Science in Agriculture 2023
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:45 AM on 8/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
Define xylem
Vascular tubes that carry water from the roots UP to other parts of the plant
2
New cards
Define phloem
Vascular tubes that carry sugar from photosynthesis and other nutrients UP & DOWN the plant
3
New cards
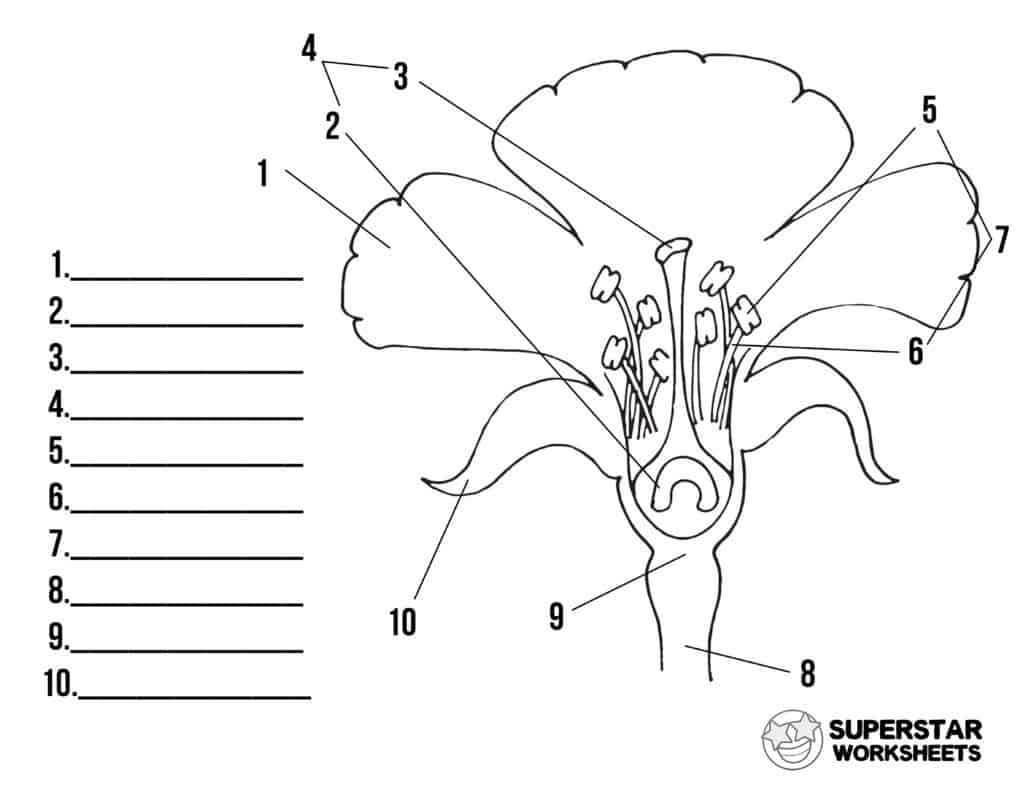
Name number 1
petals
4
New cards
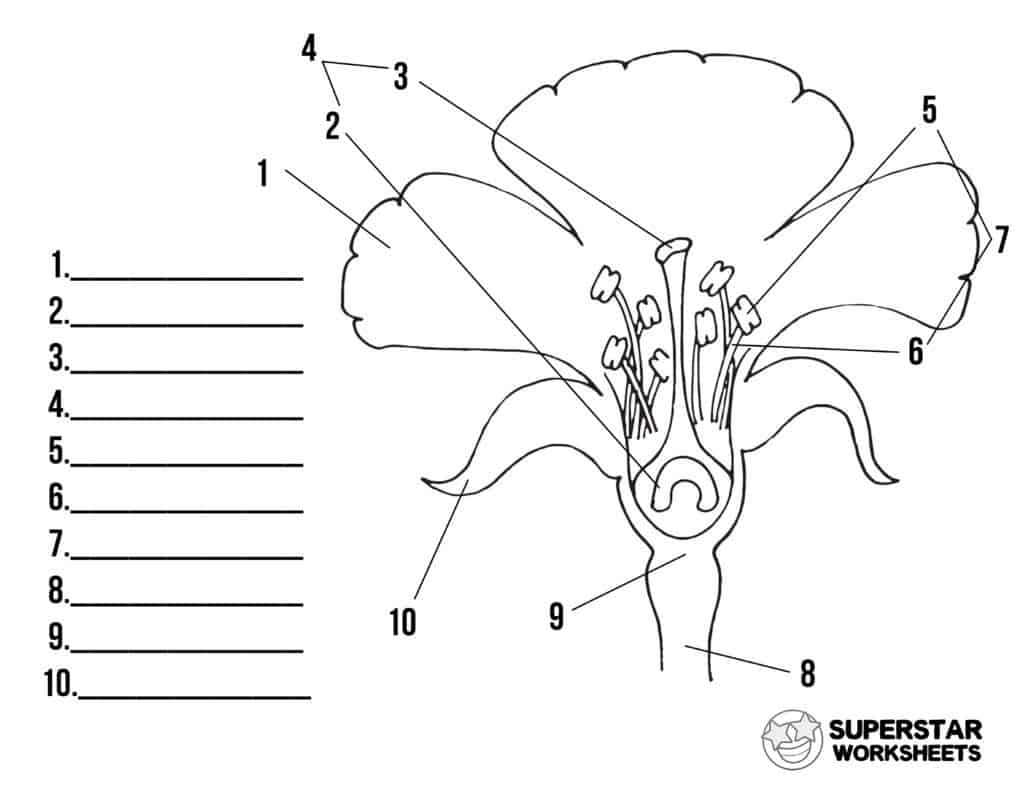
name number 2
ovary
5
New cards
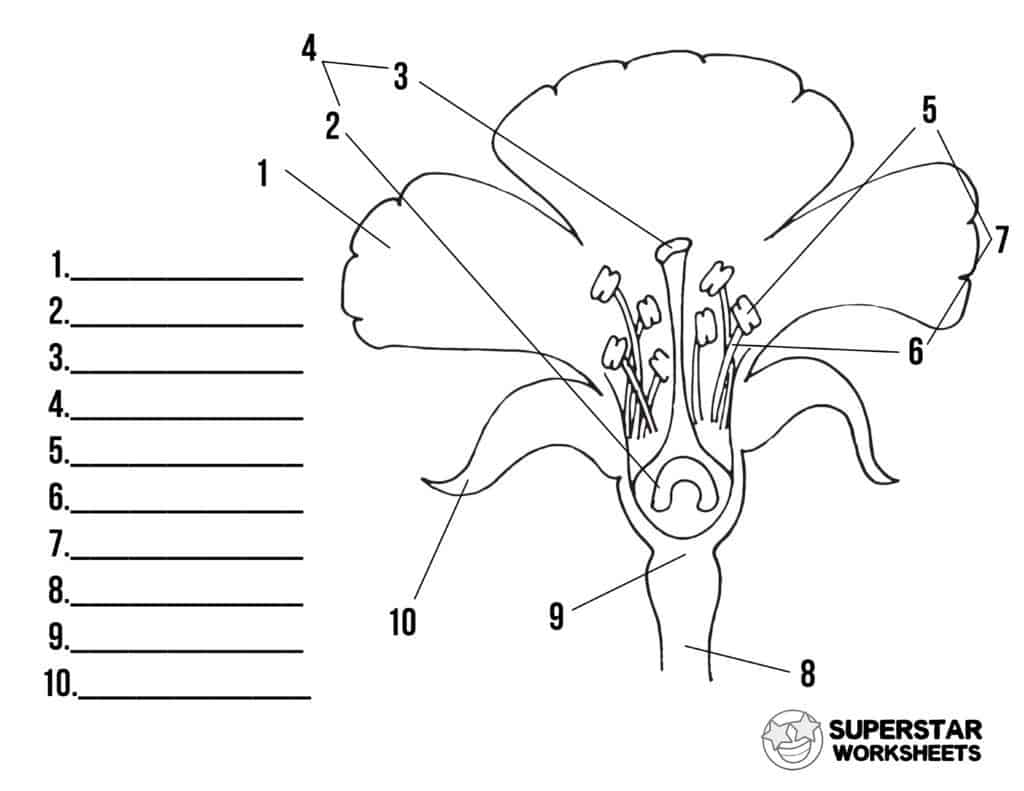
name number 3
stigma
6
