Topic 9: Cardiac Arrhythmias
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
ECG shows the instantaneous __ in electrical charge between 2 points.
difference
Depolarization waves move from __ to __ pole, and the movement of electrical current is captured in the __ pole.
-; +; +
Repolarization waves move from __ to __ pole; movement of electrical current is captured in the __ pole.
+; -; -
Both depolarization and repolarization are captured as a __ deflection.
positive
ECG detects activation/depolarization and recovery/repolarization potentials generated by the __, not the __ process.
myocardium; conduction
__ leads determine the difference between leads on the periphery versus the central EKG reading.
Prechordial
__ leads show small electrical activity not clearly shown in other EKGs. It measures the difference between one lead versus the __ of the other two leads.
augmented; sum
The EKG gives information in __ different planes: (2).
2; vertical & horizontal
Which leads are in the vertical plane? Which are in the horizontal plane?
vertical: lead I, II, III & augmented leads
horizontal: prechordial leads
Through an EKG, __ & __ abnormalities can be detected, and the __ of impulses across the myocardium can be mapped.
rhythm; rate; movement
The __ interval is the complete phase of depolarization and repolarization.
QT
An EKG interval shows the __ and __ of the impulse during that time.
strength; duration
What are the two ways heart rate is calculated?
300/(# large boxes bw 2 consecutive R waves)
1500/(# small boxes bw 2 consecutive R waves)
On average, how long is a full cardiac cycle?
25 mm/sec
Placement of EKG leads give __ that measure the direction impulses take during depolarization and repolarization.
vectors
The __ gives the main direction that impulses are taking.
resultant vector/mean electrical axis
The mean electrical axis is normally between __.
0 - 90 degrees (typically at 60)
If the mean electrical axis falls between -30 - -90 degrees, it has a __ axis deviation.
left
If the mean electrical axis falls between 90 - 180 degrees, it has a __ axis deviation.
right
Because of the many leads and vectors created as a result, EKGs can give specificity on __ of defect.
specific locations
__ describes anything that denotes from the normal rhythm of the heart.
arrhythmia
__ describes the normal rhythm of the heart.
sinus rhythm
__ function depresses automaticity of SA nodes and slows conduction, while __ exert the opposite effect.
vagal; sympathetic
What is the normal beats per minute in healthy individuals?
60-100; but can be <60/min (for athletes)
__ have faster heart beats than adults.
infants/children
The pacemaker function of the heart resides with the __ node.
SA
Cardiac arrhythmias are disorders of: (2)
impulse formation &/or impulse conduction
In impulse formation, cardiac automaticity remains __, but involves __ or __ of normal pacemaker mechanism.
normal; speeding; slowing
Sinus __ describes heart rate that is less than 60 bpm.
bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia is normally seem with: (6)
increased vagal tone
decreased sympathetic tone
certain drugs (Digoxin, beta blockers)
hypothermia
hypothyroidism
increased intracranial pressure
Sinus bradycardia is normally benign, unless if associated with: (2)
congestive heart failure or low cardiac output (then needs temporary or permanent electrical pacing)
Sinus __ describes when the heart rate is more than 100 bpm.
tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is normal in: (4)
childhood
physiologic stress
pain
anxiety
__ is often seen with fever, hypotension, hypovolemia, hypothyroidism, drugs (catecholamines, alcohol, nicotine, caffeine), cardiac ischemia, and shock.
sinus tachycardia
In __, the SA node generates faster impulses for no reason. It can occur in a healthy person due to an __ defect.
chronic inappropriate sinus tachycardia (IST); autonomic
How are abnormal impulse formations treated?
identify and correct obvious cause (in emergency and outpatient setting)
eliminate possible stimulants (coffee, alcohol, tea etc)
medical treatment: Ca channel blockers, beta blockers
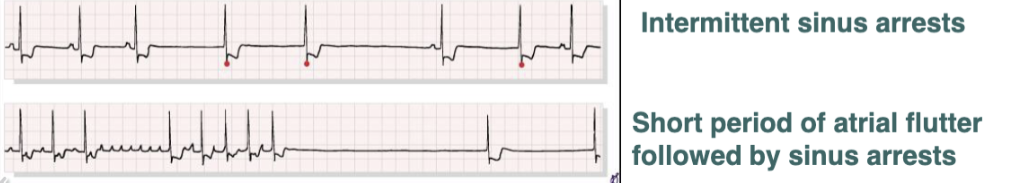
__ is characterized by intermittent sinus arrests or short period of atrial flutter followed by sinus arrests.
sick sinus syndrome
Sick sinus syndrome’s clinical expression can show persistent spontaneous __ that is not appropriate for the type of physical activity. It can also demonstrate a __ syndrome.
bradycardia; bradycardia-tachycardia
Sick sinus syndrome is often because of a __ node defect.
