A&P - 6.3 Bone Structure (bone cells and compact vs. spongy bone)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
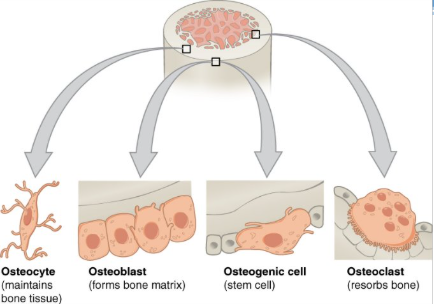
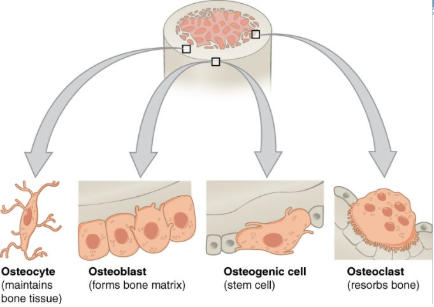
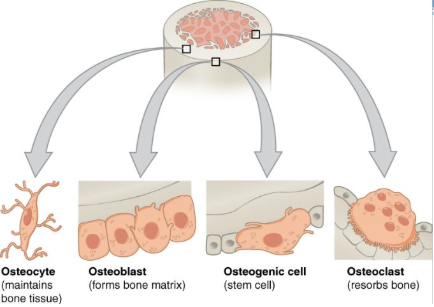
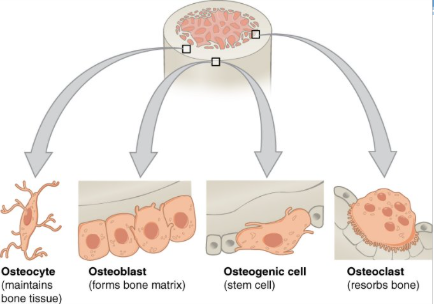
bone cells
osteogenic cell
osteoblast
osteocyte
osteoclast
osteogenic cell
undifferentiated cell with high mitotic activity as they differentiate and develop into osteoblasts
the only bone cells that divide
immature osteogenic cells are found in the deep layers of the periosteum and the marrow
function: develop into osteoblasts
location: deep layers of the periosteum and the marrow
osteoblast
cell responsible for forming new bone
found in the growing portions of bone including periosteum and endosteum
do not divide
synthesize and secrete the collagen matrix and calcium salt