New cards
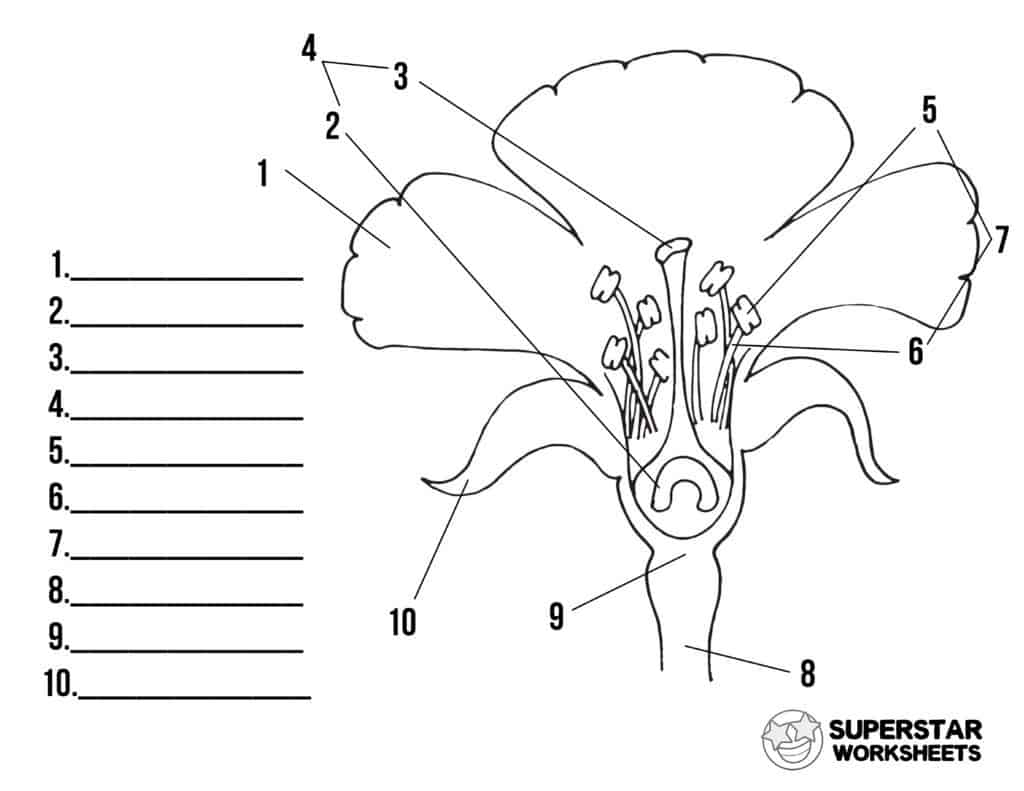
name number 4
pistil/carpel
7
New cards
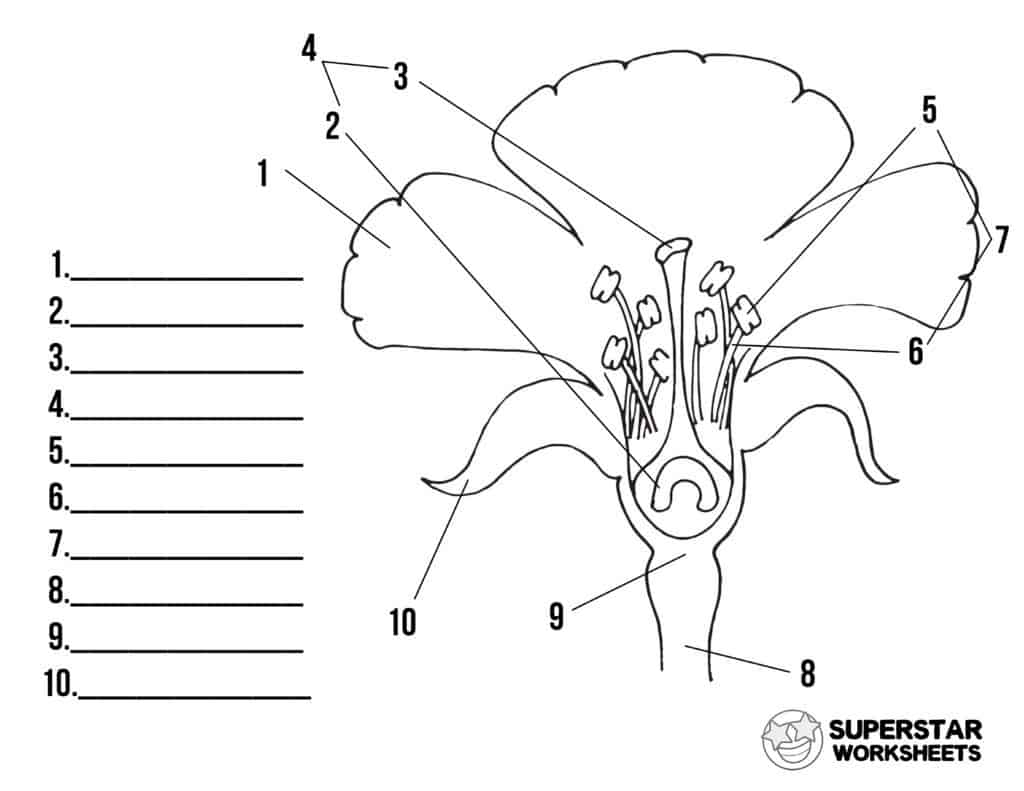
name number 5
anther
8
New cards
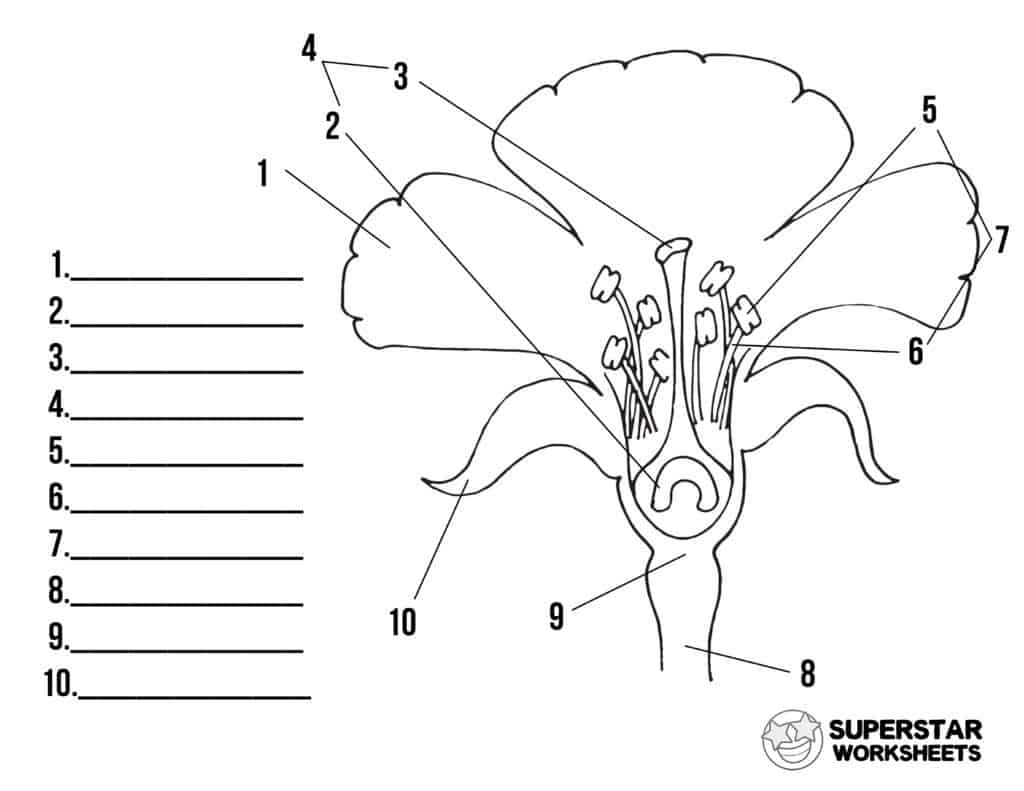
name number 6
filament
9
New cards
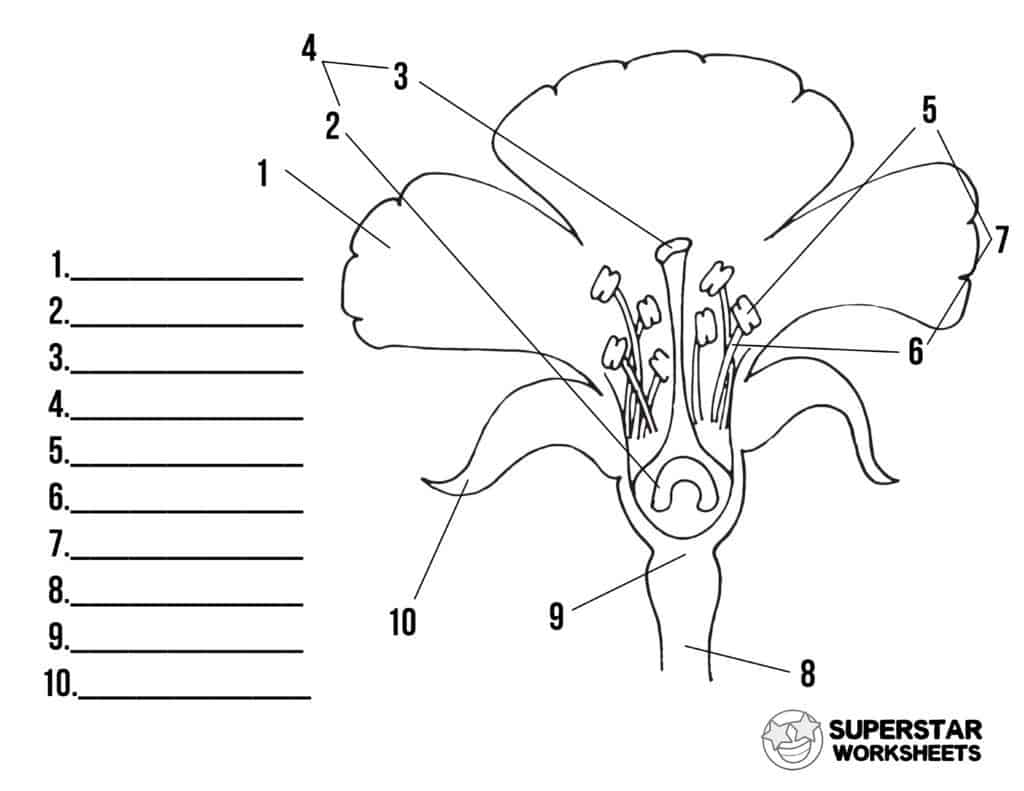
name number 7
stamen
10
New cards
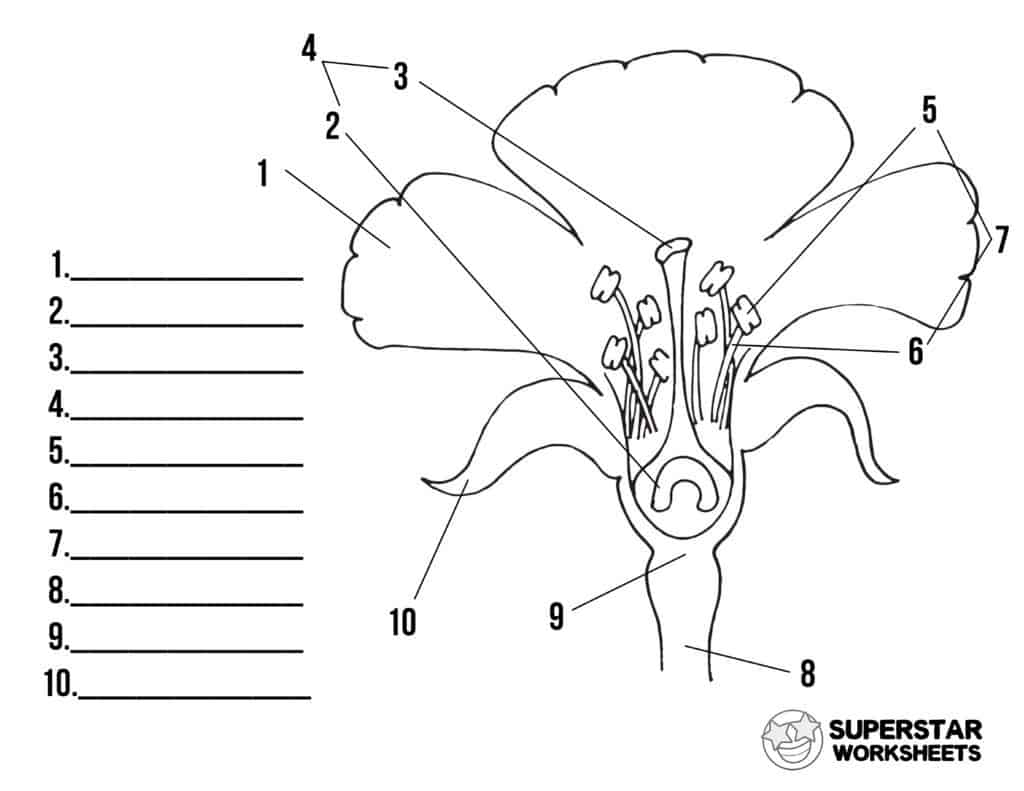
name number 8
pedicel
11
New cards
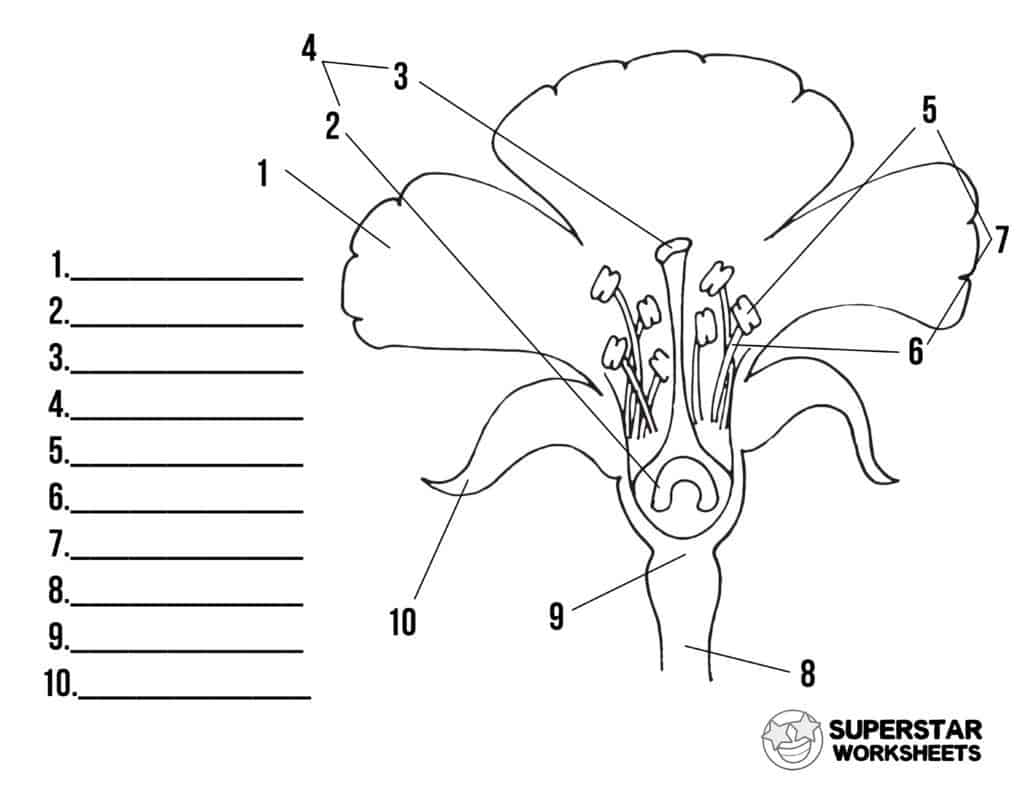
name number 9
receptacle
12
New cards
name number 10
sepal
13
New cards
What is the female reproductive part of a flower?
carpel
14
New cards
What is the male reproductive part of a flower?
stamen
15
New cards
What is the purpose of petals?
to attract pollinators
16
New cards
What is the purpose of the anthers?
to create pollen
17
New cards
What is the purpose of the stigma?
collect pollen
18
New cards
What is the purpose of the style?
connect stigma to ovary
19
New cards
What is the purpose of the ovary?
contains ovules
20
New cards
What is the purpose of the receptacle?
connect the stalk to the flower and to support the flower
21
New cards
What is the purpose of the filament
supports the anther
22
New cards
What is the purpose of the ovule?
houses the egg cells and receives pollen from another angiosperm
23
New cards
What are roots?
organs that anchor vascular plants, assisting in absorption of water and minerals
24
New cards
What is a stem?
supporting structure that connects roots and leaves and carries water and nutrients between them
25
New cards
What is a branch?
structural support for the leaves, fruits and flowers that the tree produces, carries water and food
26
New cards
What is a leaf?
a plant organ adapted specifically for photosynthesis
27
New cards
what is a flower?