SA
How is bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome, in sick sinus syndrome, treated?
pacemaker to prevent bradycardia or drugs to control tachycardia
A latent pacemaker impulse may __ and become the __ pace maker if: (2)
escape; dominant
if: SA node rate slows down or propagation of normal impulse is interrupted
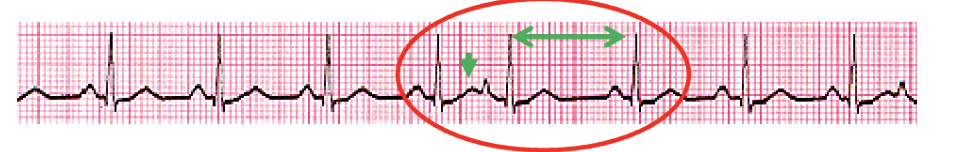
Which premature complex has a P wave that is hidden in the ST-T wave of the preceding beat, producing a camel wave?
premature atrial complex
What occurs as a result of a premature atrial complex?
longer than normal interval before the next sinus beat arrives
In a premature junctional complex, the ectopic beat from the __ captures the __, which is going retrograde/backward, and the __, which is going forward/anterograde.
AV; atria; ventricles
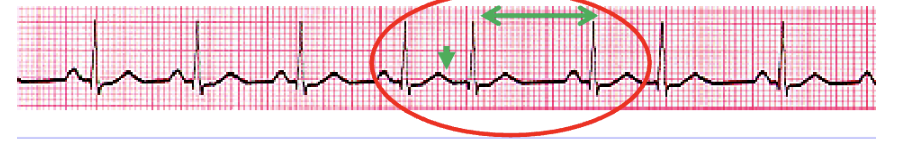
In the premature junctional complex, the premature P wave may occur __ or __ the QRS complex. As a result, there is a longer __ before the next beat.
before; in; pause
Are premature complexes harmful?
no, they are benign and everyone can have them every now and then
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia is mostly due to __ in the __ or __ or both.
reentry; atria; ventricles p
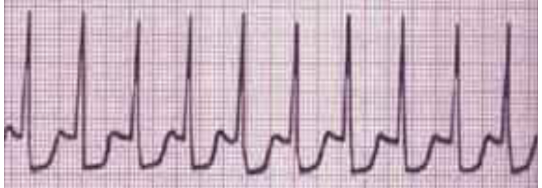
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is defined by its __ QRS complexes with no apparent __ wave.
narrow; P
Why is paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia defined as paroxysmal?
because onset is sudden and also stops abruptly
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is often seen in __ that report palpitations, pounding in chest, chest pain or pressure, weakness, SOB, or dizziness.
young adults
How is paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia treated?
cardioversion if hemodynamically unstable
vagal maneuvers and drugs
Despite a fast heart rate in paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, the rhythm is __.
very normal
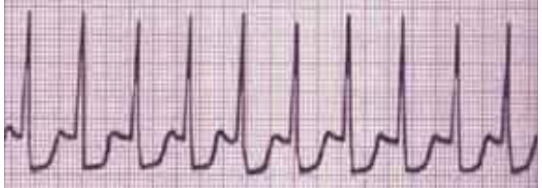
Atrial flutter has an atrial depolarization rate around 300/min & variable ventricular rate that may be __ or __.
regular; irregular
In atrial flutter, the waves have a __ shape.
new saw (sharp tips)
Atrial flutter is characterized by a:
macro reentrant atrial rhythm (meaning arrhythmia due to large electrical circuit in atria causing atria to beat rapidly and irregularly)
Atrial flutter can occur in health people or people with: (5)
lung disease
pulmonary embolism
alcoholism
hyperthyroidism
mitral valve disease
How is atrial flutter treated? (3)
atrial pacing
cardioversion if unstable
medications (antiarrhythmic drugs, calcium channel blockers, digitalis prep)
__ is characterized by chaotic atrial activity without effective contraction.
atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation may be __ or __.