function: bone formation
location: growing portions of bone, including periosteum and endosteum
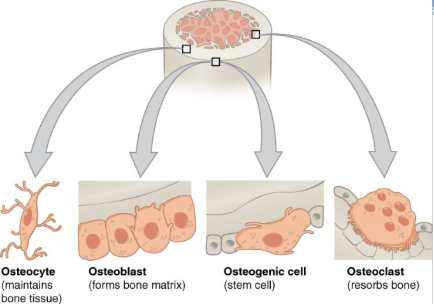
osteocyte
as the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies, the osteoblast become trapped within it; as a result, it changes in structure and becomes an osteocyte
primary cell in mature bone (most common type of bone cell)
responsible for maintaining mineral concentration of the matrix via secretion of enzymes
lack mitotic activity
function: maintain mineral concentration of matrix
location: entrapped in matrix
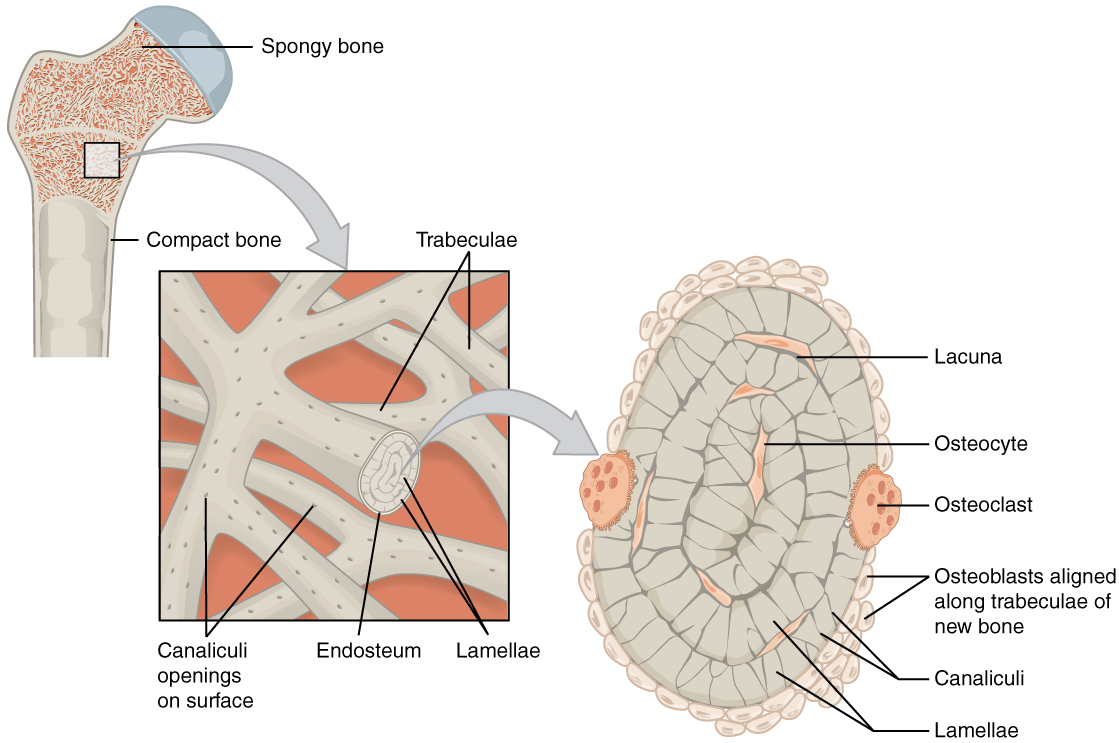
lacunae
(singular = lacuna) each osteocyte is located in a space called a lacuna and is surrounded by bone tissue
found at borders of adjacent lamellae
canaliculi