The reproductive structure of an angiosperm
28
New cards
What is a fruit?
a mature ovary that spreads seeds
29
New cards
How does a plant spread its seeds?
wind, water, animals, explosion and fire
30
New cards
How can you tell monocots and dicots apart according to the petals?
monocots have petals in multiples of threes, dicots in multiples of fours or fives
31
New cards
How can you tell monocots and dicots apart according to the cotyledons?
Monocots have one, dicots have two
32
New cards
How can you tell monocots and dicots apart according to the roots?
monocots have fibrous (adventitious) roots, dicots have a main tap root with lateral branches
33
New cards
How can you tell monocots and dicots apart according to the leaves?
Monocots have parallel leaf veins, dicots have net like veins
34
New cards
How can you tell monocots and dicots apart according to the stems?
Monocots have vascular bundles scattered across the stem, dicots have vascular bundles around the outside
35
New cards
Are organisms in the Kingdom Plantae eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic
36
New cards
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic do not have their DNA contained in a nucleus or any organelles bound in membrane
37
New cards
Are organisms in Kingdom Plantae autotrophic or heterotrophic
autotrophic
38
New cards
How do plants make their own food?
photosynthesis
39
New cards
In what organelle does photosynthesis take place?
Chloroplast
40
New cards
how is the kingdom of Fungi and Monera different to the kingdom of Plantae?
they can be single celled, while plants cannot
41
New cards
Give examples of harmful microorganisms
Bacteria causing diseases
42
New cards
Give examples of beneficial microorganisms
yeast, good microflora (e.g. in your gut, aiding with digestion), antibiotics,
43
New cards
Define parasitism
an organism that lives in or on another organism (its host) and benefits by deriving nutrients at the host's expense.
44
New cards
Define symbiosis
interaction between two different organisms living in close physical association, typically to the advantage of both.
45
New cards
Give an example of a symbiotic relationship
bee (receives nectar to make honey) and flower (gets pollinated), clownfish (protection against predators) and anemone (receives excreted nutrients)
46
New cards
Give an example of a parasitic relationship
mosquito (gains blood) and human (skin irritation and could potentially receive a disease), disease and host
47
New cards
What is a food chain?
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
48
New cards
What is a food web?
The feeding relationships between all organisms in an ecosystem
49
New cards
What are the three trophic levels?
producers, consumers, decomposers
50
New cards
What is an apex predator?
Predator at the top of the food chain and is not preyed upon by another consumer
51
New cards
what happens to apex predators?
After they die they are decomposed by decomposers
52
New cards
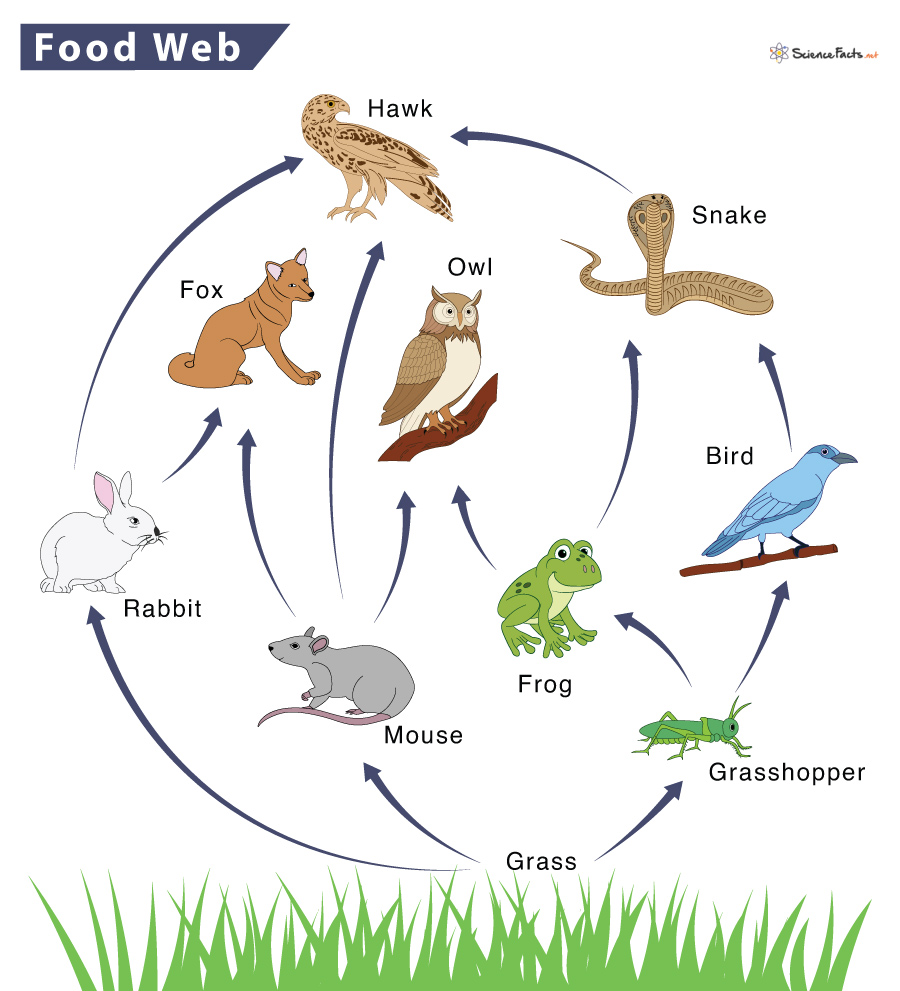
Is this a food web or food chain?
