Sports Medicine Knee Study Guide
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/93
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
1
New cards
What is the upper thigh bone?
femur
2
New cards
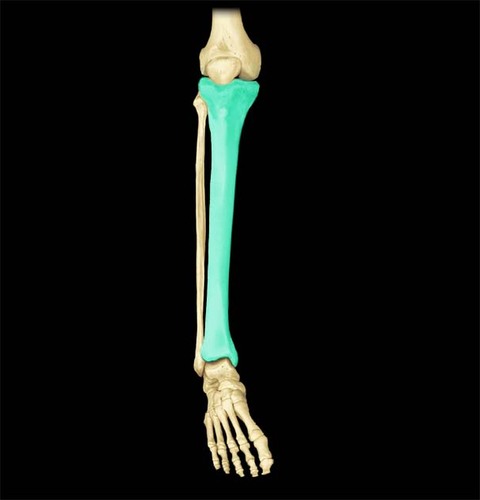
What is the larger bone of the lower leg?
tibia
3
New cards
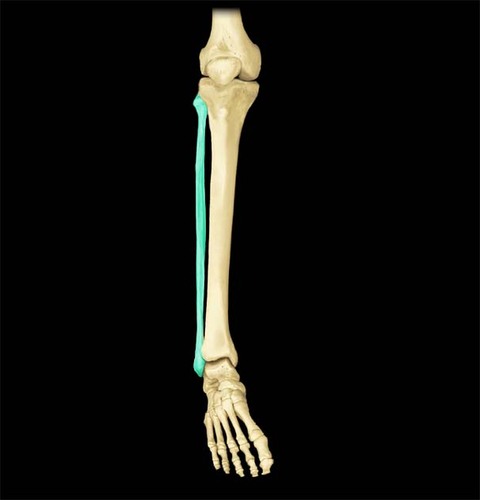
What is the smaller bone of the lower leg?
fibula
4
New cards
What does MCL stand for?
medial collateral ligament
5
New cards
What does LCL stand for?
lateral collateral ligament
6
New cards
What does ACL stand for?
anterior cruciate ligament
7
New cards
What does PCL stand for?
posterior cruciate ligament
8
New cards
What does the ACL connect?
femur to tibia
9
New cards
What does the PCL connect?
femur to tibia
10
New cards
What does the MCL connect?
femur to tibia
11
New cards
What does the LCL connect?
femur to fibula
12
New cards
What does the Patellar Tendon connect?
patella to tibia
13
New cards
How many menisci are there?
two per knee joint
14
New cards
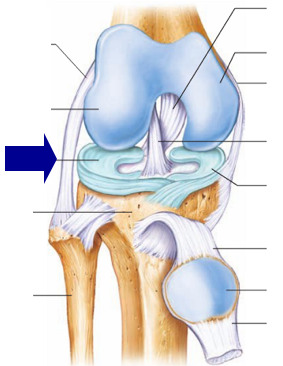
Where does the meniscus sit?
on top of the tibia (tibia plateau) between the femur and tibia
15
New cards
What are the three parts of the meniscus?
red-red zone
red-white zone
white-white zone
red-white zone
white-white zone
16
New cards
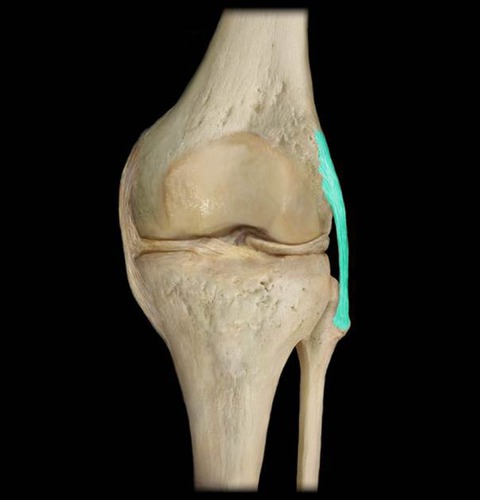
What does collateral mean?
