pathology smd
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
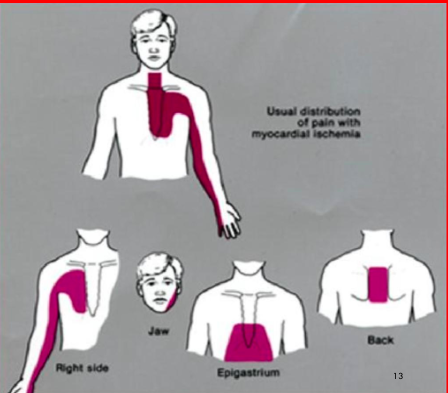
ischemic chest pain location
right side, jaw, epigastrium, back

chest pain severity due to cad
fc1: no symp w daily activities.
fc4: symptoms at rest
warfarin- anti k drug
prevent thrombosis in af
Heparin
Acute coronary syndrome
nitrates
dilate veins, reduce preload for cad
b1 receptors
reduce heart rate and contractility
calcium channel blockers
htn
statins
reduce cholesterol
ace inhibitors
reduce bp and afterload. htn, hf
digoxin
slow hr in fast af
central cyanosis
r-l shunts, tof, long l-r shunts, impaired pulm funct.
peripheral cyanosis
extremities, severe hf, circ shock, raynauds
bp measurement
both arms one leg, arm at heart level, 5 min rest
atrial pulse
patency, heart rhythm, pumping heart-bp
s1
mv, tv closure
s2
av, pv closure
s3
syst hf, vol overload
s4
dias hf
opening snap
ms
early syst click
as
mid to late syst click
mv prolapse
dias murmurs
ar, pr, ms, ts
syst murmurs
as, ps, asd, mr, tr, vsd
continuous murmur
pda, arterio venous fistula
sensitivity
pt w disease, + test
specificity
pt wo disease, - test
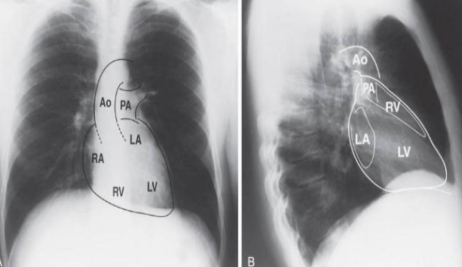
what is this?
posteroanterior chest radiograph. B.lateral chest radiograph
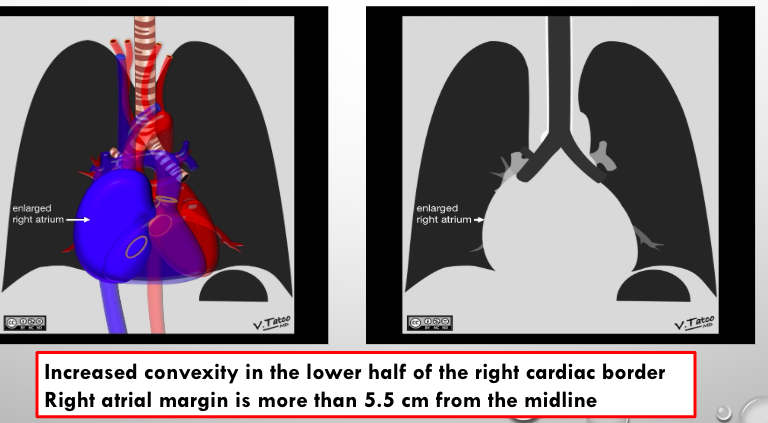
what is this?
RA enlargement
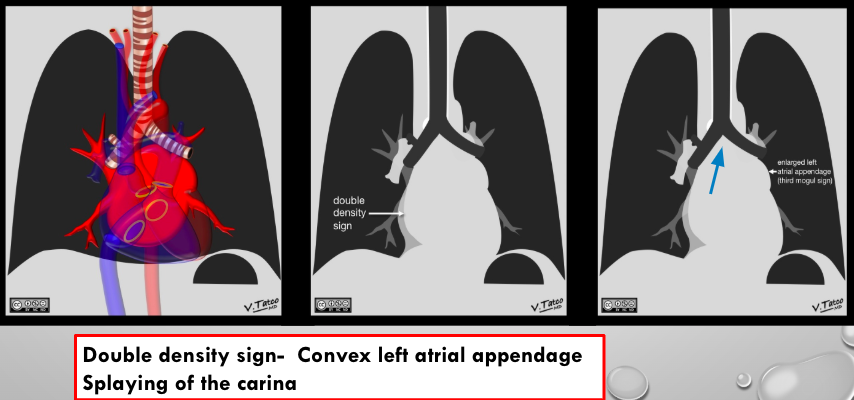
what is this?
