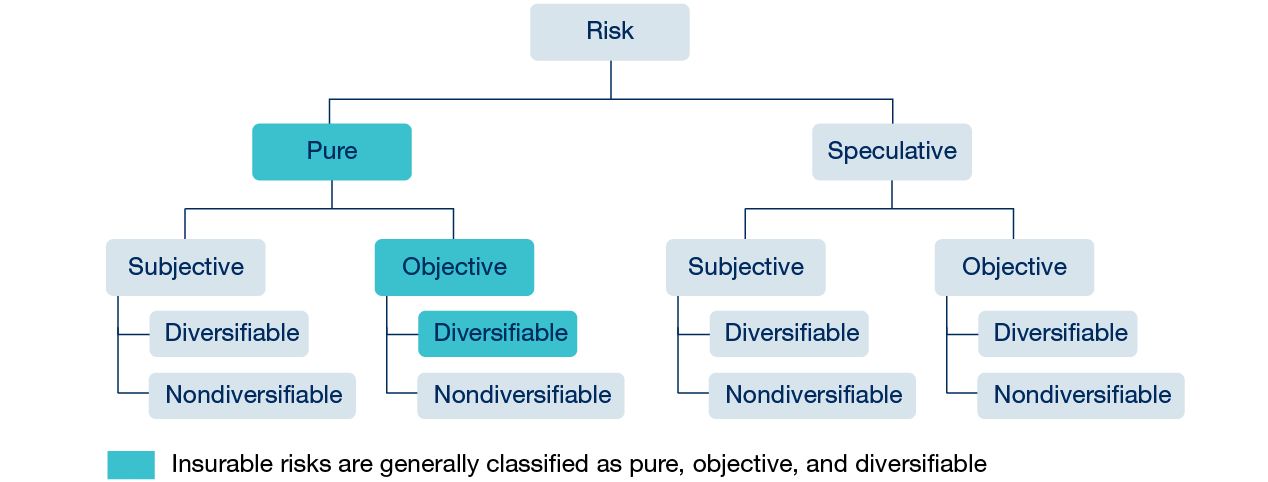
18
New cards
Arise from property, liability, or personnel loss exposures and are generally the subject of insurance
hazard risks
19
New cards
Arise from people or a failure in processes, systems, or controls, including those involving information technology
operational risks
20
New cards
Arise from the effect of market forces on financial assets or liabilities and include market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and price risk
financial risks
21
New cards
Arise from trends in the economy and society, including changes in the economic, political, and competitive environments, as well as from demographic shifts
strategic risks
22
New cards
Both of these are classified as pure risks
hazard and operational risks
23
New cards
Both of these are classified as speculative risks
financial and strategic risks
24
New cards
property risk, legal risk, personnel risk, and consequential loss are examples of
hazard risk
25
New cards
people risk, IT risk, management oversight, and business processes are examples of
operational risk
26
New cards
market risk, credit risk, price risk, and liquidity risk are examples of
financial risk
27
New cards
economic environment, political environment, demographics, and competition are examples of
strategic risk
28
New cards
a chance of loss or no loss, but no chance of gain
pure risk
29
New cards
a chance of loss, no loss, or gain
speculative risk
30
New cards
the risk that customers or other creditors will fail to make promised payments as they come due
credit risk
31
New cards
the perceived amount of risk based on an individual’s or organization’s opinion
subjective risk
32
New cards
the measurable variation in uncertain outcomes based on facts and data
objective risk
33
New cards
a risk that affects only some individuals, businesses, or small groups
diversifiable risk
34
New cards
the potential for a major disruption in the function of an entire market or financial system
systemic risk
35
New cards
uncertainty about an investment’s future value because of potential changes in the market for that type of investment
market risk
36
New cards
the risk that an asset cannot be sold on short notice without incurring a loss
liquidity risk
37
New cards
Most organizations’ sole risk management objective is to mitigate the effects of accidents.
false (A holistic risk management approach entails the pursuit of a variety of objectives besides mitigating the effects of accidents.)
