Week 1 - Medical Imaging
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
X-rays
A form of electromagnetic radiation. Projections that pass through a patient.
Rays are emitted from a projector and received by a detector.
Colours on an X-ray
The rays emitted pass through most material, however is absorbed by dense material such as bone.
Rays that are blocked from passing through and absorbed create regions that turn white on an x-ray.
How is an x-ray taken?
A minimum of 2 perpendicular projections should be taken during an X-ray, so the bone is properly perceived.
If an object is close to the projector the x-ray becomes fuzzy and large due to divergence.
The patient should be placed close to the detector and far from the projector to ensure a clear image is formed.
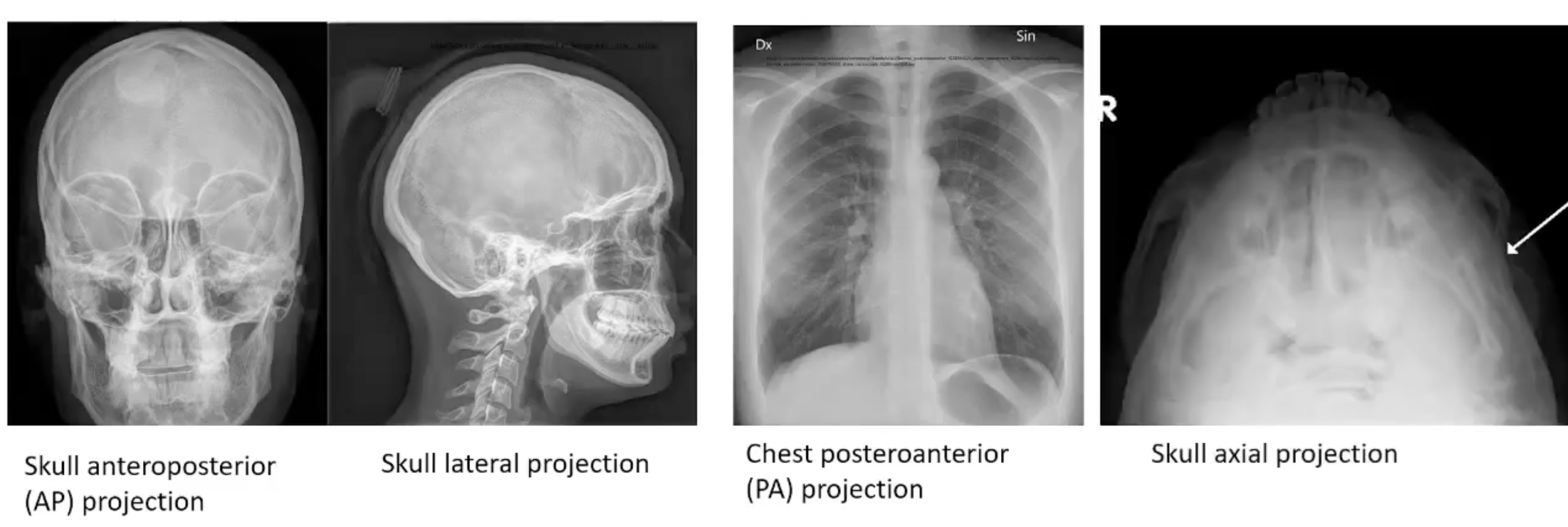
X-ray examples
Axial - from top to bottom (head to toes)
X-rays Pros & Cons

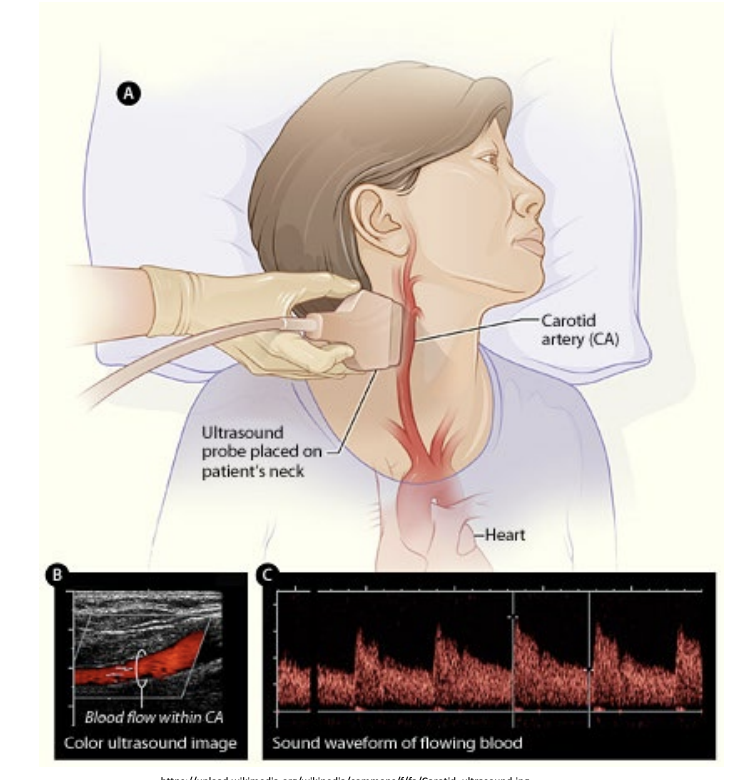
Ultrasound
Uses a transducer to emit high-frequency sound waves through patients.