La enlargement
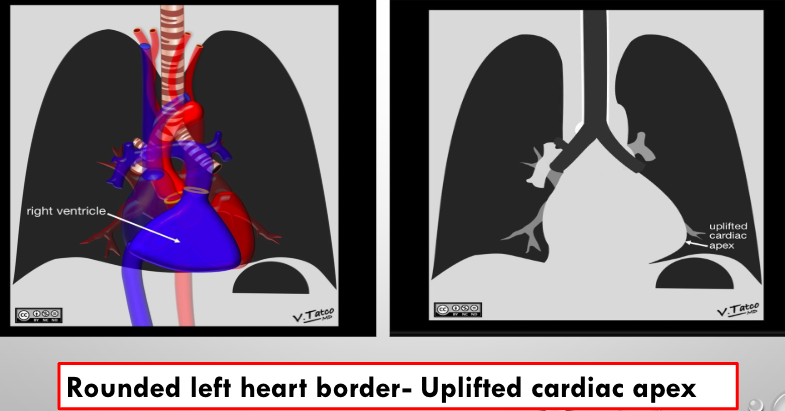
what is this?
rv enlargement.
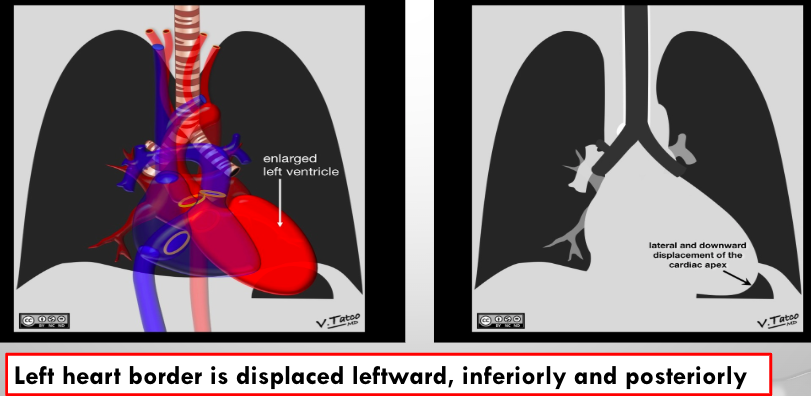
what is this?
lv enlargement
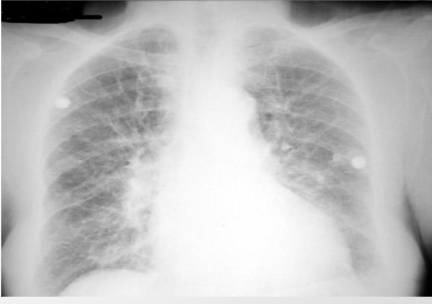
what is this?
cephalization of pulm vessels. first sign of congestive hf, phtn
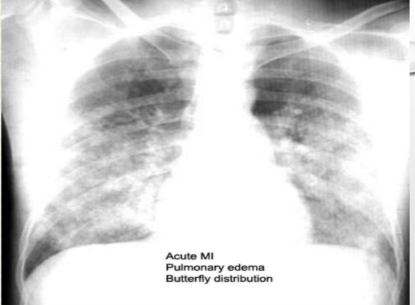
what is this?
alveolar pulm edema
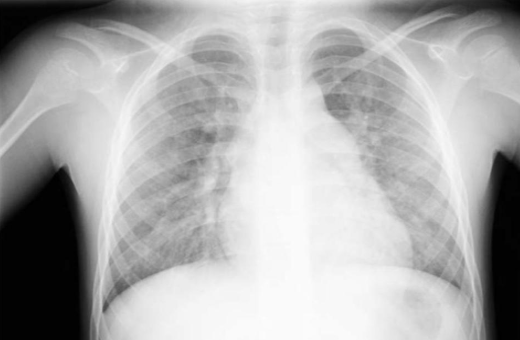
what is this?