paroxysmal; chronic
Atrial fibrillation is more common in __ and __.
elderly and men
Atrial fibrillation can eventually cause:
hemodynamic changes in the heart
In atrial fibrillation, what can be seen on an EKG?
no P waves, indicating no atrial activity at all, or fine undulations (rising and falling) resembling an old saw
irregularly irregular ventricular activity: random, no pattern
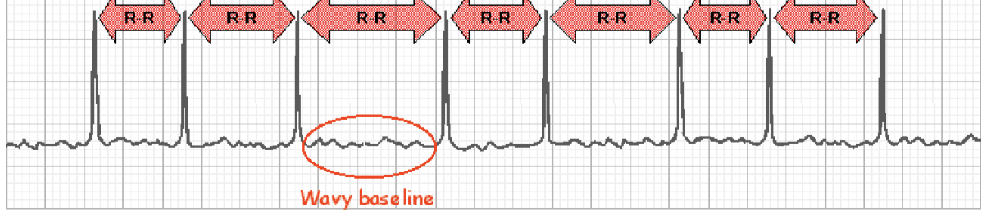
What is atrial fibrillation often associated with? (4)
cardiac disease
hyperthyroidism
pulmonary embolism
pericarditis
__ describes A-fib in the absence of heart disease or risk factors.
Lone atrial fibrillation
How does A-fib relate to blood clotting?
when there is no P wave, there is a period of no activity until the next impulse. this can cause blood to not effectively be pumped, giving a chance for the heart to come to a complete stop. blood is thus pooled and clotted and can travel to the brain, causing a stroke
What are the goals when treating A-fib? (5)
identify etiology
restore sinus rhythm
control ventricular rate
prevent recurrences
prevent thromboembolic episodes (caused by blood clots)
How is A-fib initially treated?
cardioversion via:
drugs (beta blockers, calcium channel blockers)
defibrillation/electric shock
If drugs or electrical techniques don’t work, what other options will treat A-fib? (2)
radiofrequency ablation therapy
surgery: maze procedure
What cases of A-fib can undergo radiofrequency catheter ablation therapy? (3)
cases that are paroxysmal, refractory to drugs, after resuscitation sudden cardiac death
__ drugs are also beneficial for patients with A-fib.
anticoagulation
How does the maze procedure work?
creates lesions and ultimately scar tissues that block abnormal electrical impulses from being conducted through the heart
Premature ventricular complexes is due to:
ectopic ventricular foci
What does the EKG for premature ventricular complex (PVC) look like? Do the abnormalities have a pattern?
wide QRS complexes with abnormal shapes and durations
can be occasional, bigeminy, trigeminy, quadrigeminy, or have runs of PVC
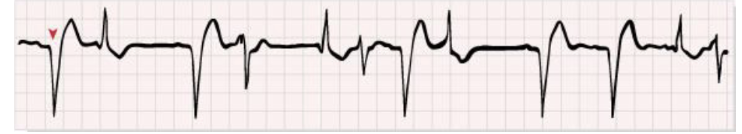
What is premature ventricular complex often associated with?
significant heart disease
When premature ventricular complex is present along with myocardial infarction, what can be seen?
more serious rhythm disturbances
If present with __, premature ventricular complexes are treated with __.