food web
53
New cards
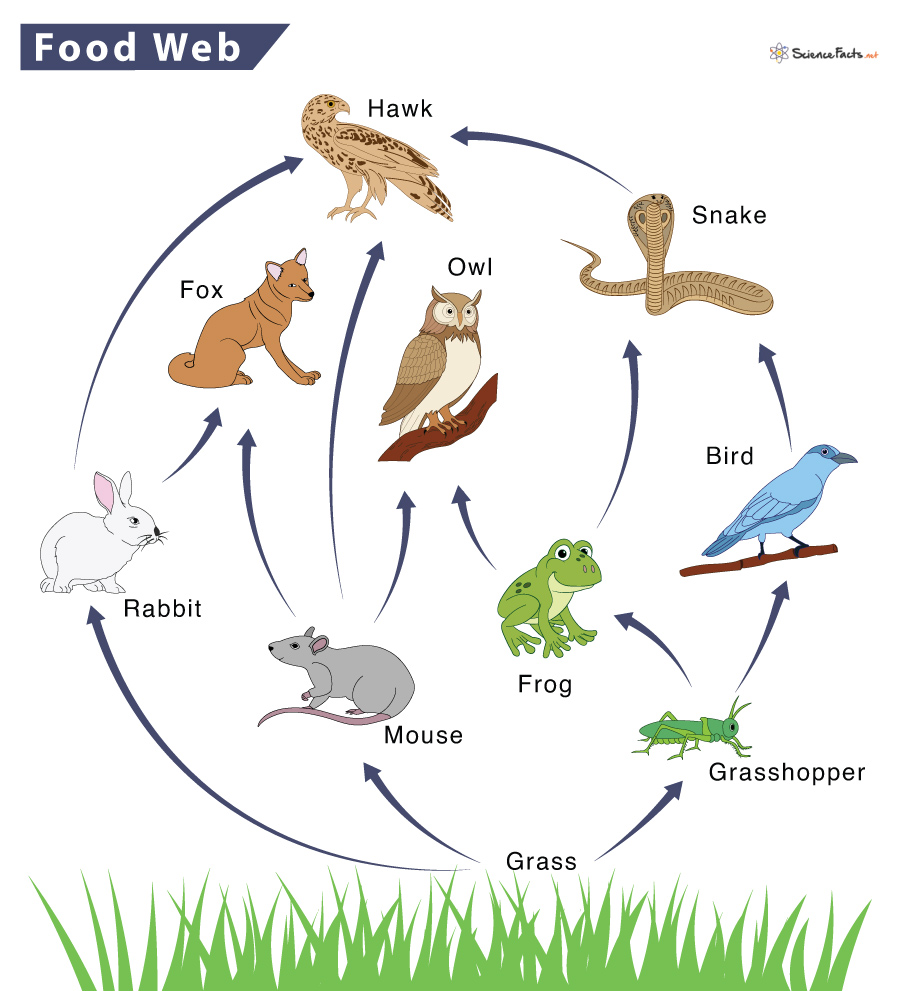
Name the producer in this web
grass
54
New cards
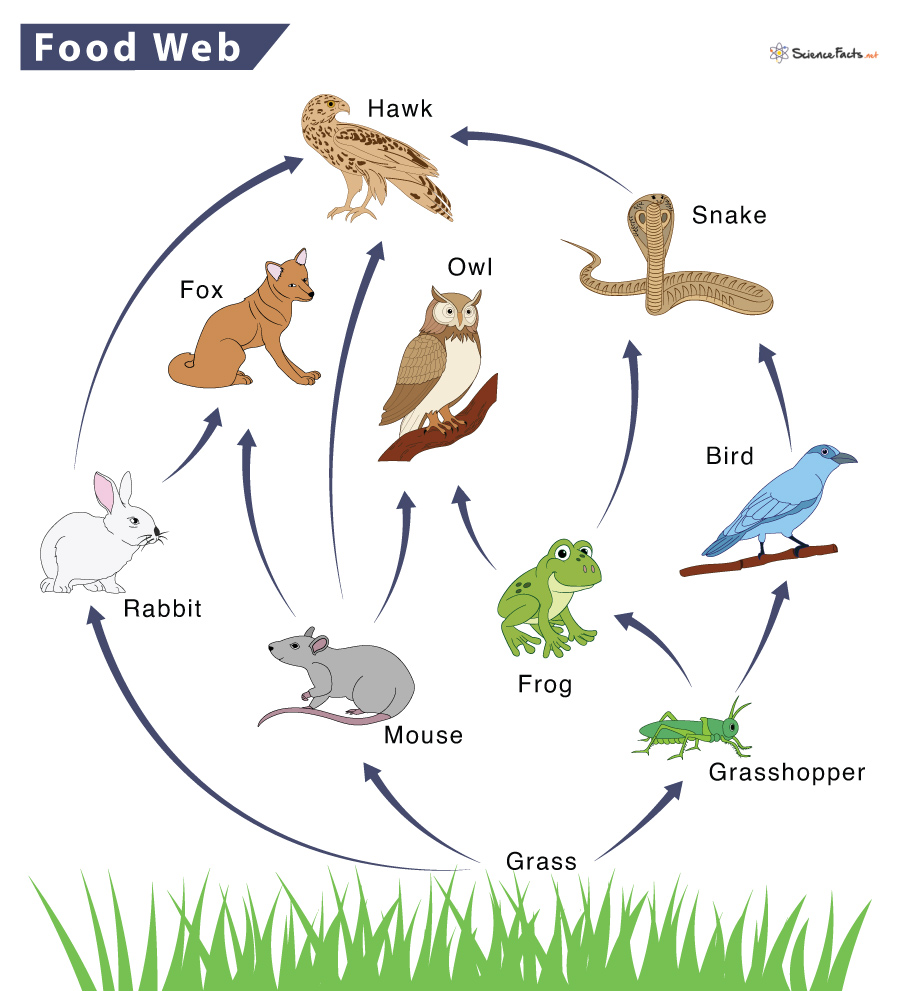
Name the apex predators in this web
hawk, owl, fox
55
New cards
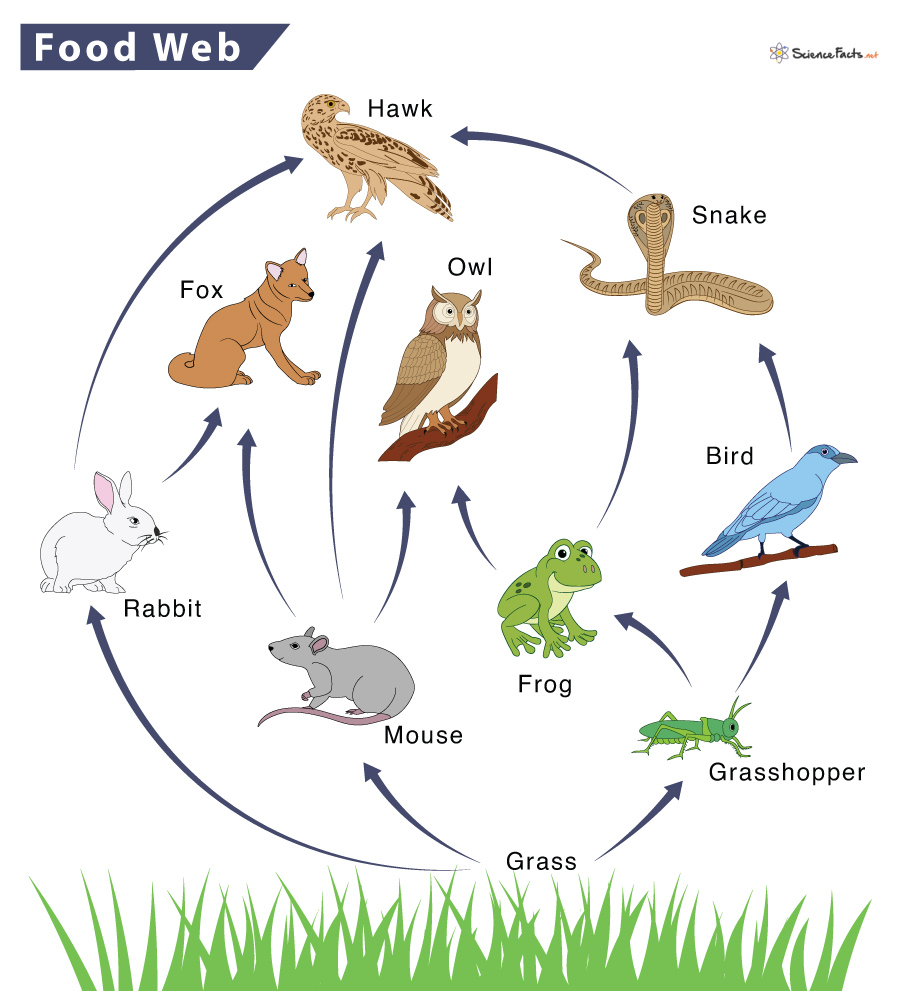