(singular = canaliculus) channels within the bone matrix that house one of an osteocyte’s many cytoplasmic extensions that is uses to communicate and receive nutrients and wastes to be removed from them
canaliculi connect with the canaliculi of other lacunae and eventually with the central canal
osteoclast
cell responsible for resorbing or breaking down old bone
found on bone surfaces
multinucleated
originate from monocytes and macrophages
function: bone resorption
location: bon surfaces and at sites of old, injured, or unneeded bone
overview of compact bone
denser, stronger of the two types of bone tissue
dense osseous tissue that can withstand compressive forces
found under the periosteum and in the diaphysis of long bones
provides support and protection
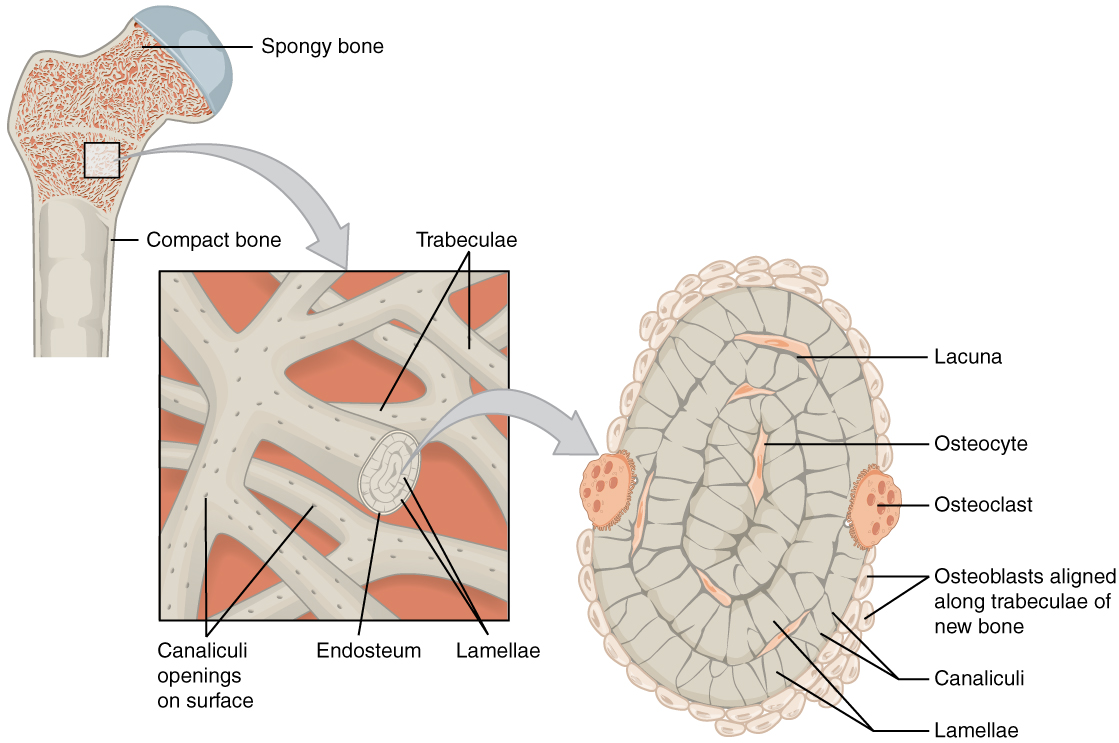
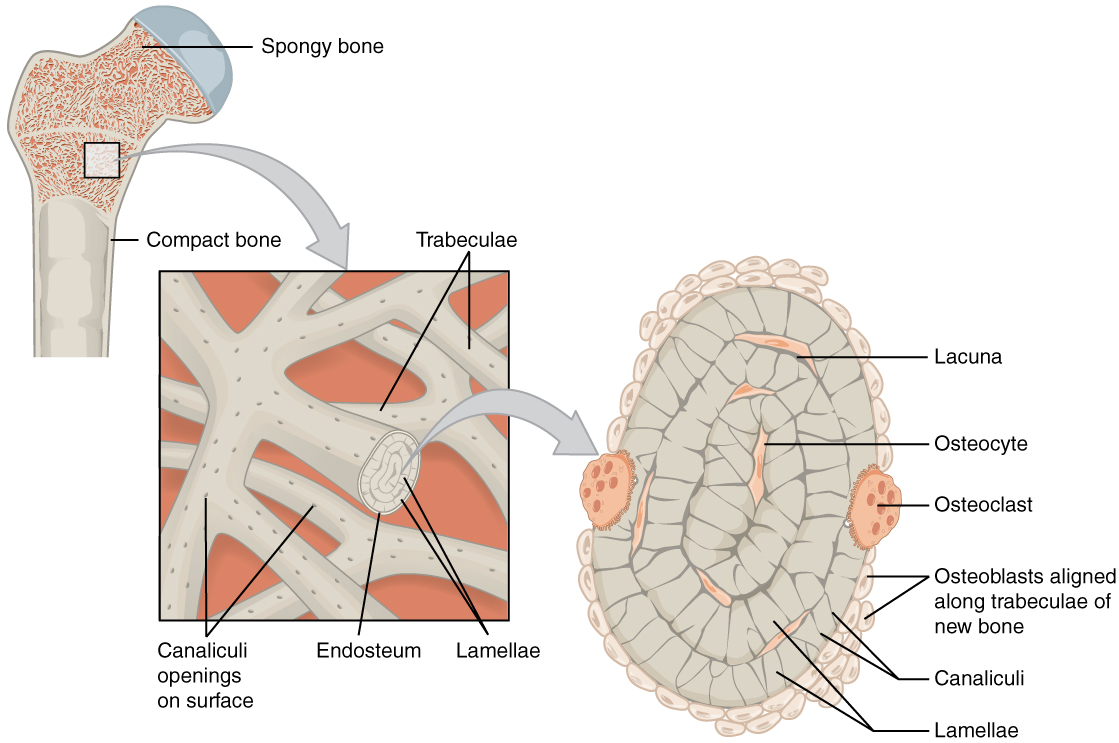
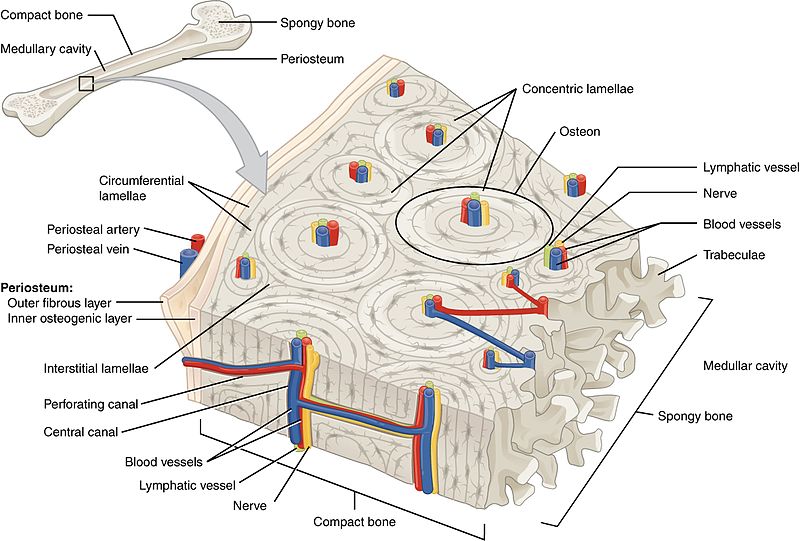