cardiac disease; anti-arrhythmics
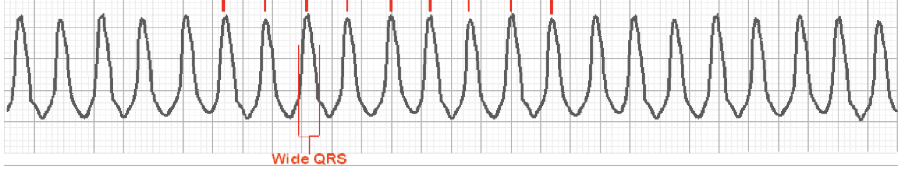
__ has an EKG showing wide QRS complexes at rates greater than 120 bpm with at least __ in a row.
ventricular tachycardia; 3
Ventricular tachycardia is __ and needs __ treatment via: (2)
life threatening; immediate
cardioversion if pt unstable or drugs
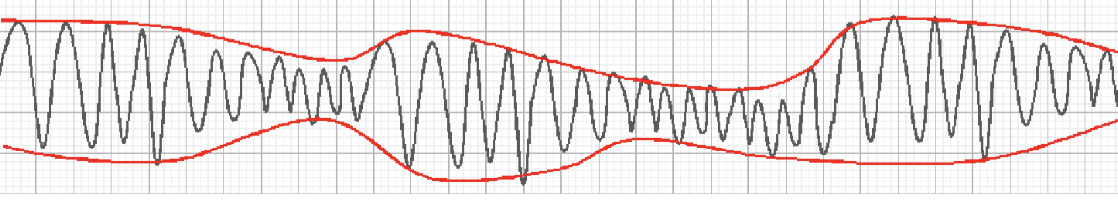
__ is a particular pleomorphic form of V-tach associated with a prolonged QT interval and QRS complexes of changing amplitude and a twisted helix shape.
Torsades de Pointes
Torsades de Pointes is usually __ or __ related.
congenital; drug
__ is chaotic ventricular activity not compatible with life.
ventricular fibrillationI
If ventricular fibrillation is not reversed in __ minutes, irreversible __ damage occurs.
3-5; brain
How is V-fib treated?
electric shock
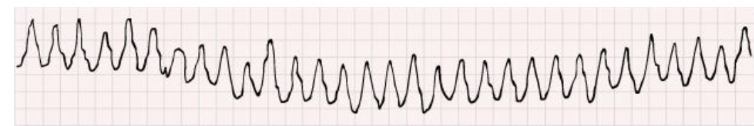
What abnormal automaticity does this EKG show?
ventricular fibrillation
What are 3 forms of conduction disturbances?
1st degree heart block
2nd degree block
3rd degree/complete heart block
In __ degree heart block, conduction is prolonged but all impulses are conducted.
first
In __ degree heart block, conduction is prolonged until an impulse is not conducted.
second
In second degree heart block, the block is occasionally not preceded by a measurable __ in conduction.
reduction (doesn’t slow down conduction after)
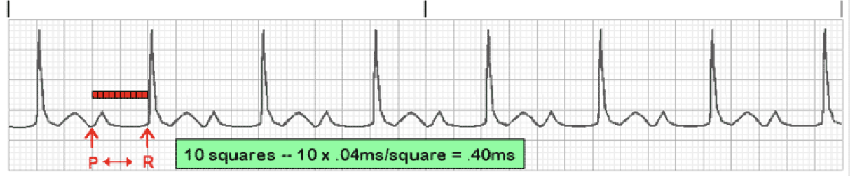
What type of heart block is shown in this EKG?
first degree heart block
In first degree heart block, are other heart diseases usually present? What is it usually associated with?
not always; usually associated with drugs and infectious diseases
Is treatment necessary for first degree heart block?
not usually
What are the two types of second degree heart block?
Mobitz Type I
Mobitz Type II
In Mobitz Type I, PR intervals become progressively __ until:
longer; no impulse/skipped beat followed by impulse starting again
In Mobitz Type I, 2nd degree heart block is associated with __.
myocardial ischemia (may be reversible)
Is Mobitz Type I dangerous?
usually not; usually does not need pacemaker
In Mobitz Type __, there is periodic failure to transmit atrial stimulation (sudden block of a P wave without PR elongation).
II
What does Mobitz Type II indicate?
danger of a serious bradycardia (pace can significantly drop) and requires pacemaker
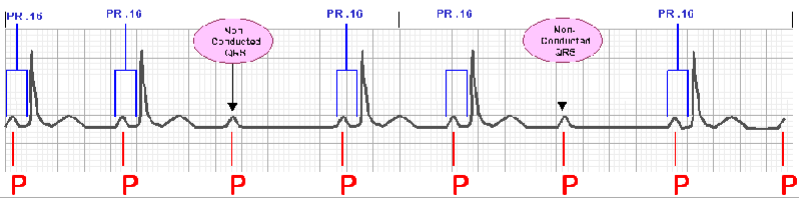
What type of heart block is shown?
2nd degree Mobitz Type II heart block
In third degree heart block, the atrium and ventricle are depolarizing __ with no __ waves conducted.
independently; P
In complete heart block, what treatment is required?
pacemaker