38
New cards
It’s important for an organization to insure against common hazard risks, and this approach to risk management should be conducted separately from holistic risk management.
false (Traditional risk management practices that focus on common hazard risks are a part of holistic risk management; the two should not be separated. Holistic risk management examines all areas of the business, including hazard risks.)
39
New cards
to provide the structure to organize and analyze the data gathered during the investigation. It also helps to identify gaps and deficiencies in knowledge as the investigation progresses.
the purpose of causal factors charting
40
New cards
The agents that directly result in one event causing another.
causal factors
41
New cards
An approach to accident causation that views accidents as energy that is released and that affects objects, including living things, in amounts or at rates that the objects cannot tolerate.
energy transfer theory
42
New cards
An approach to accident causation that views the cause of accidents to be a result of management’s shortcomings.
technique of operations review (TOR)
43
New cards
An analysis that projects the effects a given system change is likely to have on an existing system.
change analysis
44
New cards
An analysis that dissects a repetitive task, whether performed by a person or machine, to determine potential hazards if each action is not performed.
job safety analysis (JSA)
45
New cards
A conscious act or decision not to act that reduces the frequency and/or severity of losses or makes losses more predictable.
risk control
46
New cards
The selection and implementation of actions to help manage or mitigate a risk.
risk treatment
47
New cards
The level of risk remaining after actions are taken to alter the level of risk.
residual risk
48
New cards
A risk control technique that involves ceasing or never undertaking an activity so that the possibility of a future loss occurring from that activity is eliminated.
avoidance
49
New cards
A risk control technique that reduces the frequency of a particular loss.
loss prevention
50
New cards
A risk control technique that reduces the severity of a particular loss.
loss reduction
51
New cards
The shifting of risk from one individual or organization to another.
risk transfer
52
New cards
A risk financing technique that involves assumption of risk in which gains and losses are retained within the organization.
retention
53
New cards
A risk management technique that includes steps to pay for or transfer the cost of losses.
risk financing
54
New cards
Artificial intelligence in which computers continually teach themselves to make better decisions based on previous results and new data.
machine learning
55
New cards
Loss ______reduces the frequency of a particular loss without affecting loss severity
prevention
56
New cards
Loss ______reduces the severity without affecting frequency.
reduction
57
New cards
A financial transaction in which one asset is held to offset the risk associated with another asset.
hedging
58
New cards
A financial instrument whose value is derived from the value of an underlying asset, which can be an index, an asset, yield on an asset, weather conditions, inflation, loans, bonds, an insurance risk, or other items.
derivative
59
New cards
A risk control technique that spreads loss exposures over numerous projects, products, markets, or regions.
diversification
60
New cards
A risk management technique that transfers the potential financial consequences of certain specified loss exposures from the insured to the insurer.
insurance
61
New cards
In many jurisdictions, anti-indemnity statutes forbid broad form hold-harmless agreements in construction contracts.
True. (In jurisdictions having such laws, a broad form hold-harmless agreement in a construction contract is void.)
62
New cards
The intentional relinquishment of a known right.
waiver
63
New cards
A contractual provision purporting to excuse a party from liability resulting from negligence or an otherwise wrongful act.
exculpatory clause/agreement
64
New cards
A contractual provision that obligates one of the parties to assume the legal liability of another party.
hold harmless agreement (indemnity)
65
New cards
A large deductible operates in the same way as a self-insured retention (SIR).
False. Large deductibles and SIRs both require insureds to retain covered losses up to a specified amount. However, there’s a key difference in how they apply. With large deductibles, the insurer adjusts and pays the entire loss and then bills the insured for the deductible amount. With SIRs, the insured is responsible for adjusting and paying its own losses up to the SIR amount.