active hyperemia in asd
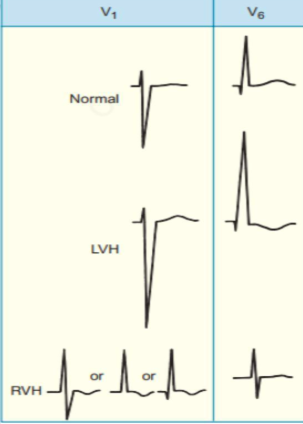
lvh- st dep, prominent r
rvh- t inv,
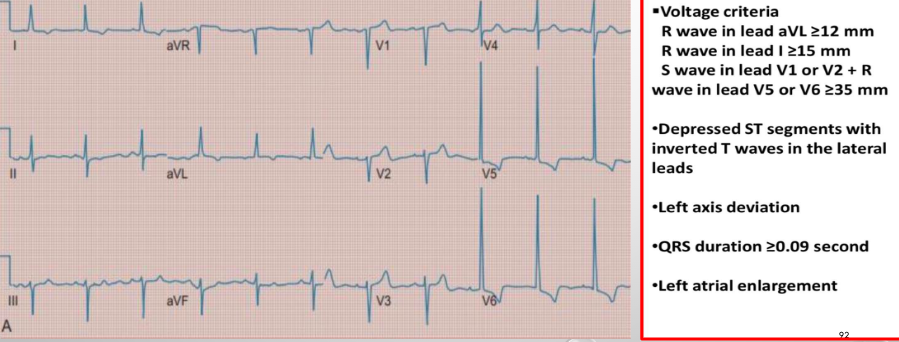
what is this?
lvh
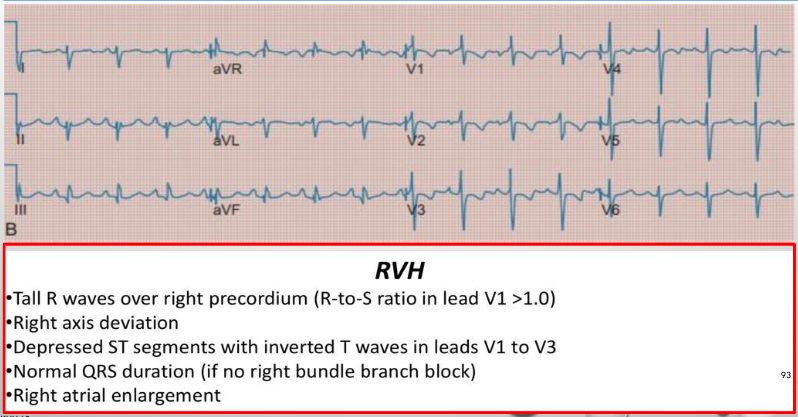
what is this?
rvh
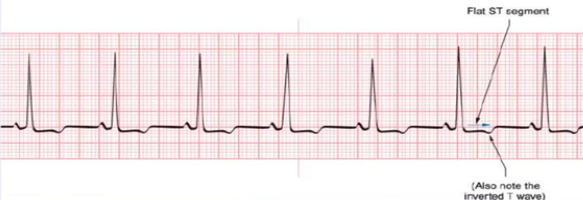
flat st depression
subendocardial infarction
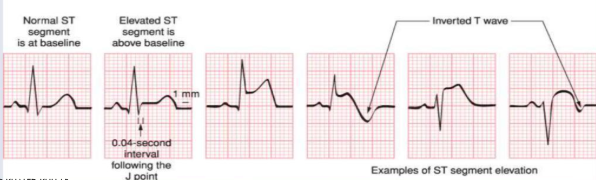
st elevation
earliest sign of mi
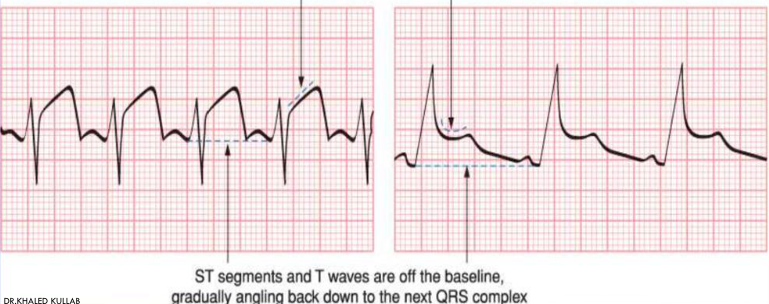
what is this?
st elevation w pericarditis
what is this?
ischemia
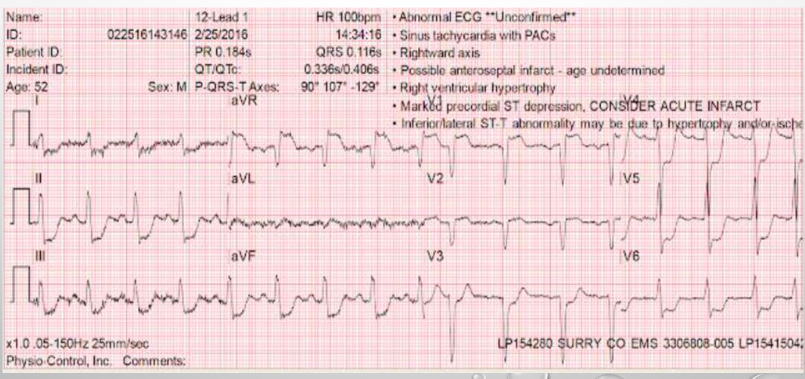
what is this?