diagram of compact bone: this cross-sectional view of compact bone shows the basic structural unit, the osteon
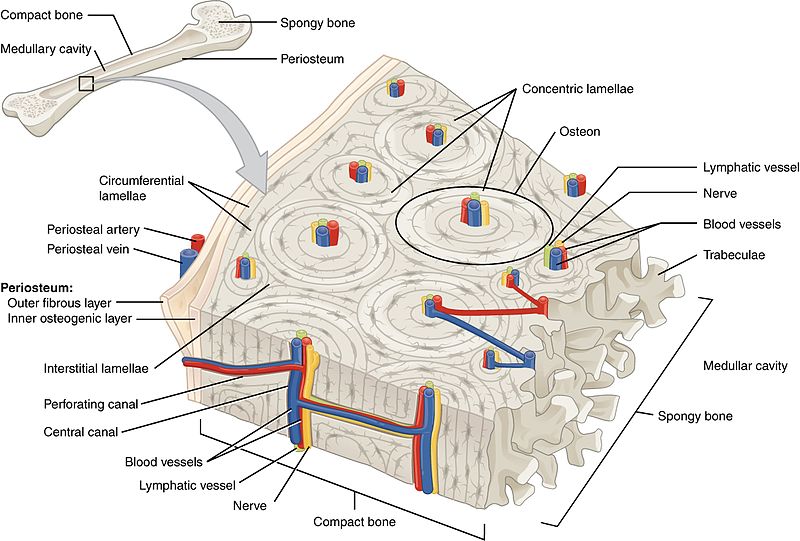
microscopic anatomy: compact bone
NOTE: OSTEON with central canal (aka Haversian system)
the microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon, or Haversian system
concentric lamellae
circumferential lamellae
interstitial lamellae
osteocytes in lacunae
perforating canal
compact bone vs spongy bone
osteon
(also, Haversian system) basic structural unit of compact bone
made of concentric layers of calcified matrix called lamellae
lamellae
concentric rings of calcified matrix
types:
concentric lamellae
circumferential lamellae
interstitial lamellae
concentric lamellae
form cylindrical osteons
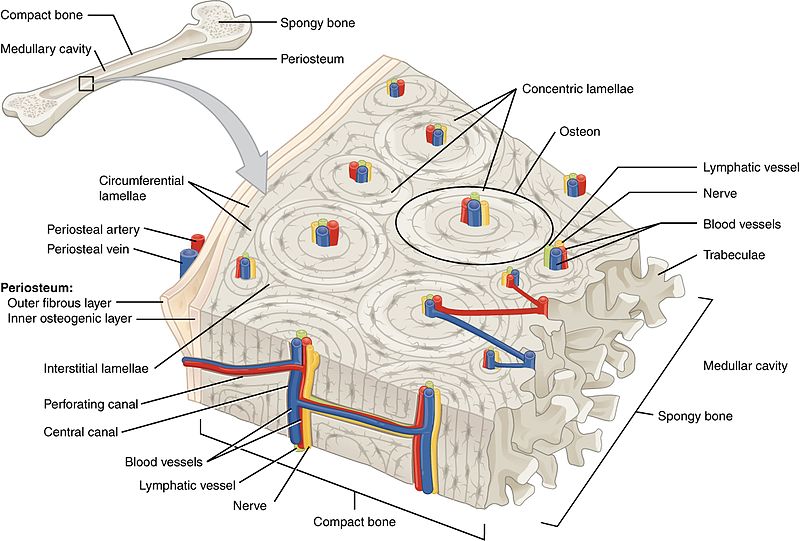
circumferential lamellae
layers that wrap around the entire bone