66
New cards
For example, for a piece of real estate, the historical cost includes the building’s total original purchase price, including the value of the land it occupies, plus real estate commissions, closing costs, and any other legitimate business expenses attributable to that purchase.
true
67
New cards
Which one of the following best describes the management of process risk?
a. Process risk is best managed through training and development and performance management.
b. Process risk is best managed through a framework of procedures and a mechanism to identify nonconforming practices.
c. Process risk is best managed by developing procedures to manage market and credit risk.
d. Process risk is best managed by using best practices acquired from competitors without their knowledge.
a. Process risk is best managed through training and development and performance management.
b. Process risk is best managed through a framework of procedures and a mechanism to identify nonconforming practices.
c. Process risk is best managed by developing procedures to manage market and credit risk.
d. Process risk is best managed by using best practices acquired from competitors without their knowledge.
b. Process risk is best managed through a framework of procedures and a mechanism to identify nonconforming practices.
68
New cards
To be effective, a key risk indicator should be a
a. Lagging indicator.
b. Leading indicator.
c. Loss ratio.
a. Lagging indicator.
b. Leading indicator.
c. Loss ratio.
b. Leading indicator
69
New cards
Risk assurance is developed through internal resources because external resources could provide biased information and opinions that don’t reflect the strength of an organization’s financial status.
false (Internal and external resources both have a role to play as an organization builds risk assurance.)
70
New cards
When the United States dollar appreciates against the euro,
a. One dollar buys more euros than it had previously.
b. Swiss banks are forced to hedge currencies to make up the difference.
c. Imports rise because of demand for U.S. dollars.
d. There is no effect on importing companies who use U.S. banks.
a. One dollar buys more euros than it had previously.
b. Swiss banks are forced to hedge currencies to make up the difference.
c. Imports rise because of demand for U.S. dollars.
d. There is no effect on importing companies who use U.S. banks.
a. One dollar buys more euros than it had previously.
71
New cards
On a balance sheet, what is a term for the value calculated by subtracting liabilities from assets?
a. Owners' equity
b. Book value
c. Surplus
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
a. Owners' equity
b. Book value
c. Surplus
d. All of the above
e. None of the above
d. All of the above (Owners' equity, shareholder’s equity, book value, net worth, and surplus are all terms for the value calculated by subtracting liabilities from assets.)
72
New cards
What kinds of assets: cash, marketable securities, receivables (accounts and notes), inventories, and prepaid expenses.
current assets
73
New cards
What kinds of assets: assets that will be used over a period greater than one year; they are grouped into tangible assets (such as land, buildings, and equipment) and intangible assets (such as patents, copyrights, trademarks- intellectual property)
noncurrent assets
74
New cards
working capital =
current assets - current liabilities
75
New cards
current ratio =
current assets / current liabilities
76
New cards
quick ratio (acid-test) =
(cash + marketable securities + accounts receivable)/ current liabilities
77
New cards
debt-to-equity ratio = (how are you doing vs other companies)
long term debt / shareholder’s equity
78
New cards
debt-to-assets ratio = (how many assets have you financed by debt. DONT want over 0.5 typically)
total liabilities / total assets
79
New cards
The activity of buying a bundle of mortgage loans and then selling to investors an interest in those income-producing assets is
a. Prohibited if subprime home loans are involved.
b. Transacted with a commercial mortgage broker.
c. Required under statutory accounting as a means to mitigate financial risk.
d. Performed by an intermediary known as a special purpose vehicle.
a. Prohibited if subprime home loans are involved.
b. Transacted with a commercial mortgage broker.
c. Required under statutory accounting as a means to mitigate financial risk.
d. Performed by an intermediary known as a special purpose vehicle.
d. Performed by an intermediary known as a special purpose vehicle.