injury acute isch subendo
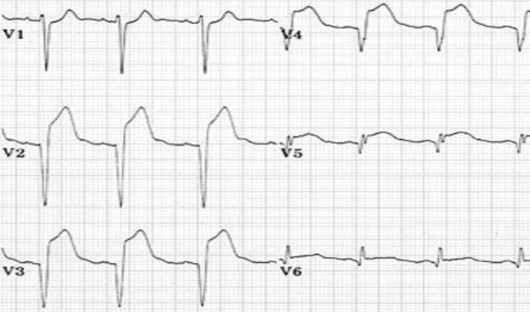
what is this?
injury acute isch transm
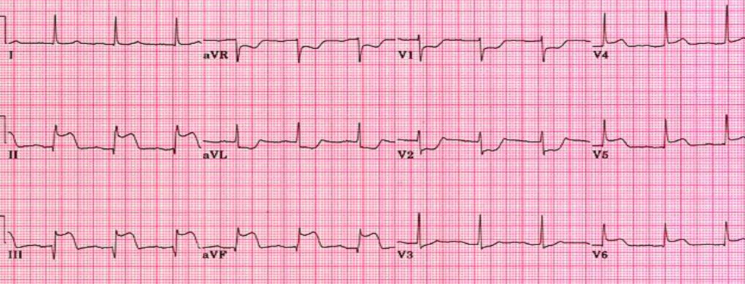
what is this?
acute inferior mi
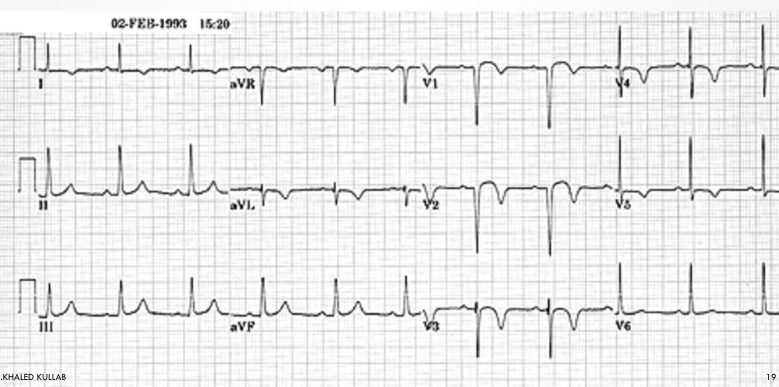
what is this?
old antero-septal mi
what is this?
old inf infraction
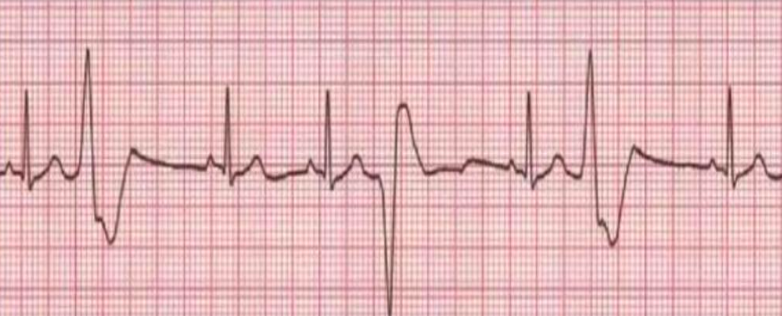
what is this?
hyperkalemia
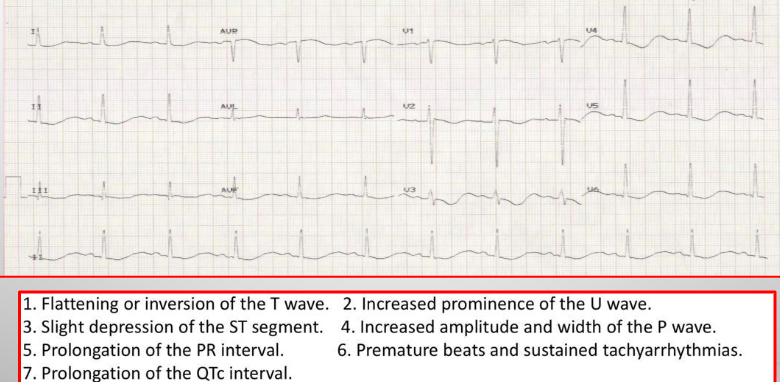
what is this?