Ultrasound colours
Soundwaves are reflected back based on the density of tissues.
The denser a tissue, the more soundwaves are reflected, hence the whiter the colour on the ultrasound.
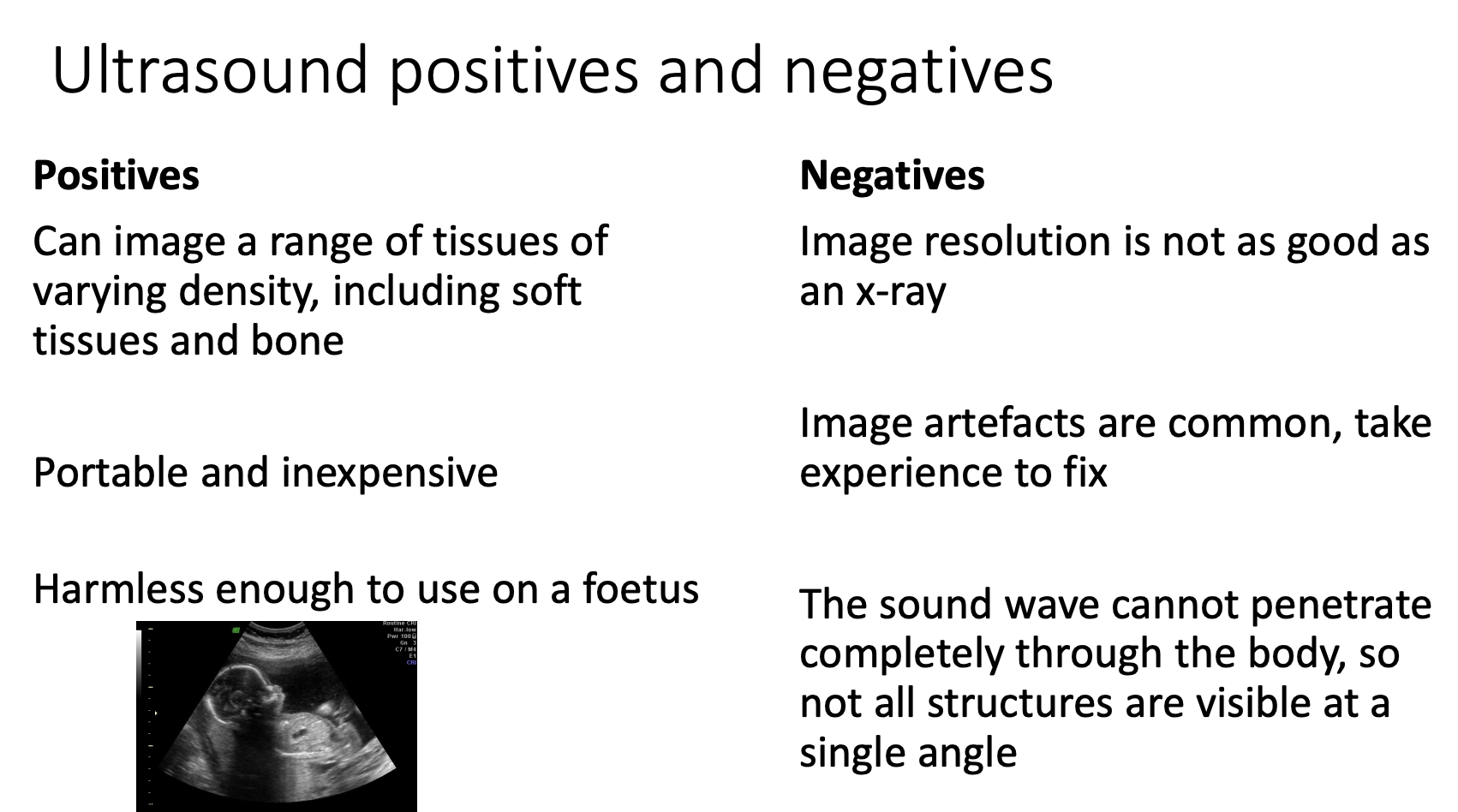
Ultrasound pros & cons
MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
A extremely powerful magnet is used to resonate with hydrogen atoms in the human body.