80
New cards
a facility established for the purpose of purchasing income-producing assets from an organization, holding title to them, and then using those assets to **collateralize** securities that will be sold to investors.
special purpose vehicle
81
New cards
Which one of the following is a tool that can be used by fraud investigators to compare documents and analyze notes?
a. text mining
b. blockchain
c. root cause analysis
d. telematics
a. text mining
b. blockchain
c. root cause analysis
d. telematics
a. text mining
82
New cards
Which one of the following is an example of a wearable?
a. heart monitors
b. robots
c. unmanned aircraft
d. helmets that monitor fatigue
a. heart monitors
b. robots
c. unmanned aircraft
d. helmets that monitor fatigue
d. helmets that monitor fatigue
83
New cards
The emerging technologies applied to risk assessment and control link the physical domain to the virtual domain. Together, these domains linked by the emerging technologies create a
a. smart system
b. risk management matrix
c. connected ecosystem
d. risk management information system
a. smart system
b. risk management matrix
c. connected ecosystem
d. risk management information system
c. connected ecosystem
84
New cards
Risk managers today differ from traditional risk managers in which one of the following ways?
a. They attempt to minimize threats and optimize opportunities.
b. They generally look backward for risk factors.
c. They struggle with data that is too large to capture, store, and analyze.
d. They attempt to identify a loss's predominant cause.
a. They attempt to minimize threats and optimize opportunities.
b. They generally look backward for risk factors.
c. They struggle with data that is too large to capture, store, and analyze.
d. They attempt to identify a loss's predominant cause.
a. They attempt to minimize threats and optimize opportunities.
85
New cards
Which one of the following statements is true with regard to preventive analytics?
a. Preventive analytics uses smart products and data analytics to identify root loss causes and their implications.
b. Preventive analytics involves data collection at discrete points in time, such as 10 AM or 4 PM each day, and comparison of these values at discrete points in time.
c. Preventive analytics is backward-looking, basing corrective prescriptions on the organization's past loss history.
d. Preventive analytics uses human assets to analyze data collected by smart products.
a. Preventive analytics uses smart products and data analytics to identify root loss causes and their implications.
b. Preventive analytics involves data collection at discrete points in time, such as 10 AM or 4 PM each day, and comparison of these values at discrete points in time.
c. Preventive analytics is backward-looking, basing corrective prescriptions on the organization's past loss history.
d. Preventive analytics uses human assets to analyze data collected by smart products.
a. Preventive analytics uses smart products and data analytics to identify root loss causes and their implications.
86
New cards
Which one of the following risk management objectives is critical for a manufacturer seeking new capital from investors, stockholders, and creditors?
a. social responsibility
b. reduce the deterrent effects of hazard risks
c. eliminate downside risk
d. anticipate and recognize emerging risks
a. social responsibility
b. reduce the deterrent effects of hazard risks
c. eliminate downside risk
d. anticipate and recognize emerging risks
b. reduce the deterrent effects of hazard risks
87
New cards
The focus of risk quadrants is different from the focus of risk classifications in general. While the classifications of risk focus on some aspect of the risk itself, the four quadrants of risk focus on
a. the source of risk and who has traditionally managed it
b. subjective and objective risks
c. pure and speculative risks
d. the determination of whether the risk is diversifiable
a. the source of risk and who has traditionally managed it
b. subjective and objective risks
c. pure and speculative risks
d. the determination of whether the risk is diversifiable
a. the source of risk and who has traditionally managed it
88
New cards
Delmond Manufacturing is opening a new manufacturing facility in a building that it purchased from a competitor. Using Information below, which one of the following represents the cost of risk of opening the new facility? New building cost: $60.0 Million. Safety system upgrades: $6.0 Million. Insurance Premiums: $1.5 Million. Retained losses: $3.0 Million. Risk management department budget at the site: $1.0 Million.
a. $7.0 Million
b. $10.0 Million
c. $11.5 Million
d. $71.5 Million
a. $7.0 Million
b. $10.0 Million
c. $11.5 Million
d. $71.5 Million
c. $11.5 Million
89
New cards
During the past year, International Toys has undertaken four capital projects. The company has renovated and refurbished one of its aging warehouse buildings. It has purchased the most recent version of its current order processing computer software. It has added two trucks to its fleet of delivery vehicles. Lastly, it has purchased a new production machine that will allow it to launch a new product line. Which one of the following company projects is the most speculative risk?