hypokalemia
myocardial o2 consumption
hr, syst bp, contractility
mechanism of arrhythmias
disturbance of impulse formation and propagation
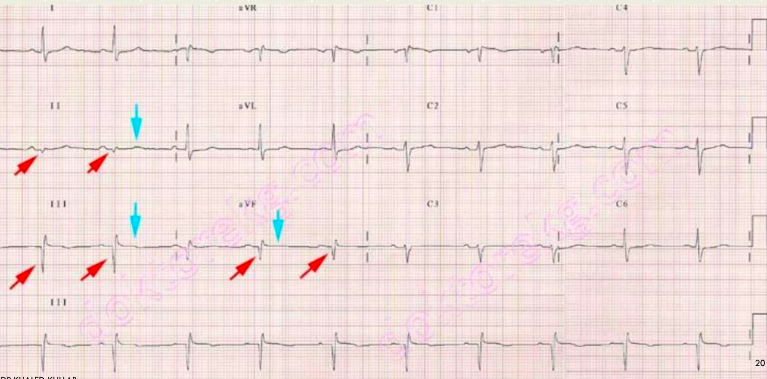
what is this?
multifocal pvc
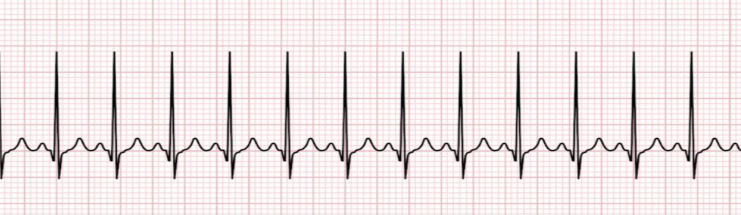
what is this?
sinus tachycardia
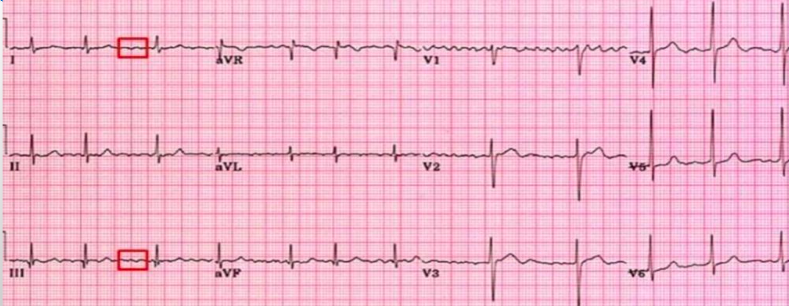
what is this?
af
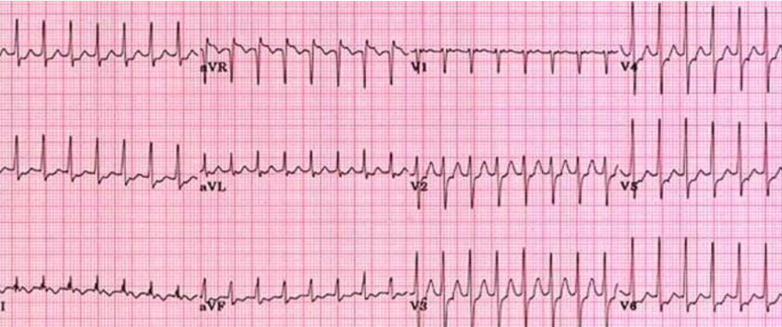
what is this?
psvt
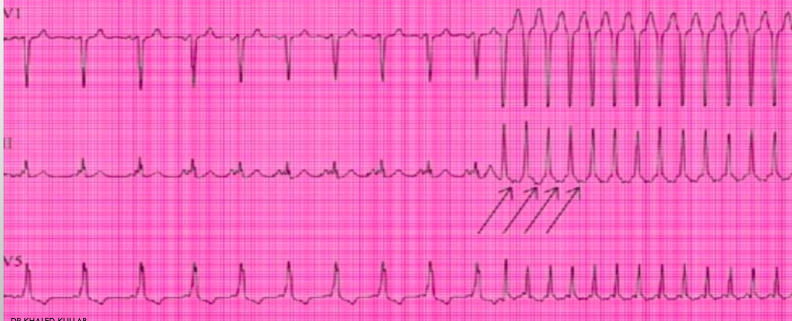
what is this?