Name all of the primary consumers in this web
mouse, grasshopper, rabbit
56
New cards
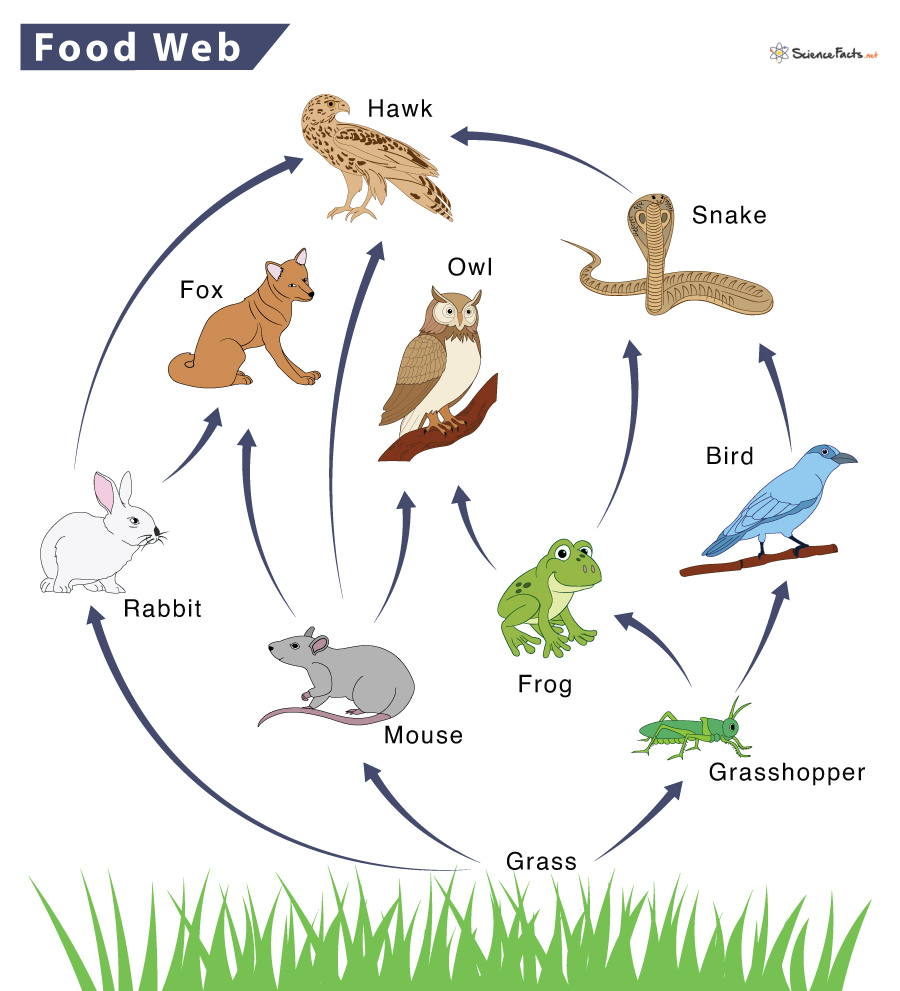
Name all of the secondary consumers in this web
fox, owl, bird
57
New cards
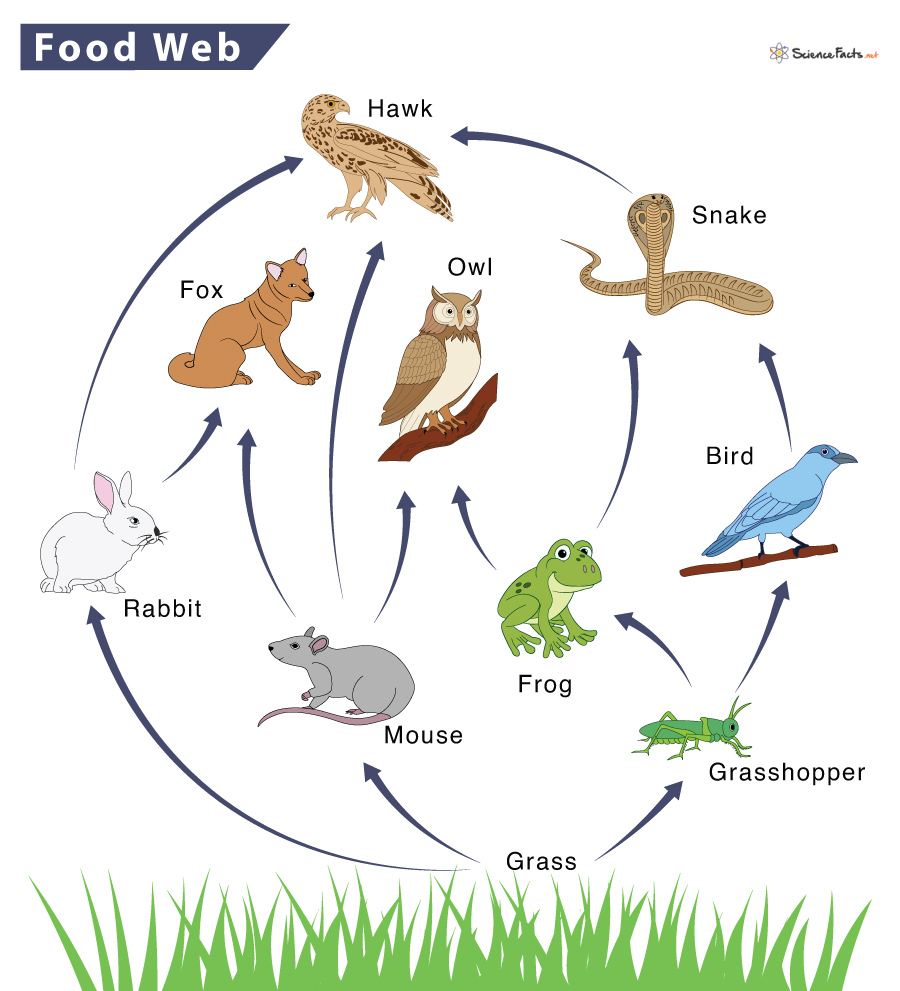
What would happen if the grasshopper population decreased?