a. the warehouse refurbishment
b. the software upgrade
c. the two new trucks
d. the new production machine
a. the warehouse refurbishment
b. the software upgrade
c. the two new trucks
d. the new production machine
d. the new production machine
90
New cards
Concerning fundamental guidelines of contractual risk transfer management, it is wise to:
a. Be aggressive in negotiations - the more ruthless the better.
b. Try to be as general and nonspecific as possible.
c. Avoid being named as an additional insured on the transferee's policy.
d. Require a certificate of insurance for contractual liability before contract operations begin.
a. Be aggressive in negotiations - the more ruthless the better.
b. Try to be as general and nonspecific as possible.
c. Avoid being named as an additional insured on the transferee's policy.
d. Require a certificate of insurance for contractual liability before contract operations begin.
d. Require a certificate of insurance for contractual liability before contract operations begin.
91
New cards
In transferring risk to a transferee's insurer, which one of the following is an advantage for the transferor of using a named insured endorsement?
a. The transferee's insurer may have a right to inspect the transferor's business and financial records.
b. The transferee or its insurer does not have to pay for the cost to defend the transferor for liability losses.
c. The transferor may agree to provide periodic reports to the insurer.
d. The transferor's agents, employees, officers, and directors are considered insureds.
a. The transferee's insurer may have a right to inspect the transferor's business and financial records.
b. The transferee or its insurer does not have to pay for the cost to defend the transferor for liability losses.
c. The transferor may agree to provide periodic reports to the insurer.
d. The transferor's agents, employees, officers, and directors are considered insureds.
d. The transferor's agents, employees, officers, and directors are considered insureds.
92
New cards
Which one of the following is a major benefit that smart insurance contracts can provide to insurance customers?
A. Smart contracts can significantly increase the speed of premium payments.
B. Smart contracts can dramatically increase the speed of loss payments.
C. Smart contracts can render a risk completely preventable.
D. Smart contracts can provide broader coverage at a lower cost.
A. Smart contracts can significantly increase the speed of premium payments.
B. Smart contracts can dramatically increase the speed of loss payments.
C. Smart contracts can render a risk completely preventable.
D. Smart contracts can provide broader coverage at a lower cost.
B. Smart contracts can dramatically increase the speed of loss payments.
93
New cards
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding characteristics of ideally insurable loss exposures?
A. A common function that insurance provides is a spreading of risk across a large number of similar exposure units within the same period.
B. Intertemporal risk transfer, the spreading of risk through time, requires a large number of similar exposure units.
C. One requirement of the law of large numbers is that past events occur under different circumstances in the future.
D. Loss exposures such as homes and automobiles generally will not meet the ideally insurable requirement that the exposure be of a large number of similar exposure units.
A. A common function that insurance provides is a spreading of risk across a large number of similar exposure units within the same period.
B. Intertemporal risk transfer, the spreading of risk through time, requires a large number of similar exposure units.
C. One requirement of the law of large numbers is that past events occur under different circumstances in the future.
D. Loss exposures such as homes and automobiles generally will not meet the ideally insurable requirement that the exposure be of a large number of similar exposure units.
A. A common function that insurance provides is a spreading of risk across a large number of similar exposure units within the same period.