psvt sudden onset
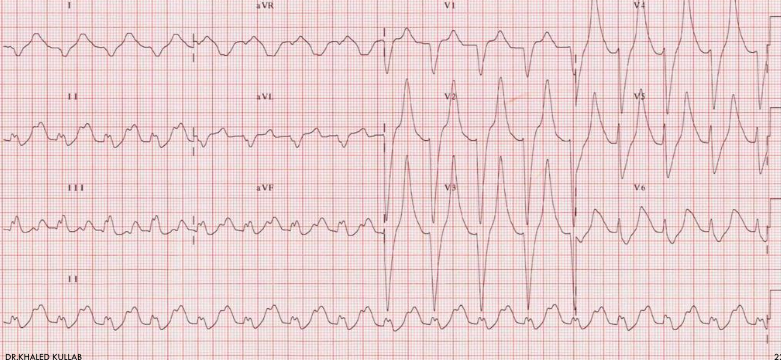
3 pvcs
vent tachycaria

what is this?
vf
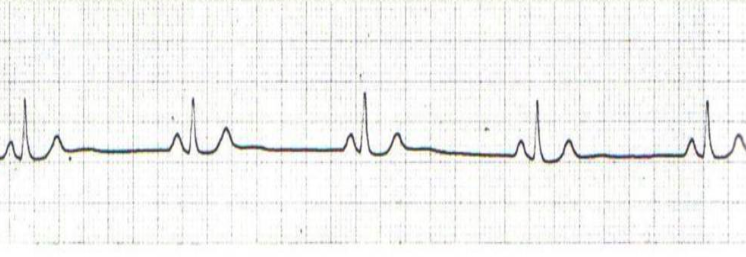
what is this?
sinus bradycardia
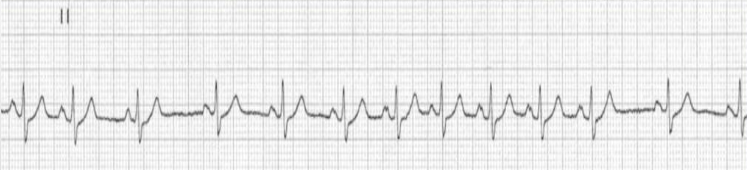
what is this?
sinus arrhythmia
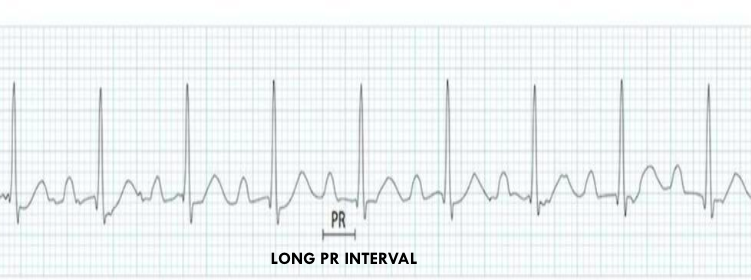
what is this?
1 deg av block
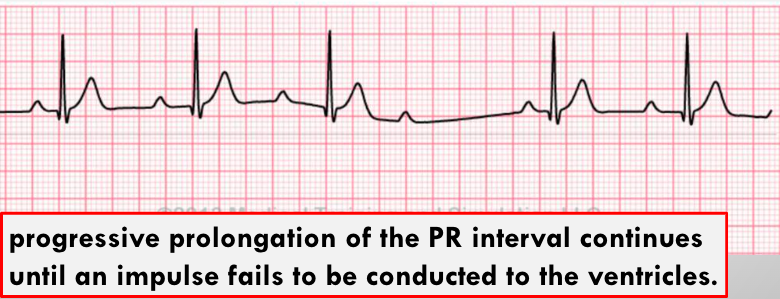
what is this?
2 deg. mobitz type 1
what is this?
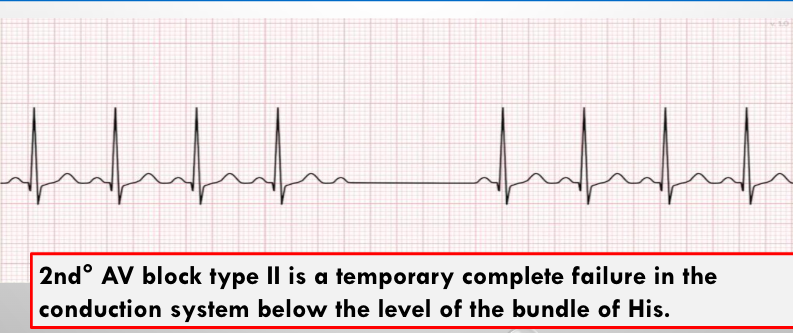
2 deg. mobitz type 2
what is this?