To support (ligaments that stabilize and support knee joint)
17
New cards
What does cruciate mean?
criss-crossed shaped ligaments
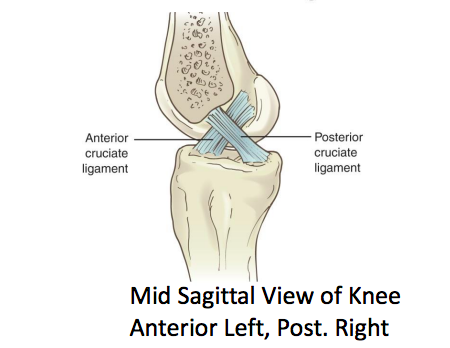
18
New cards
What is valgus?
A deformity where the knee joint is pushed toward the midline of the body. (knock-kneed)
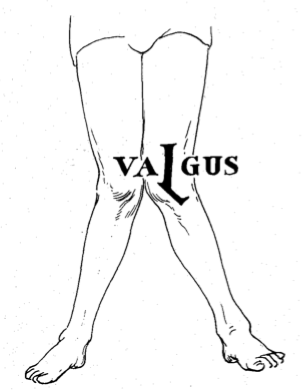
19
New cards
What gets stretched in a varus injury?
LCL
20
New cards
What is the weight bearing bone of the lower leg?
tibia
21
New cards
What connects the tibia and fibula?
Syndesmosis
22
New cards
What muscles do flexion?
hamstrings
23
New cards
What muscles do extension?
Quadriceps
24
New cards
What are the hamstring muscles?
Biceps femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimemberbranosus
Semitendinosus
Semimemberbranosus
25
New cards
What are the quadriceps muscles?
Rectus Femoris (Wreck From Front)
Vastus Medialis
Vastus Lateralis
Vastus Intermedius
Vastus Medialis
Vastus Lateralis
Vastus Intermedius
26
New cards
How do you prevent knee injuries?
Do total body conditioning
Know the Kinetic Chain (everything connects to one another)
Shoes with traction
Change shoes depending on surface
Braces if needed
Prophylactic- Preventative (used for MCL injuries in football linemen only)
Know the Kinetic Chain (everything connects to one another)
Shoes with traction
Change shoes depending on surface
Braces if needed
Prophylactic- Preventative (used for MCL injuries in football linemen only)
27
New cards
What is a valgus test for?
To see if the MCL is injured or torn.
For a valgus test, place one hand on the pts ankle, and another hand lateral to their knee. Push medial to lateral while standing lateral to pt.
For a valgus test, place one hand on the pts ankle, and another hand lateral to their knee. Push medial to lateral while standing lateral to pt.
28
New cards
What is the Lachman test for?
To see if the ACL is injured or torn.
29
New cards
What does the Lachman test look like?
For the Lachman test, place one hand on the pt's upper thigh, and the other on their tibia or patellar tendon. Pull the tibia anterior.
30
New cards
What is the anterior drawer test for?
To see if there is a tear or injury in the ACL.
31
New cards
What is the posterior drawer test for?
To see if the PCL is injured or torn
32
New cards
Joint Contusion:
MOI- A direct impact to the area. (seen most in anterior/quadriceps)
S&S- p!, swelling, ecchymosis, decrease in movement
Trmt: PRICE, Cryokinetics (Icing, then doing ROM), preventing an increased injury by using a donut pad or RTP protocol.
S&S- p!, swelling, ecchymosis, decrease in movement
Trmt: PRICE, Cryokinetics (Icing, then doing ROM), preventing an increased injury by using a donut pad or RTP protocol.
33
New cards
What would cause further injury after an MCL sprain?
Instability
34
New cards
What can be associated with LCL sprains?
Avulsions fx (fibula head is pulled off)
35
New cards
What causes girls to have more ACL tears compared to boys?
Women have child-bearing hips (an increase in Qangle, Valgus)
36
New cards
What is the average rehab following an ACL tear?
6 months
37
New cards
What would indicate you need sx following an ACL tear?
If the tear is active or unstable
38
New cards
What are the three options for surgery post ACL tear?