94
New cards
Location is a key pre-loss activity to control earthquake damage because
A. The availability of other temporary facilities helps an organization return to operations more quickly.
B. The availability of construction operations in a location is crucial.
C. Structures situated on stable earth can absorb most earthquake shock waves.
D. Designs for earthquake-resistant buildings are ineffective.
A. The availability of other temporary facilities helps an organization return to operations more quickly.
B. The availability of construction operations in a location is crucial.
C. Structures situated on stable earth can absorb most earthquake shock waves.
D. Designs for earthquake-resistant buildings are ineffective.
C. Structures situated on stable earth can absorb most earthquake shock waves.
95
New cards
Insurance claim manager Andy wants to know how many new claim representatives to hire. Based on the marketing department’s estimate and industry data, Andy has determined the mean number of new claims to be 2,000, with a standard deviation of 1,000 in a normal distribution. If a claim representative can adjust 600 claims per year and Andy wants at least 66% certainty, he has enough representatives, how many representatives will Andy need to hire?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 5
d. 10
a. 2
b. 3
c. 5
d. 10
c. 5
96
New cards
Which one of the following describes the law of large numbers?
a. it states that the more times a particular event has occurred in the past, the greater likelihood of that same event occurring in the future
b. it states that events that have occurred in the past under identical conditions and resulting from unchanging causal forces will increase at a predictable rate into the future
c. it states that as the number of similar but independent exposure units increases, the relative accuracy of predictions about future outcomes also increases
d. it states that, in order to be able to predict the relative probability of future events, those events must both be frequent, and independent of one another
a. it states that the more times a particular event has occurred in the past, the greater likelihood of that same event occurring in the future
b. it states that events that have occurred in the past under identical conditions and resulting from unchanging causal forces will increase at a predictable rate into the future
c. it states that as the number of similar but independent exposure units increases, the relative accuracy of predictions about future outcomes also increases
d. it states that, in order to be able to predict the relative probability of future events, those events must both be frequent, and independent of one another
c. it states that as the number of similar but independent exposure units increases, the relative accuracy of predictions about future outcomes also increases
97
New cards
An insurance or risk management professional may use dispersion to compare the characteristics of probability distributions. Which one of the following statements is true in this regard?
a. when two or more distributions are plotted on a graph, the one with the most sharply peaked curve has the smallest standard deviation
b. the greater the dispersion around a distribution’s expected value, the greater the likelihood that actual results will fall within a given range of that expected value
c. when a distribution is plotted on a graph, the more dispersed the distribution is, the more sharply peaked the curve is
d. in general, the less dispersion around the central tendency, the more risk is involved in the exposure
a. when two or more distributions are plotted on a graph, the one with the most sharply peaked curve has the smallest standard deviation
b. the greater the dispersion around a distribution’s expected value, the greater the likelihood that actual results will fall within a given range of that expected value
c. when a distribution is plotted on a graph, the more dispersed the distribution is, the more sharply peaked the curve is
d. in general, the less dispersion around the central tendency, the more risk is involved in the exposure
a. when two or more distributions are plotted on a graph, the one with the most sharply peaked curve has the smallest standard deviation
98
New cards
Determining earnings-at-risk (EaR) entails modeling the influence of factors such as
a. differences in the prices of products from competitors’ prices
b. changes in the prices of products and production costs on an organization’s earnings
c. employee satisfaction and other subjective variables that can be used for financial organizations but not nonfinancial organizations
d. the potential for both positive and negative credit risk for the organization
a. differences in the prices of products from competitors’ prices
b. changes in the prices of products and production costs on an organization’s earnings
c. employee satisfaction and other subjective variables that can be used for financial organizations but not nonfinancial organizations
d. the potential for both positive and negative credit risk for the organization
b. changes in the prices of products and production costs on an organization’s earnings
99
New cards
When it comes to finding a data-driven solution to these situations, which would be best suited for a descriptive approach and which would be best suited for a predictive approach:
a. A construction company is looking to lower accident frequency when equipment is being driven to work sites.
b. A retailer is concerned about rising theft losses.
c. An automotive retailer is looking for a more reliable supplier for a particular product.
d. A bank is considering offering a new small business loan program.
a. A construction company is looking to lower accident frequency when equipment is being driven to work sites.
b. A retailer is concerned about rising theft losses.
c. An automotive retailer is looking for a more reliable supplier for a particular product.
d. A bank is considering offering a new small business loan program.
b and c are descriptive (one time) and a and d are predictive (multi-need)