The frog and bird populations would decrease as well. Grass populations would thrive
58
New cards
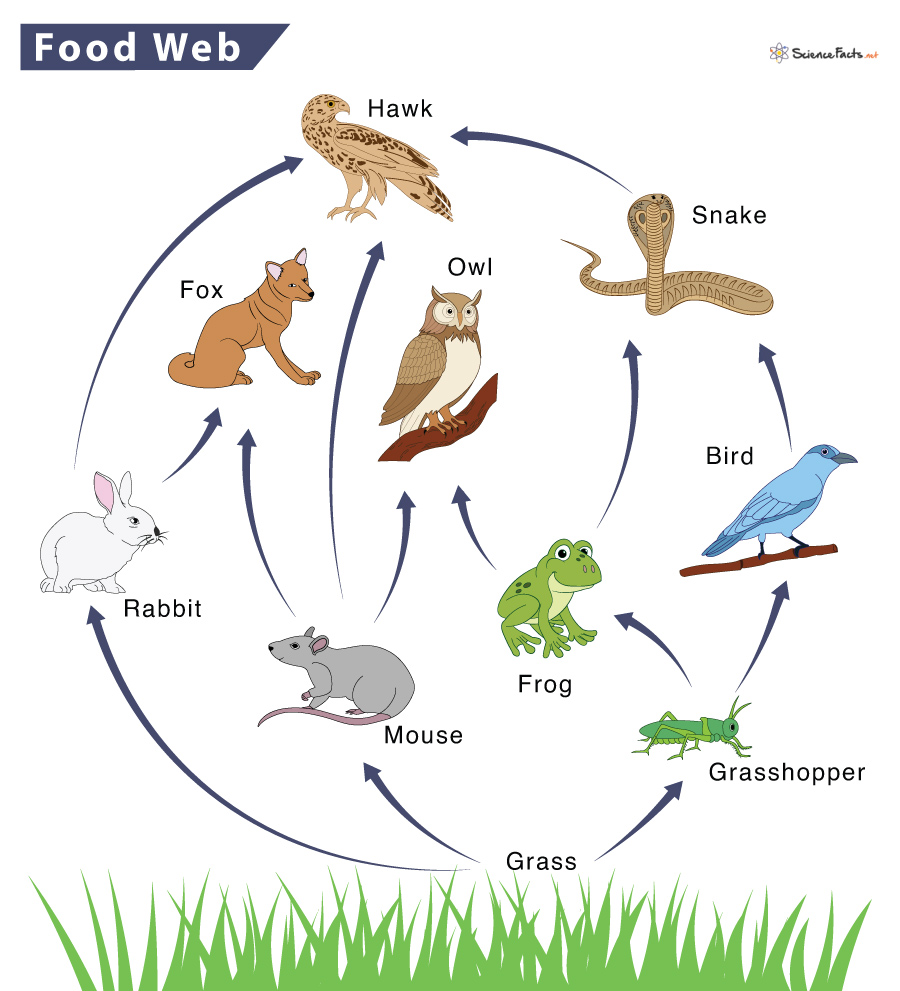
What would happen if the hawk population decreased?
Snake and rabbit population (especially snake) would thrive
59
New cards
What are producers?
Organisms that make their own food
60
New cards
What is another name for producers?
autotroph
61
New cards
What are the two types of autotroph?
photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs
62
New cards
What are phototrophs?
Organisms that use energy from sunlight to make food by photosynthesis
63
New cards
What are chemoautotrophs?
organisms that use energy from chemical compounds to make food by chemosynthesis
64
New cards
Define photosynthesis
the process by which energy from the sun is harnessed by chloroplasts to make food from carbon dioxide and water
65
New cards
Write the photosynthesis chemical equation.
6CO2 + 6H2O \------\> C6H12O6 + 6O2
66
New cards
Define chemosynthesis
the synthesis of organic compounds by bacteria or other living organisms using energy derived from reactions involving inorganic chemicals, typically in the absence of sunlight.
67
New cards
What are consumers?
Organisms that get their energy by consuming other living organisms.
68
New cards
What is another name for consumers?
heterotrophs
69
New cards
What are the three types of heterotrophs?
herbivores, carnivores, omnivores
70
New cards
What are herbivores?
animals that eat plants
71
New cards
What are carnivores?
animals that eat other animals
72
New cards
What are omnivores?
organisms that eat both plants and animals
73
New cards
What are decomposers?
Organisms that break down the remains and other wastes and release simple inorganic molecules back to the environment
74
New cards
What are the three types of decomposers?
scavengers, detritivores, saprotrophs
75
New cards
What are scavengers?
Organisms that consume the soft tissues of dead animals.
76
New cards
What are detritivores?
organisms that consume detritus - the dead leaves, animal faeces, and other organic debris that collects on the soil or at the bottom of a body of water.
77
New cards
What are saprotrophs?
organisms that feed on any remaining organic matter that is left after other decomposers do their work.
78
New cards
what is the difference between food webs and chains?
A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem
79
New cards
What is the source of energy for all life?
sun
80
New cards
What is the equation for cellular respiration?
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + energy
81
New cards
What part of a plant allows for gaseous exchange?
Stomata
82
New cards
Define stomata
A pore surrounded by guard cells in the epidermis of a leaf. When stomata are open, CO2, enters a leaf, and water and O2 exit. A plant conserves water when its stomata are closed
83
New cards
Define guard cells
One of a pair of epidermal cells that adjust their shape to form a stomatal pore for gas exchange.