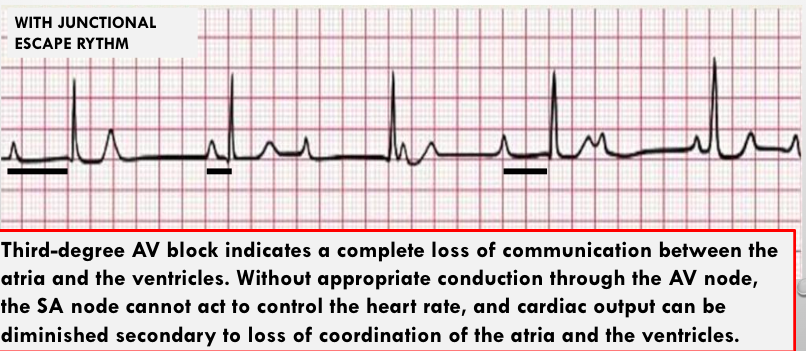
3 deg complete av block
what is this?
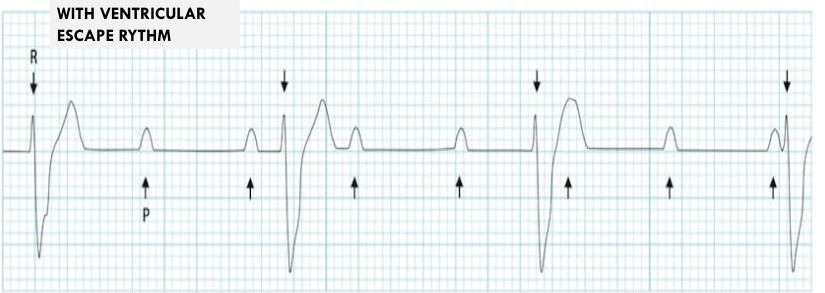
3 deg w vent escape rhythm
supply
hr, blood o2, coronary perfusion
demand
hr, contractility, afterload (bp)
consequences of myocardial isch
acute reversible isch, chronic sev isch, necrosis, electrical instability
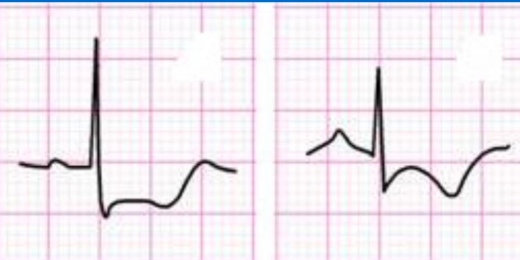
what is this?
acute demand. exercise w cad
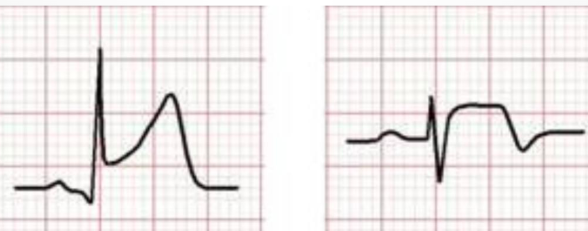
what is this?
acute supply. thrombus or spasm
clinical syndromes of ihd
angina pect, mi, arrhythmia, heart failure
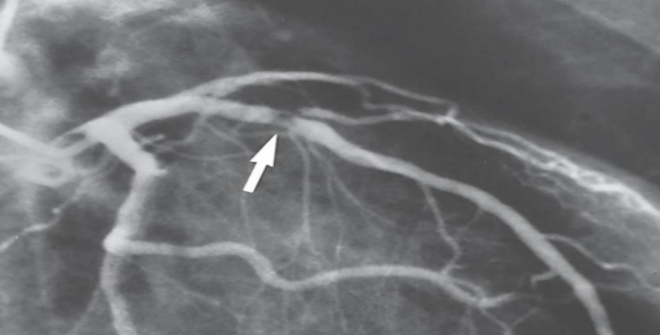
what is this?