This resonance emits a radio frequency that the MRI’s receiver picks up and is able to map
MRI colours
The image colours are determined by the presence of hydrogen in tissues (e.g water or H2O present)
More water present, whiter image
Less water present, darker image
Hence rigid tissue like bone is not detected
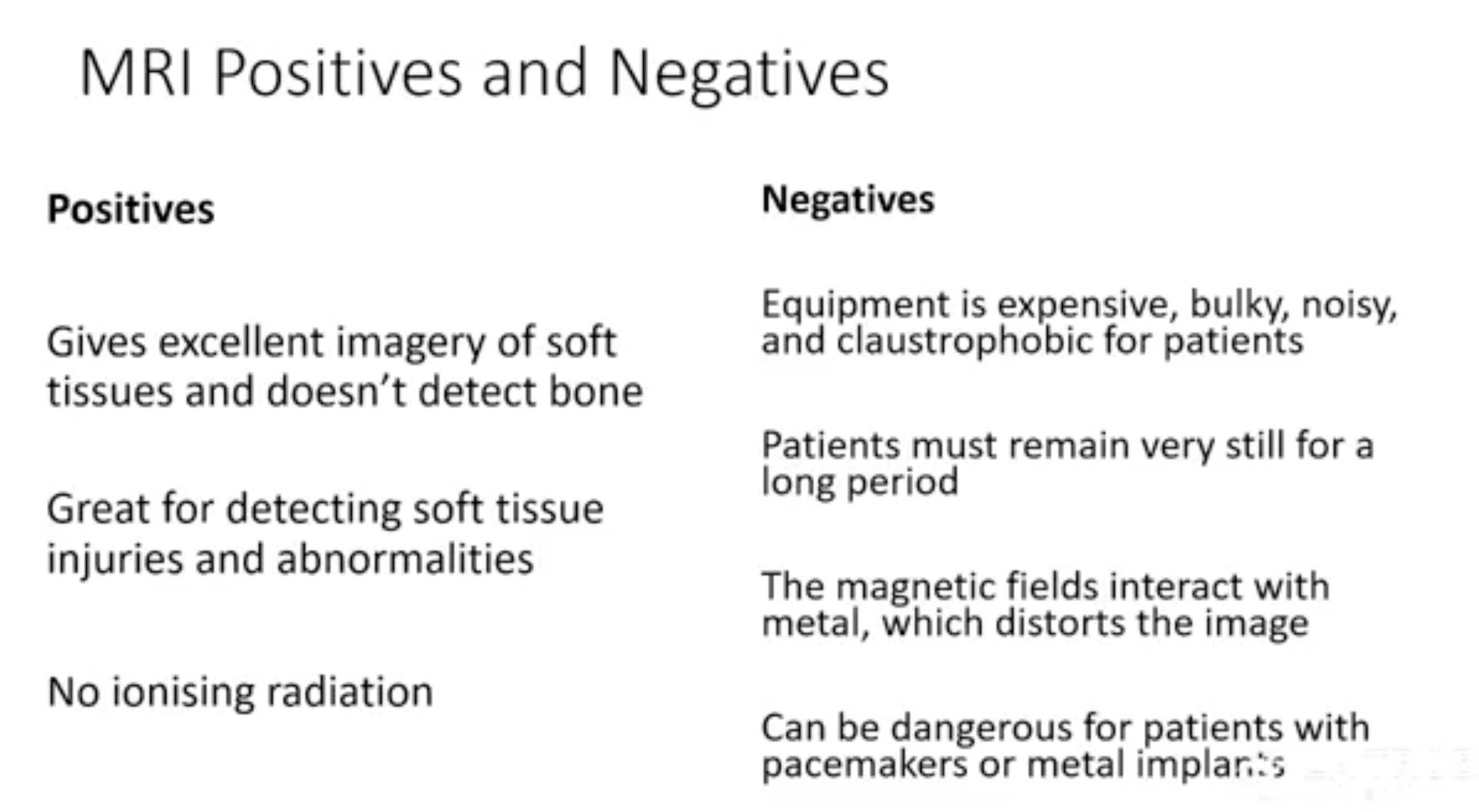
MRI pros & cons