1. No surgery (If it is not unstable) *Can lead to arthritis
2. Allograft (Taking tendon from Cadaevor)
3. Autograft (pt uses own tendon) Taken from the patellar tendon, hamstring, or quadriceps.
2. Allograft (Taking tendon from Cadaevor)
3. Autograft (pt uses own tendon) Taken from the patellar tendon, hamstring, or quadriceps.
39
New cards
What three types of autografts are there?
Patellar Tendon
Hamstring
Quadriceps
Hamstring
Quadriceps
40
New cards
What is another name for PCL tear?
Dashboard Injury
41
New cards
What are the two MOI's for a PCL tear?
Dashboard injury
Falling on a flexed knee
Falling on a flexed knee
42
New cards
What injury would be associated with popping, clicking, etc?
Meniscal injures
43
New cards
When would you want a meniscal repair versus a meniscectomy?
Meniscal repair (if the injury is in the red-red zone)
Meniscectomy (if the injury is in the red-white or white-white zone) They cut out the injured area.
Meniscectomy (if the injury is in the red-white or white-white zone) They cut out the injured area.
44
New cards
Why would you use cryokinetics following a joint contusion?
The cold will decrease pain
It will help the swelling to decrease
It will help the swelling to decrease
45
New cards
What is another name for runner's knee?
Ilotibial Band Friction Syndrome
46
New cards
What strengthening is important for runner's knee?
Strengthening the gluteus medius
47
New cards
What way does the patella normally dislocate?
When one foot is planted on the ground, the rest of the body moves in a different direction. Or one bone stays and the other moves.
48
New cards
What is another name for jumper's knee?
Patellar Tendinosis/itis
49
New cards
What degenerates in osgood schlatter?
The tibial turbercle
50
New cards
What are the 6 types of fractures?
Green Stick
Oblique
Transverse
Linear
Spiral
Communiuted
Oblique
Transverse
Linear
Spiral
Communiuted
51
New cards
What adds bone to a bone?
Ligaments add bone to bone
(Osteoblasts are bone-forming cells.)
(Osteoblasts are bone-forming cells.)
52
New cards
What breaks down bone?
Osteoclasts break down bones.
53
New cards
What is a closed fracture?
Not a lot of movement of the broken bone or broken skin.
54
New cards
What is an open fracture?
A break that is moved so much that it breaks open the skin and punctures tissues.
55
New cards
How long does each phase take?
IRP: 2-4 days
FRP: first hours after healing to 4-6 weeks
MRP: 3 weeks, sometimes can take years depending on injury
FRP: first hours after healing to 4-6 weeks
MRP: 3 weeks, sometimes can take years depending on injury
56
New cards
What are the three phases of healing?
Inflammatory Response Phase
Fibroblastic Repair Phase
Maturation-Remodeling Phase
Fibroblastic Repair Phase
Maturation-Remodeling Phase
57
New cards
What is osteoarthritis?
The hyaline cartilage is wearing down
58
New cards
What is a trigger point and how does it differ from a cramp?
Tightness in an area of tight band muscle
Cramps are involuntary movements in the whole muscle
Trigger points are a small part of contracted muscle
Cramps are involuntary movements in the whole muscle
Trigger points are a small part of contracted muscle
59
New cards
What happens in the IRP phase?
IRP:
Starts right after injury
Most important phase
Destruction of tissue hurts soft tissues/cells
Ruined tissue is cleaned up by Phagocytic cells
Injured cells release chemicals to start healing process
Inflammation makes area warm, red, swollen, and painful
Starts right after injury
Most important phase
Destruction of tissue hurts soft tissues/cells
Ruined tissue is cleaned up by Phagocytic cells
Injured cells release chemicals to start healing process
Inflammation makes area warm, red, swollen, and painful
60
New cards
What happens in the FRP phase?
FRP:
Regenerative & Proliferative activity fix tissue and produce scarring
Fibroplasia (scar formation) starts
Fibroplasia begins in first hours after healing
Scar helps inflammation go away
Regenerative & Proliferative activity fix tissue and produce scarring
Fibroplasia (scar formation) starts
Fibroplasia begins in first hours after healing
Scar helps inflammation go away
61
New cards
What happens in the MRP phase?