thrombus in unstable angina
unstable angina clues
crescendo angina, rest angina, onset angina
most common cause of deaths after mi
electrical- arrhythmia, v tach, v fib, av blocks
tx arrhythmia
vf: defib w dc shock
vt: anti arrhythmia or dc shock
ruptures
pap musc- mr
septal - vsd
free wall - pericardial tamponade
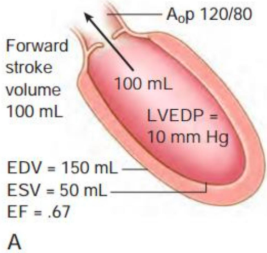
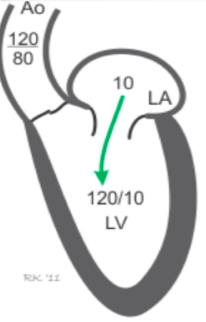
what is this?
normal ao
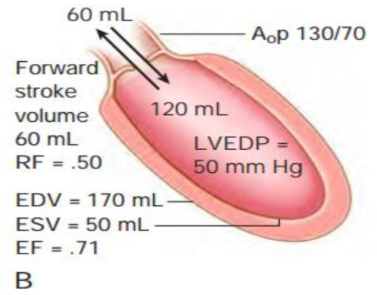
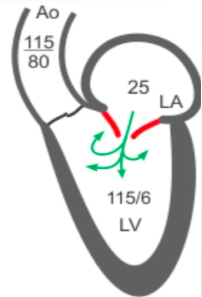
what is this?
severe acute ar
tsv inc, fsv red, lvedp inc
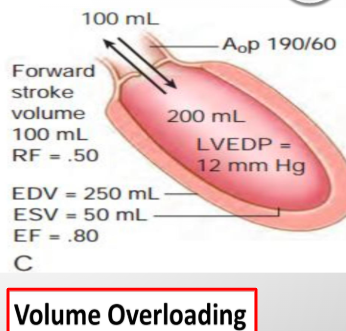
what is this?
chronic compensated ar
edv inc, sv inc, lvedp normal
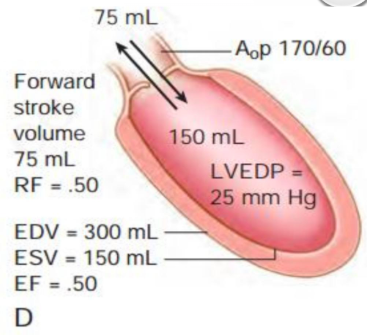
what is this?
decomp ar
esv inc, ef red, sv red
what is this?
normal mv
what is this?
ms
lap inc, pv p inc, phtn
mva and mg depend on
sv and dias filling time (hr)
complication of ms
thrombus, a fib, systemic embolism
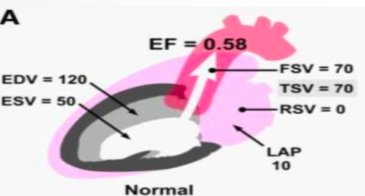
what is this?
normal mv
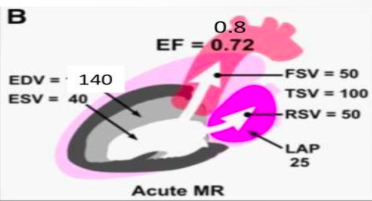
what is this?
acute mr
lap inc, ef inc
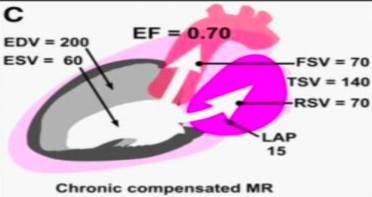
what is this?
chronic comp mr
lap dec, ef inc
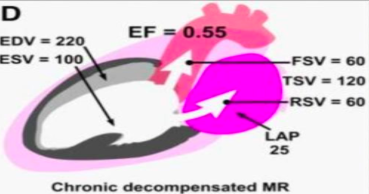
what is this?
chronic decomp mr
lap inc, ef dec
htn
140/90
masked htn
daytime 140/90, nighttime 120/70
pressure overload hypertrophy
lvh leads to lv dias dysf, la dilation, and a fib
hhd
htn present, concentric and symm lvh
hocm
htn absent, asymm lvh
pulm htm causes
1: arterial htn (l-r shunts)
2: left heart disease
3: lung disease (hypoxia, cor pulm)
4: chronci throboembolic phtn
5: multifactor
rv pressure overload
high PAP leads to RVH, syst failure, dilation
cor pulmonale
pulm disease, sev ph, rv syst failure, tr
hocm
lvh, dias dysf, la dilation, mr
hcm symp and signs
dyspnea, syncope, angina, s4
dcm
lv rv dilation, syst dysf (low ef), 2 mr, isch cmp
eisenmenger’s syndrome
l-r shunt leads to sev phtn, r-l shunt, cyanosis
tof
vsd, overriding ao, ps, rvh