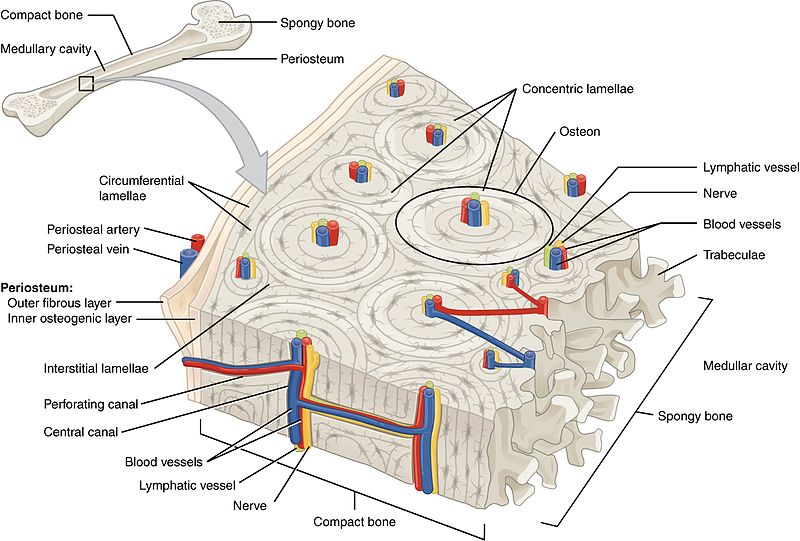
interstitial lamellae
fill the spaces between osteons, often being remnants of remodeling
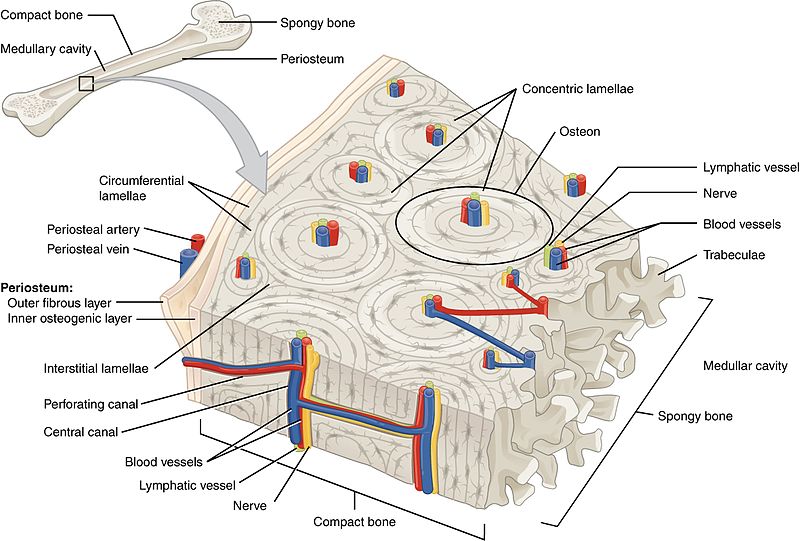
central canal or haversian canal
longitudinal channel in the center of each osteon
contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels
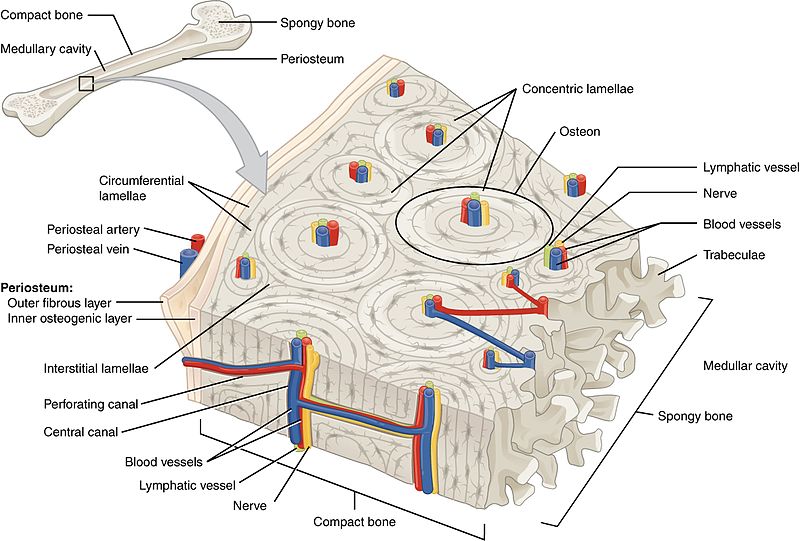
perforating canal or volkmann’s canal
vessels and nerves from central canal (haversian canal) branch off at right angles through a perforating canal (volkmann’s canal) to extend to the periosteum and endosteum
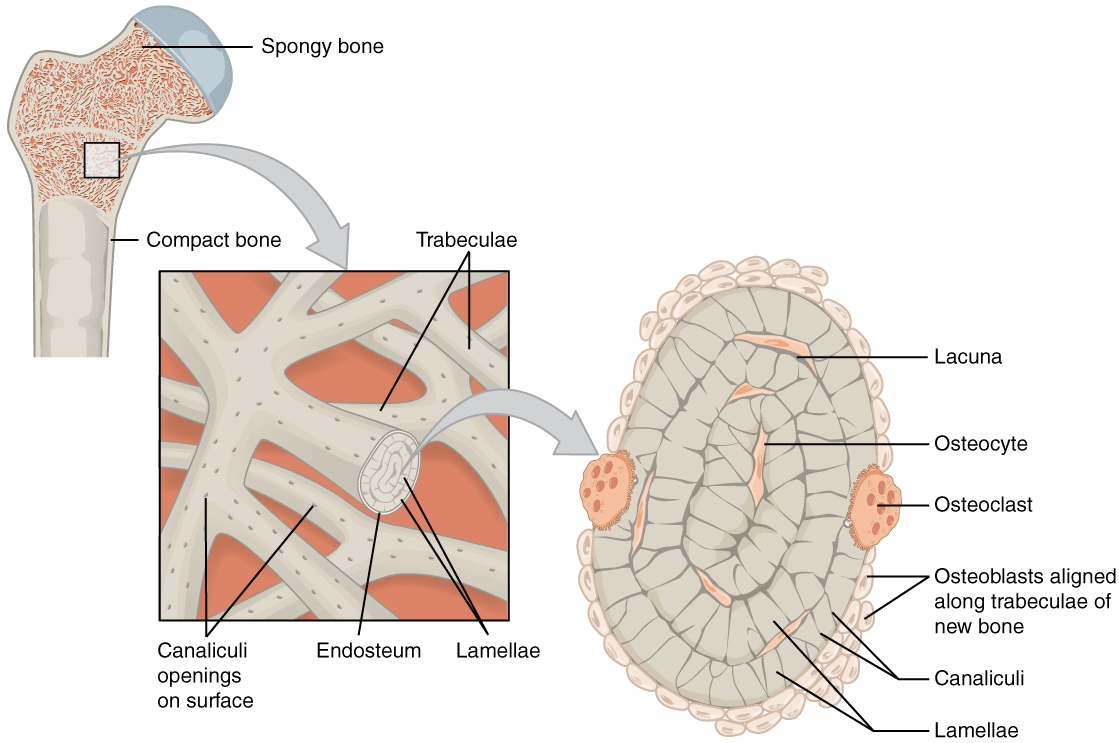
overview of spongy bone
(also, cancellous bone) trabeculated osseous tissue that supports shift in weight distribution
spongy (cancellous) bone has open spaces
located where bone are not heavily stressed or stress in many directions (ex: flat bone)
contains osteocytes housed in lacunae, but not arranged in concentric circles
microscopic anatomy: spongy bone
lamellae form struts and plates (trabeculae) creating an open network
reduces weight of skeleton
no blood vessels in matrix
nutrients reach osteons through canaliculi open to trabeculae surfaces
red bone marrow is found between trabeculae
trabeculae
lacunae and osteocytes are found in a lattice-like network of matrix spikes called trabeculae
trabeculae may appear to be a random network, but each trabeculae forms along lines of stress to provide strength to the bone
the spaces of the trabeculated network provide balance to the dense and heavy compact bone by making bones lighter so that muscles can move them more easily
spaces in some spongy bones contain red marrow, protected by trabeculae, where hematopoiesis occurs