MRP:
Longest process
Remodels the scar tissue
Adjusts to the tensile forces
Collagen fibers realign & prepare for stress against area
Longest process
Remodels the scar tissue
Adjusts to the tensile forces
Collagen fibers realign & prepare for stress against area
62
New cards
What is osteoarthritis?
The hyaline cartilage is wearing down
63
New cards
What is a bursae?
Synovial membrane pieces that contain fluid
64
New cards
What is crepitus?
A crackling sound/feel
Caused by tendon wanting to stick to the surrounding while sliding back and forth
Sticking caused by production of chemicals that create inflammation
Caused by tendon wanting to stick to the surrounding while sliding back and forth
Sticking caused by production of chemicals that create inflammation
65
New cards
What is Tendinopathy?
Any tendon injury
66
New cards
What is tendinosis?
Tendon has failed to heal
Irritate area
Apply friction
Stop all NSAIDS
heat
Irritate area
Apply friction
Stop all NSAIDS
heat
67
New cards
What is tendonitis?
Tendon is inflamed
Needs PRICE and NSAIDS
Needs PRICE and NSAIDS
68
New cards
What are signs of inflammation?
Warmth
Swelling
P!
Redness
Loss of Function in area
Swelling
P!
Redness
Loss of Function in area
69
New cards
How fast does a nerve regenerate?
3-4 mm of nerve regeneration occurs per day.
70
New cards
What is neuritis?
A chronic nerve issue
Symptoms range from minor pain to paralysis
Can cause physical disability
Symptoms range from minor pain to paralysis
Can cause physical disability
71
New cards
What is Paresthesia?
Numbness or tingling occurring from a direct blow or even stretch in the area
72
New cards
What is hyper-esthesia?
Increased feeling or p! Or touch to the area
73
New cards
What is hypoesthesia?
Loss of feeling
74
New cards
What is DOMS? And when does it occur?
(Delayed- onset muscle soreness)
Occurs 12 hours after the exercise is finished.
It is the most extreme in the 24-48 hour mark.
It goes away after 3-4 days.
Leads to muscle tension, swelling, resistance to stretching, and stiffness.
Can come from small tears in muscle fibers or disruption with the connective tissue holding the muscle tendon fibers together.
To best avoid: start moderate exercise then increase as body gets stronger
Stretch before and after exercise
Occurs 12 hours after the exercise is finished.
It is the most extreme in the 24-48 hour mark.
It goes away after 3-4 days.
Leads to muscle tension, swelling, resistance to stretching, and stiffness.
Can come from small tears in muscle fibers or disruption with the connective tissue holding the muscle tendon fibers together.
To best avoid: start moderate exercise then increase as body gets stronger
Stretch before and after exercise
75
New cards
What is a cramp?
Highly painful muscle contractions
Most seen in the calf, hamstring or abdomen.
Occurs when the body is lacking water, electrolytes, or ions
Most seen in the calf, hamstring or abdomen.
Occurs when the body is lacking water, electrolytes, or ions
76
New cards
What is muscle guarding and how is it different from other muscle injuries?
Muscle guarding: when the muscles around the injured area contract as a response to pain.
Also known as "splinting" not the same as muscle spasms.
It is an involuntary muscle contraction
Also known as "splinting" not the same as muscle spasms.
It is an involuntary muscle contraction
77
New cards
What are the two causes of myositis ossificans?
Repeated impact to a certain area
One large impact
One large impact
78
New cards
What is myositis ossificans?
Calcium deposits are formed by the constant trauma to an area
Calcium found in fibers of the muscle belly
Can restrict movement
To prevent this: protect the area with padding, rest the area so that the calcium and reabsorb
The quadriceps and biceps have the most contusions.
Calcium found in fibers of the muscle belly
Can restrict movement
To prevent this: protect the area with padding, rest the area so that the calcium and reabsorb
The quadriceps and biceps have the most contusions.
79
New cards
What is injured in a contusion?
Capillaries or the blood vessels and soft tissues.
80
New cards
What is a contusion?
A bruise
External items hit soft tissues and push them against the bone.
Hard blow = torn capillaries, bleeding into tissues.
Mild bleeding = blue/purple discoloration for many days
Can be tender to the touch
Pain goes away after a few days, the color goes away after a few weeks.
External items hit soft tissues and push them against the bone.
Hard blow = torn capillaries, bleeding into tissues.
Mild bleeding = blue/purple discoloration for many days
Can be tender to the touch
Pain goes away after a few days, the color goes away after a few weeks.
81
New cards
What is a first grade sprain?
Slight separation/ stretching between ligament fibers.
Little bit of instability with joint
Mild pain, swelling in area, stiff joints
Little bit of instability with joint
Mild pain, swelling in area, stiff joints
82
New cards
What is a second grade sprain?
Some tearing between ligament fibers
Mild instability with joint
Mild to severe pain, swelling in area, stiff joints.
Mild instability with joint
Mild to severe pain, swelling in area, stiff joints.
83
New cards
What is a third grade sprain?
Complete tearing of ligament fibers
Instability in joint
First it is a severe pain, then because the nerves are damaged, the pain can go away.
Large amounts of swelling, the joint is very stiff for a long time.
Instability in joint
First it is a severe pain, then because the nerves are damaged, the pain can go away.
Large amounts of swelling, the joint is very stiff for a long time.
84
New cards
What is a first grade strain?
A few muscle fibers are stretched
Some mild pain/tenderness when in motion
Movement hurts, but full range of motion is possible
Some mild pain/tenderness when in motion
Movement hurts, but full range of motion is possible
85
New cards
What is a second grade strain?
Many muscle fibers are torn or stretched
Contracting muscle causes severe pain
Divot can be found in muscle belly where it is torn
Swelling and discoloration are mild
Contracting muscle causes severe pain
Divot can be found in muscle belly where it is torn
Swelling and discoloration are mild
86
New cards
What is a third grade strain?
Muscle fibers are completely torn
Almost a total loss of movement
First pain is harsh, then it dies down because of nerve damage and separation.
Almost a total loss of movement
First pain is harsh, then it dies down because of nerve damage and separation.
87
New cards
What is a sprain?
Injury to the joint or ligament that connects bone to bone.
88
New cards
First time dislocations should always be treated as a...
possible fracture.
89
New cards
What is a subluxation?
A bone is pushed fully out of its normal position, but then goes back
Most seen in the kneecap or shoulder joint
Most seen in the kneecap or shoulder joint
90
New cards
What is a dislocation?
A bone or joint is pushed fully out of its normal position
Must be surgically or manually placed back
Most seen in the elbow, shoulder, and finger
Can happen where any two bones articulate.
Must be surgically or manually placed back
Most seen in the elbow, shoulder, and finger
Can happen where any two bones articulate.
91
New cards
What is a stress fracture?
Created from overuse rather than an acute trauma
Most common fracture in physical activity
Mostly seen in legs and arms which are weight-bearing bones
The continuous force being placed on the bones causes the periosteum to be irritated, and fatigue fractures of the underlying bone form.
Pain starts dull, then it grows more, at first the pain is most prominent during the activity, but once the stress fracture is created, the pain comes on when the activity is stopped.
Does not usually show up on Xrays until osteoblasts start laying down on the bone
White line on X Ray indicates a stress fracture
Athlete must stop activity for at least 14 days and slowly ease themselves back into the activity
Do not usually need a cast, unless it is not dealt with correctly.
Most common fracture in physical activity
Mostly seen in legs and arms which are weight-bearing bones
The continuous force being placed on the bones causes the periosteum to be irritated, and fatigue fractures of the underlying bone form.
Pain starts dull, then it grows more, at first the pain is most prominent during the activity, but once the stress fracture is created, the pain comes on when the activity is stopped.
Does not usually show up on Xrays until osteoblasts start laying down on the bone
White line on X Ray indicates a stress fracture
Athlete must stop activity for at least 14 days and slowly ease themselves back into the activity
Do not usually need a cast, unless it is not dealt with correctly.
92
New cards
How long does long bones take to heal?
Long bones take about 6 weeks to heal with a cast
93
New cards
How long do short bones take to heal?
Short bones take 3-4 weeks to heal with a cast
94
New cards
What endpoint do you want for your patient when testing?
A hard endpoint